Unit 3: Fixing the Economy Part 1-Fiscal Policy
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Real Wealth Effect
PL Increase→ Savings increase→ rGDP decreases
Interest Rate Effect
PL increase→ interest rates increase→ rGDP decrease
Net Export Effect
PL increase→ exports decrease→ rGDP decreases
AD shifters on a aggregate supply/demand graph
any change in C, I, G, or Nx
Demand pull inflation
when AD increases
Cost-push inflation
when SRAS decreases
Stagflation
PL increase and U increase
Aggregate demand
sum of all demands for all the goods and services in all final markets
AD=C+G+I+Xn
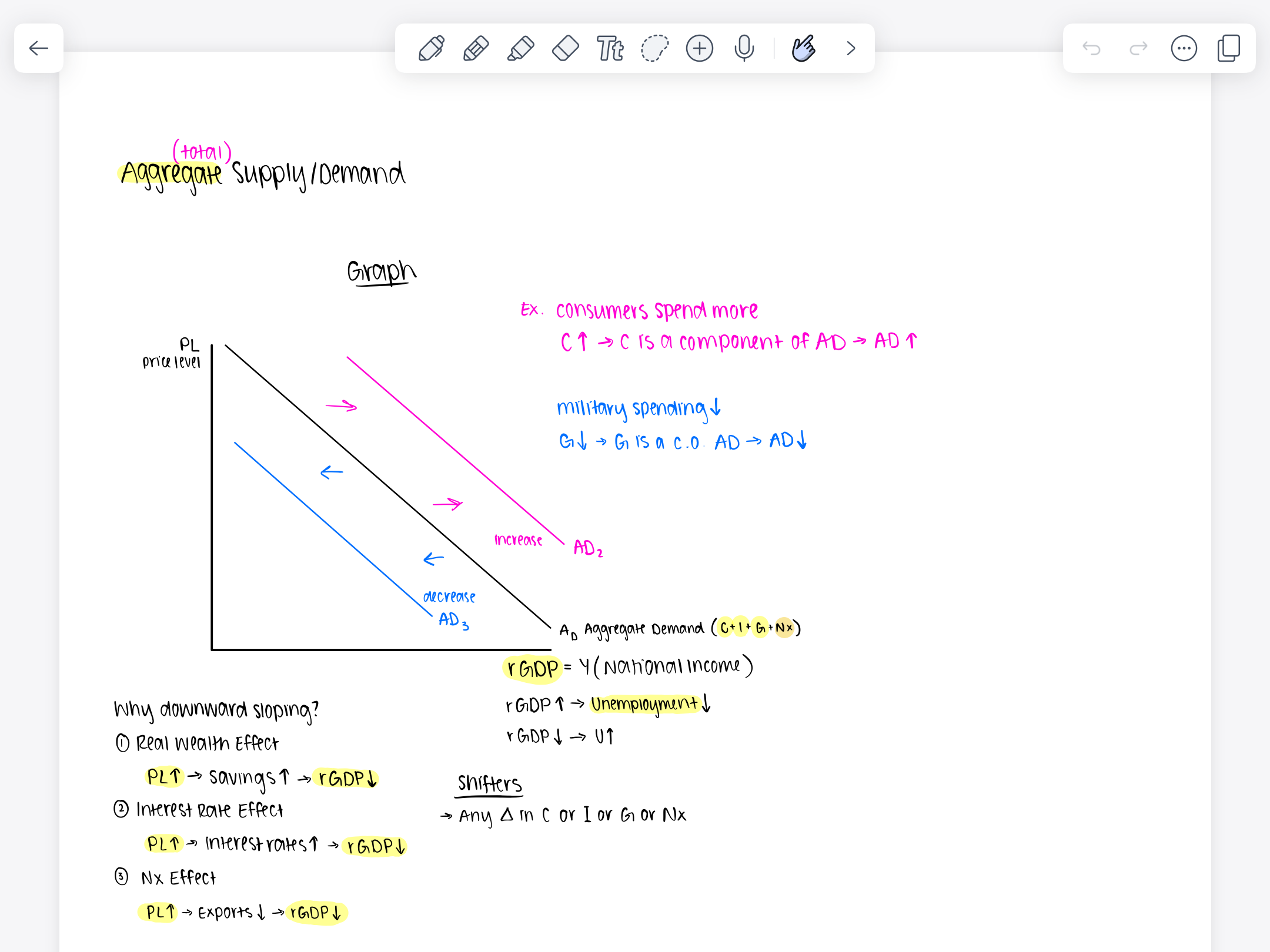
Aggregate demand formula
AD=C+G+I+Xn
Aggregate Supply
Sum of all supply of all the goods and services in all final markets
Two types of AS
Short-run aggregate supply and long-run aggregate supply.
Sloped Short-run AS
-In short run, factor cost are ____. ____ are sticky in the short run
fixed
wages
Sloped Short-run AS
-In the short run, increase in price level will ______ firms’ profits
increase
Sloped Short-run AS
-Higher profits encourage production so on the SRAS curve, rGDP ___ with price level
increases
Sloped Short-run AS
-In the short run, we have booms and busts: ___ and ____
expansions and recessions
Shifting SRAS
occurs when factor costs change, ex oil prices, wages shift, government tax policies on businesses change, or dramatic national events, weather affects production
Short-run equilibirum
Where AD and SRAS intersect illustrates the current state of the economy. Shows the current rGDP and PL.
Vertical Long-run AS
LRAS is a vertical line in the aggregate supply curve representing the full employment output of an economy, indicating that in the long run, supply is not influenced by price levels.
Shifting LRAS
Any permanent change in FOPs
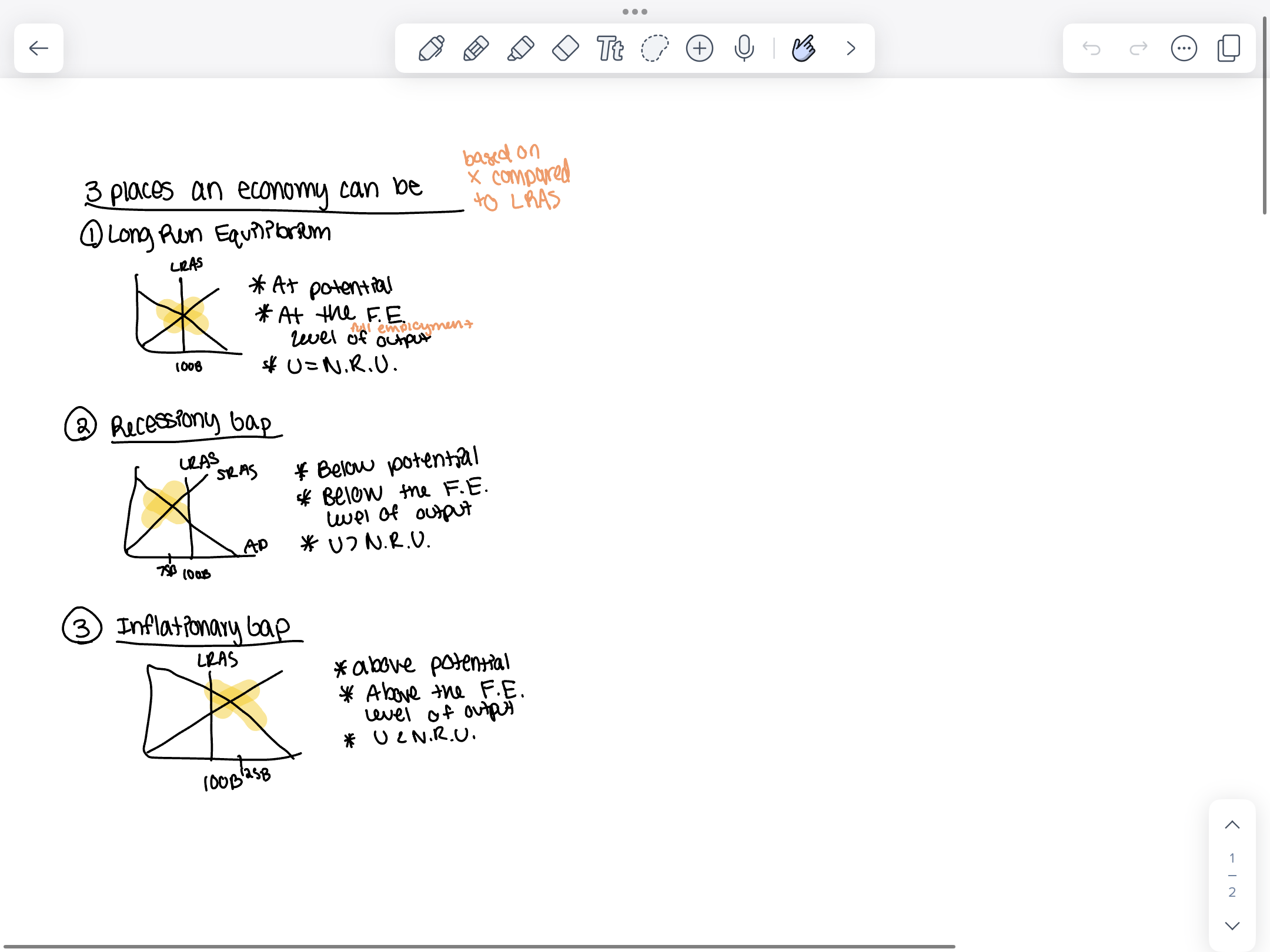
3 Places an economy can be
Long run equilibrium: at potential, at the full employment level of output, U=NRU
Recessionary Gap: Below potential, below the full employment level of output, U>NRU
Inflationary Gap: Above potential, above the full employment level of output, U<NRU
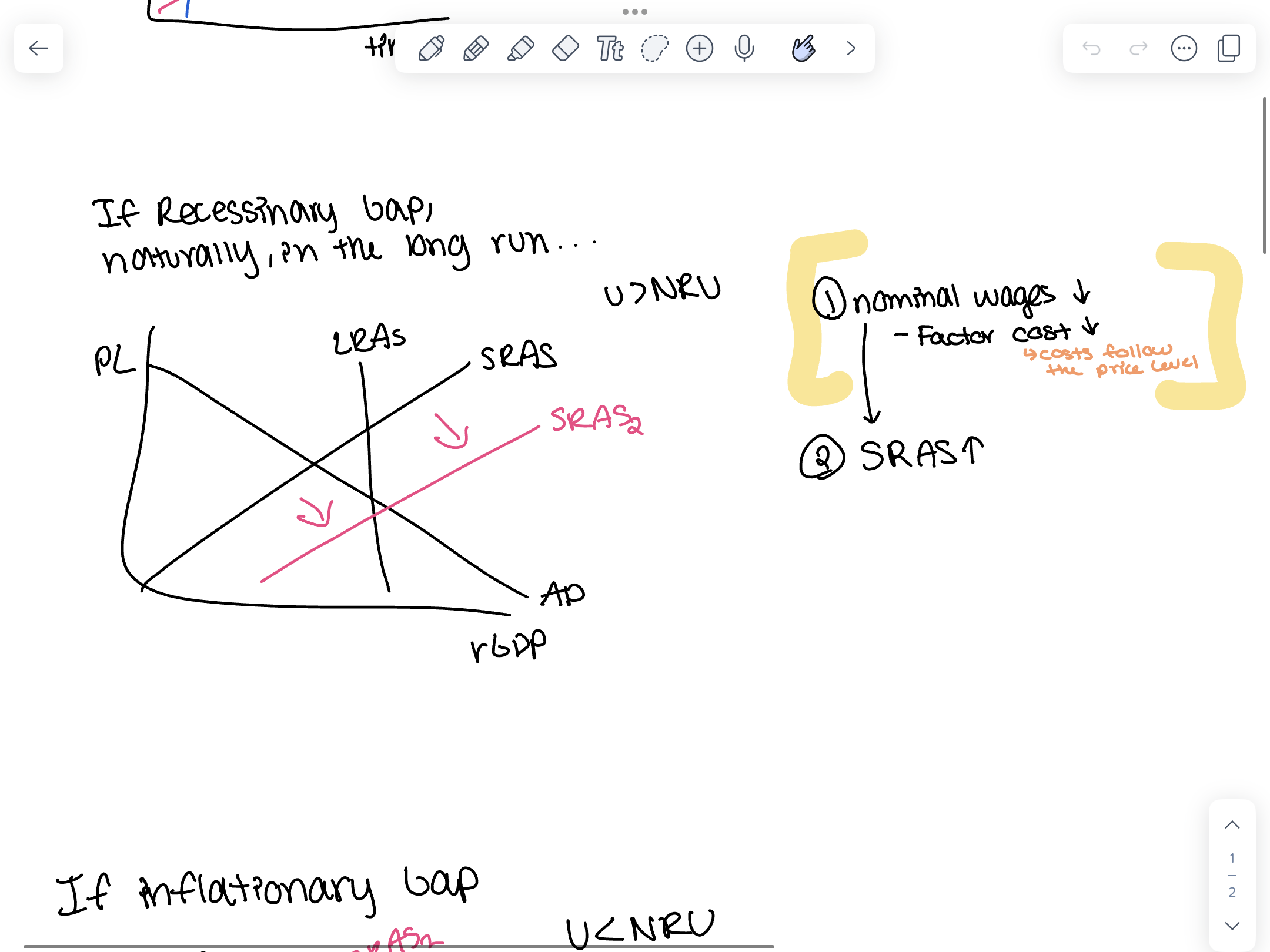
If recessionary gap, naturally, in the long run nominal wages ___ factor costs ___ SRAS ____
decreases
decreases
increases
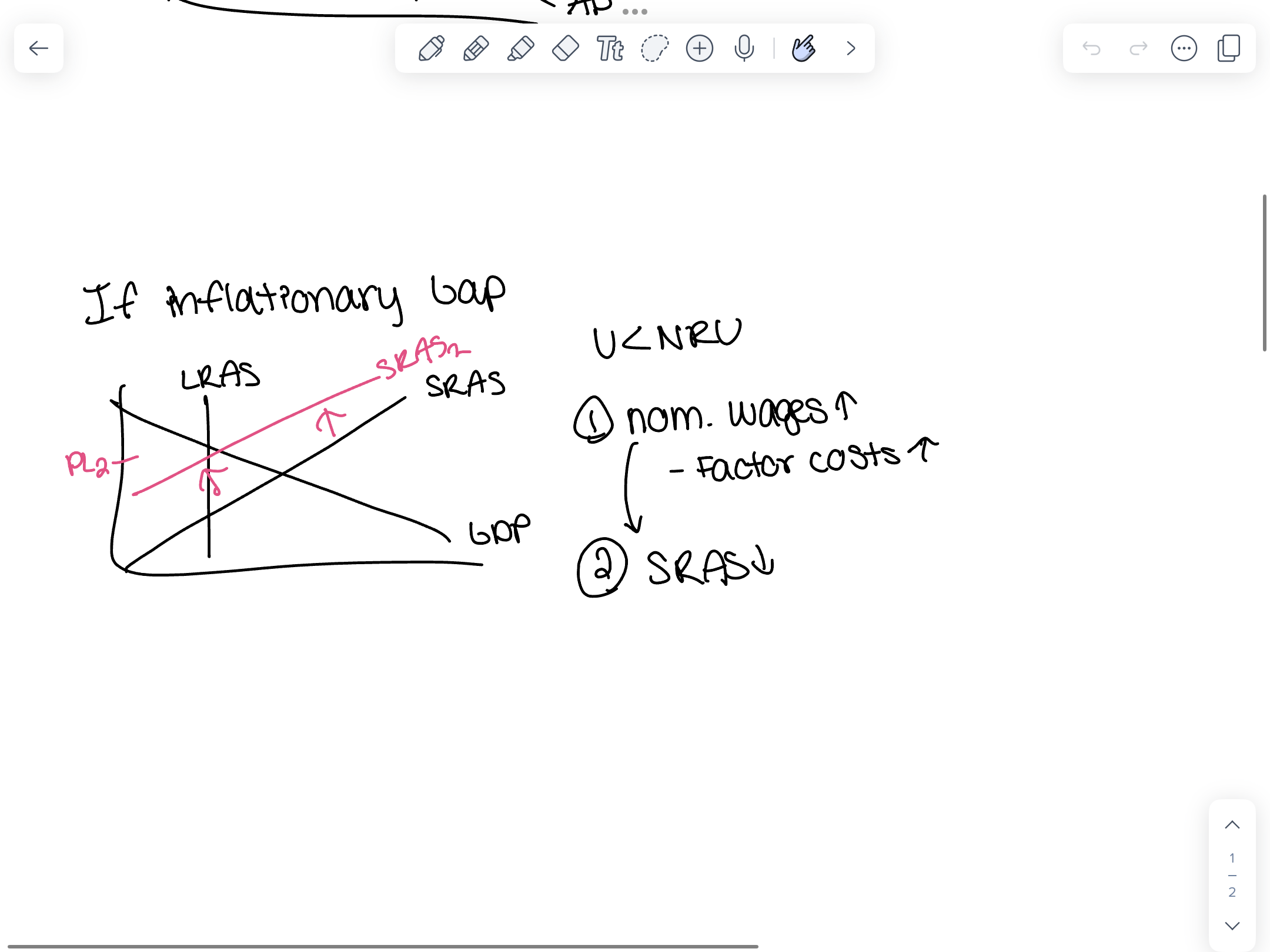
In inflationary gap nominal wages ___ factor costs ____ SRAS ____
increase
increase
decrease
Fiscal Policy
Government (pres and congress) power to tax and spend to stabilize an economy and it refers to government policies, like taxes, budgets, government purchases, and laws
3 tools pres and congress can use in fiscal policy
Change in gov spending: Impacts the G in AD
Change Taxes: Impacts C
Change transfer payments: impacts the C
Automatic stabilizers
ex) unemployment benefits, progressive tax
No need for a new policy
What is the goal of expansionary fiscal policiy
to increase aggregate demand and stimulate economic growth by
-Increasing G spending
-Lowering taxes (T)-Impacts C
-Increase transfer (TR)-Impacts C
What is the goal of contractionary fiscal policy
to decrease aggregate demand and reduce inflation by
-Decreasing G spending
-Increasing taxes (T)-Impacts C
-Decreasing transfer payments (TR)-Impacts C
Two approaches to fiscal policy
Demand-side policies and supply side policies
Demand-side policies (fiscal policy)
Policies targeted at consumers. Goal=Government stimulates demand to spur output. Focus on increasing aggregate demand through government spending and tax adjustments, aimed at stimulating economic growth.
Supply-side policies (fiscal policy)
Policies aimed at producers like firms/businesses. Goal=stimulate production to grow output, often by tax cuts, cut gov regulations, increase subsidies for businesses to increase incentives. Also known as trickle down economics
MPC=
Marginal propensity to consume
MPS=
Marginal propensity to save
MPC+MPS=
1
Government multiplier/Investment multiplier/Net Exports Multiplier=
1/MPS
Tax multiplier=
-MPCx(1/MPS)
Government multiplier is (larger/smaller) than the tax multipler
larger
Short-run phillips curve
shows the inverse relationship between inflation and unemployment in the short run, illustrating how inflation can decrease when unemployment rises.
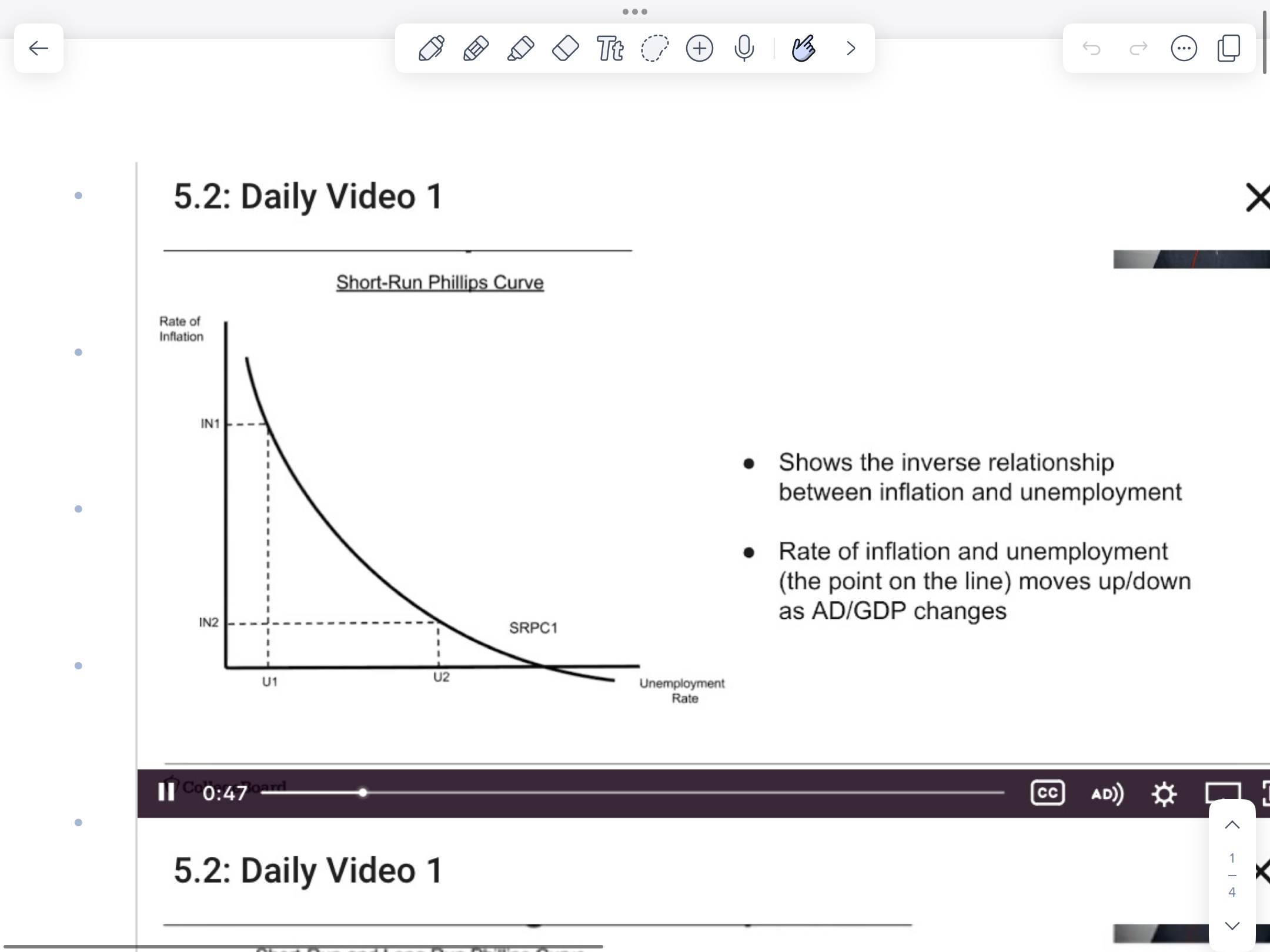
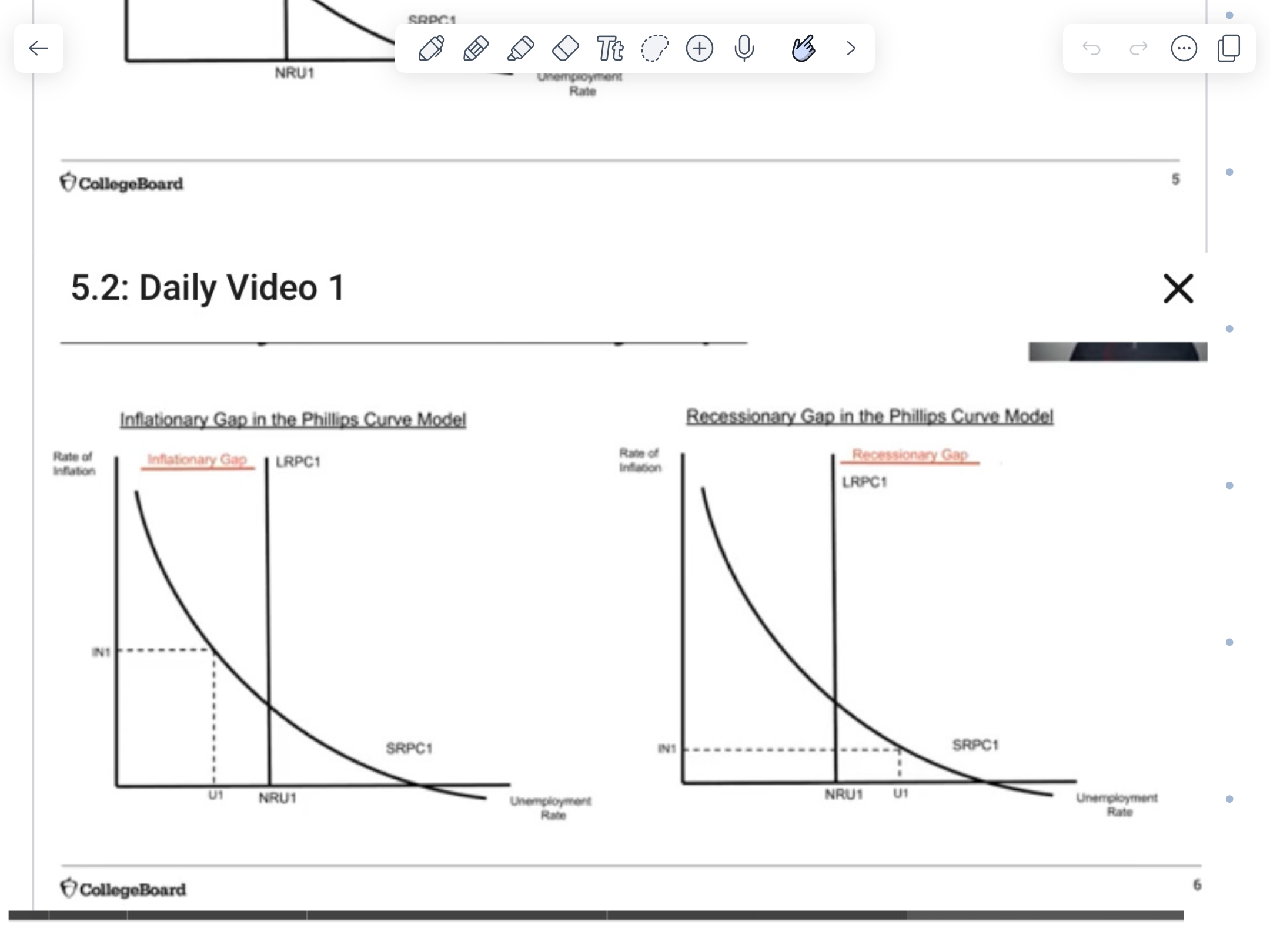
If the economy is operating at a point left to the LRPC curve, it’s in an ___ gap
inflationary
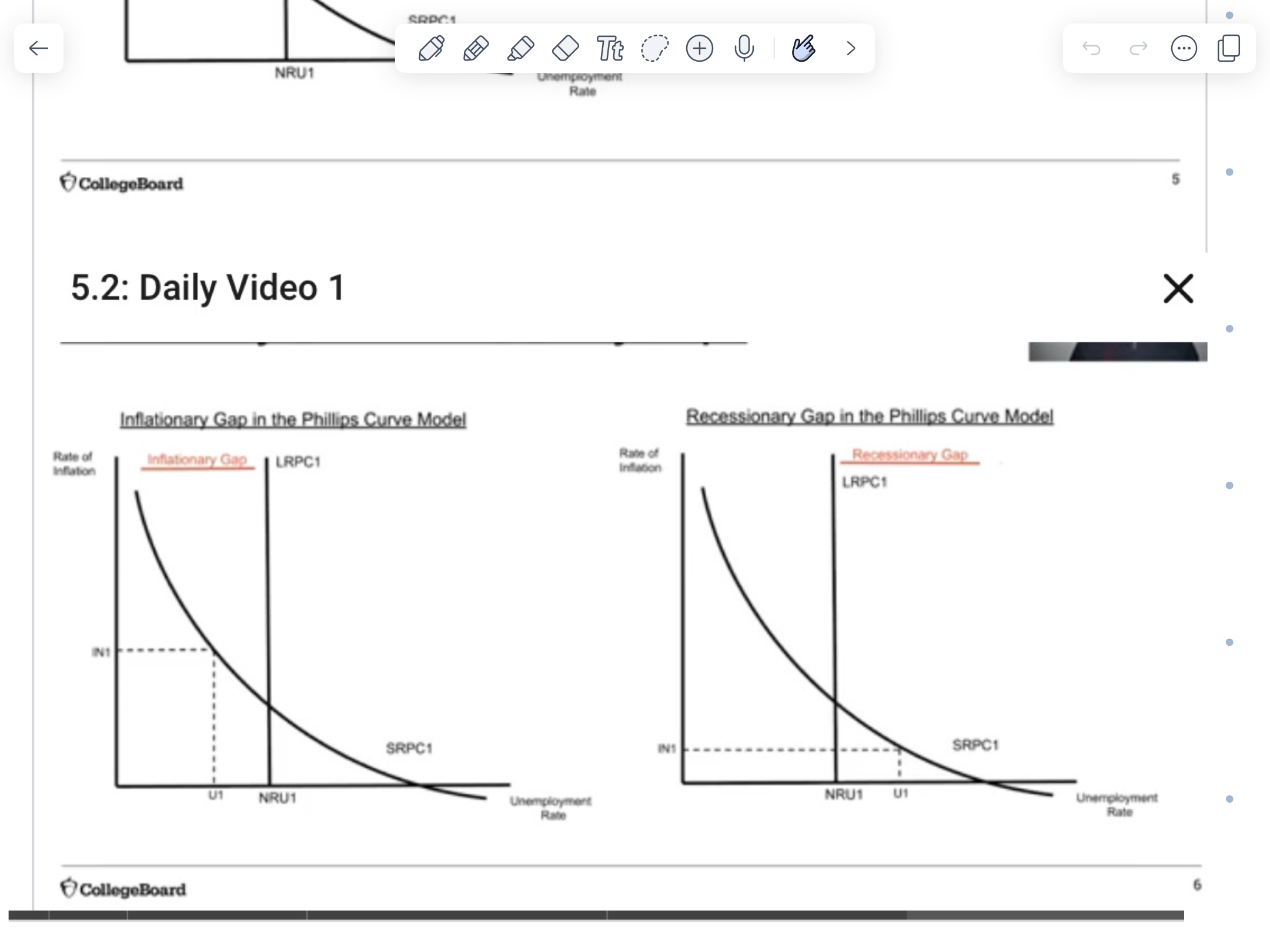
If the economy is operating at a point to the right of the LRPC curve, it’s in a ___ gap
recessionary
Demand shocks: (slide/shift) on the SRPC
slide in the opp direction as demand shift
Supply shocks: (Slide/Shift) the SRPC
shift in the opp direction as supply
On the Phillips curve slides/shift move in the (same/opp) direction as the preceding AD/AS shift
opp