6. Organisation socialisation, employer branding, and job satisfaction. Engagement and commitment
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Organisational socialisation
Process by which employee becomes aware of values and organisational procedures; starts at the recruitment; extent to which skills, abilities, and interests of individual are compatible with job demands; P-O fit
3 stages of OS
Getting in (learning about prospective organisations)
Breaking in (first encounters with the new organisation)
Settling in (making full entry into the organisation)
Positive effects of OS
Role performance, extra-role performance; social cohesion, internal stability, external representation
Schneider’s ASA model
Organisations attempt to attract and select particular types of people; attrition occurs through direct of indirect actions
Recruitment → Selection—Attrition→ Socialisation
Job satisfaction
Positive attitude or emotional sate resulting from appraisal to one’s job
Herzberg’s two-factor principles

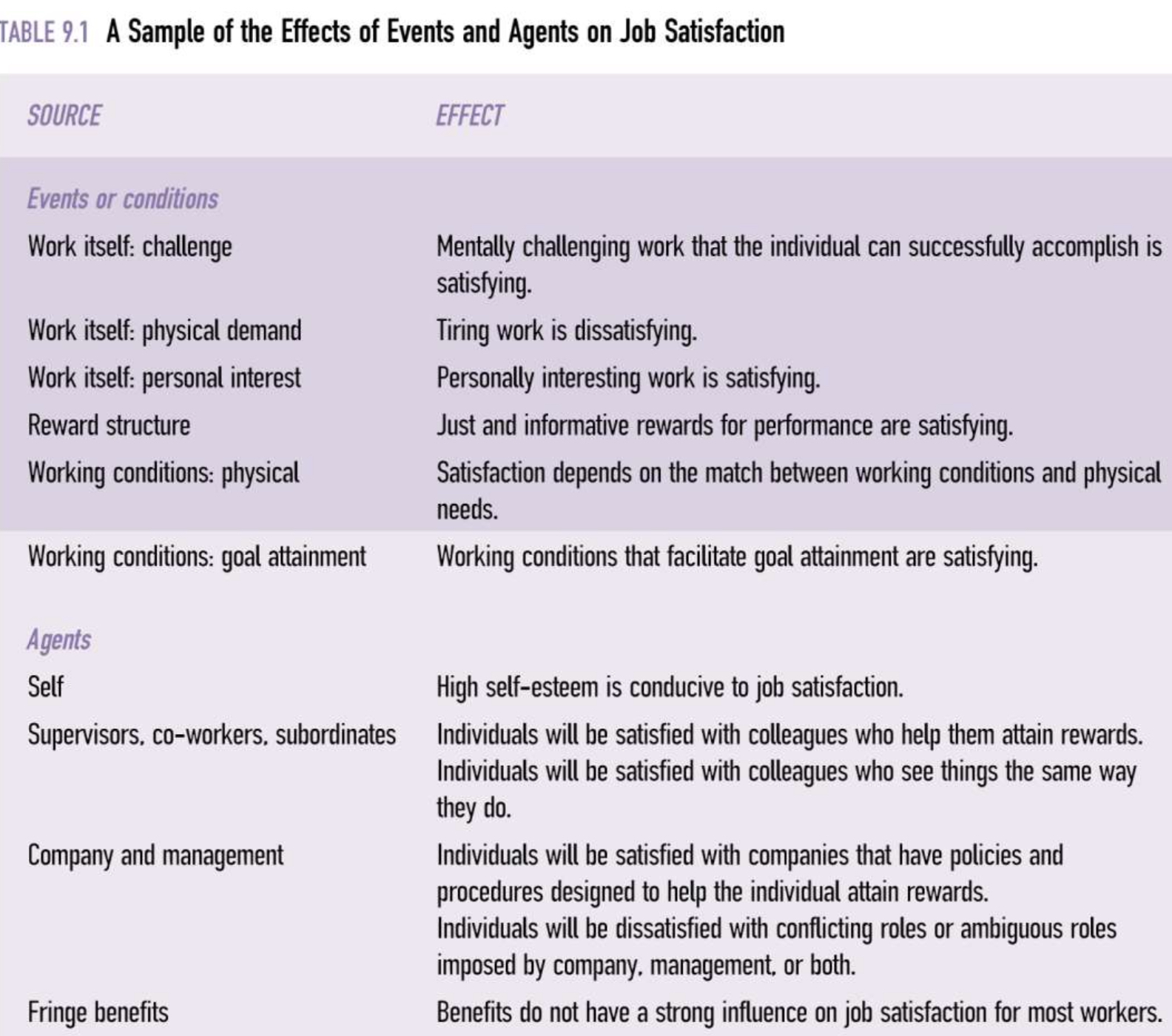
A sample of effects of events and agents on job satisfaction
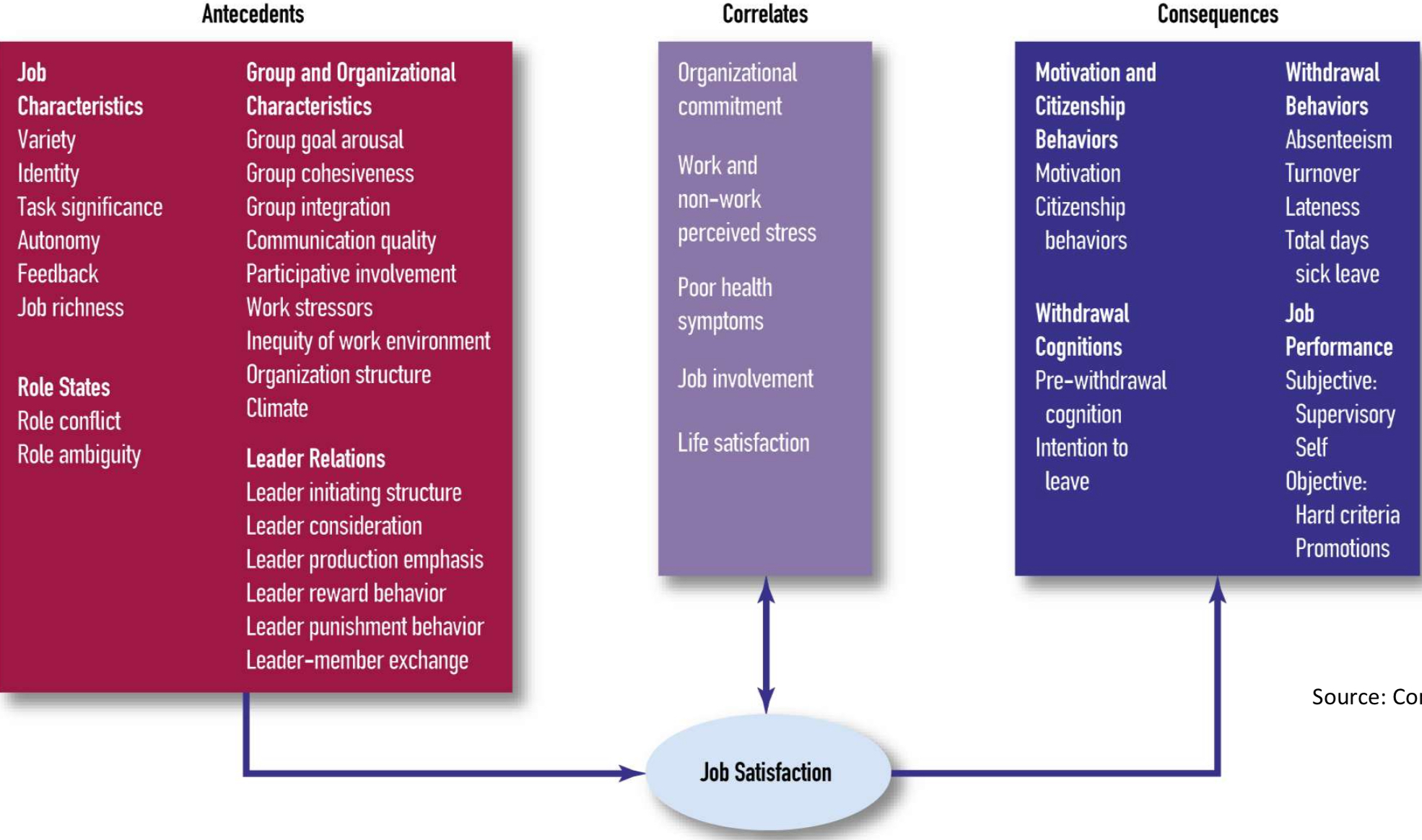
Presumed antecedents, correlates, & consequences of job satisfaction
Measurement of job satisfaction: overall vs facet satisfaction
Overall: results either from mathematically combining scores based on satisfaction or a single overall evaluative rating of the job
Facet: information related to specific elements of job satisfaction
Satisfaction questionnaires
JDI: assesses satisfaction with work itself, supervision, people, pay, promotion; heavily researched but lengthy
MSQ: calculates extrinsic and intrinsic satisfaction scores
Commitment
Psychological and emotional attachment an individual feels to a relationship, organisation, goal, or occupation
3 elements of organisational commitment
acceptance and belief in organisational values
A willingness to exert effort on behalf of the organisation to help meet goals of the organisation
A strong desire to remain in the organisation
Forms of organisational commitment
Affective: emotional attachment to an organisation
Continuance: perceived cost of leaving the organisation
Normative: obligations to remain in the organisation
Factors influencing organisational commitment
Psychological and socialisation processes, organisational changes, HR practices, interpersonal relations, employee-organisational relations
Employee engagement
Positive work-related state of mind that includes high levels of energy, enthusiasm, and identification with one’s work → overlaps positively with job satisfaction, organisational commitment, and job involvement → but is distinct from these constructs and has important organisational implications
Withdrawal behaviours
Work withdrawal: attempt to withdraw from work but maintain ties to the organisation and work role
Job withdrawal: willingness to sever ties to organisation and work role
Progression hypothesis
Employee turnover
intention to leave; organisational commitment and job satisfaction influencing it; different factors influence turnover for different employees
Enthusiastic leavers
Reluctant leavers
Enthusiastic stayers
Reluctant stayers