Enzymes: Biological Catalysts, Functions, and Applications
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Enzyme
a biological catalyst that speeds up chemical reactions and helps to break down/build molecules.
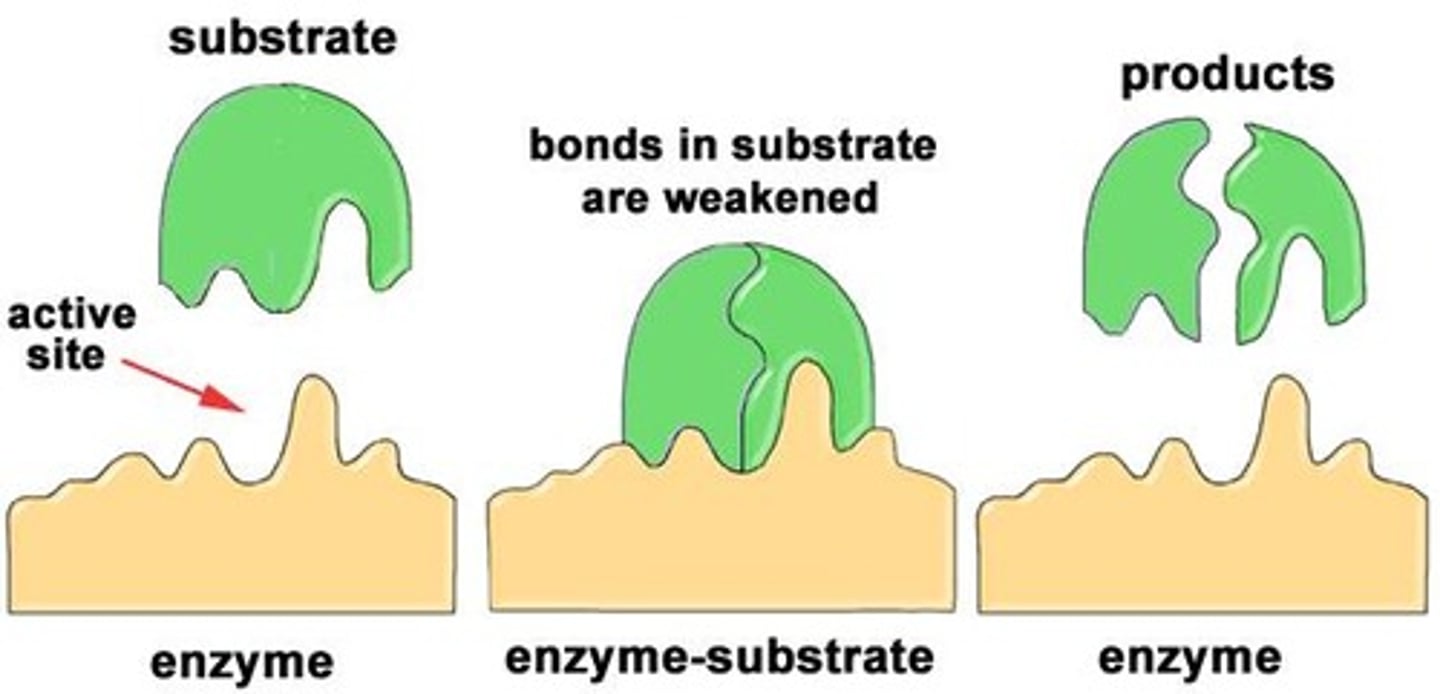
Substrate
the substance that reacts with an enzyme.
Active Site
a pocket/groove in an enzyme that binds to the substrate.
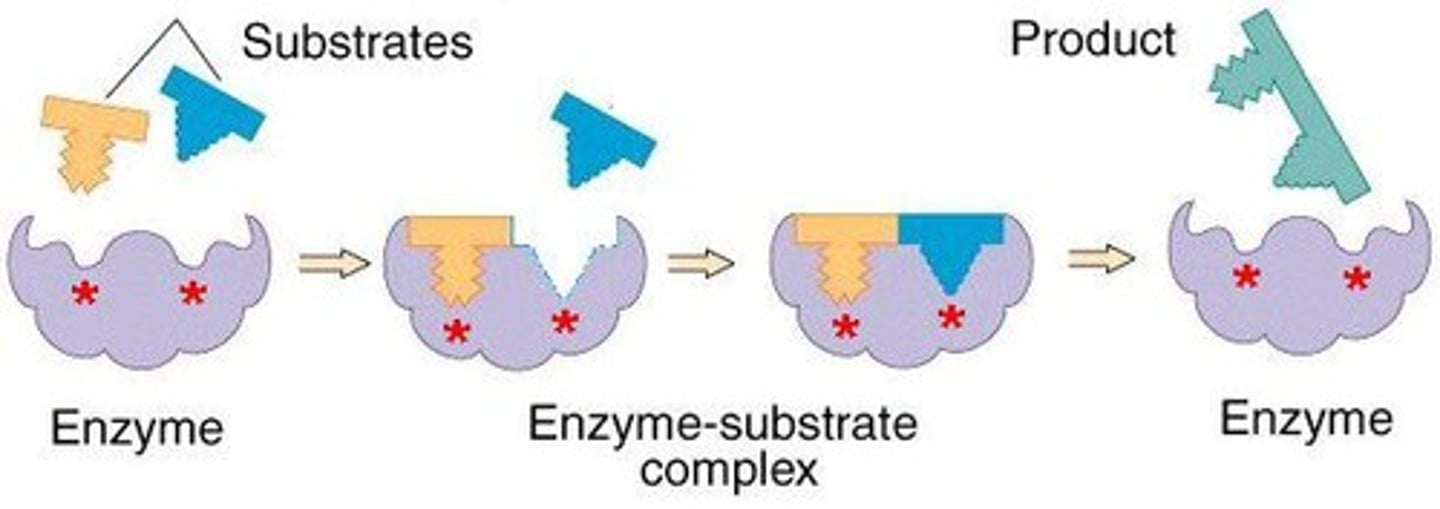
Induced-Fit Hypothesis
describes how enzymes change shape to better attach to a substrate.
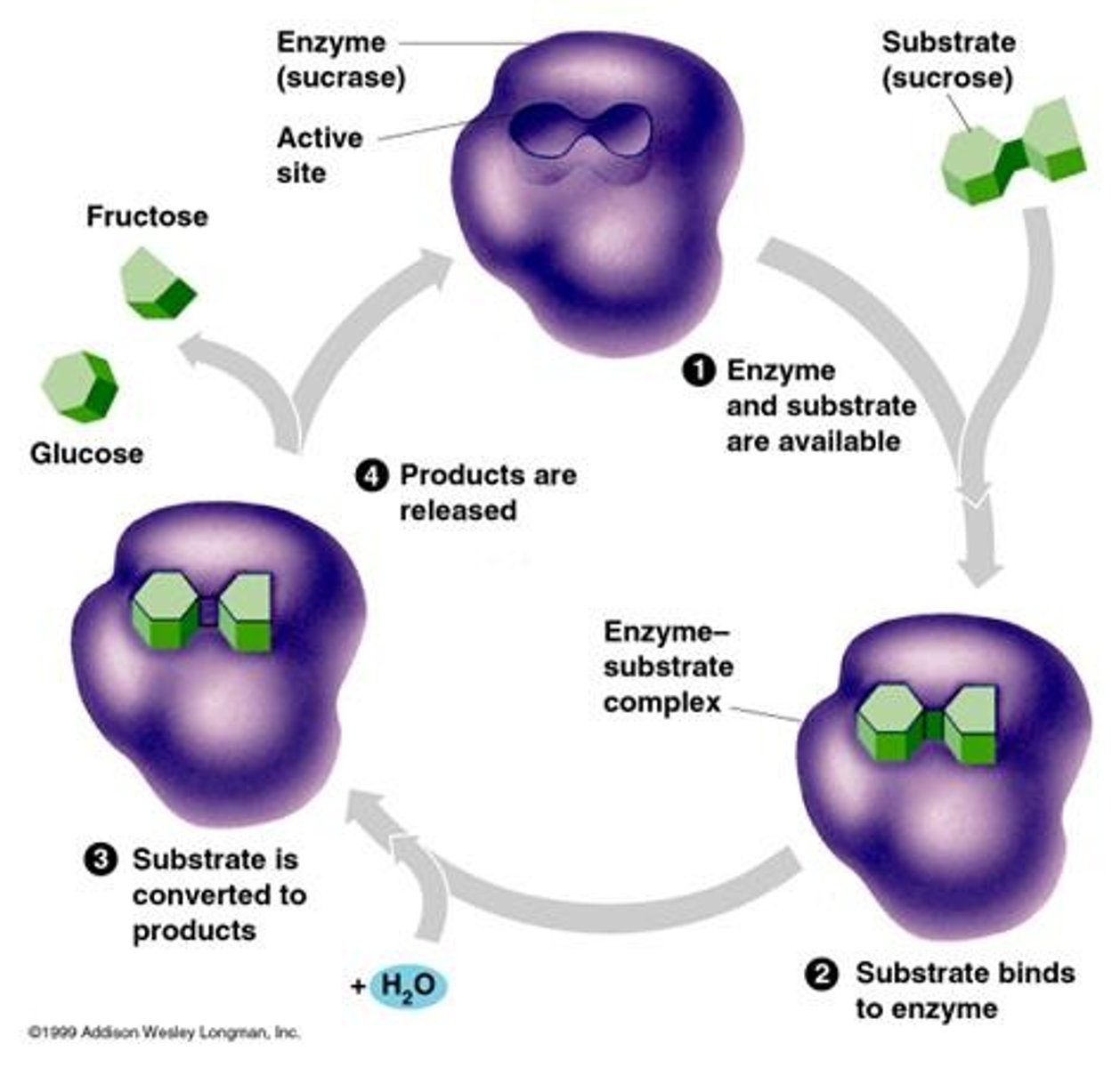
Enzyme-Substrate Complex
term used to describe enzymes bonded to substrate(s).
Cofactor
non-protein group that binds to enzymes and helps them function, often metals such as copper, iron, zinc etc.
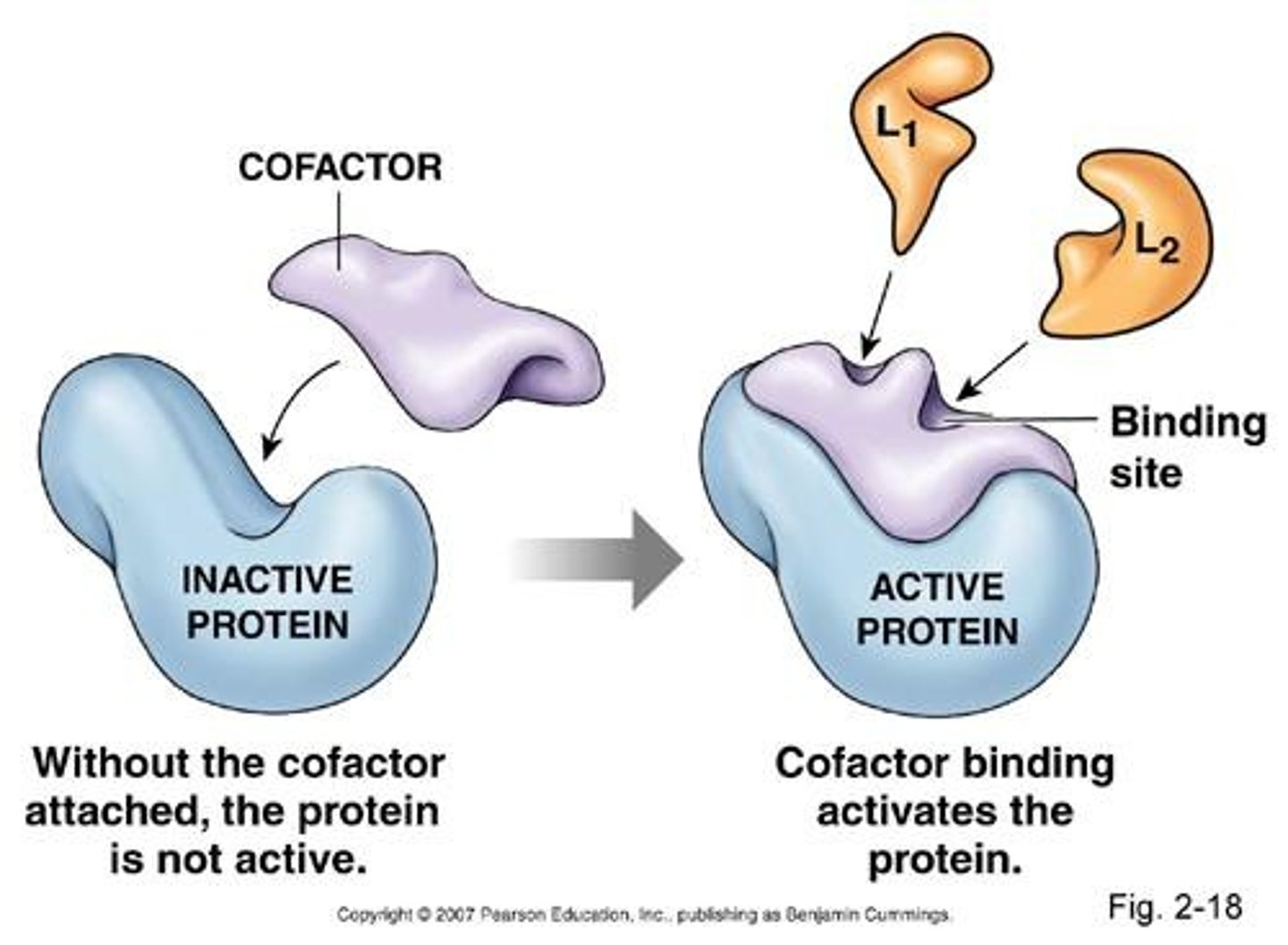
Coenzyme
an organic molecule that acts as a cofactor of an enzyme, may be derived from vitamins.
Competitive Inhibitor
binds to active site directly to prevent substrate from binding.
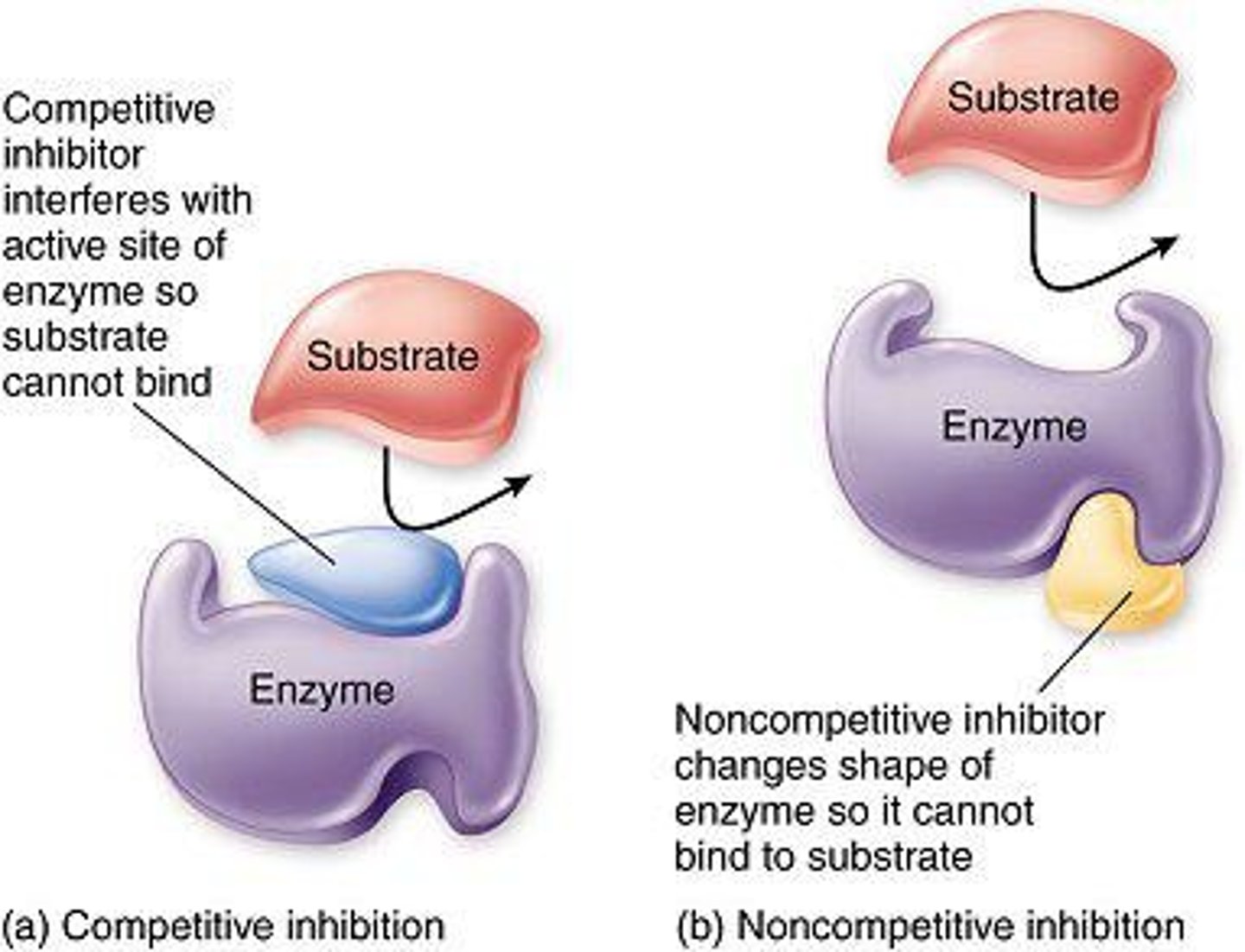
Non-competitive Inhibitor
binds to enzyme and changes its shape, indirectly prevents substrate from binding.
Irreversible Inhibitors
often highly toxic to cells as they prevent enzymes from functioning (Ex. Cyanide binds to cytochrome oxidase and interferes with cellular respiration).
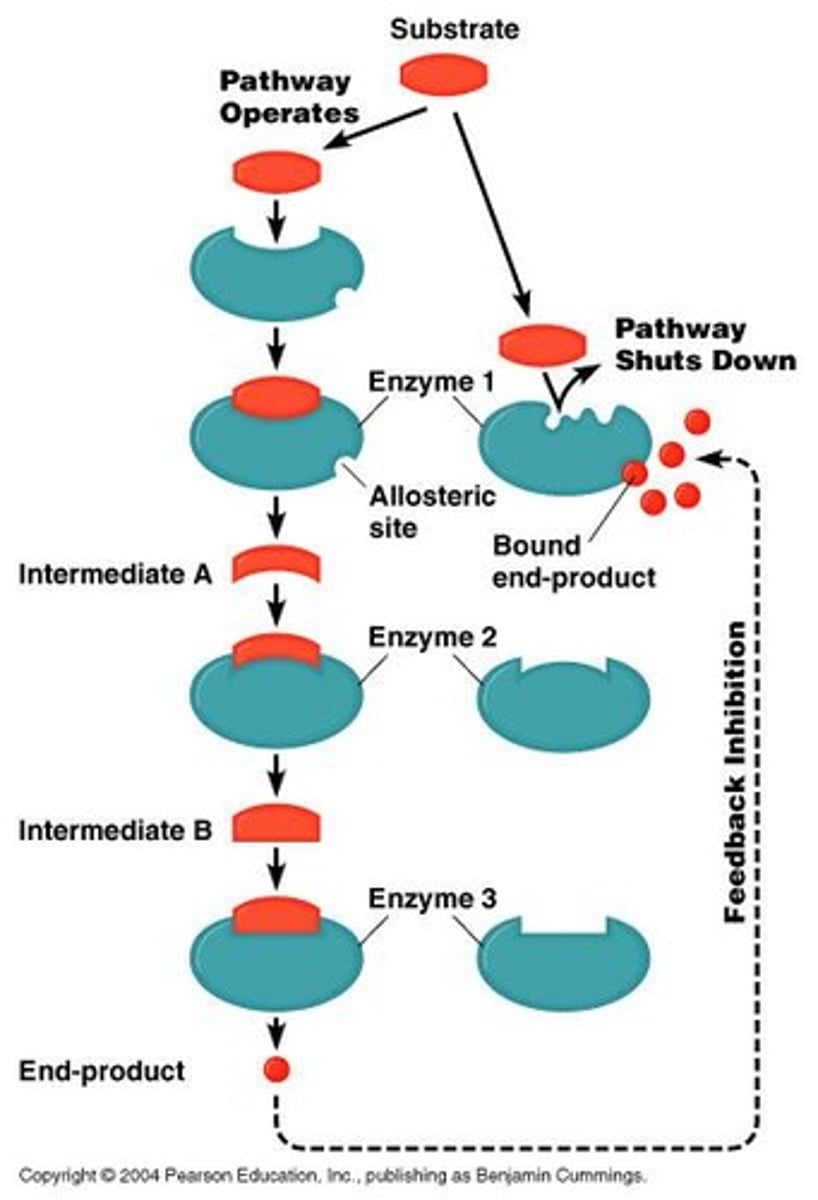
Allosteric Regulation
regulation of enzyme function using other molecules that bind to the enzyme.
Allosteric Site
a binding site on an enzyme where allosteric molecules attach.
Allosteric Inhibition
stabilizes enzyme into an inactive form.
Allosteric Activation
stabilizes enzyme into an active form.
Feedback Inhibition
the regulation of a pathway by one of the products of the pathway.
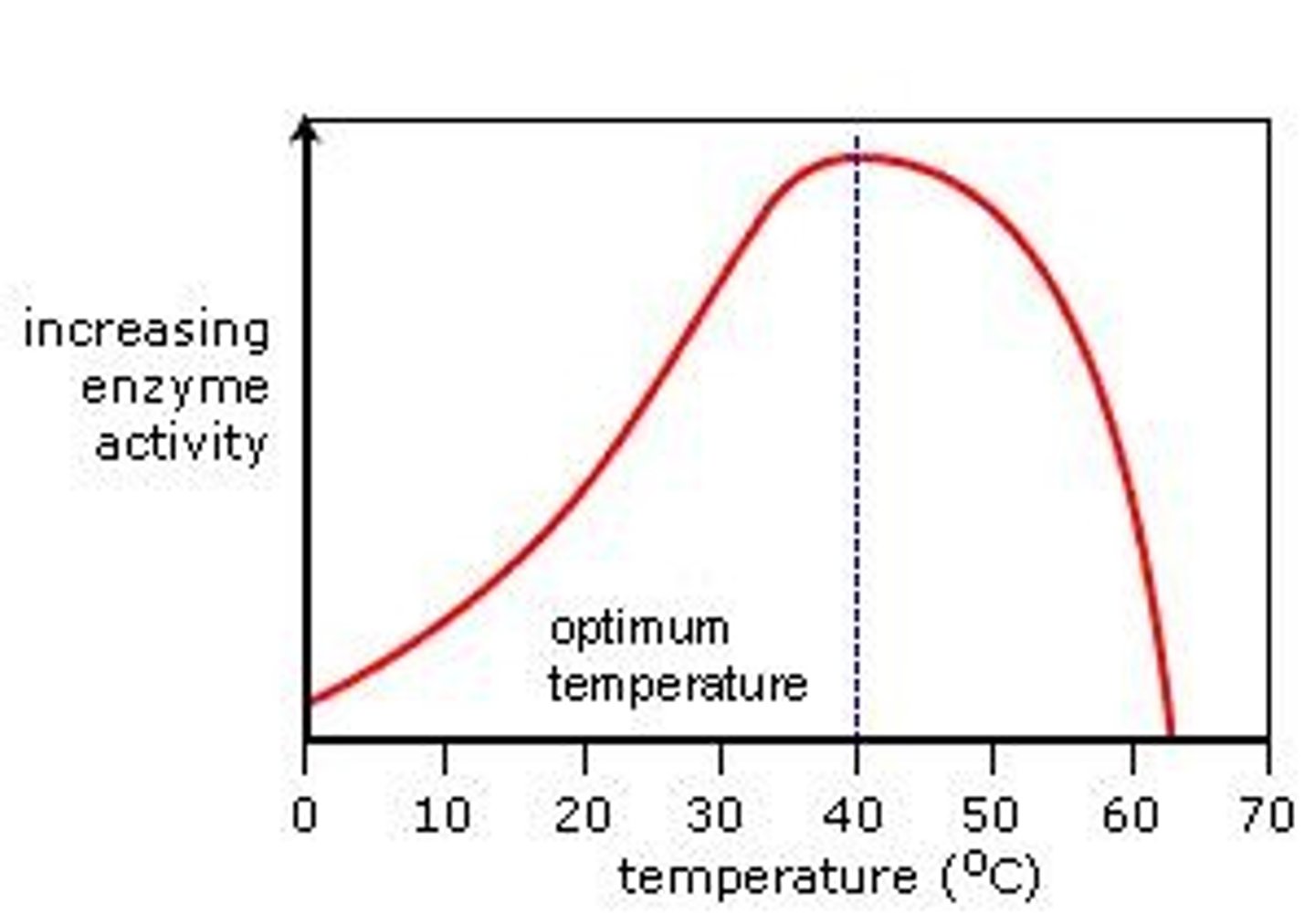
Temperature and pH
can both affect enzyme activity; enzymes will often only function optimally within a specific range of temperatures and pH levels.
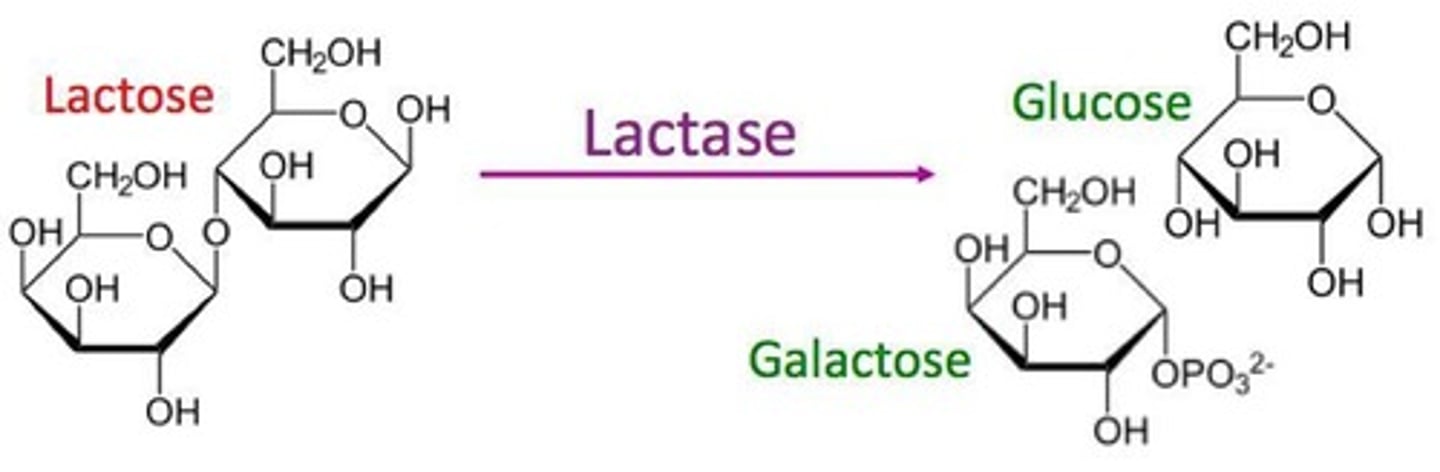
Lactase
an enzyme used to help break down lactose in dairy products.
Making Cheese
enzymes used to solidify milk into cheese.
Breaking Down Starch
enzymes used to break down plant starches into sugars.
Stain Removal
used to break apart certain types of staining molecules without heating (Cold Water Detergents).
Enzyme Activity Rate
may occur at a rate of 100 to 10 million molecules per second!