Private Pilot Exam YouTube
1/292
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Notes from Free Pilot Training Youtube
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
293 Terms
Non-hard surfaced airport with a control tower and services
...
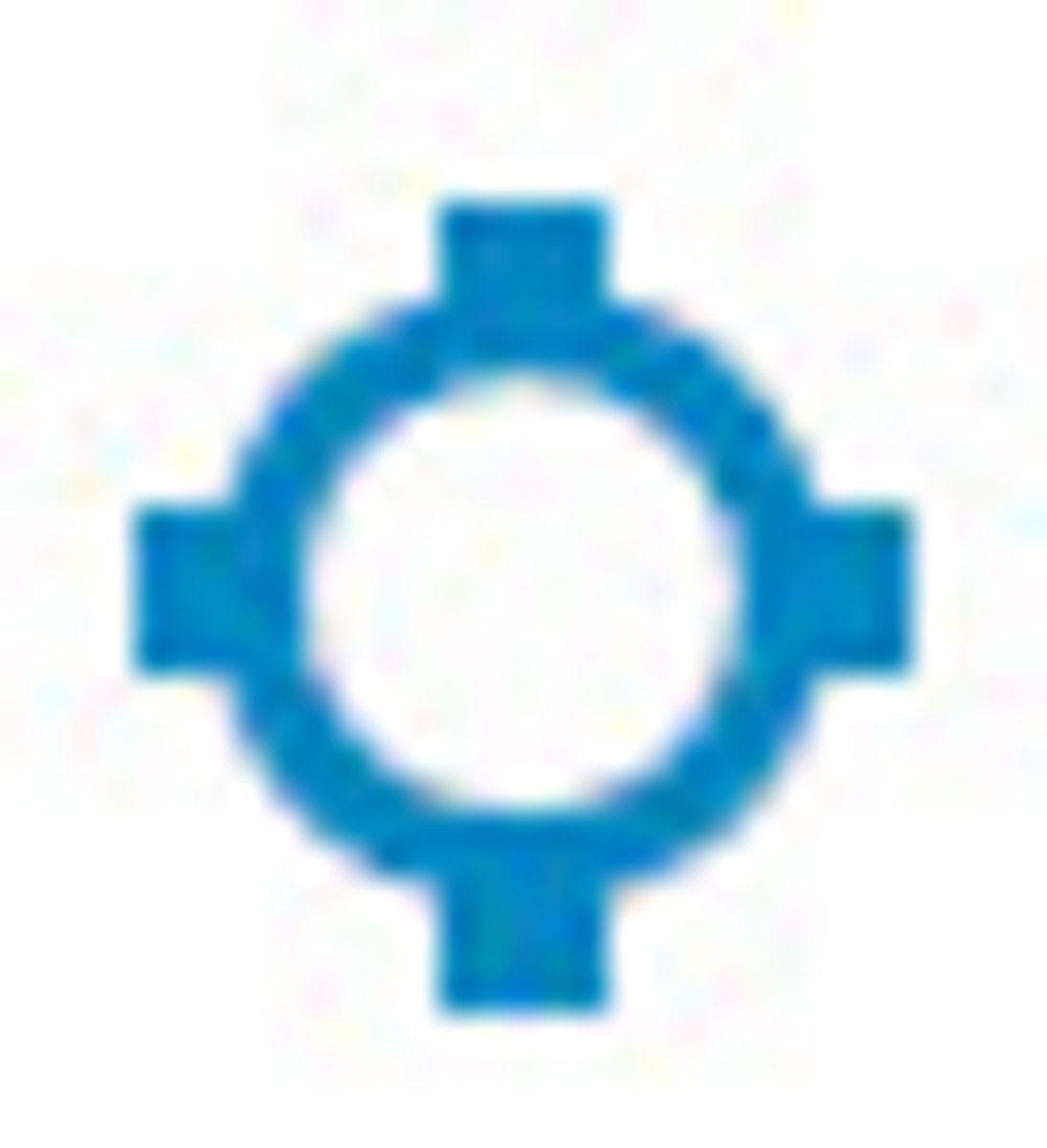

Non-hard surfaced airport with services but no control tower
...
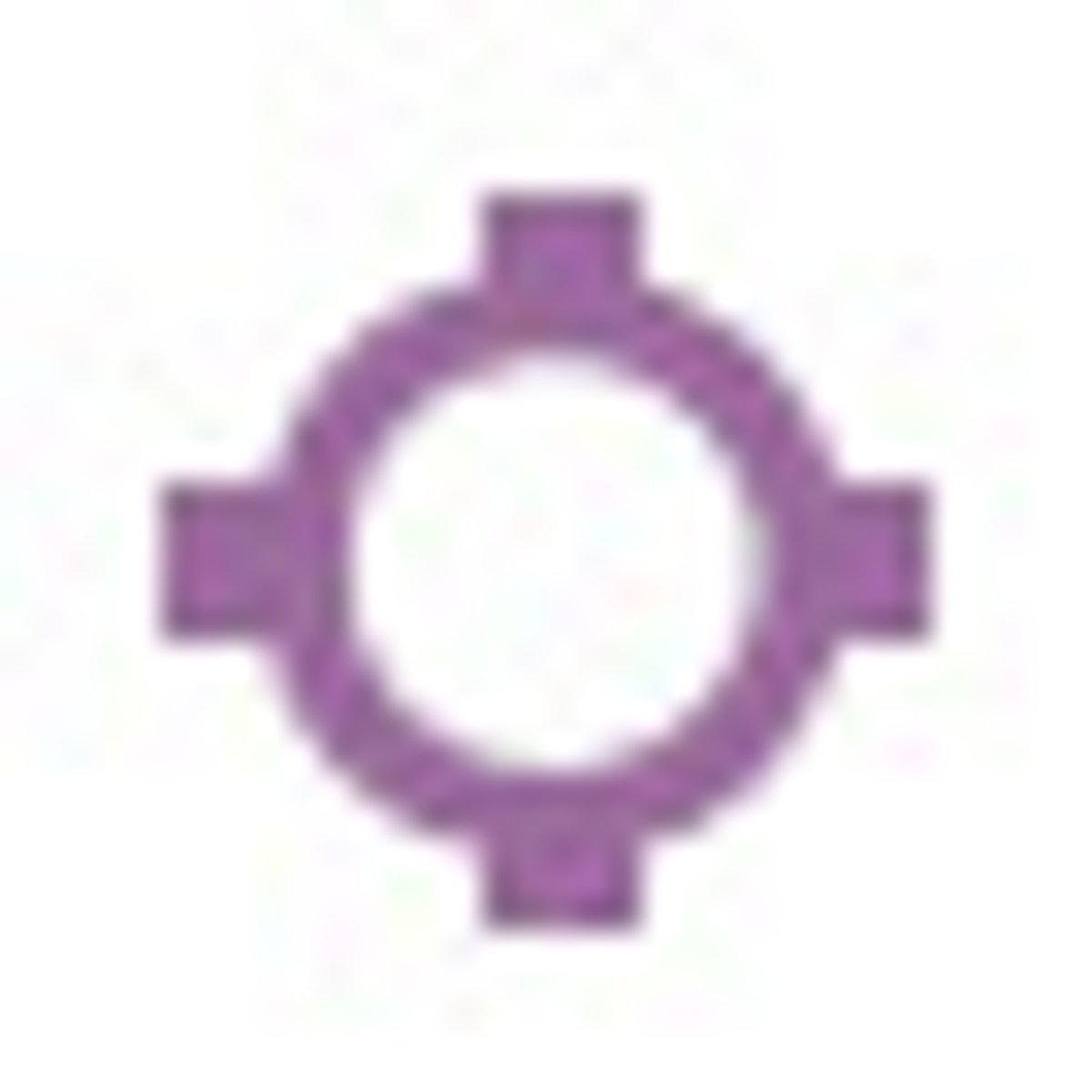

Hard surfaced runways 1500 to 8069 ft
...
Military / other than hard surfaced
...
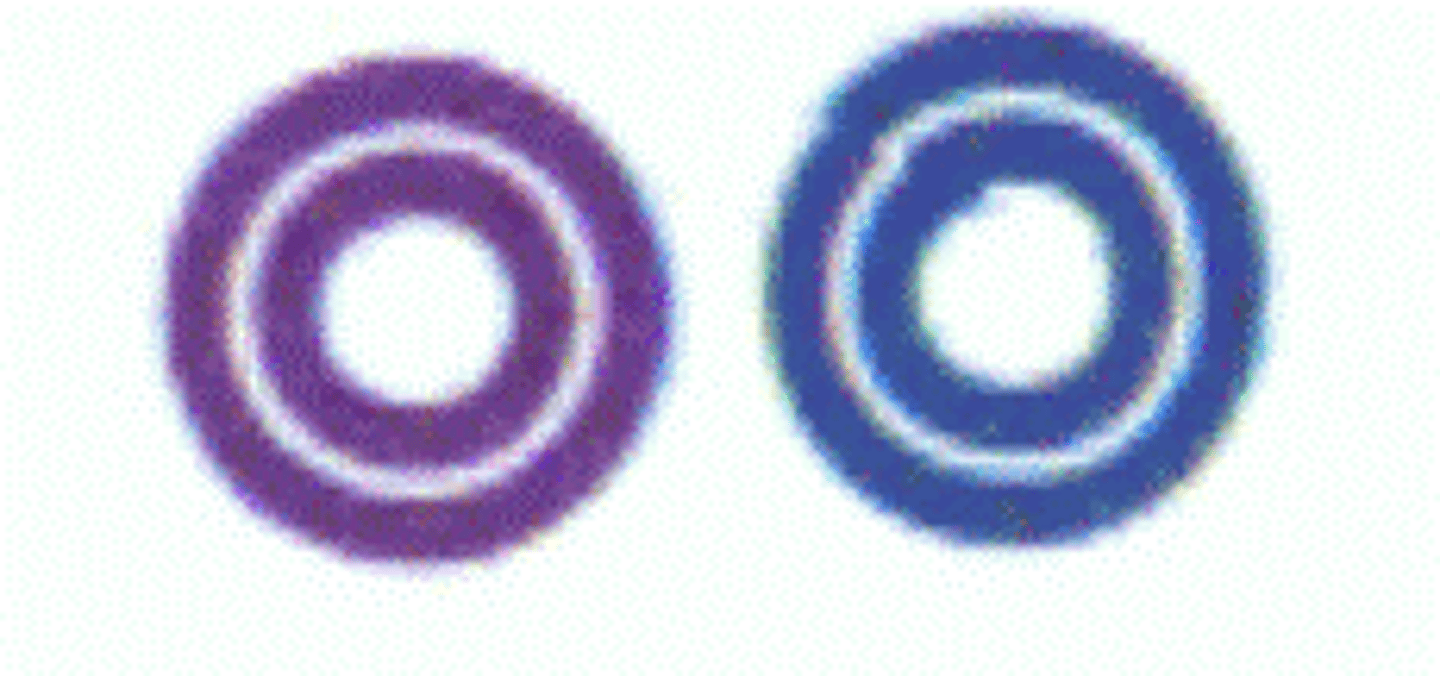

Hard surfaced runways greater than 8069 ft, or, some multiple runways less than 8069 ft
...

Hard surface runways greater than 8069 ft, dot indicates approximate location of VOR, VORTAC, VOR-DME.
...
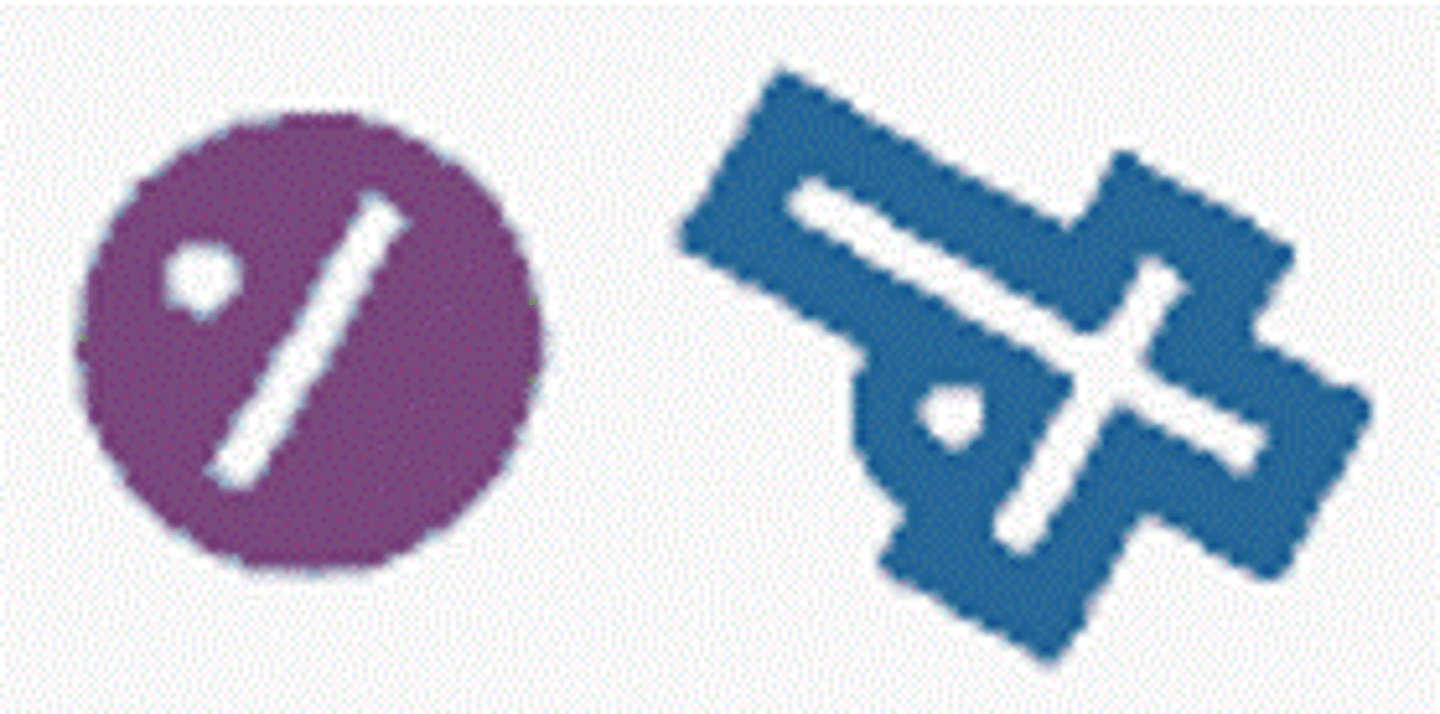

Rotating Beacon in operation from sunset to sunrise
...
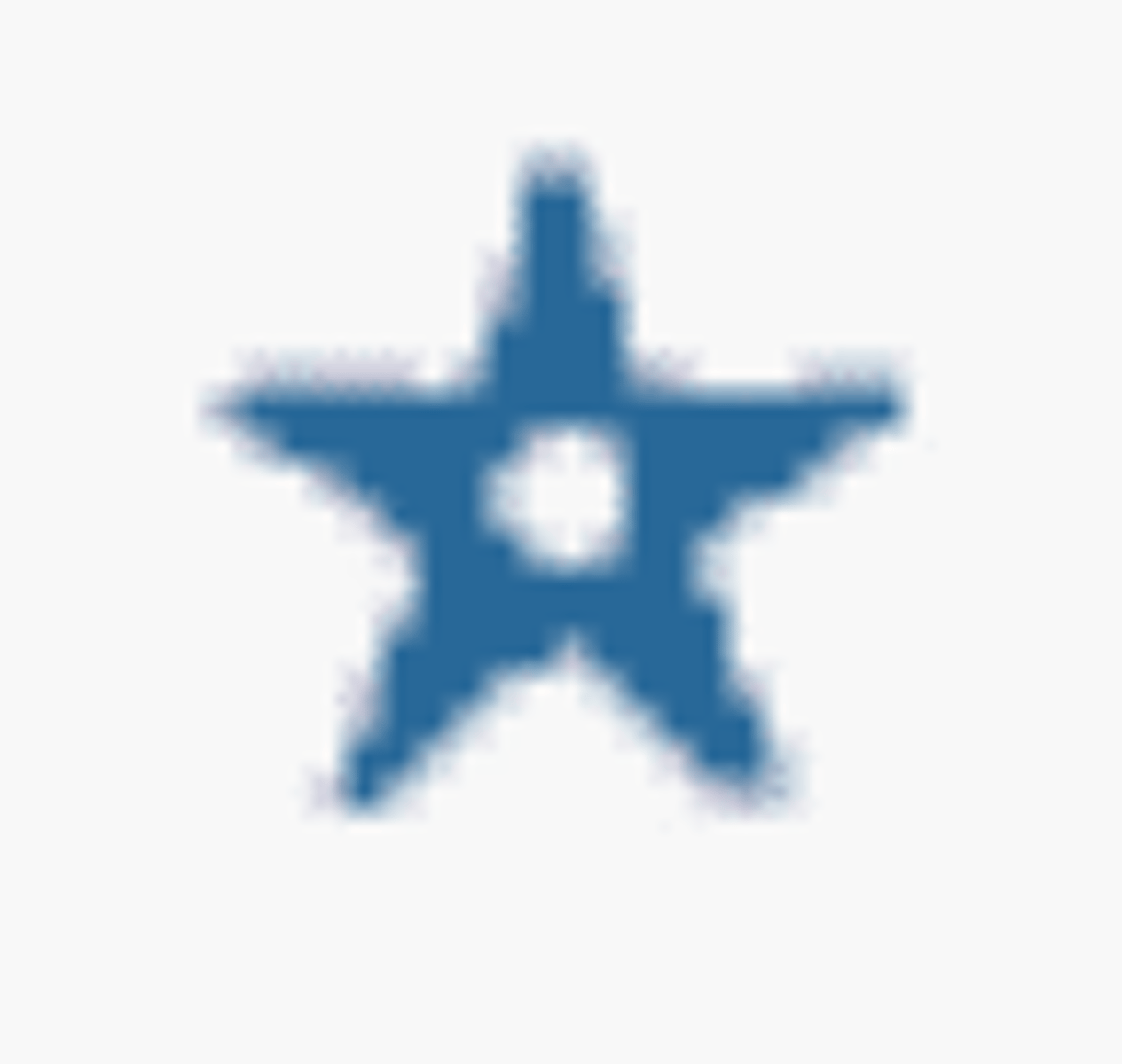

Private / Non public use
...

Heliport /Unverified
...

Seaplane area without facilities
...
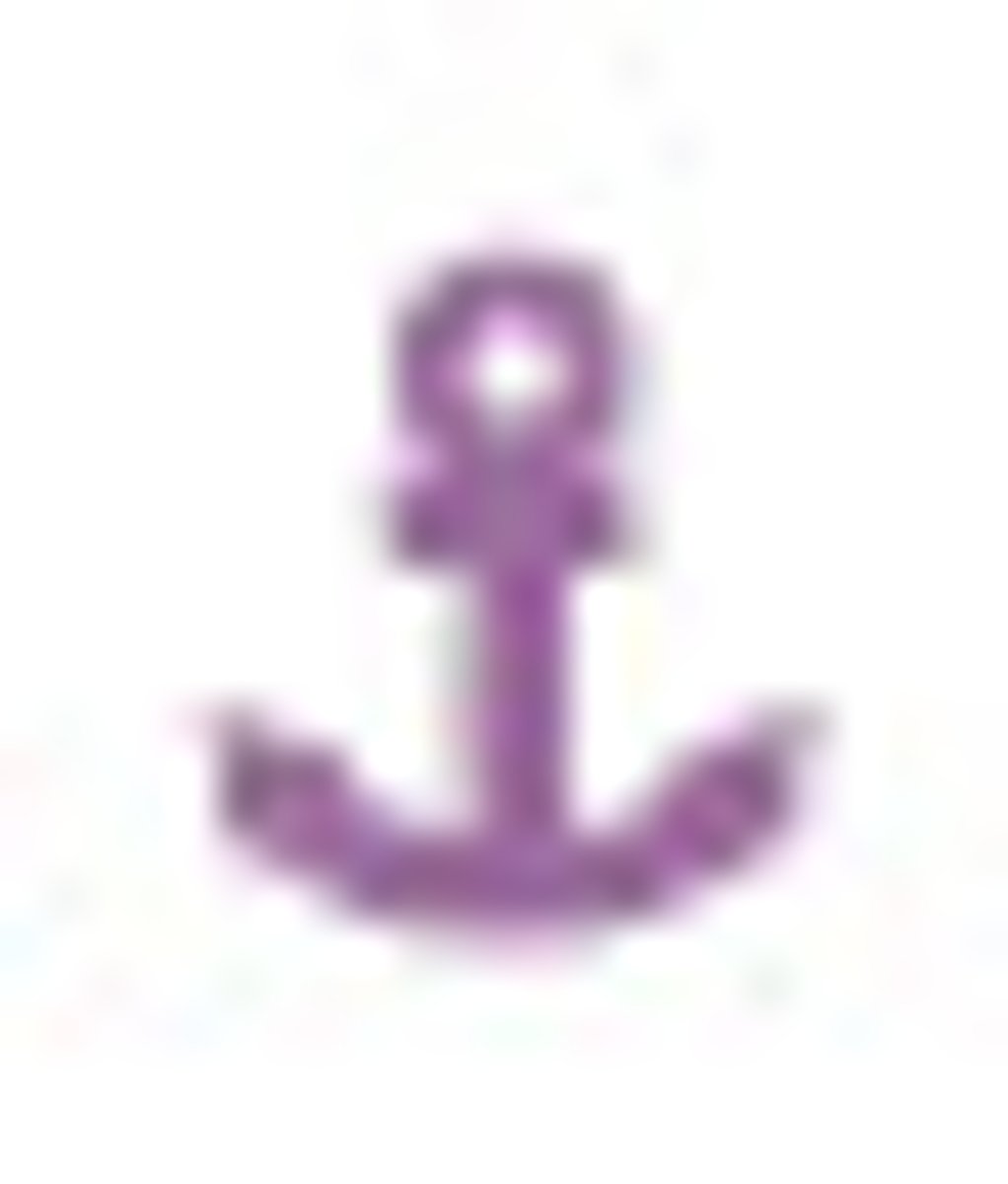

VOR range
...
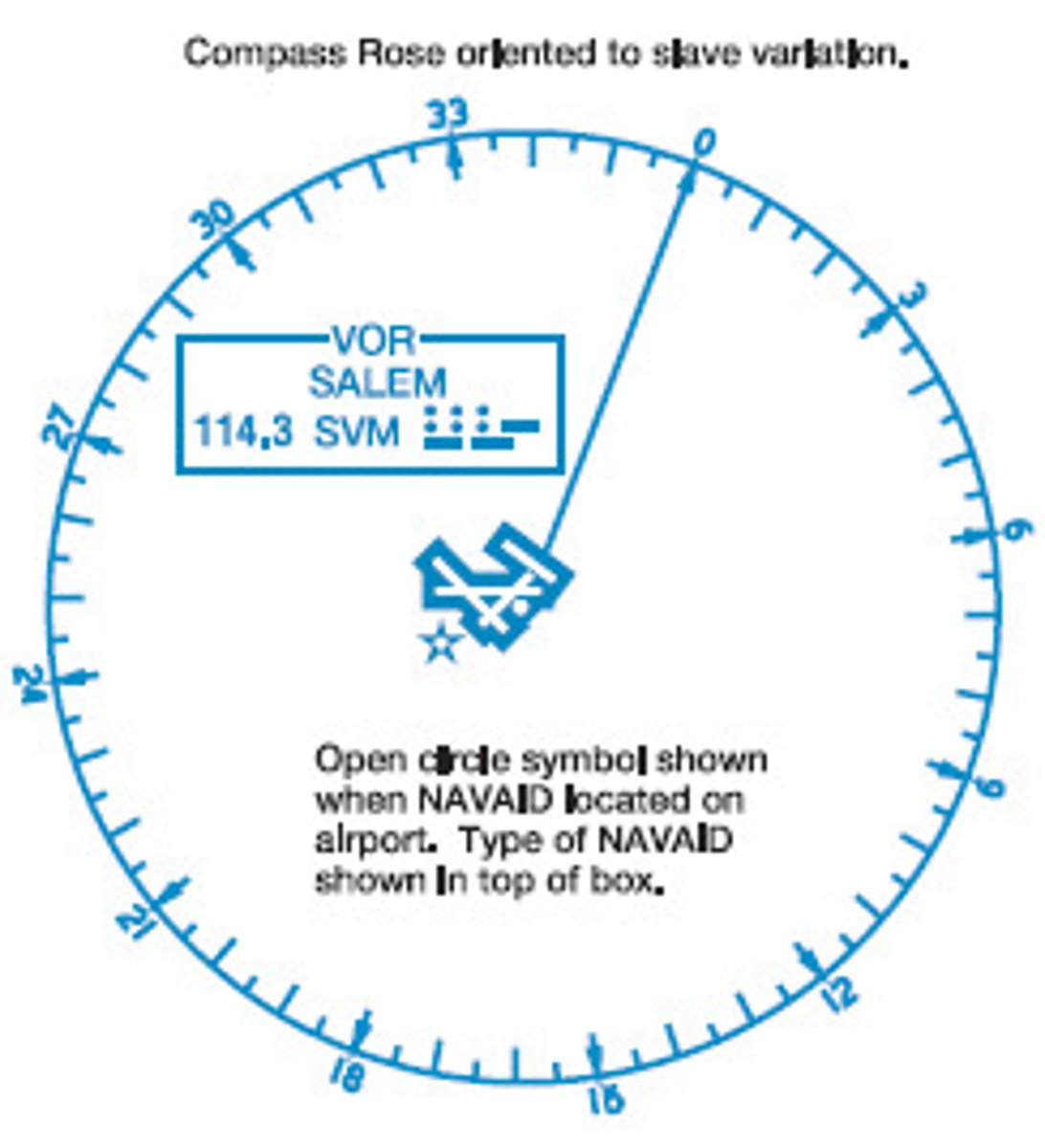
VOR
...

VORTAC
...
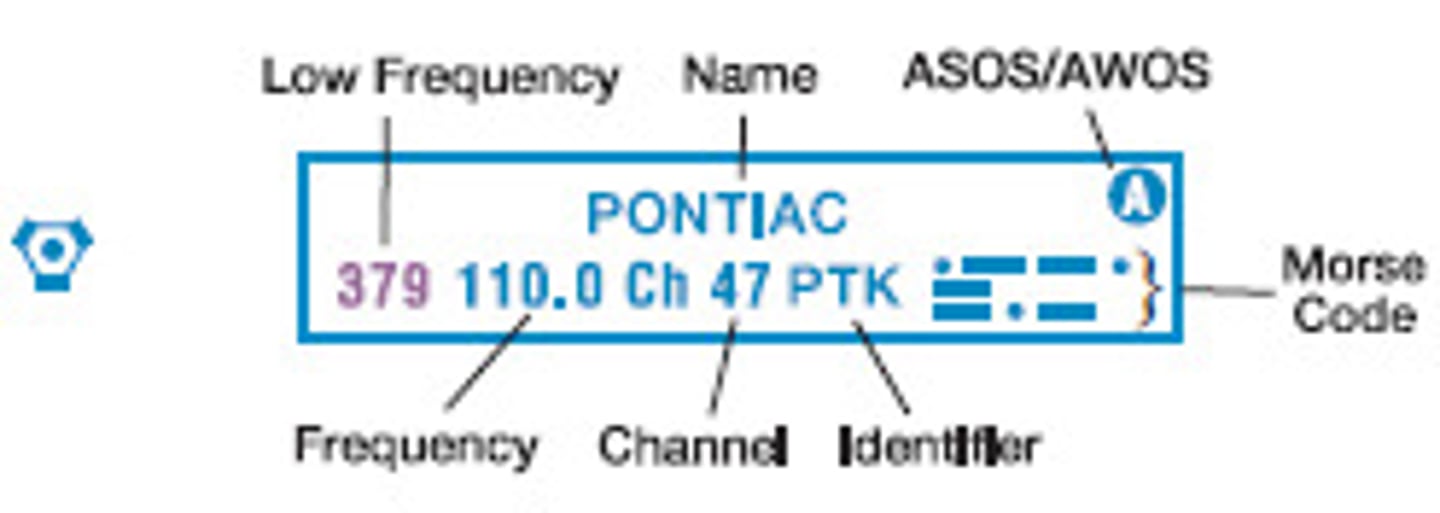
VOR-DME
...

NDB
...
NDB-DME
...
Localizer
Shown when component of airway system or used in the description of Class B airspace

Locator beacon
...

ILS - DME
Shown when component of airway system or used in the description of Class B airspace

Broadcast stations
On request by the proper authority or when a VFR Checkpoint

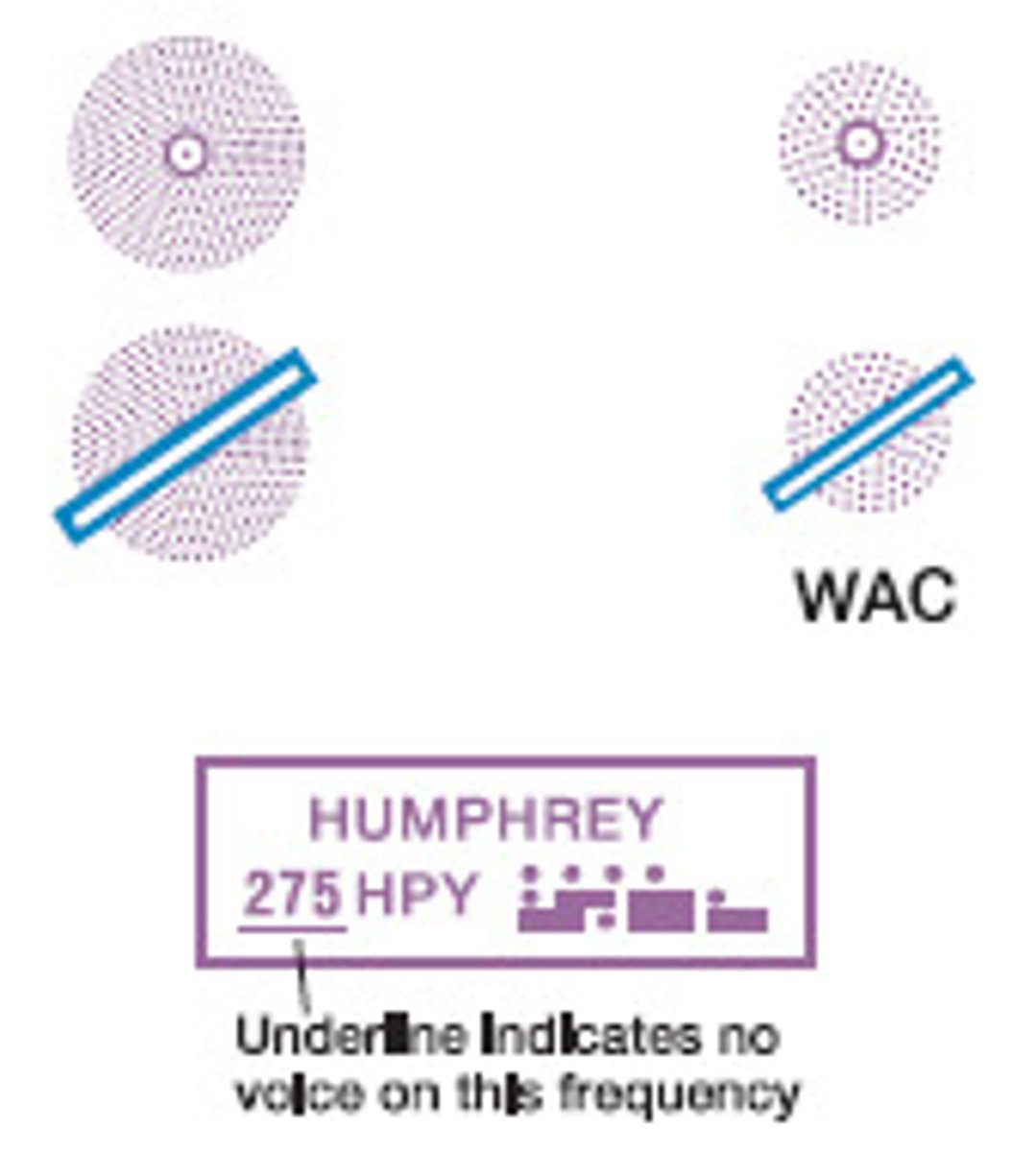
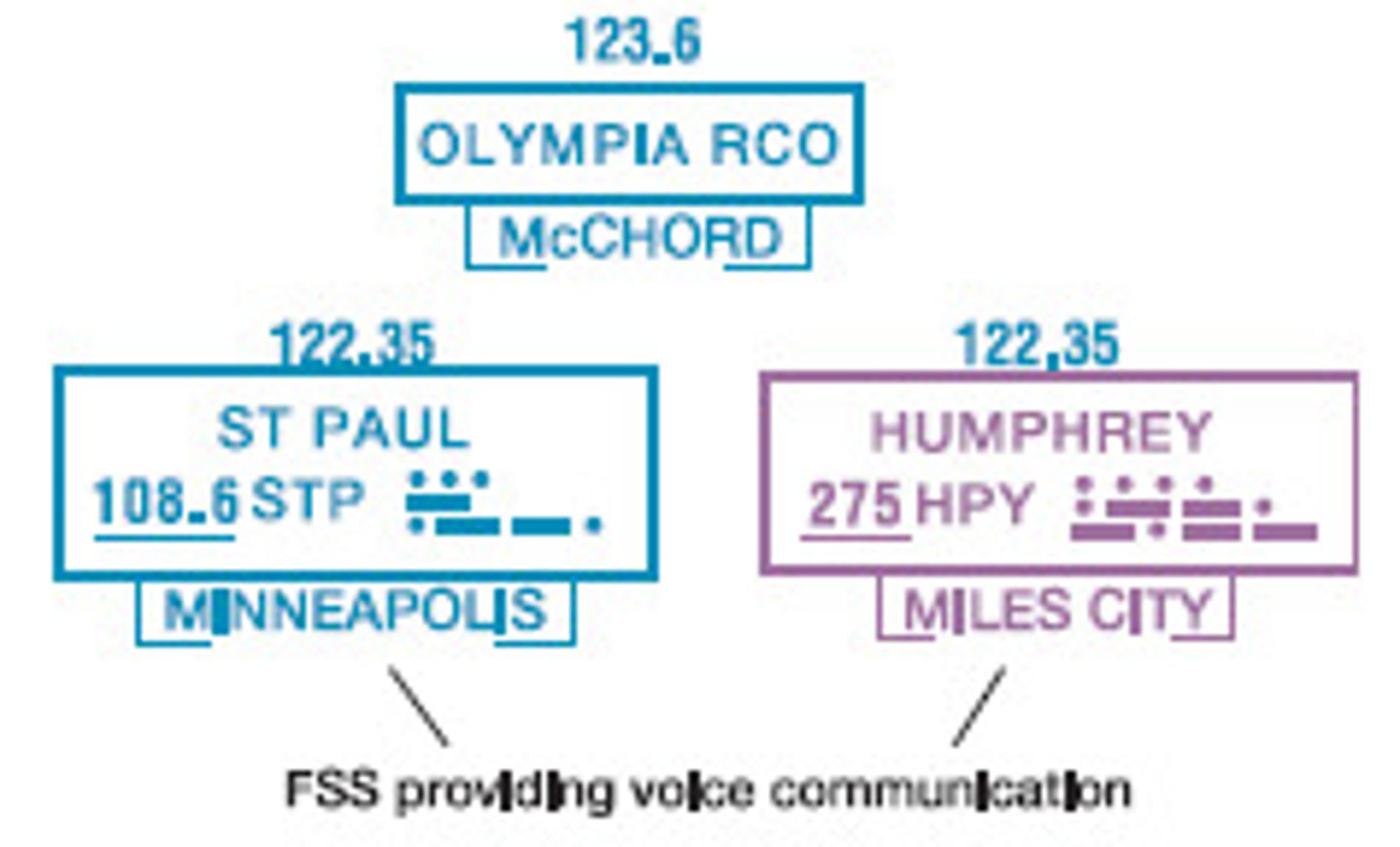
Flight service station (FSS)
...
Remote communications outlet (RCO)
...
Class B Airspace
Class C Airspace
Class D Airspace
...

Ceiling of Class D in hundreds of feet
...

Ceiling of Class D, MINUS = up to but not including 4,500ft
...

Class E Airspace
Class E Airspace w/floor 700 ft above surface
Class E Airspace w/floor 1200 ft above surface
...
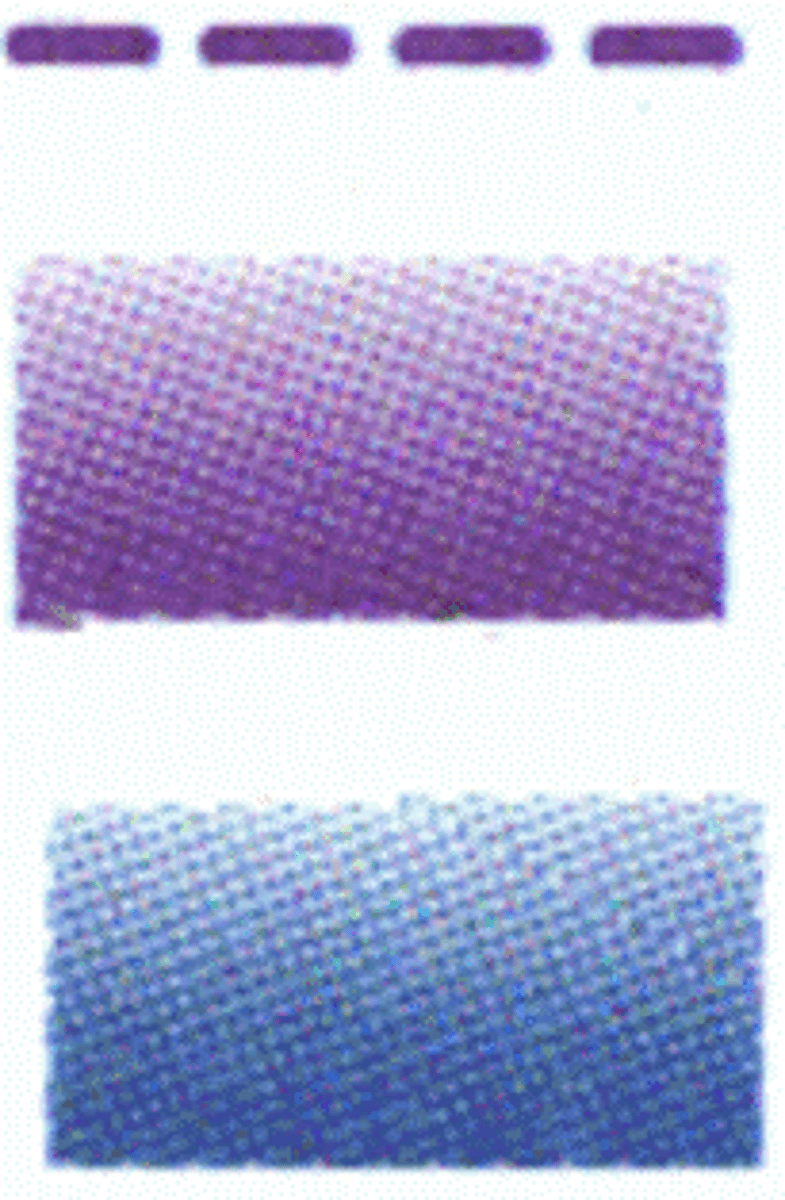
Class E airspace w/floor 700 ft above surface that laterally abuts Class G

Differentiates floors of Class E Airspace greater than 700 ft above surface
...

Prohibited, Restricted, Warning, Alert areas
Military Operations / MOA
...
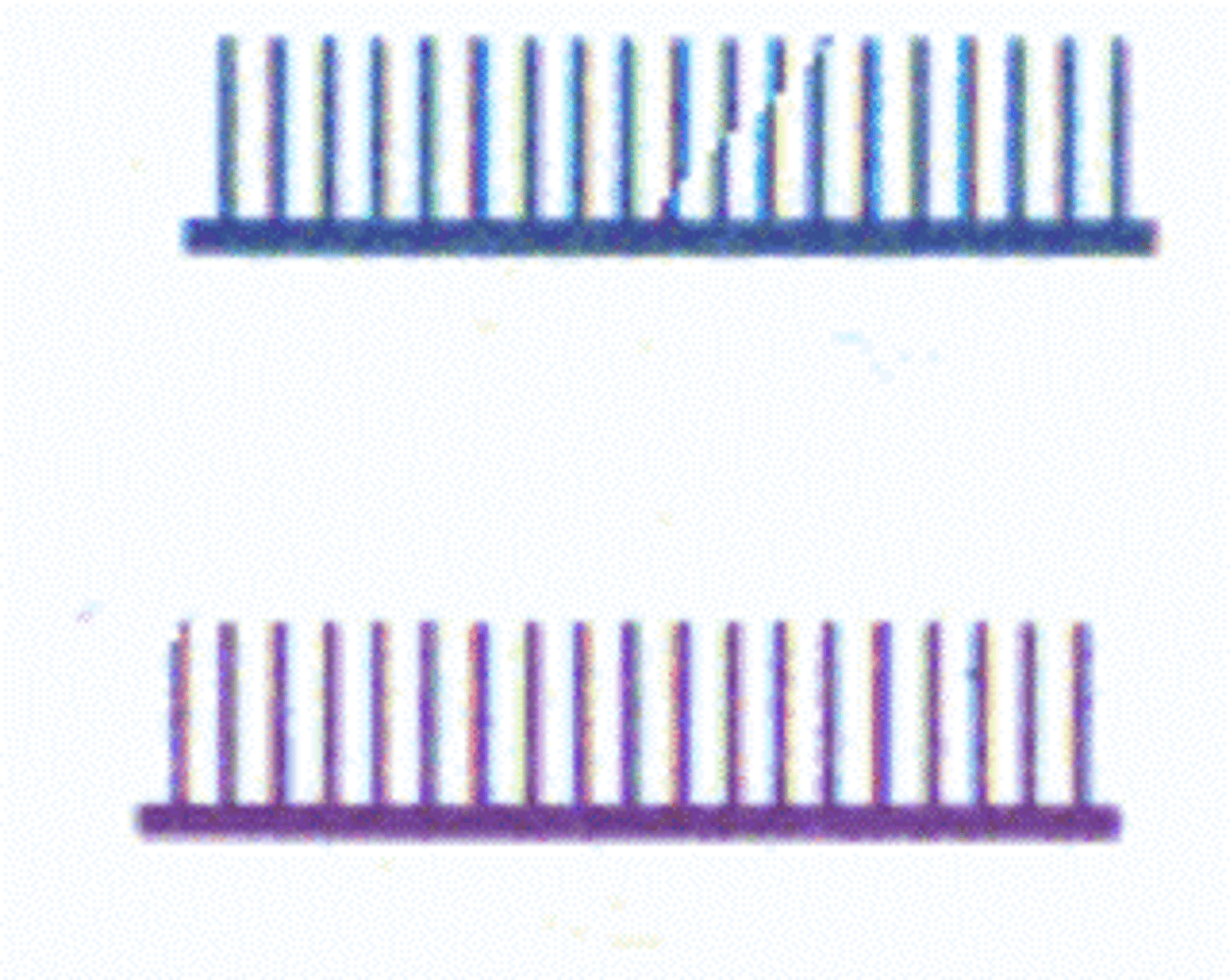
Special Military Activity Route
Floor and Ceiling of area
Special Airport Traffic Area
Air Defense ID Zone / ADIZ
...
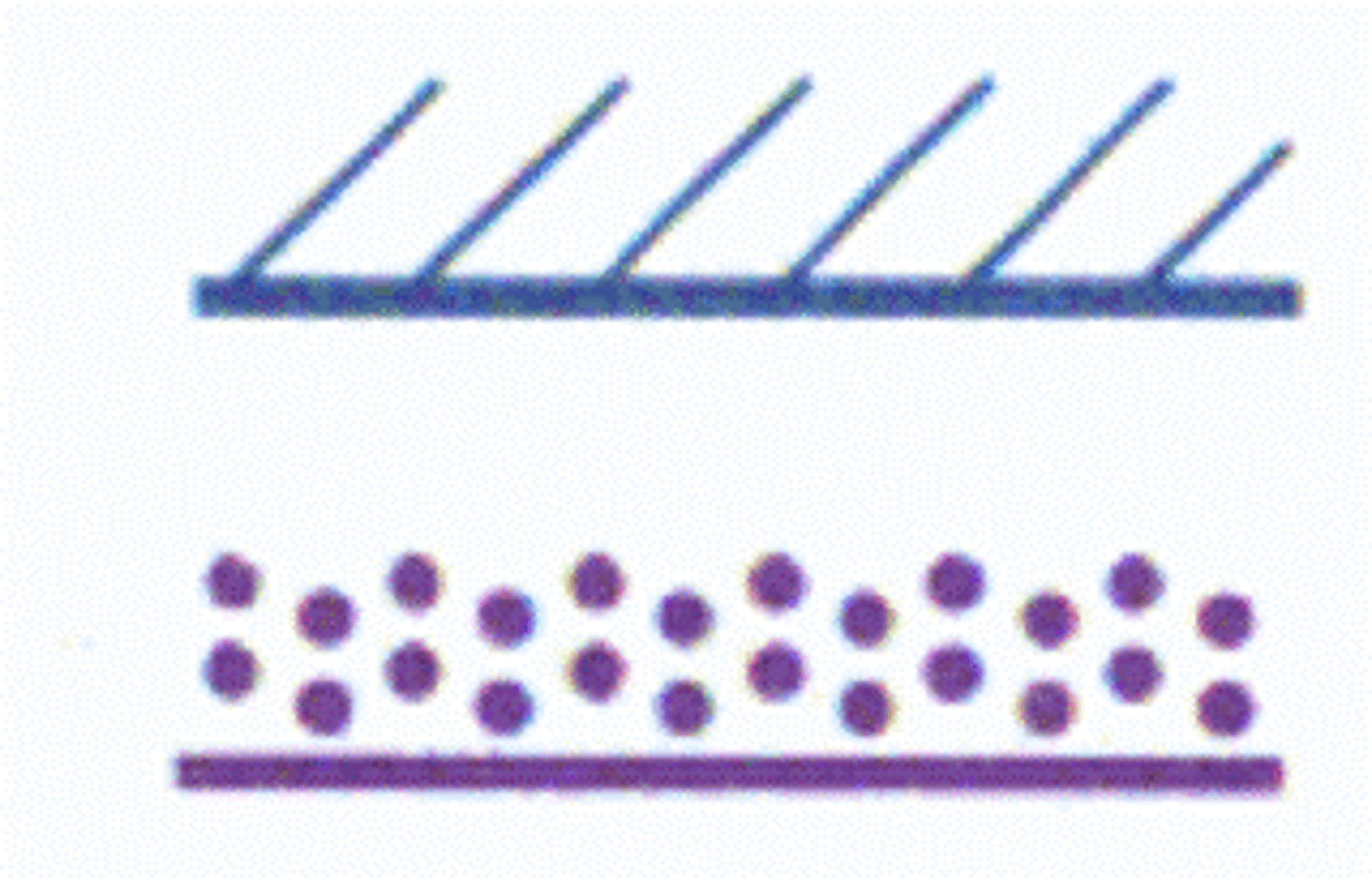
Special Conservation Area

Mode C
National Security Area
Terminal Radar Service Area
...
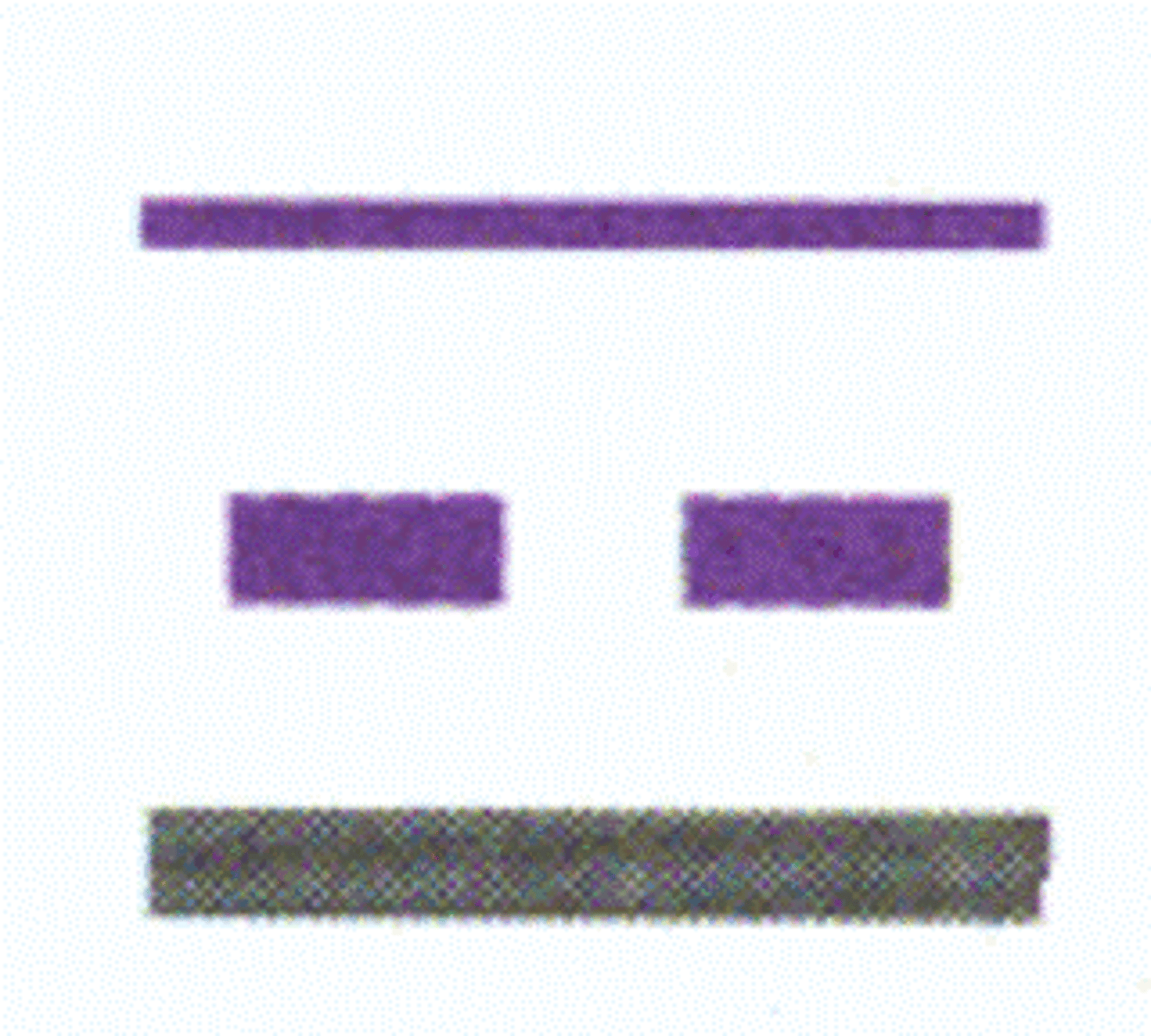

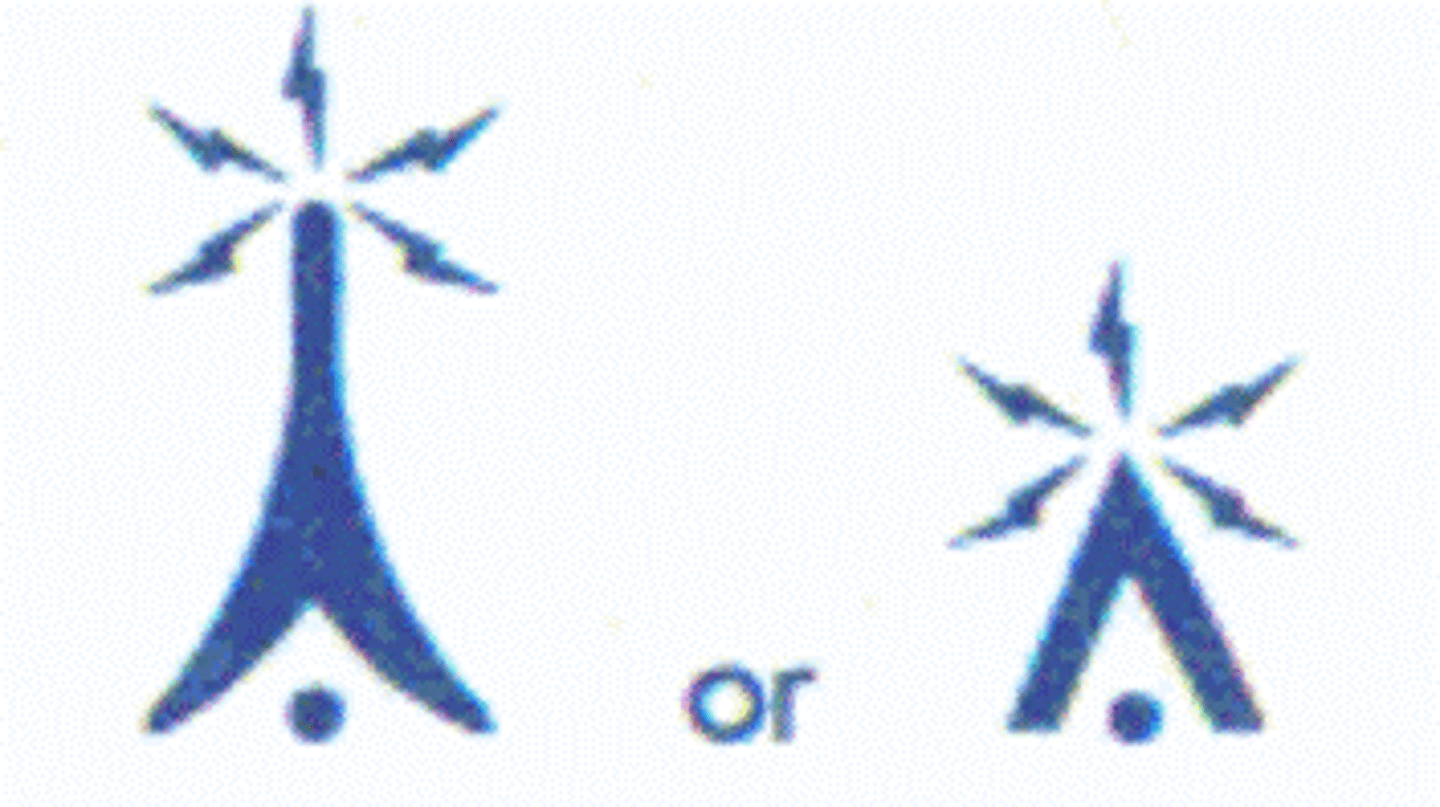
Obstruction / 1000 ft & higher / AGL
...

Obstruction / below 1000 ft / AGL
...

Group Obstruction
...
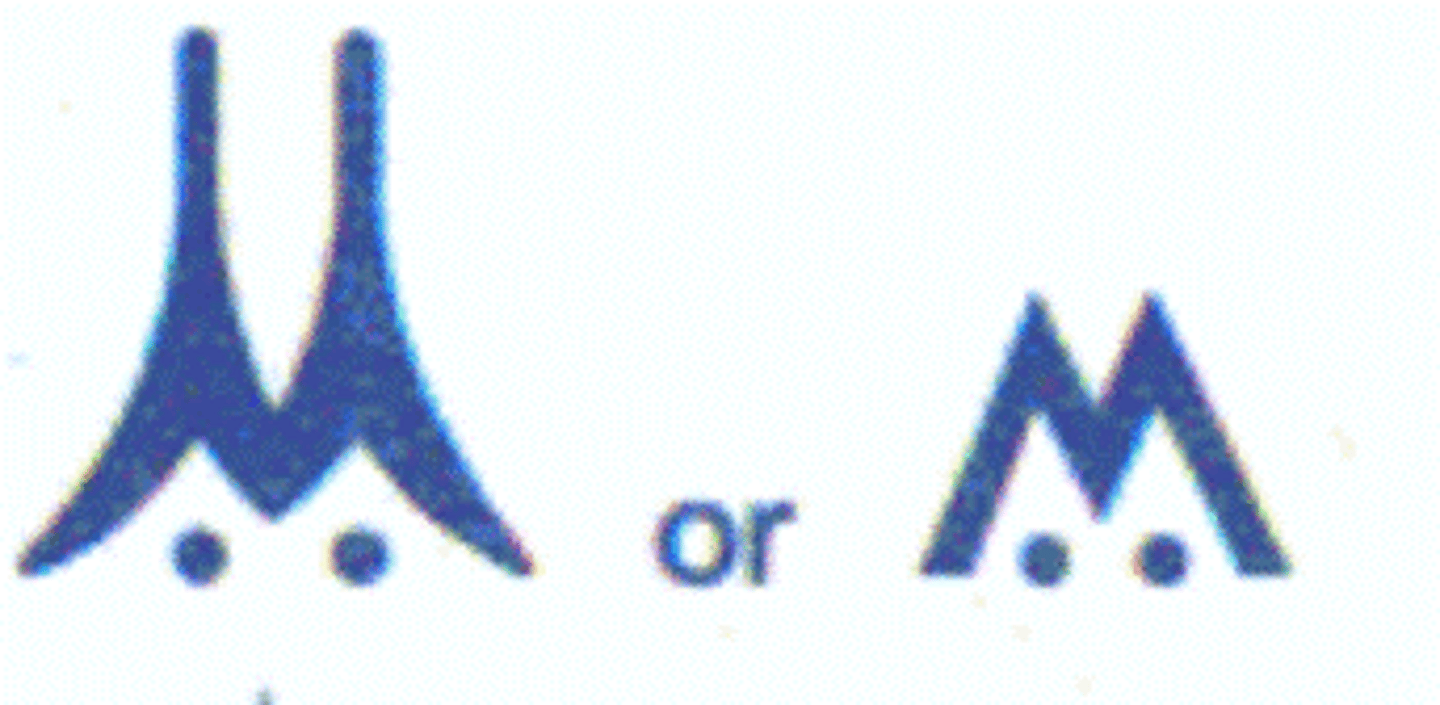
Obstruction w/high intensity lighting
...

Obstruction top MSL
Obstruction top AGL
Under Construction or reported, position & elevation unverified
...
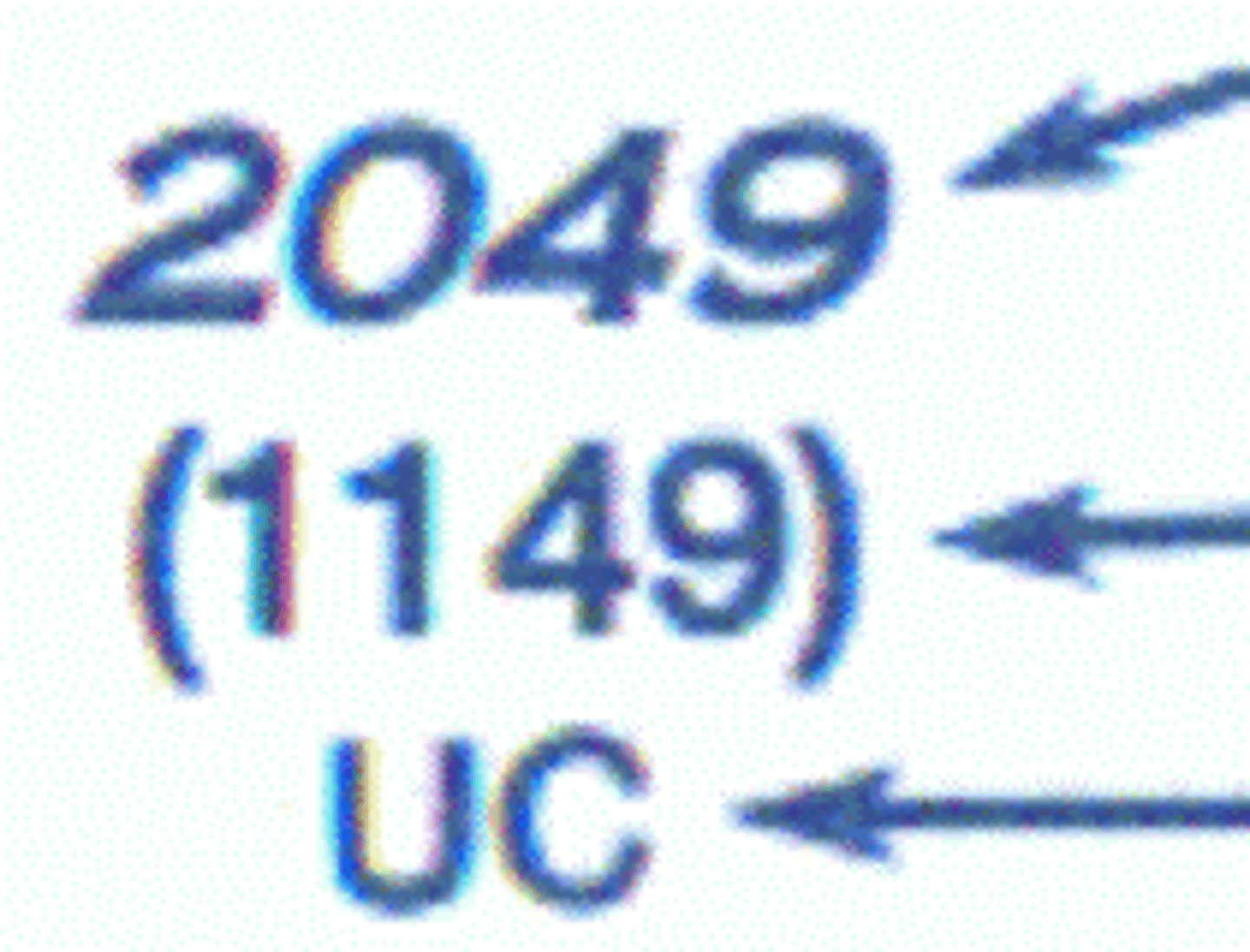
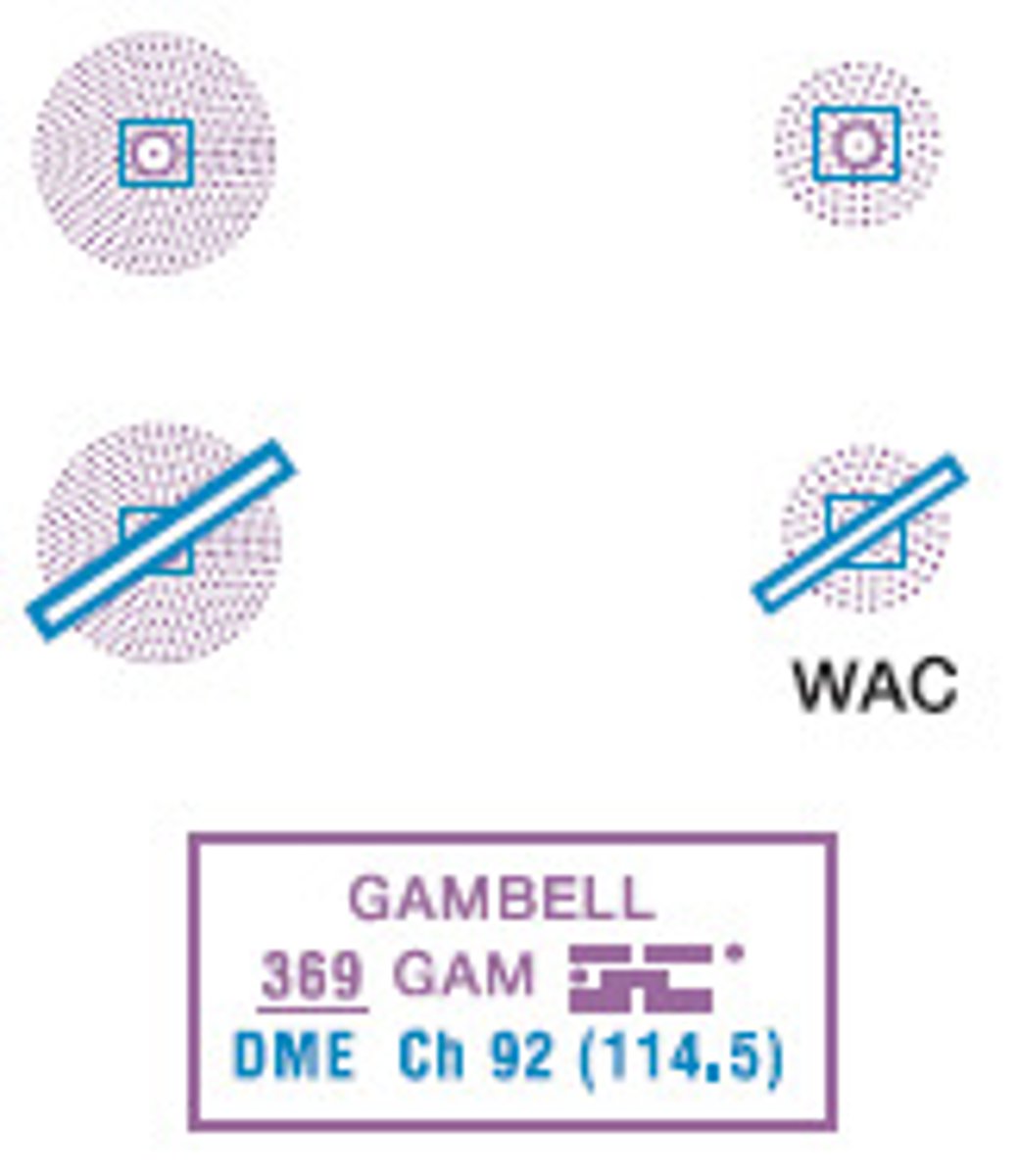
VOR
VORTAC
VOR-DME
Other Facilities / FSS Outlet, RCO
...

Isogonic Line
...

Ultralight Activity
Hang Glider Activity
Glider Operations
...
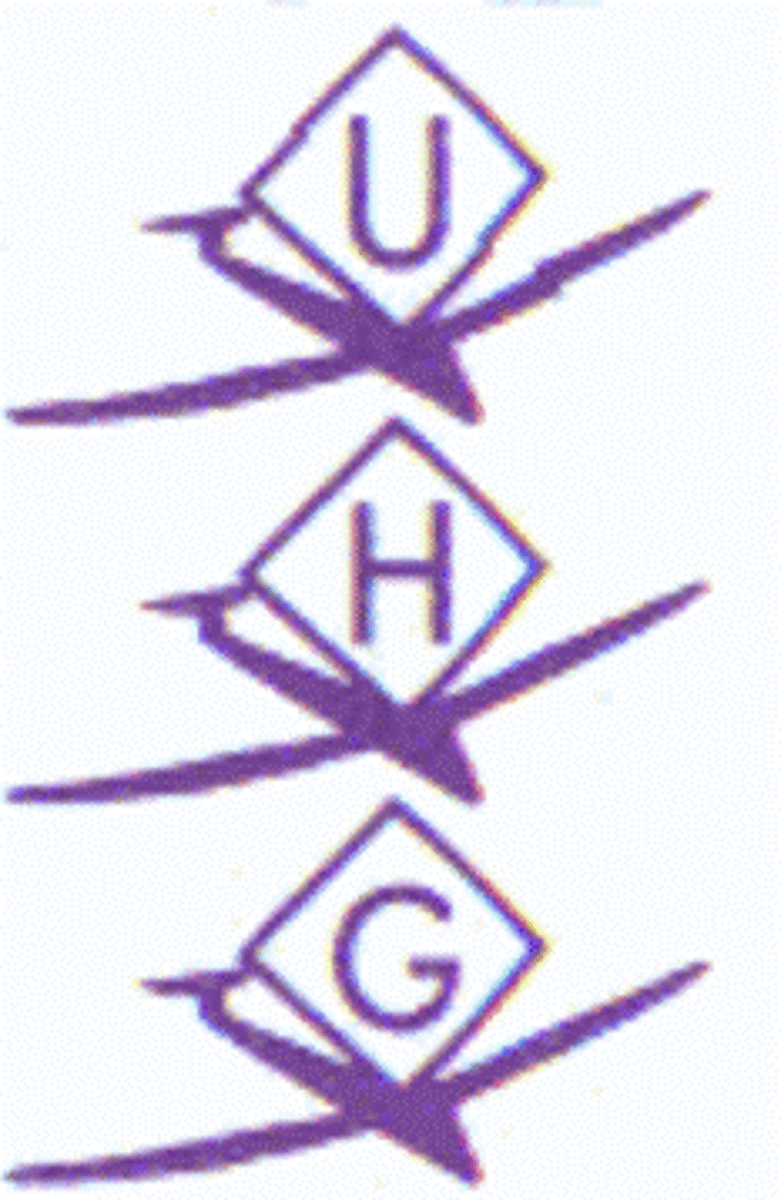
VFR Waypoints
...

Interstate
State Highway
Road
Rail Road
...
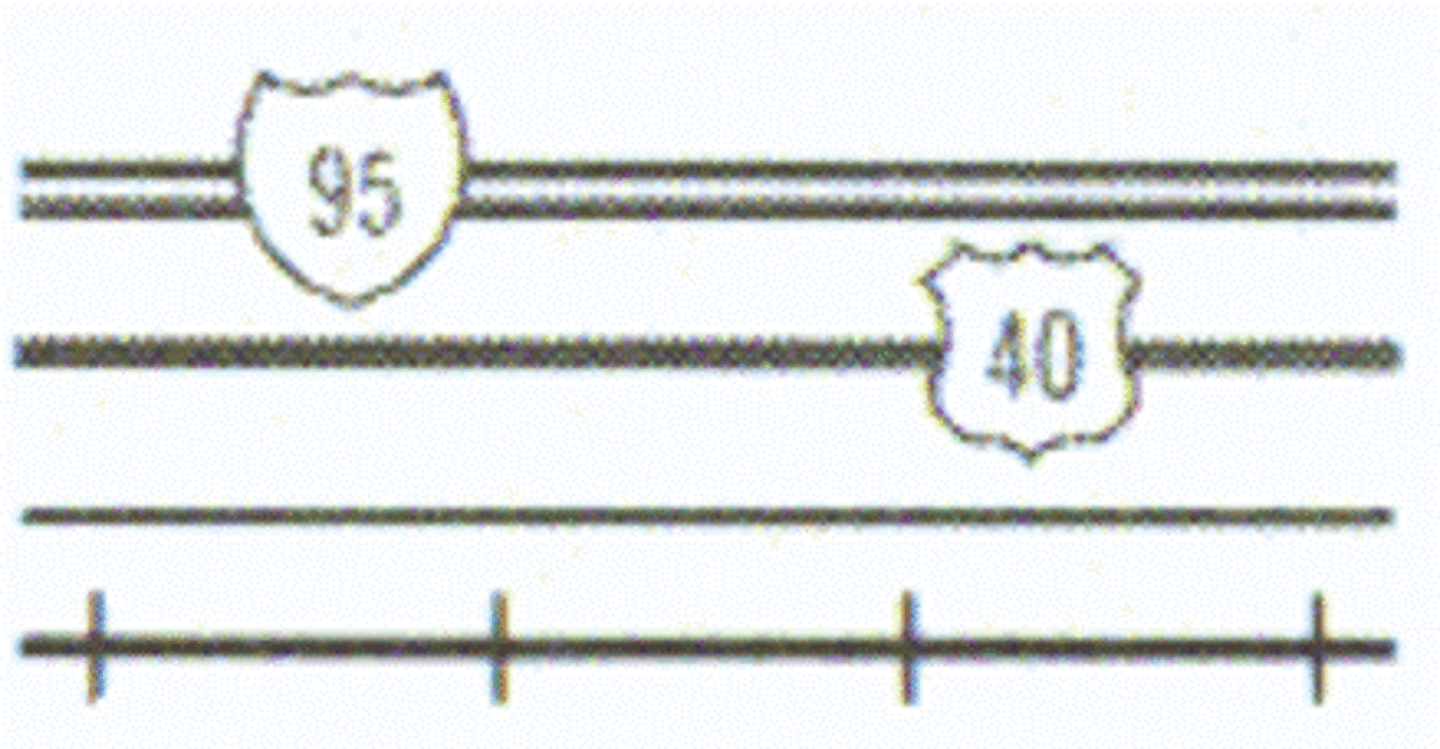
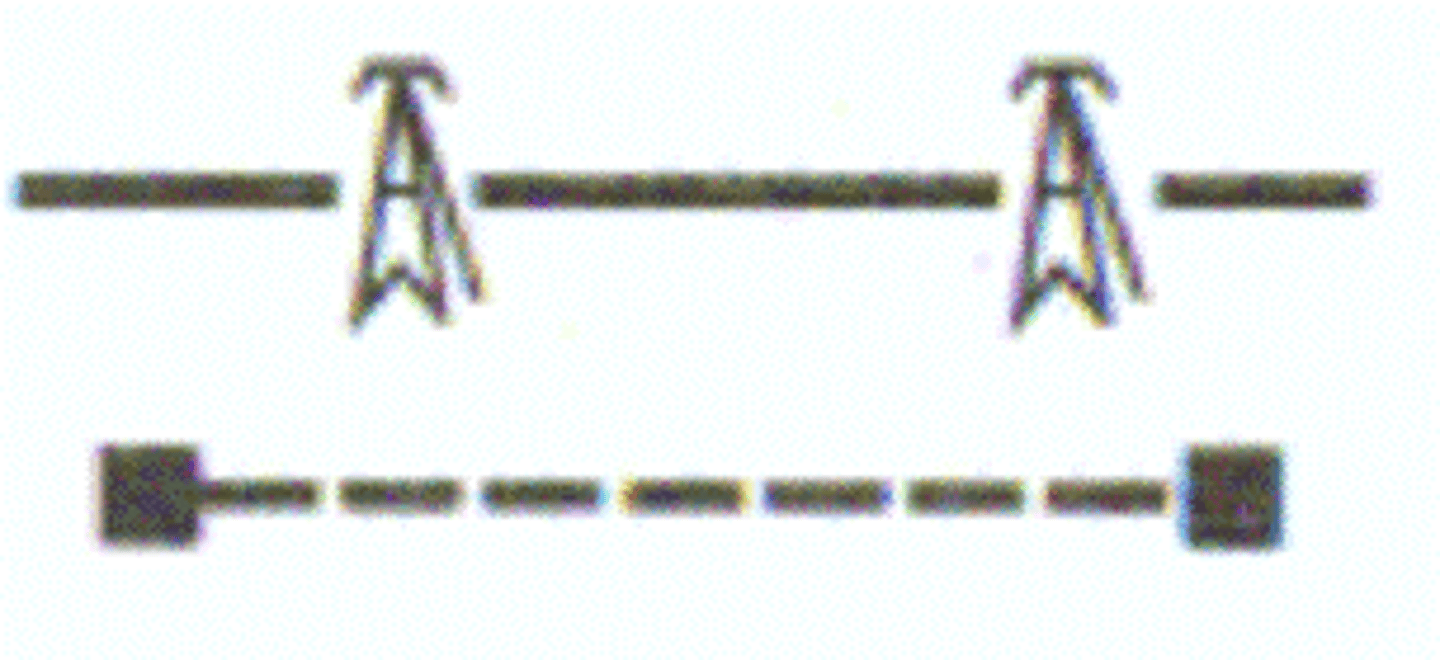
Power Transmission Line
Aerial Cable
...

Landmark Feature
Outdoor Theatre
...
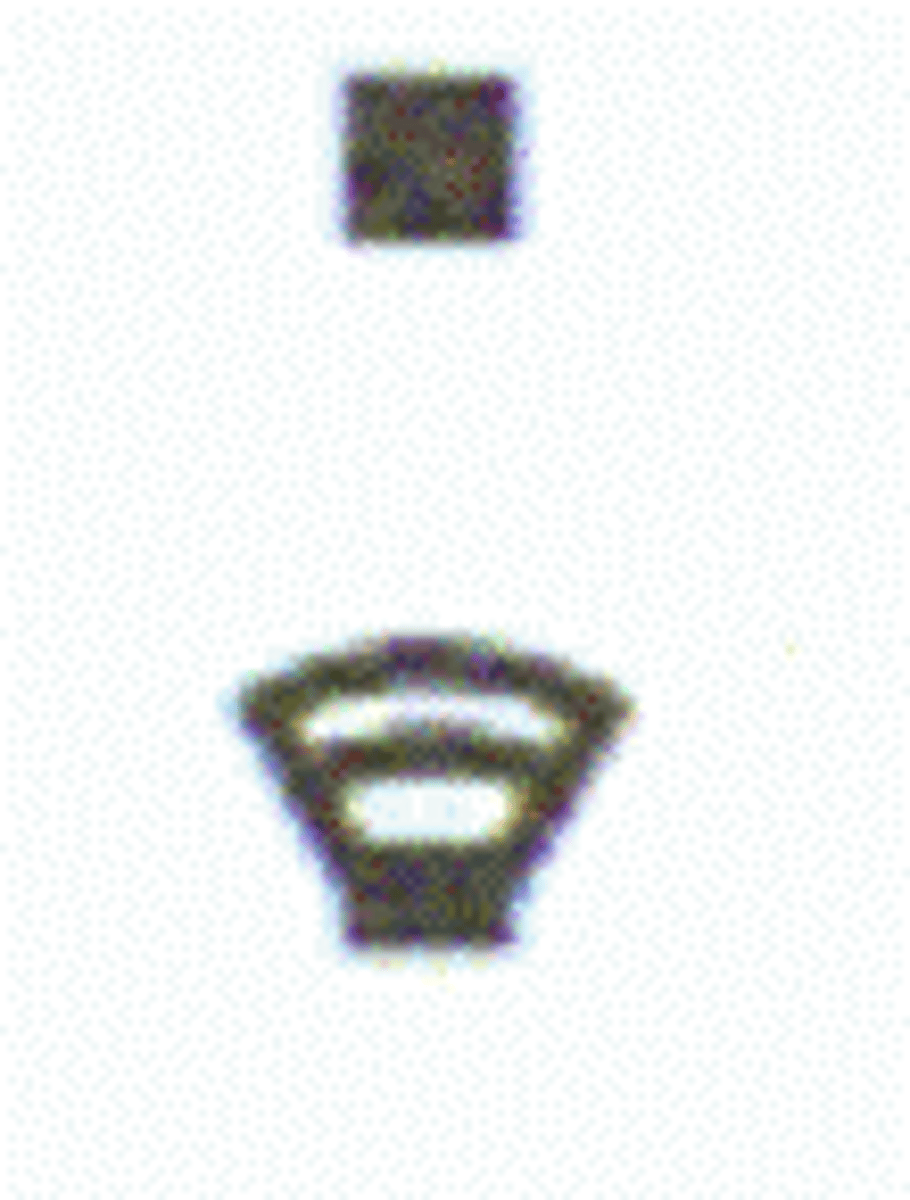

Non-Perennial Canal or Irrigation Ditch
...

Depression, Perennial Lake, Quarry.
...
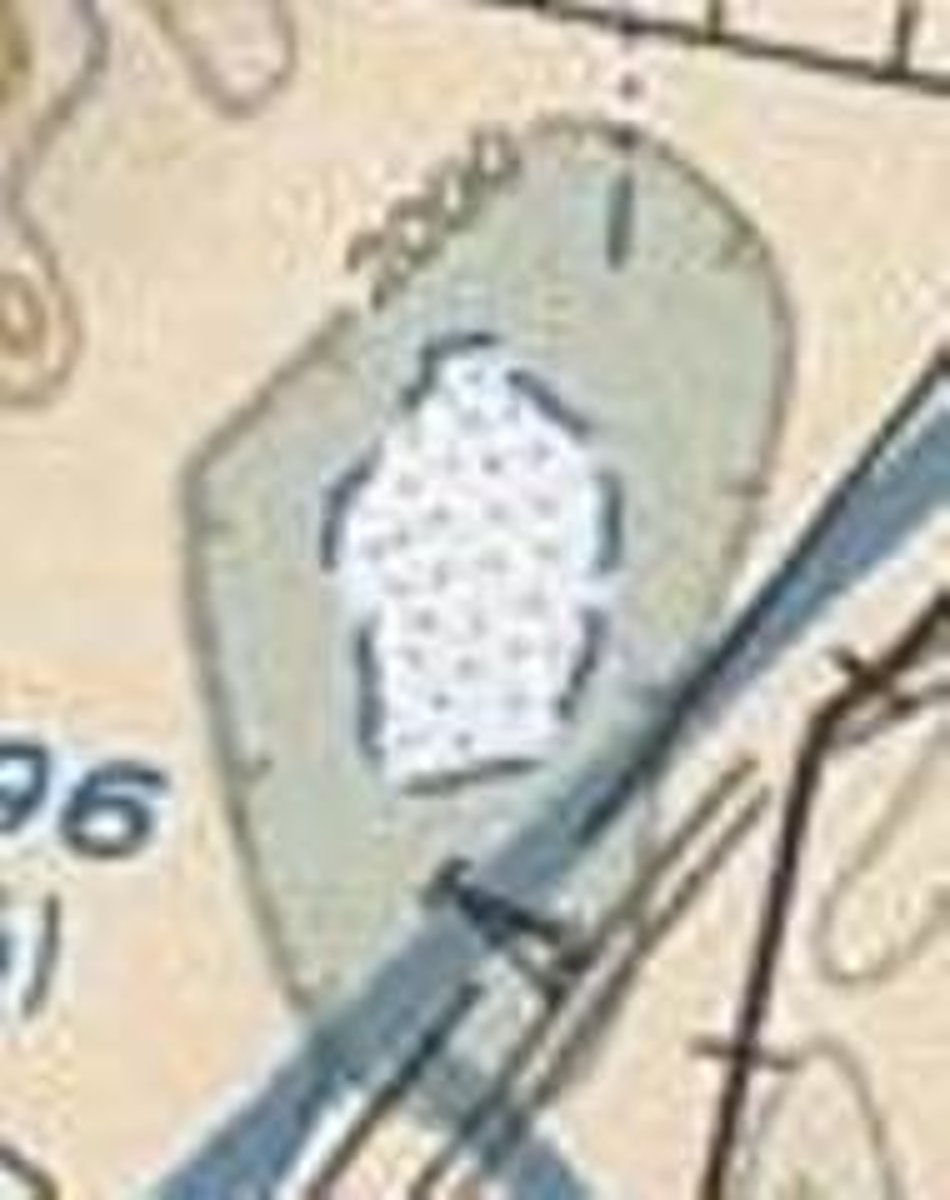
Flight Service Station on field
Airport
Control Tower - primary frequency - star=part time
ATIS - automated terminal information system - frequency
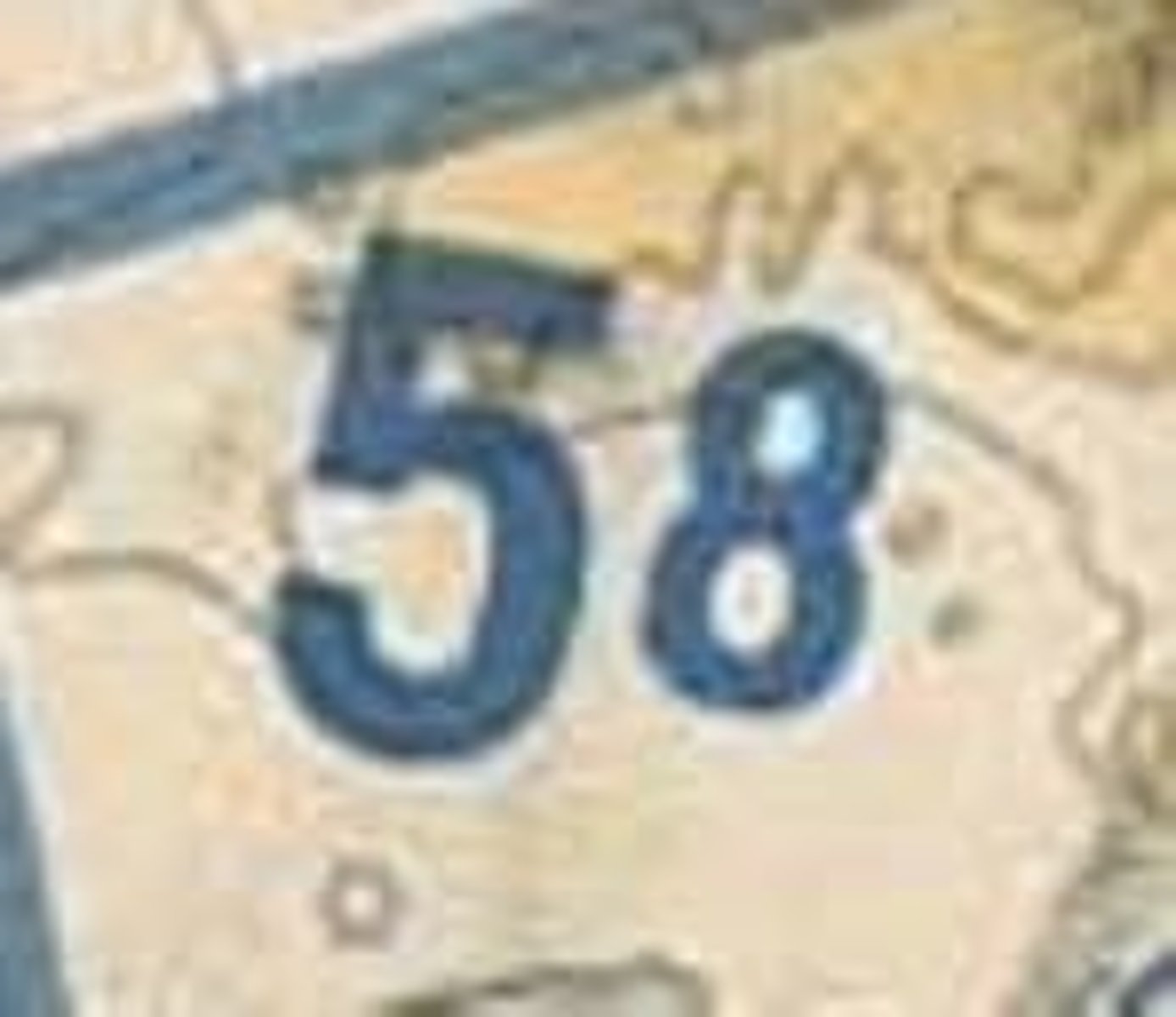
285 field elevation / L = lighting /
72 = rnwy length in hundreds ft / (68) usable length
VFR advisory shown when ATIS unavailable
...

Maximum Elevation Figure / Rounded up to the nearst hundredth. EXAMPLE: 5,800 ft
Man made Obstructions:
Elevation + 100(error) + 200(allowance) + rounded to the nearest hundredth.
What are the 4 forces that act on a plane in flight?
Thrust, Drag, Lift, Weight
Airfoil
Name for wing design
Center of Gravity (COG)
Point where plane balan
Steady unaccelerated flight
Thrust = Drag, Weight = Lift
2 Types of drag
Parasite & Induced
3 types of parasite drag
Form, skin friction, interference
LD Max
Lift:Drag ratio
How induced drag changes as airspeed increases
decreases exponentially
How parasite drag changes as airspeed increases
increases exponentially
Bernoulli’s Principle
faster speeds mean less pressure
3 components of Relative Wind
wind from thrust, prop wash, natural wind
Newton’s 3rd law
every action has equal & opposite reaction
Ways to create more lift
more speed, more camber (lower flaps), increase AOA
Stall
Rapid loss of lift
name for line between leading and trailing edge of air foil
chord line
Angle of Attack (AOA)
Angle between relative wind and chord line
How does steeper AOA affect lift
More lift
laminar air flow
individual planes of air going over wings
Boundary layer seperation
occurs when there is a steep AOA, causes turbulence, air doesn’t glide over wings smoothly anymore
Critical Angle of Attack
Exceeding this will always cause a stall
Lower AOA
Main way to break a stall
Spin
Aggravated stall (stall when uncoordinated), one wing stalls more than the other
What is the acronym PARE for?
Getting out of a spin
PARE
Power - Idle
PARE
Ailerons & Elevator neutral
PARE
Rudder - opposite (until spinning stops)
PARE
Elevator - up (to resume level flight)
How many wings are stalled in a spin?
Both, but one more than the other
Lateral Axis
Pitch Axis
Longitudinal axis
roll axis
Vertical Axis
Yaw axis
How to control lateral axis?
Elevator
How to control longitudinal axis?
Ailerons
How to control verical axis?
Rudder
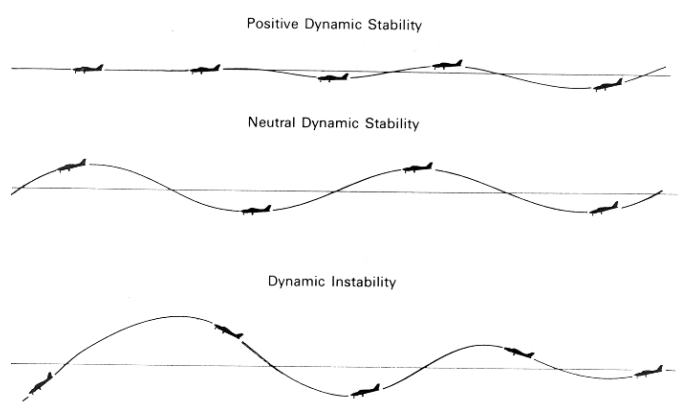
Stability
the ability to correct for disturbances and return to flight path
static stability
initial tendency of the airplane after a disruptiond
dynamic stability
reaction over time after a disturbance to flight path
What is the positive static stability result after a ↗ disturbance?
↘
What is the neutral static stability result after a ↗ disturbance?
↗
What is the negative static stability result after a ↗ disturbance?
⬆
Dynamic stability types
Controllability
The measure of how well an airplane responds to inputs
As stability decreases, what happens to controllability?
It decreases as well
COG too far back
Makes recovering from stall (lowering AOA) more difficult
Slip stream
air flow over form of airport
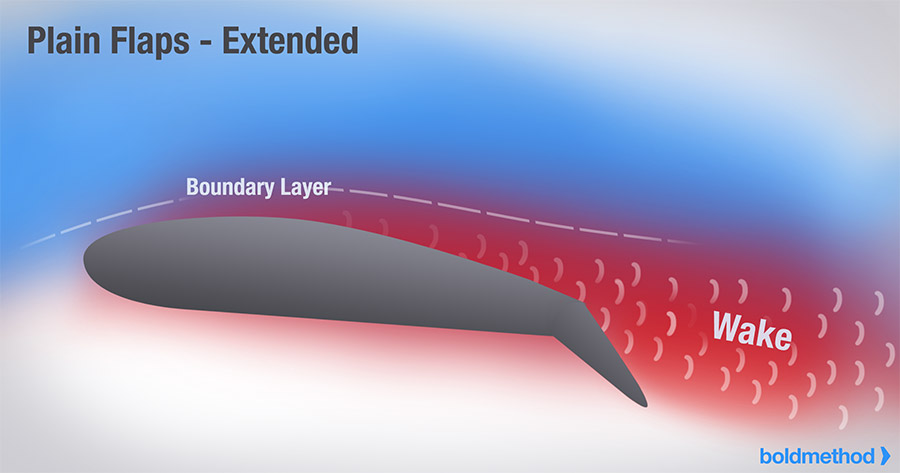
Flaps
Increase lift & drag
Main benefit of flaps
Allows landing at slower airspeeds and allows for an increased descent angle
Plain flaps
simplest type of flap
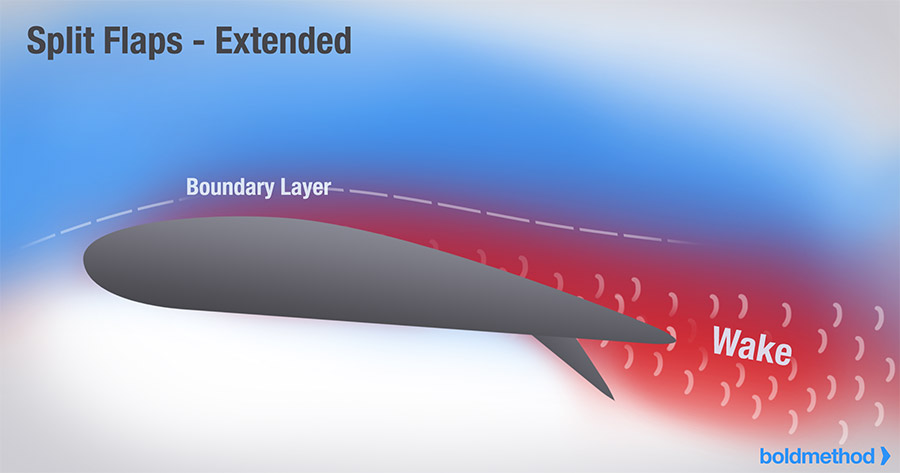
Split flap
flaps that deflect from lower surface of wings
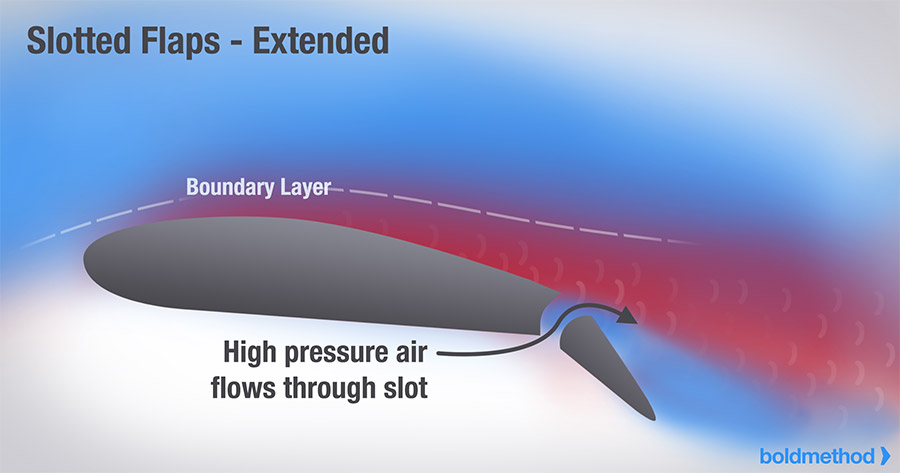
slotted flap
most common flaps (allows for extra lift without too much drag)
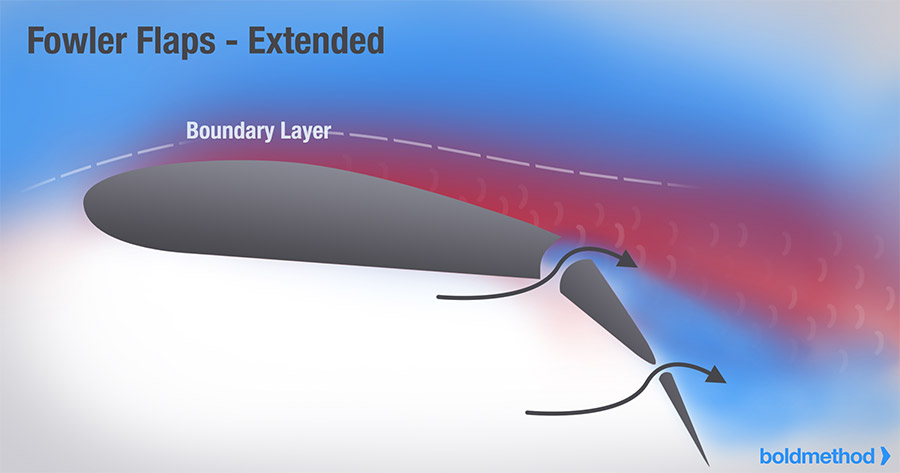
(slotted) fowler flap
flaps that extend on rails or tracks