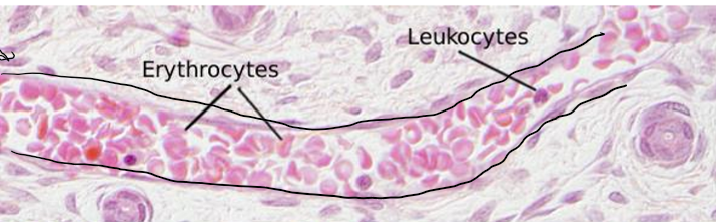
Blood, Bone marrow, & Hematopoiesis - Lecture 5
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
What is composed in the Embryonic Connective tissue?
Mucous
Mesenchymal
What is composed in the Connective tissue proper?
Loose tissue
Dense Irregular Tissue
Dense Regular Tissue
Elastic Tissue
Reticular Tissue
Adipose Tissue
Specialized (Bone, Cartilage, blood)
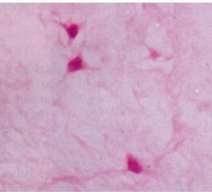
What kind of tissue is this, and where is it located?
Mucous membrane
In the Embryonic Connective tissue
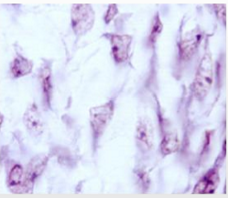
What kind of the tissue is this and where is it located?
Mesenchymal tissue
Located in the Embryonic connective tissue

What kind of tissue is this and where is it located?
Loose connective tissue
Lamina propria of the small intestine

What kind of tissue is this and where is it located?
Dense Irregular Tissue
Found in the dermis
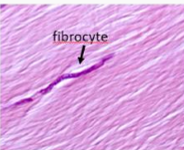
What kind of tissue is this and where is it located?
Dense Regular Tissue
tendons of the knee joint

What kind of tissue is this and where is it located?
Reticular tissue
Bone marrow

What kind of tissue is this and where is it located?
Elastic
Blood vessels
What is composed in plasma?
About 55% of the blood
What is the function of red blood cells (Erythrocytes)? and how is it done?
It Contains hemoglobin
Transport oxygen (O2) and carbon dioxide (CO2)
What are the function of platelets (Thrombocytes)?
Blood clotting
Helps prevent bleeding by forming clots
What are the functions of white blood cells (Leukocytes)?
Granulocytes/ Polymorphnuclear
PMN
Neutrophils
Eosinophils
Basophils
Agranulocytes
Lymphocytes
Monocytes
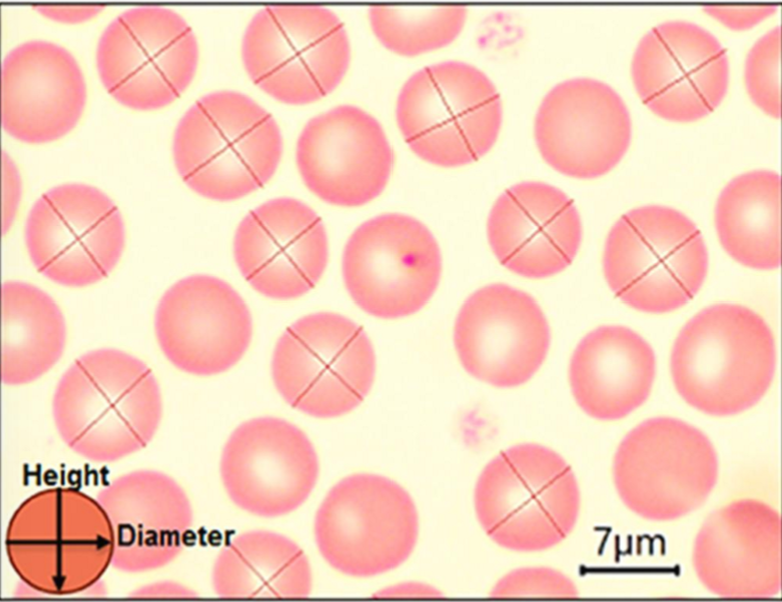
What kind of cells are these?
Erythrocytes (Red Blood Cells)
What is the strucute of the Erythrocyte?
Contains hemoglobin
Flexible because it lacks cellular organelles
Biconcave Shape, so it can facilitate gas exchange
Cell membrane is rich in actin

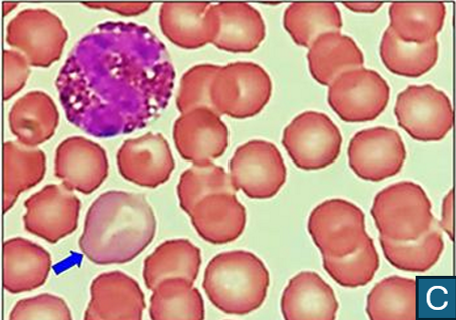
What is the arrow indicating in the blood smear?
Platelets
Indicate what kind of cell is in the blood smear. Describe why it looks that way.
Polychomatophilic erythrocyte
It has a bluish cytoplasm and are larger than a normal rbc
Are all nucleated cells in the blood erythrocytes?
False!
All nucleated cells in the blood are leukocytes.
In mammals, erythrocytes lack a nucleus
What are the type of Granuolocytes (WBCs)?
Neutrophils
Eosinophils
Basophils
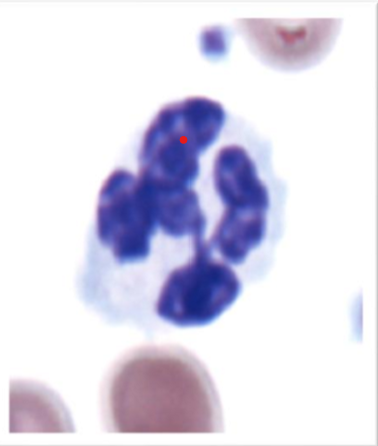
What kind of granulocyte is indicated in the image?
Neutrophil
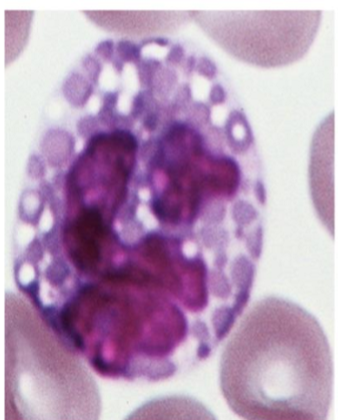
What kind of granulocyte is indicated in the image?
Eosinophil
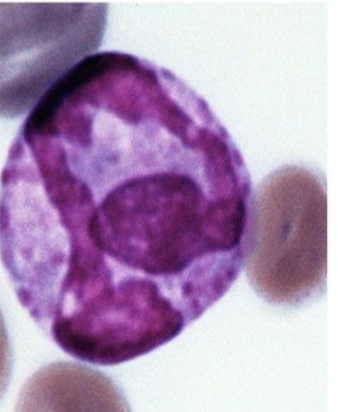
What kind of granulocyte is indicated in the image?
Basophil
What are the types of Agranulocytes (Mononuclear)?
Lymphocytes
Monocytes

What kind of Agranulocyte is indicated in this image?
Lymphocyte
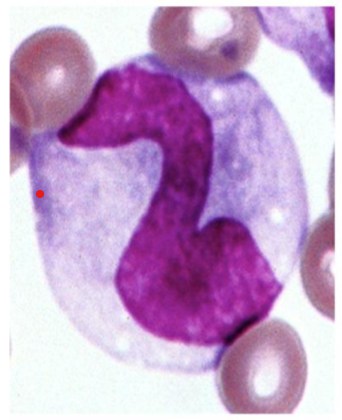
What kind of Agranulocyte is indicated in this image?
Monocyte
How does platelets aggregate? Where do they adhede to? What does the coagulation activity involve?
Platelet adhesion to the subendothelial matrix
Platelet aggregation occurs by binding fibrinogen
Platelet coagulation activity involves thrombin
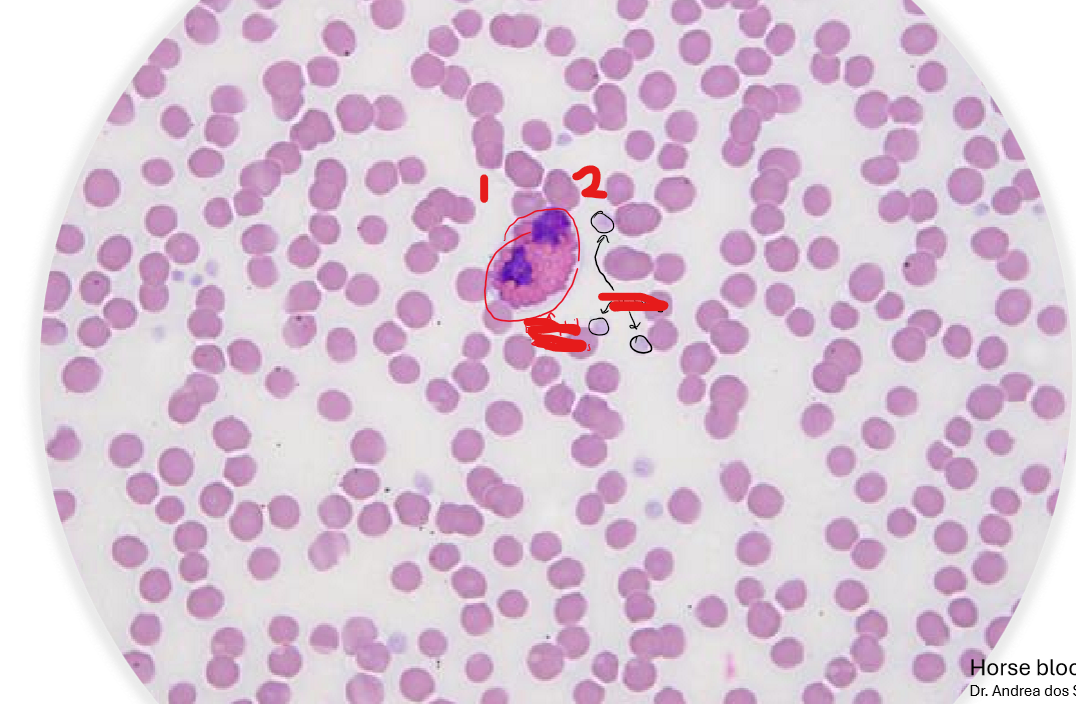
Indicate the labels in the blood smear. Wha kind of cells are in in the slide?
Eosinohil
Platelets
Surrounded by RBCs
What are the two compartments of the bone marrow?
Marrow Stromal (endosteal) compartment.
Hematopoieteic (endosteal) compartment
What is composed in the marrow stromal compartment?
Adipose cells
Fibroblasts
Stromal Cells
Vascular endothelial cells
macrophages
blood vessels
What is composed in the hematopoietic compartment?
Developing elements of the blood
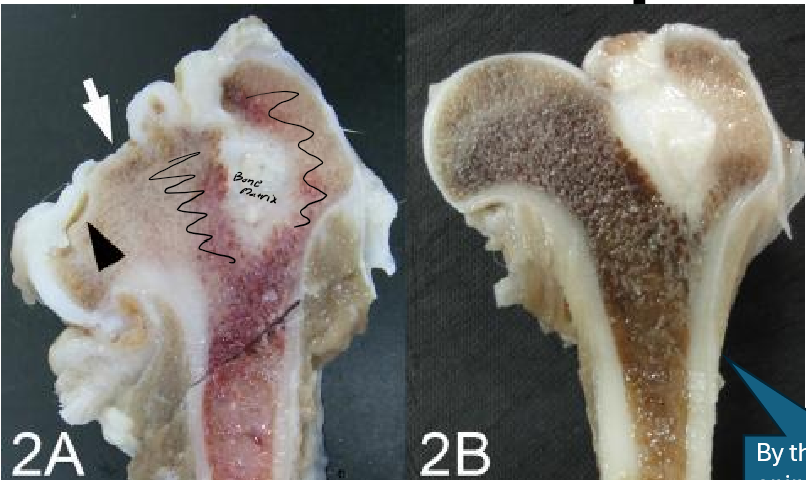
Indicate what kind of bone marrow this is. Describe 2A and 2B.
Red Hematopoietic Bone Marrow
A: The longitudinal cut surface of the left femoral head
B: Age-matched control at the same magnification
Tell me some of the components of the red bone marrow.
The Spongy bone contains red marrow
There are blood vessels in bone marrow
It is highly vascularized
Describe the hierarchical order of the blood supply through the bone’s internal vasculature.
Nutrient Artery: Main vessel enters the none through the nutrient forament and enters into the medullary cavity.
Central Longitudinal Artery: Once inside the medullary cavity, the nutrient artery continues longitudinally along the bone’s shaft.
Network of arterioles and capillary plexuses: The central longitudinal artery then branches into smaller arterioles, forming a capillary network (Sinusoids) that pervades the hematopoietic tissue of the bone marrow.
Supply to hematopoitic tissue: These fine capilarry networks deliver oxygen and nutrients directly to the bone marrow’s hematopoietic cells
Describe the circulation pathway, transitioning from arterial flow to venous exchange within the bone marrow.
Medullary sinusoids: thin-walled that are fenestrated (small pores) that allow for easy exchange, wide vascular channels (mix of capillaries and veins) found throughout the body. Collect blood from the capillary plexuses.
Sites of exchange: oxygen, nutrients, and metabolic waste move across these sinusoid walls, and newly formed blood cells produced in the marrow
Blood and Hematopoietic cells: The sinusoids acts as the interface where mature blood cells leave the marrow and enter the systemic venous circulation
Describe the stromal (supportive) framework of yellow bone marrow.
Adventitial reticular cells (ARCs) (Modified fibroblasts): Provides structural support and are connective tissue cells in the bone marrow.
Reticular Fiber Network: Supports adipocytes. Made of type 3 collagen secreted by ARCs
Can convert to adipocytes. Subsequently, yellow marrow is formed.
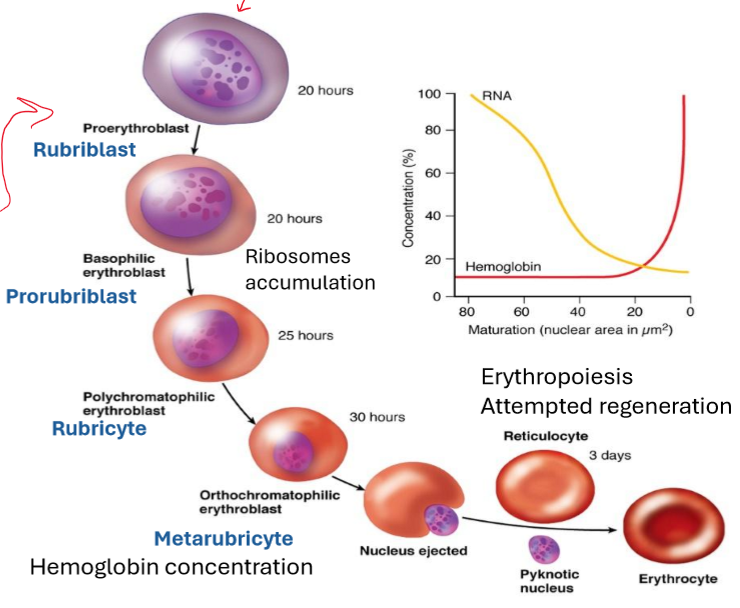
Describe Erythropoiesis.
Multipotent hematopoietic stem cells (HSC)
Erythroid progenitor cells called CFU-E (Colony-Forming Unit-Erythroid)
Erythropoietin (Kidney) binds to its receptors on CFU-E cells, promoting their survival, proliferation, and differentiation.
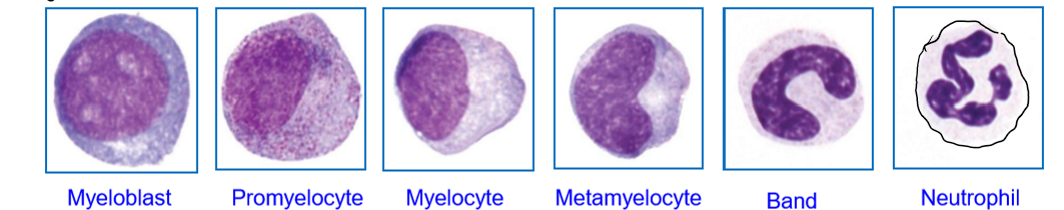
Describe Neutrophils and what are their functions.
First responders of the innate immune system.
Phagocytosis of invading pathogens by the host
Antimicrobials substances from granules
Formed of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs)
When there is tissue damage, neutrophilic activity is damaged
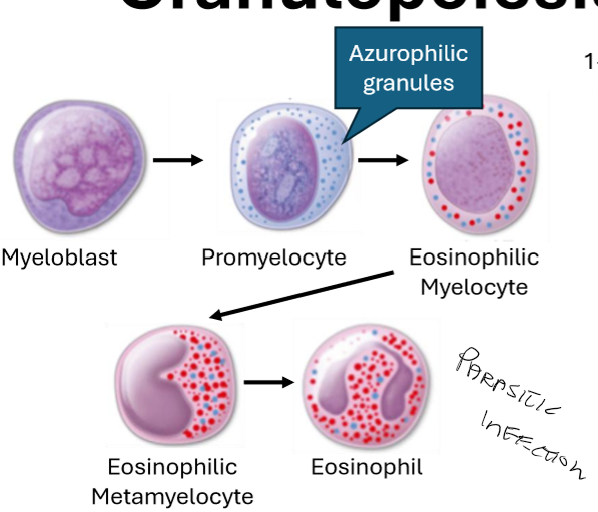
Describe Eosinophils and what are their functions.
Toxic granules
Activated during parasitic infection
Triggers inflammation
vasoactive substance
lipid mediators
cytokines
Degrading or inactivating mediators
Describe basohils and what are their functions.
Histamine and heparin
Activated to fight off allergens, pathogens, and parasites
Trigger allergy symptoms like itching and swelling.
Increases blood flow
Inflammatory responses
Cytokines, bridge between the innate and adaptive immune.
Makes blood vessels more permeable for more cells.
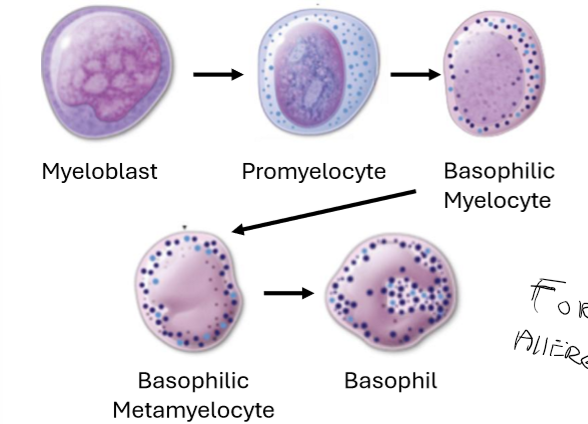
Describe the different between Agrunolopoiesis and Lymphopoiesis.
Agrunolopoiesis: Monopoiesis and Lympopoiesis
Innate immune system
Migrating into tissues to become macrophages and dendritic cells.
Lymphopoiesis:
Adaptive immune response
Targeting particular pathogens
B-cells produce antibodies
T-cells directly kill infected cells or regulate immune function
Where are T-lymphocytes differentiated?
Thymus
after maturating in the red bone marrow from HSCs
Where is the B-lymphocytes and NK cells maturated?
Maturated in the red bone marrow
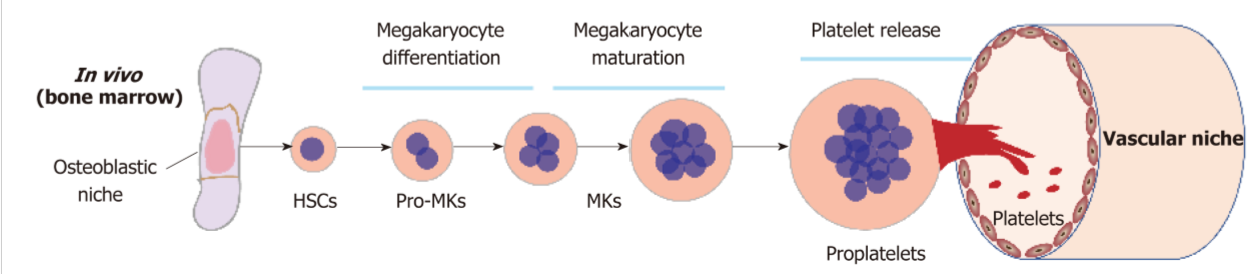
Describe Thrombopoiesis.
Thromboxane A2 (TXA2) is a potent signaling molecule released by activated platelets. Platelets function for vasoconstriction and the recruitment of more platelets
Thrombin a central enzyme in coagulation cascade. Converts fibrinogen into fibrin, and activates platelets, and the platelets changes shape and become sticky
Fibronogen between GP IIb/ IIIa receptors. The fibrinogen bridges connection between these glycoproteins by binding to the receptors creating a platelet aggregation.
Describe a disorder involving the blood.
Aplastic Anemia
Unable to produce enough new blood cells.
This can lead to deficiency of all blood cell types, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
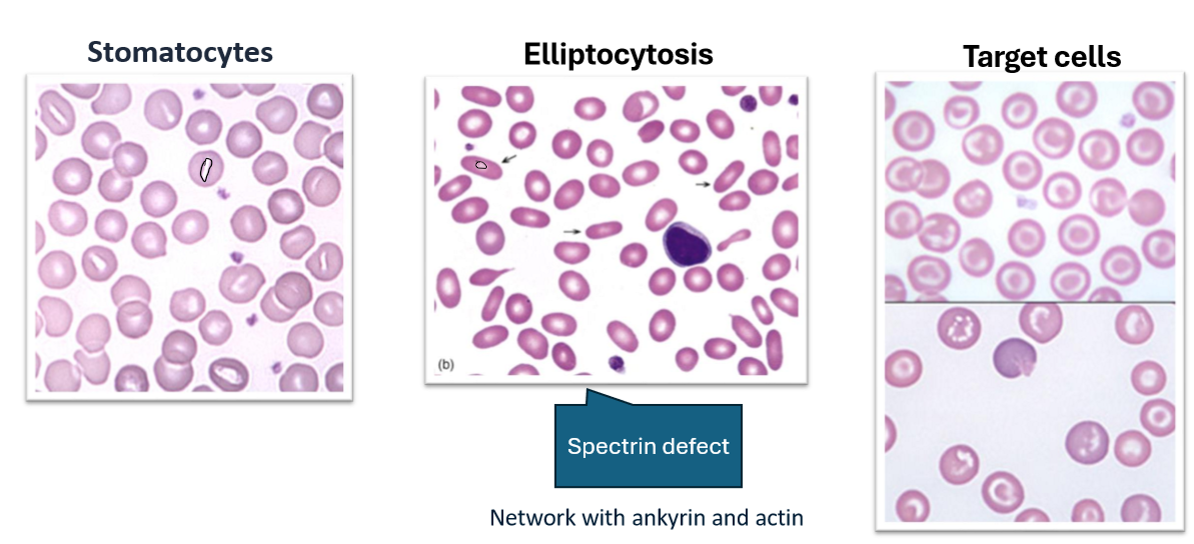
What are the RBC alterations?
Stomacytes
Elliptocytosis
Target Cells