Excretory system (up to liver)
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
What is excretion?
The process of removing metabolic waste from an organism. Excretory products include urea, carbon dioxide, excess water and salts.

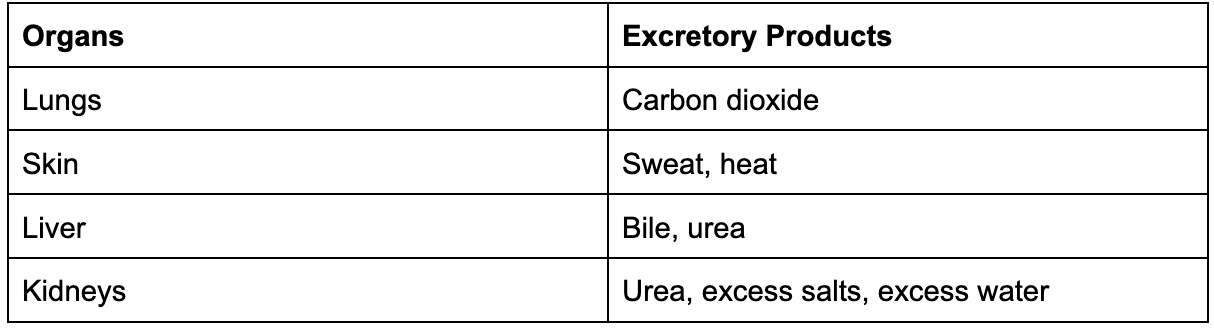
What are the 4 main excretory organs and their excretory products?
Where does the liver get its blood supply from?
Hepatic Artery: Carries oxygenated blood from the general circulation.
Hepatic Portal Vein: Carries nutrient-rich, deoxygenated blood from the digestive organs for processing.
What are the 3 main functions of the liver in the body?
helps regulate blood glucose levels
makes bile, which helps emulsify fats during digestion
deaminates excess amino acids
What is assimilation?
the final stage of nutrient uptake, where the simple molecules that were absorbed during digestion are converted into or incorporated into the body's own substances and structures
What happens to amino acids after digestion?
After digestion, amino acids are absorbed into the blood and transported to the liver. The liver uses some of these amino acids to build new proteins, such as enzymes and plasma proteins (proteins present in the blood plasma), which are used by the body.
What happens if there are excess amino acids?
If there are excess amino acids that aren’t needed, the liver can’t store them, so it breaks them down during a process called deamination:
Hepatocytes remove the amine group from the acid group
The acid group of the amino acid is used to produce energy or new glucose molecules
The amine group is converted into ammonia.
What happens to the ammonia?
As ammonia is toxic, it is transformed into urea, which is less toxic. Urea is then carried by the blood to the kidneys, where it is excreted in the urine.