Alkyl Free Radicals
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Heterolytic cleavage
What we’ve been doing already. One atom is more electronegative than the other and creates ions. Think hetero - two different ions.
Homolytic cleavage
This is what free radicals do. A and B both take an electron for itself. This is unlike heterolytic cleavage where one A or B has both electrons to form an anion.
Reaction conditions (reagents), what works for free radicals to break into two pieces for what we were talking about in homolytic clevage
Peroxides ROOR with HO . . OH
Halogens X2 with X . . X
NBS, NCS
Usually heat or UV light promotes these reagents to happen and form radicals.
stability free radicals general rule
allylic free radicals are generally more stable than tertiary > secondary > primary > methyl > vinyl
Allylic is radical on a carbon NEXT TO the carbon of a double bond.
Methyl is a radical on a CH3 group with no other carbons attached,
Vinylic is a radical directly on the carbon that is PART OF A of a double bond
Why is the general stability rule the way it is free radicals.
Hyperconjugation. It’s a subset of electronic effects.
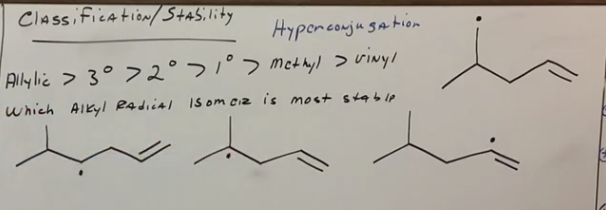
Which alkyl radical is more stable and why?
The most stable is the tertiary free radical.
The vinyl one here is NOT allylic because the carbon bearing the free radical is ON the pi bond, not on the carbon next to it.
Where do free radicals exist
In the p orbital. However unlike carbocations or other molecules free radicals are not charged. They are represented by a dot.
How hyperconjugation works
Favorable overlap between filled and unfilled sigma or pi bonds. The overlap from one orbital to the next helps stabilize the electron deficient orbital.
Geometric shape of free radicals bond angle and hybridization
Trigonal planar, bond angle is approximately 120 degrees, sp2 hybridized.
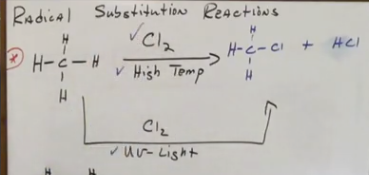
Radical sub reactions - alkanes to alkyl halides
Use X2 on top of arrow with high temperature or UV light to replace an H in the alkane with the halogen. A product of the halogen and H is also formed.
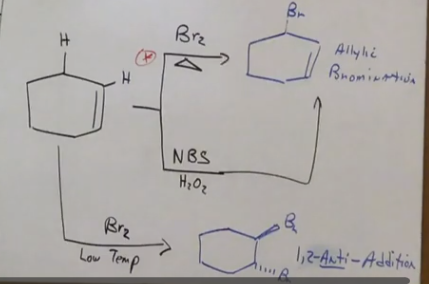
Radical sub reactions - from alkenes
Anti is on the bottom. Markovnikov reaction!
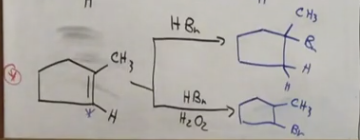
Br is regioselective
When using Br in a reaction to create an alkyl halide from an alkane, only one product. Whereas with chlorine there are two products.
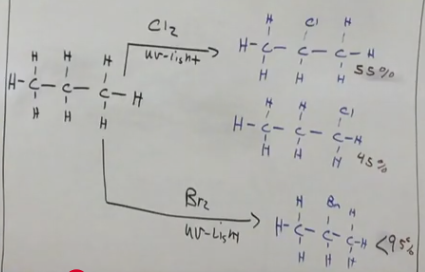
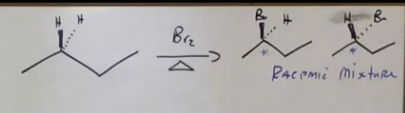
Stereochemistry from alkanes
A racemic mixture is created if there are chiral carbons.
Radical sub reactions rings and pi bonds.
If you have time learn this
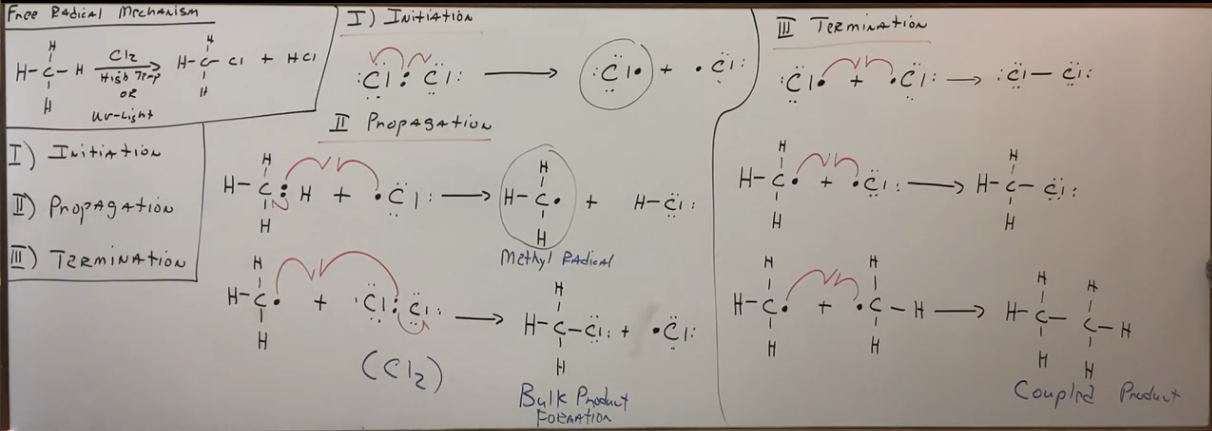
Free radicals all share these three phases in common with mechanisms.
Initiation, propagation, and termination.
For free radical reaction mechanisms use…
HOOKS not arrows. Arrows are two electrons, hooks are just one.
What happens during propagation phase of alkane to alkyl halide mechanism
The bulk of the product is formed and there are TWO steps. More specifically, the bulk of the product is formed during the SECOND STEP of the propagation phase.
What happens during termination phase of alkane to alkyl halide mechanism
THREE STEPS. Find all the free radicals generated (two) and make all the possible combinations. The hooks are literally just both towards the plus signs. One of the steps should have carbon coupling, and this step is important because it helps to validate the mechanism. It’s called the coupled product.
Whole free radical mechanism of alkanes to alkyl halides (draw it).
Bromine selectivity vs chlorine selectivity free radicals
bromine is selective because it's less reactive, making it sensitive to the stability of the new radical formed (preferring tertiary > secondary > primary C-H bonds) due to a high-energy barrier/late transition state. In contrast, chlorine is non-selective (or less selective) because it's highly reactive, overcoming small energy differences and reacting almost indiscriminately with all types of C-H bonds (primary, secondary, tertiary)