Bio 006 - Cell Respiration II & Fermentation
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
Pyruvate Kinase
Enzyme that converts ADP to ATP and glucose to pyruvate.
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase
Enzyme that makes Pyruvate then adds it to Coenzyme A to Acetyl CoA + CO2 and NAD to NADH.
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Uses the enzyme ATP synthase, which synthesizes ATP using energy from redox reactions.
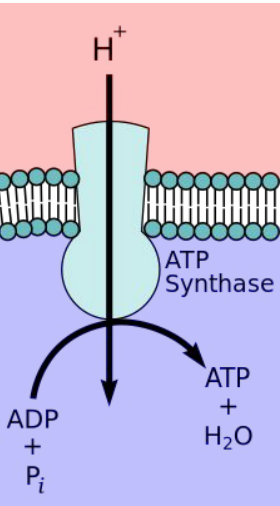
ATP Synthase
An integral protein that sits in the inner membrane of mitochondria and is powered by H+ (hydrogen ions).
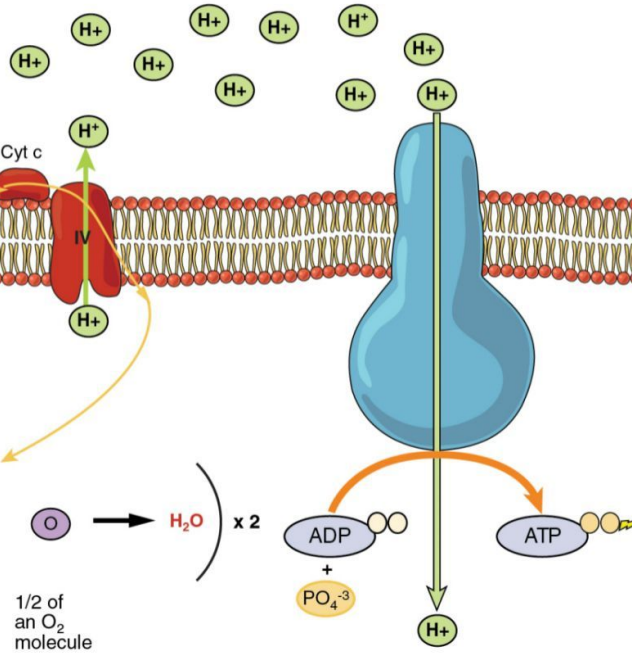
H+ Storage
For ATP Synthase to function, a lot of H+ must be stored in the inner-membrane space.
NADH & FADH2
Molecules involved in cell respiration that provide H+ needed to power ATP synthase.
Energy carriers
Electron Transport Chain
A series of integral proteins in the inner-membrane that pass along the H+ (electrons) of NADH & FADH2.
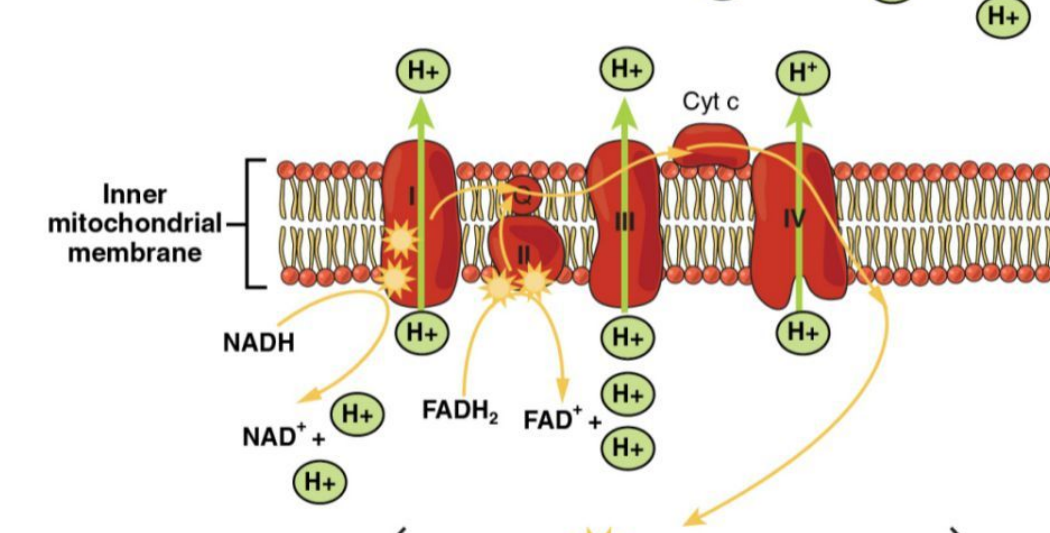
Active Transport
The process used by the electron transport chain to push H+ into the inner-membrane space.
Chemiosmosis
Powers ATP synthase
The natural movement of ions across a membrane moving down their concentration gradient.
Opposite of active transport.
Substrate-Level Phosphorylation
A process that generates ATP directly in the Citric Acid Cycle using mitochondrial enzymes.
Integral Proteins
Proteins that assist in the active transport of pyruvate across mitochondrial membranes.
Mitochondrial Matrix
The cytoplasm of the mitochondria where Pyruvate Oxidation and the Citric Acid Cycle occur.
Acetyl CoA
A product of Pyruvate Oxidation that enters the Citric Acid Cycle.
CO2 Production
A significant output of both Pyruvate Oxidation and the Citric Acid Cycle.
NADH Production
A key output of Glycolysis, Pyruvate Oxidation, and the Citric Acid Cycle.
FADH2 Production
Generated during the Citric Acid Cycle and used in oxidative phosphorylation.
Energy Source for ATP Synthase
The energy required for ATP Synthase comes from the redox reactions of NADH and FADH2.
ATP Yield
The total ATP produced from Glycolysis, Citric Acid Cycle, and Oxidative Phosphorylation combined.
Redox Reactions
Chemical reactions that involve the transfer of electrons, crucial for oxidative phosphorylation.
Chemiosmosis
The natural movements of ions across a membrane moving down their concentration gradient.
ATP synthase
The enzyme that is powered by chemiosmosis to synthesize ATP.
Oxidative Phosphorylation
The stage of cellular respiration that occurs across the inner membrane and produces 26 or 28 ATP.
Fermentation
A form of respiration that continues the process of glycolysis to generate ATP without oxygen.
Anaerobic Respiration
Respiration that occurs when oxygen isn't available (fermentation)
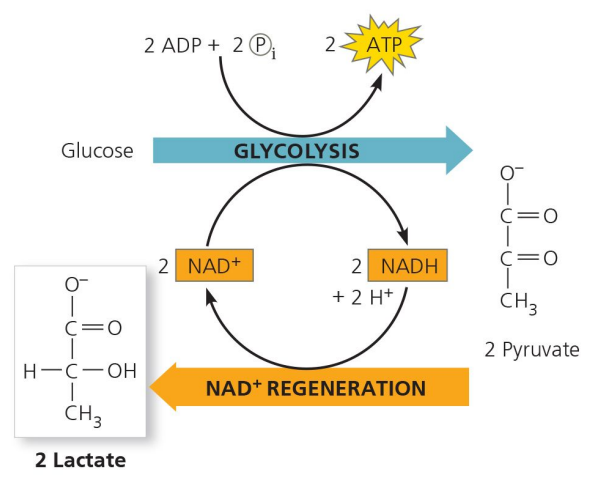
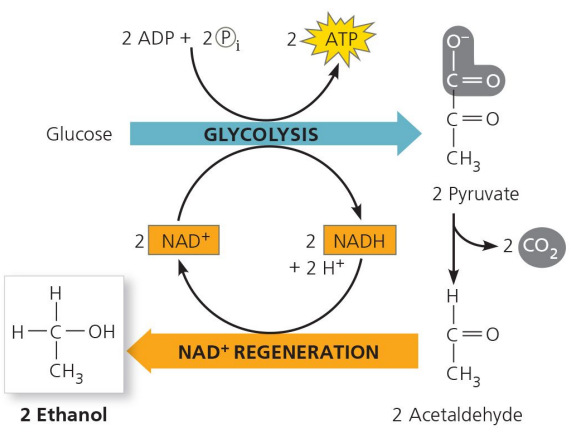
Glycolysis
The first stage of cell respiration that occurs outside the mitochondria in the cytoplasm, with an input of glucose and NAD, producing pyruvate, NADH, and H2O, yielding 2 ATP.
Substrate-level phosphorylation
A method of generating ATP during glycolysis and fermentation.
Lactic Acid Fermentation
A process where hydrogens from NADH are added to pyruvate to form lactic acid, allowing glycolysis to continue.
Alcoholic Fermentation
A process where pyruvate is broken down to acetaldehyde and CO2, and hydrogens are added to acetaldehyde to form ethanol.
Happens in the cytoplasm
Usually makes food
Glucose and NAD
Input of Glycolysis
Pyruvate, NADH, and H2O
Output of Glycolysis
2
ATP yield of Glycolysis
Regenerating NAD
The process required to repeat glycolysis, which involves oxidizing NADH back to NAD.
Pyruvate
The output of glycolysis that can be used in fermentation.
Ethanol, CO2 , NAD
The output of alcoholic fermentation.
Lactic Acid, NAD
The output of lactic acid fermentation.
Pyruvate,NADH
The input of alcoholic fermentation.
Citric Acid Cycle
A stage of aerobic respiration that requires oxygen.
NADH
An electron carrier that is oxidized back to NAD during fermentation.
Oxygen in Aerobic Respiration
Required for aerobic respiration to occur.
Fermentation vs Aerobic Respiration
Fermentation does not require oxygen, whereas aerobic respiration does.
Fermentation in Humans
Used during intense exercise, leading to muscle soreness due to lactic acid.
Fermentation in Yeast
Used in baking and brewing, producing CO2 and ethanol.
GADPH
Enzyme that converts ADP to ATP and NAD to NADH.
Pyruvate,NADH
The input of lactic acid fermentation.