Money and Banking Final Exam Flashcard Study
1/503
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards for money and banking chapter 12-18 and 20
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
504 Terms
What are Bank assets?
uses of funds
What is the accounting equation for banks?
total bank assets = total bank liabilities + bank capital
What represents the owner’s stake in the bank?
Bank Capital is the owner’s stake in the bank
What represents a bank’s net worth?
Bank Capital
The difference between a bank’s asset and liabilities is ______.
Bank Capital
Assets are what banks do with _____________.
The funds they have
What is included in the asset side of a bank’s balance sheet?
Cash
Securities
loans
buildings and equipment
there are ___ types of cash items
three
What are the 3 types of cash items?
reserves
cash items in the process of collections
correspondent banking
What is the most important type of cash item?
Reserves
What are reserves?
Cash in the bank’s vault as well as its deposits are the federal reserve
What is the equation for reserves?
Reserves = vault cash + fed deposits
Paycheck funds that the bank is waiting to receive would be considered ______
Cash items in the process of collections
what are cash items in the process of collections?
uncollected funds the bank expects to receive
Balances of accounts that banks hold at other banks are called?
Correspondent banking
T or F: correspondent banking is considered cash
The second largest component of bank assets
securities
T or F: Since banks cannot hold stock, many american banks have bonds as their form of securities
What are the different types of securities?
US treasury securities
state government bonds
local government bonds
Why are securities sometimes called ‘secondary reserves”?
highly liquid
can be sold quickly and easily
can serve as backup reserves
What accounts for ½ of a bank’s assets
loans
loans are the primary asset of _______
Modern commercial banks
What loans do commercial banks offer?
business loans
Commercial and Industry (C&I)
real estate loans
consumer loans
interbank loans
loans for purchase of other securities
What is the primary difference among various types of depository institutions?
The composition of their loan portfolio
Where may commercial banks loan to?
businesses
credit unions
individuals
governments
T or F: banks can use funds (assets) to have reserves, buy securities, funds not yet received from depositors, and make loans to businesses and individuals
What are the two broad categories of liabilities?
Deposit Accounts
Borrowings
What are the bank’s sources of funds?
liabilities
From who does the bank gets its sources of funds?
Savers and borrowers
_______ _______ allow customers to withdraw funds w/o notice on a 1st come 1st serve basis
Demand Deposits
What are checkable deposits?
A typical bank will offer 6 or more types of checking accounts that allow customers to write checks and access funds immediately.
why have the number of checkable deposits declined over the years?
these accounts pay low interest rates
These include savings and time deposits
non-transaction deposits
non-transaction deposits account for nearly _____ of all commercial bank liabilities?
2/3
Time deposits include
Certificate of deposits or CDs (small <100k or large >100k)
Large CDs can be bought and sold in what kind of markets?
Wholesale money markets
Non-transaction deposits for savings are also called
Passport savings
What are the second most important source of bank funds
Borrowings
What are 3 different types of borrowings?
discount loans
banks with excess reserves
repurchase (repo) agreements
What are discount loans?
when banks borrow from Federal Reserve
How do banks borrow from banks with excess reserves?
from other banks in the federal funds markets
What is a repurchasing agreement (repo)?
Short-term collateralized loan in which a security is exchange for cash, with the agreement that the parties will reverse the transaction on a specific future date
What is the equation for net worth?
Assets - liabilities
What is the cushion that banks have against a sudden drop in the value of their assets or an unexpected withdrawal of liabilities
Bank Capital (net worth)
Bank capital provides what kind of insurance for banks?
insurance against insolvency
what is an important component of bank capital
loan loss reserves
What are loan loss reserves?
an amount the bank sets aside to cover potential losses from defaulted loans
What are the four basic measures of bank profitability
Return on assets
Return on equity
Net interest income
Net interest margin
What are return on assets?
A bank’s net profit after taxes divided by its total assets
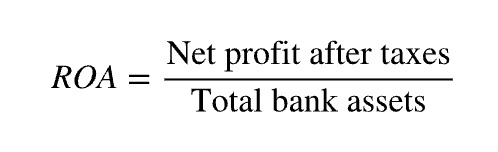
What is return on equity?
Net profits after taxes divided by Bank Capital

What questions does ROA answers?
How profitable is the bank?
How efficiently does a bank use its assets?
What questions does ROE answer?
What are the bank’s return to owners?
What is net interest income?
The difference between the interest a bank pays and what it receives
How can net interest income be expressed?
A percentage of total assets or net interest margin or bank’s interest spread
Where does a banks interest expense come from?
deposits and bank borrowing
Where does a bank’s interest income come from?
Securities and loans
What is net interest margin?
an indicator of future profitability as well as current profitability
T or F: Net interest margin is closely related to ROA
TRUE
What is the banks interest rate spread, exactly?
the Weighted average difference between the interest rate received on assets and interest paid for liabilities
What are off-balance-sheet activities?
Transactions or events that do not arise on the balance sheet (assets or liabilities)
What do off-balance sheet activities do?
generate fee income which include providing customers with lines of credit
____ __ ____ guarantee that a customer will be able to make a promised payment
“Our client will pay and are able to”
Letters of Credit
How does letters of credit work?
Banks act as guarantors for payments and enable a transaction to go forward in exchange for a fee
Should the borrower default, the bank promises that it will repay the lender by sending a
Standby letter of credit
What does it mean when a standby letter acts as a form of insurance for lenders?
“if our client screws up, we will pay”
Why have off-balance-sheet activities come under scrutiny in the recent years
they create risks for financial institutions that cannot be seen on the balance sheet
Depository institutions are highly _______.
Leveraged
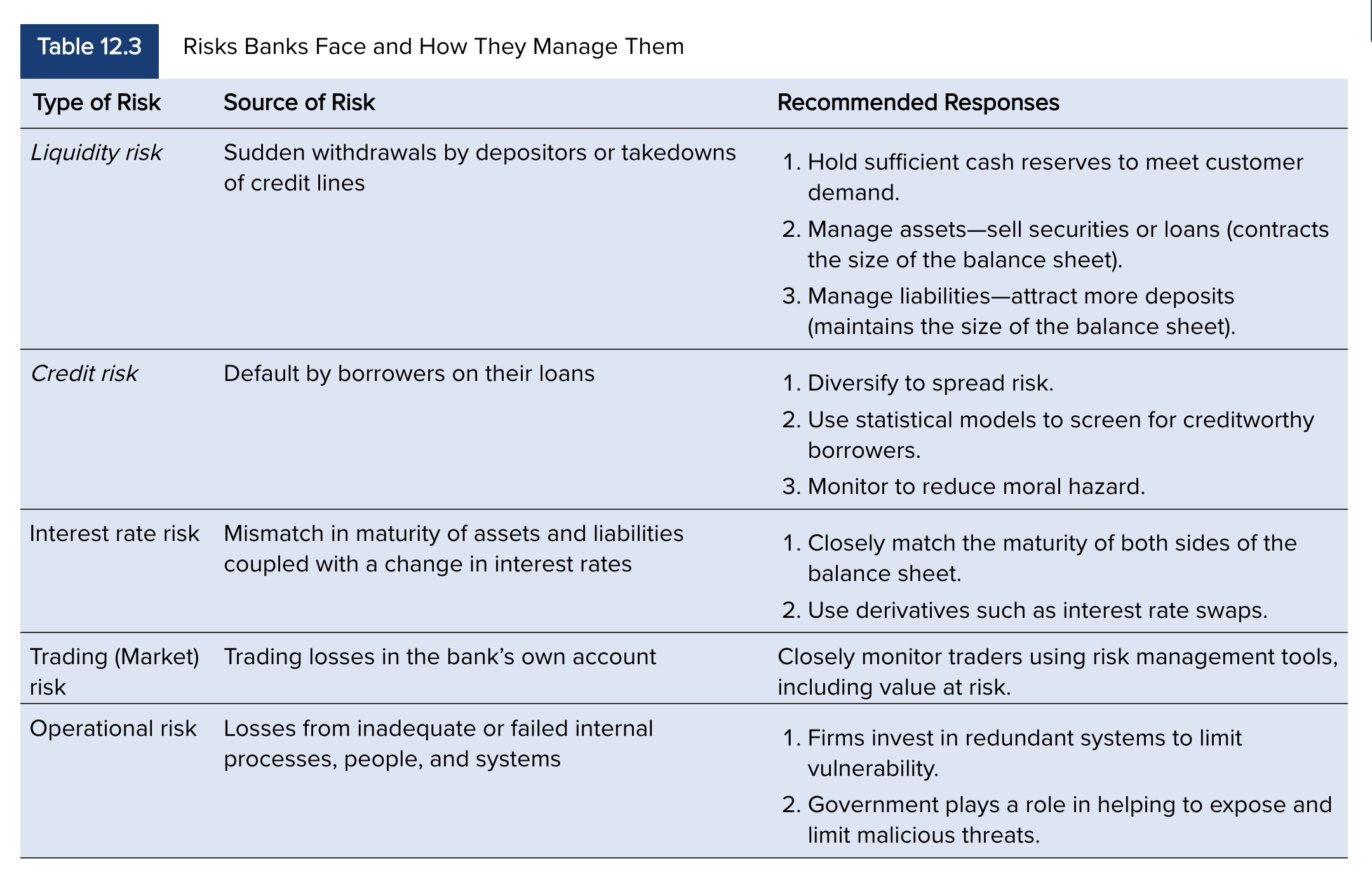
What are the different types of bank risks?
Liquidity risk
Credit risk
Interest rate risk
Trading risk
Foreign exchange risk
operational risk
What is liquidity risk?
the risk of a sudden demand for liquid funds (deposit withdrawal- liability side risk) and the risk of failure if banks cannot meet customers’ immediate needs
What are three ways to manage liquidity risk?
hold sufficient excess reserves
adjust assets
adjust liabilities
How do holding sufficient excess reserves help manage liquidity risk?
it’s like having a piggy bank for a rainy day
What are the cons of holding sufficient excess reserves to manage liquidity risk?
expense as interest is foregone
How does a bank adjusts assets help manage liquidity risk?
sell a portion of its securities or loan to another bank
refusing to renew a customer loan that has come due (to get the money they owe you rather than delaying principal payment and interest that is now due so you can have that money to give)
why is adjusting assets not a good way to manage liquidity risk?
reduces the balance sheet
The smaller the balance sheet, the lower the profits
The smaller the asset, the smaller the size of the bank
How do banks adjust liabilities to help manage liquidity risk?
Banks can use liability management to obtain additional funds by borrowing
from the federal reserve
attracting additional deposits (issuing large CDs) AKA borrowing in the wholesale money market
What is credit risk?
The risk that loans will not be repaid
What are two ways the credit risk is managed?
diversity loan (lending) portfolio
using statistical models and information specific to the loan applicant
what does it mean for a bank to diversify their lending portfolio
they are spreading risk and not putting their eggs all in one basket
Why would a bank use models and specific loan info to manage credit risk?
to examine borrower credit history to determine the appropriate interest rate to change
What is interest rate risk ?
When a bank’s liabilities are more interest rate sensitive (since they are short-term) than their assets are (since they are long-term), an increase in interest rates cuts into the bank’s profits due to this mismatch
What are two other definitions for interest rate risk?
the risk that interest rate will change, causing the price of a bond to change with it
The risk that changes in interest rates will affect a financial intermediary’s net worth.
What type of assets/liabilities are more sensitive to changes in interest rates
short term
what type of interest rates are sensitive to changes
variable interest rates
How can interest rate risk be managed?
The bank must determine how sensitive its balance sheet is to a change in interest rates via gap analysis
what is gap analysis?
highlights the gap or difference between the yield on interest sensitive assets and the yield on interest-sensitive liabilities
Gap analysis equation
Asset amount IR sensitive- Liability amount IR sensitive
how can gap analysis be further refined?
to take account of differences in the maturity of assets and liabilities
Matching the interest rate sensitivity of assets with the interest rate sensitivity of liabilities increases what
it increases credit risk
Like interest rate swaps, what can help manage interest rate risk and its one of the best options?
Derivatives
What is trading risk?
The risk that traders who work for a bank will create a loss on the banks account
How is trading risk managed?
Bank risk managers place limits on the amount of risk any individual trader is allowed to assume using standard deviations and value at risk
To remain solvent, what to banks need to do if there is more risk in their portfolio
hold more capital
What is foreign exchange risk?
the risk from unfavorable moves in the exchange rate
What is sovereign risk?
the risk from a government prohibiting the repayment of loans on international operations
How can foreign exchange risk be managed?
attracting deposits denominated in the same currency as the loans, and by using foreign exchange futures and swaps to hedge the risk
matching assets with their liabilities
How can sovereign risk be managed?
diversification
refusing to do business in a particular country or set of countries
using derivatives to hedge the risk
What is operational risk?
The risk that their computer system may fail or that their business may burn down
the risk of loss resulting from inadequate or failed internal processes, people, and systems
How is operational risk managed?
Make sure that bank computer systems and buildings are sufficiently robust to withstand potential disasters
What are the risks banks face and how they manage them?
Chart from textbook
Until what year was the there no national currency in the US
1863