Cone Beam Computed Tomography: Anatomy & Interpretation part 1
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Field of View
Reduce volume size to region of interest
What does reducing the field of view do?
Lower radiation dose (ALARA)
Increase resolution
Improve image quality
Less anatomy to review
What are the dental applications of CBCT in oral surgery?
Dento-alveolar trauma
Pathology (intraosseous lesions)
Impacted 3rd molar extraction and orthognathic surgical planning)
What are the dental applications of CBCT in periodontics?
Implant and surgical planning
What are the dental applications of CBCT in orthodontics?
Airway and cephalometric analysis
Impacted and supernumerary teeth
What are the dental applications of CBCT in endodontics?
Root canal morphology
Fractures
Resorption
What are the dental applications of CBCT in oral medicine?
Temporomandibular joints
Osteonecrosis
What is the main metric for resolution
Voxel size (minecraft, bigger pixels- blocky)
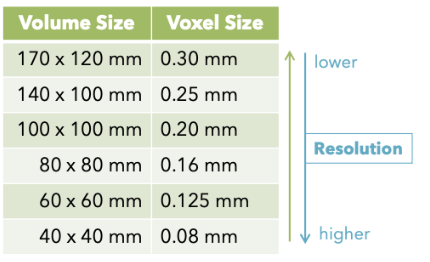
What is the relationship between voxel size and volume size?
As we increase FOV (or volume), voxel size increases
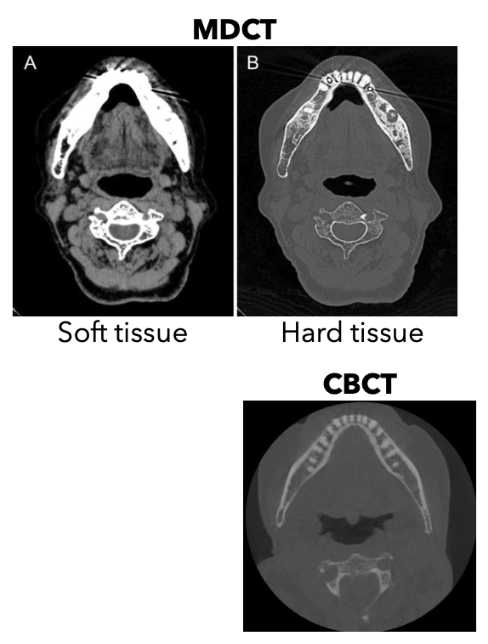
When there is evident or suspected soft-tissue involvement, what is the preferred modality?
MDCT is the preferred CT modality
What can you not really see in CBCT imaging, but can see in MDCT
Pathoses: Soft Tissue
Why is MDCT better for soft tissue windowing?
It has a higher/better contrast resolution
It enables soft tissue eval that is not possible with CBCT
IV contrast improves detection of soft tissue conditions due to enhancement (inflammation, malignancy, lymph node involvement)
What does the ADA have to say about the use of CBCT in Dentistry?
It is considered adjunct to standard oral imaging modalities, you have to use it when conventional radiography is insufficient
You also need appropriate clinical justification
It is NOT used for screening purposes
You have to use it when the diagnostic yield is expected to benefit patient care and enhance patient safety/improve clinical outcomes
What does the AAOMR say about radiology in dental implantology?
CBCT should be considered as the modality of choice for preoperative imaging of implant sites
You have to use PAs for post-op implant assessment in the absence of clinical signs or symptoms
DO NOT use CBCT for interval/periodic assessment of clinically asymptomatic implants
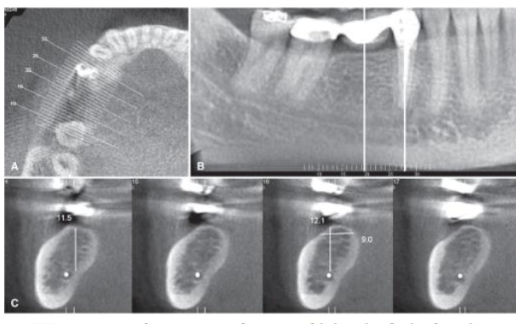
What does CBCT allow in implant planning?
Visualization of implant site in all dimensions
Reliable, accurate measurements
Evaluation of bone density and cortical thickness
Assessment of adjacent vital structures
What are the discrepancies using CBCT and PAs in implant planning?
Intraoral imaging is limited by superimposition and distortion (particularly in the buccal-lingual dimension)
Measurements from PA showed -1.7 to +2.1mm discrepancies compared to CBCT
PAs overestimate measurements 66% of the time
Panoramic is limited by superimposition, distortion and magnification
Dual scan
Image fusion
What is image fusion?
The integration of 2+ imaging datasets, examples include
Intra-oral scan
Cast/model
Dual scan
What is image guided navigation in implant planning?
Real-time virtal guidance based on planned implant
What is a good modality for assessing impacted 3rd molars, why?
CBCT is better than panoramic because you can see the number of roots, apical divergence, direct contact with IAC and predicting IAN exposure during surgery but was NOT better at predicting postoperative complications
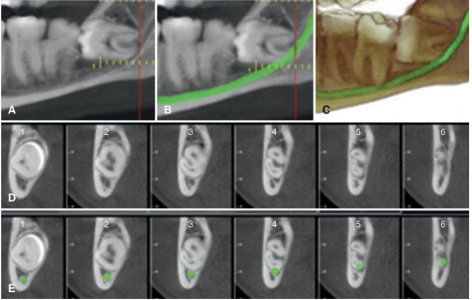
What is the evidence that CBCT Is better than a pano for assessing 3rd molars?
There is none - no evidence that CBCT improves prediction of treatment outcomes or helps prevent complications
But it is still advised that CBCT be utilized bc it indicated the proximity to IAC
What is the best modality for endodontics?
Intraoral radiographs should be considered the modality of choice because there are indications for limited field of view in CBCT
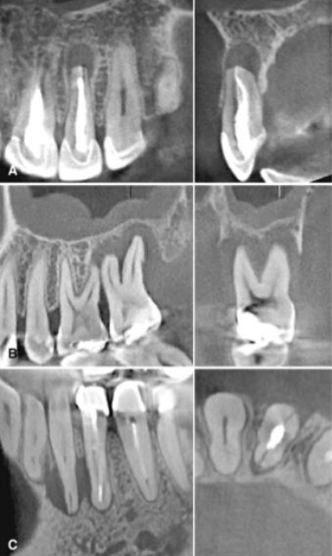
What are the indications for limited field of view in endodontics?
Contradictory or nonspecific clinical signs and symptoms
Suspect extra canals or complex morphology
Identification/localization of calcified canals
Non-healing previously treated teeth
Limited dentoalveolar trauma, root fractures, luxation, and/or displacement of teeth, and localized alveolar fractures
External and internal resorptive defects
Assess endodontic treatment complications
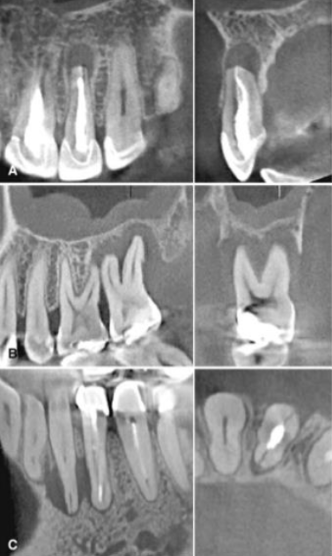
What are the findings in CBCT in endodontics?
Odds of CBCT locating a lesion are 2x as good as PAs
CBCT has high accuracy for tooth fractures
High confidence in positive result
Negative result should be interpreted with caution esp. in previously treated teeth
**Fairly significant limitations in the study (resolution is not that good- might not see tiny fractures)
Can make artifacts
Not 100% reliable for predicting fractures
What are the clinical recommendations regarding the use the CBCT in Orthodontics?
The pediatric population is radiosensitive
They are 2-10x more prone to radiation-induced carcinogenesis than mature adults
Higher rate of cellular growth and longer life expectancy
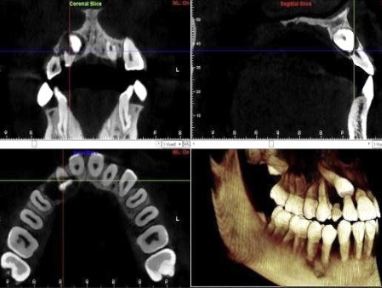
How has CBCT demonstrated use in Orthodontics?
It has demonstrated clinical efficacy in treatment planning for impacted maxillary canines, unerupted teeth, severe root resorption, severe skeletal discrepancies
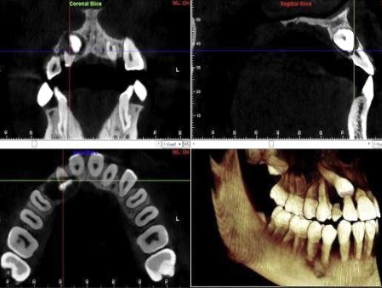
In what cases should CBCT be USED in orthodontics?
When clinical question cannot be adequately answered by conventional imaging
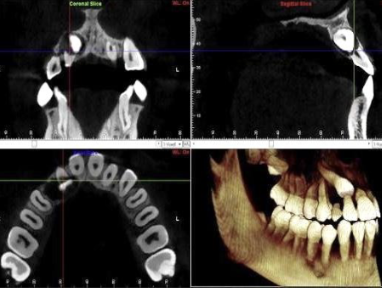
In what cases should CBCT be AVOIDED in orthodontics?
Solely to produce a lateral cephalometric and/or panoramic view if it would result in higher radiation exposure than conventional imaging
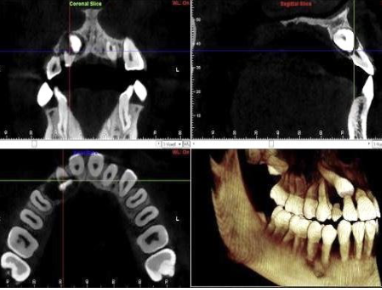
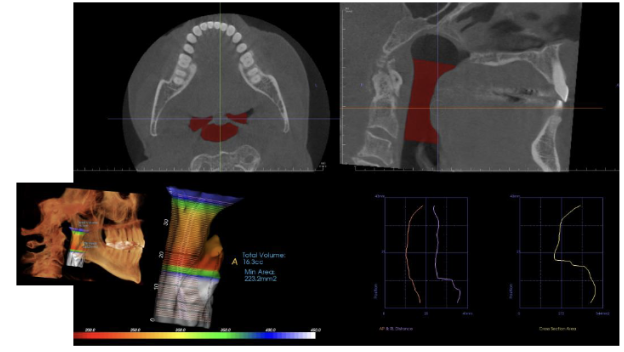
What would you use CBCT for when looking at the airway?
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA); severe OSA patients had significantly narrower cross-sectional area at uvula, more inferiorly positioned hyoid bone, and thicker soft palate
What are the risk factors for obstructive sleep apnea (OSA)?
Obesity
Decreased muscle tone of upper airway
Sleeping on back
Relaxants: ETOH, CNS depressant meds
Narrow nasal passages
Enlarged tonsils, adenoids, uvula, soft palate, tongue
Skeletal discrepancies
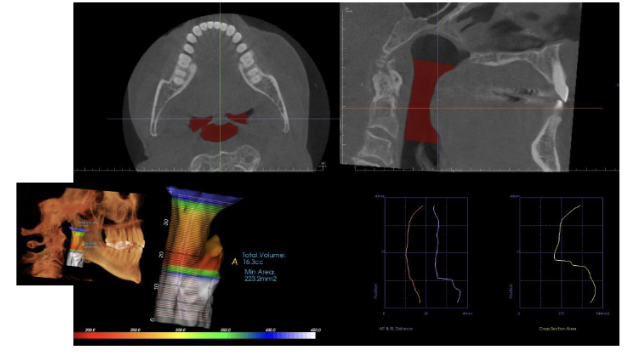
What are the measurements made in CBCT for airway analysis?
Cross sectional area and volume
Narrow minimum cross-sectional area has been
associated with OSAUse and applicability of these measurements is
controversial
What are the limitations of using CBCT for airway analysis/OSA?
Airway size and shape are variable depending on head posture and breathing stage
Does not accurately reflect airway during sleep
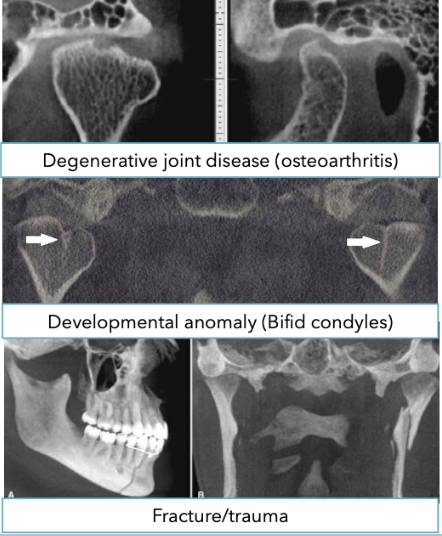
What is the use of CBCT for evaluation of TMJ?
What is the initial imaging exam for patients with TMD symptoms?
Panoramic
It is not sensitive to small changes
Entire condylar surface is not clearly depicted (obscured by superimposition and distortion)
What is used for the evaluation of osseous abnormalities in TMJ evaluation?
CBCT and MDCT are equivalent for evaluation
MDCT with contrast is recommended if malignant lesion is suspected
MRI has superior soft tissue resolution to MDCT and the only technique that shows the disk
CBCT in TMJ disorders
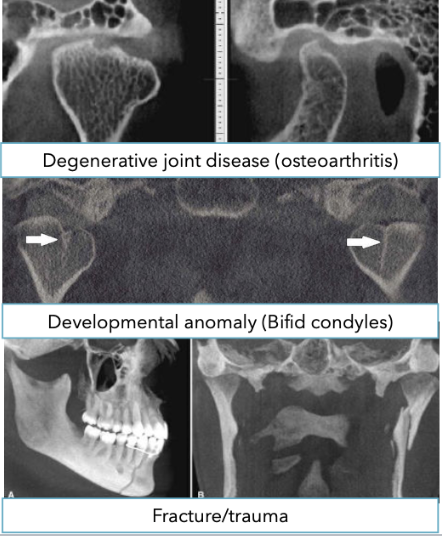
When taking a CBCT for TMJ evaluation, what should the patient do?
Be in occlusion. Open-mouth CBCT has limited impact on TMD diagnosis and management
The what are the display modes of CBCT
Multiplanar reformation
Orthogonal projections
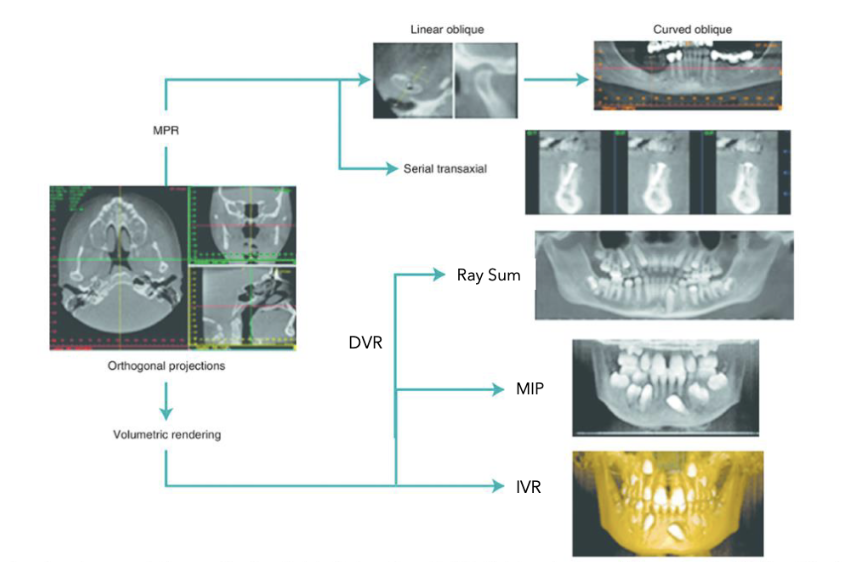
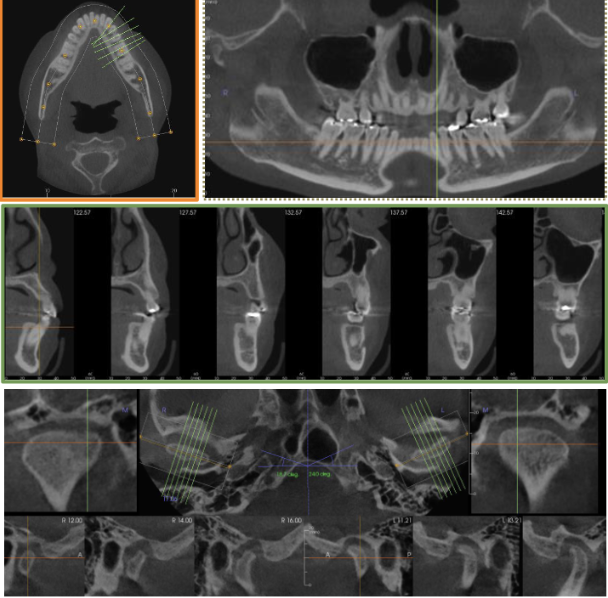
What are the types of multiplanar reformations?
Linear oblique
Curved oblique
Serial transaxial
What are the volume renderings of orthogonal projections in display modes?
Direct volume rendering
Ray sum
Maximum intensity projection
Indirect volume rendering
What are the standard orthogonal planes?
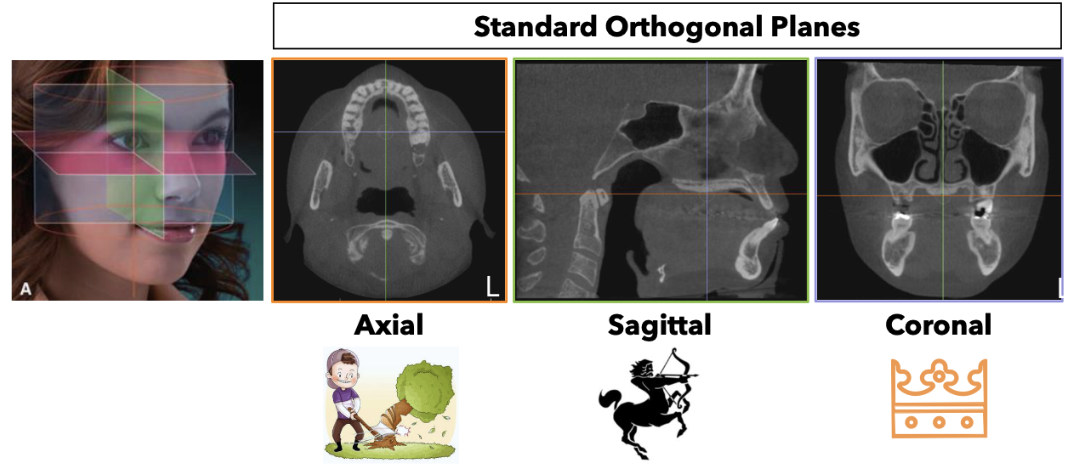
What are multiplanar reformations?
Display of data in different sections/planes
non-orthgonal or oblique
The options are software dependent
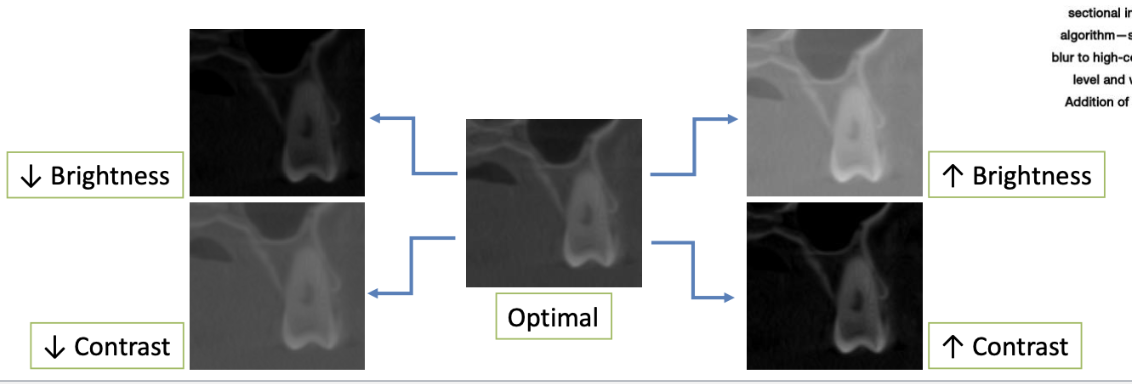
What are some awys you can optiminze imaging?
Using contrast and brightness
adjust for clear distinction between dentin and enamel, soft tissue and air, cortical and trabecular bone
Thin cortical bone should be distinct
Enhancements: smoothing or sharpening
Enhancements of image optimization
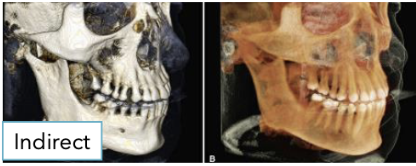
What is indirect volumetric rendering?
Computationally complex
Uses segmentation process to produce volumetric surface reconstruction with depth
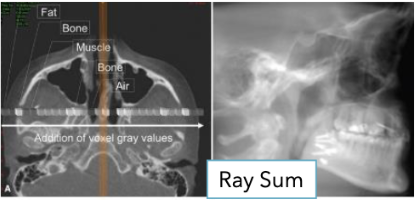
What is Ray Sum (Direct) volumetric rendering?
Image slab created by increasing number of adjacent voxels included in display
Gives appearance of anatomic superimposition (2D)
without magnification or distortion
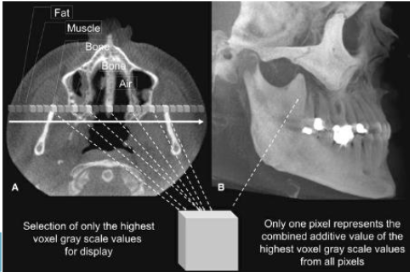
What is Maximum Intensity Projection (Direct) volumetric rendering?
Displays only highest gray level voxels along an
imaginary beam pathUseful in representing bony surface morphology
What are some task-specific tools?
It is dependent on software
Inferior alveolar canal tracing
Virtual implant planning
Surgical guide and restoration design
Superimposition
Overlay scans taken at different time points to assess change
Cephalometric analysis
Airway analysis
TMJ viewer
Endodontic specific reformats and volumetric renderings
What are some liability considerations when taking a CBCT?
Regardless of the primary purpose for the scan, the complete volume must be interpreted by an appropriately qualified provider
Interpreting provider is held to the standard of a specialist
Interpreting provider must be able to recognize significant findings
Endodontists and endo residents had interpretation accuracy of 60% compared to gold standard (consensus of experienced endodontist + OMFR) for limited FOV CBCTs
High rate of errors – missed lesions and false positives – by orthodontists and ortho residents
Findings must be documented in patient chart
What are some incidental findings in CBCT?
“Any abnormal or pathological finding that is unrelated to
the original purpose of the imaging test or tests being
performed.”
Presence of significant incidental findings in CBCT scans
well-documentedIncidence of ~24-94%
Most are not life-threatening
Frequency of incidentally found malignancy: 0.003 to 1.4%
Case report: 66yo female who had CBCT (80mm) for maxillary implant planning
Incidentally noted left sphenoid sinus mass
Further evaluation confirmed metastatic renal cell cancer
Incidental finding of metastatic malignancy
Example of a CBCT report
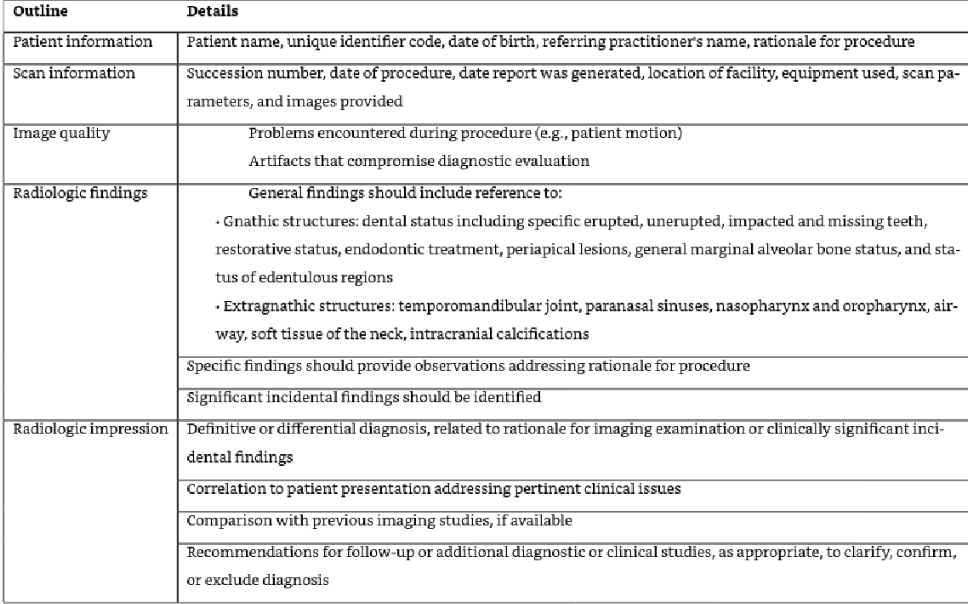
What is the other responsbility that you as a provider need to do in addition to taking the CBCT?
You need to be able to export and archiving it. Properly store it
CBCT volumes must be saved and stored like other patient images
Must be able to provide patients (and other providers) with usable copies
DICOM Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine
Standard format for image archiving and transmissionUsed by all viewing software
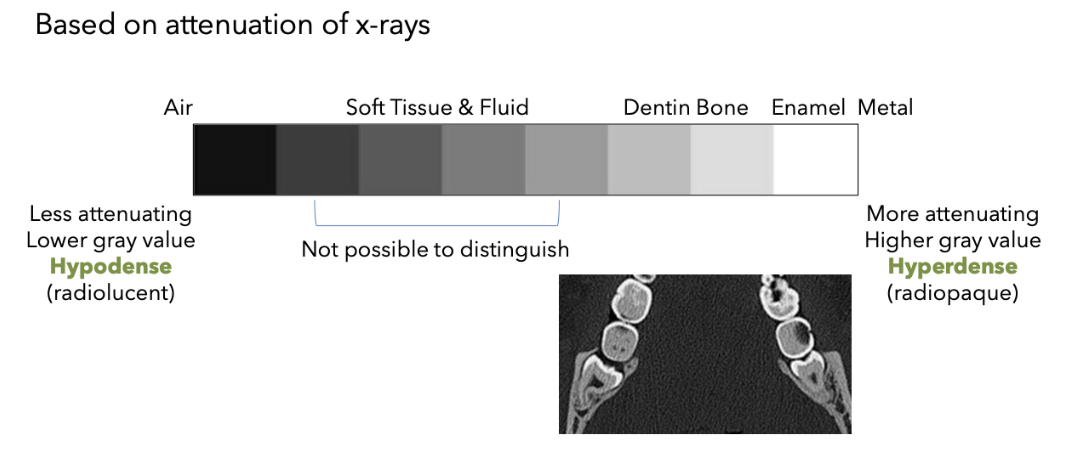
What term do you use to talk about radiographic density instead of radiolucent?
Hypodense
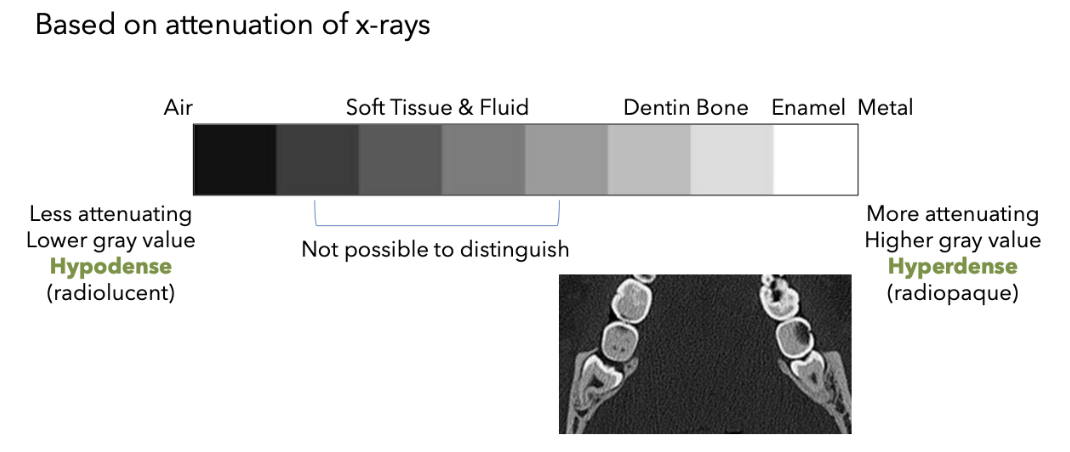
What term do you use to talk about radiographic density instead of radiopaque?
Hyperdense
List some tips for interpretation
✓ Use a systematic approach
✓ Start with panoramic rendering
✓ View entire volume in all 3 standard planes
✓ Focus on region(s) of interest last
✓ Avoid satisfaction of search
To ensure you don’t miss any incidental findings and/or pathology, review this list of anatomical structures contained in the FOV in all imaging places (axial, sagittal, coronal)
✓ Oral cavity (dentition, paradental bone)
✓ Nasal cavity
✓ Paranasal sinuses
✓ Cranial base
✓ Orbits
✓ Airway
✓ Temporomandibular joints
✓ Cervical spine
List all the anatomical structures you’d find in the mandible
Body
Ramus
Coronoid process
Mylohyoid ridge
Submandibular fossa
Inferior alveolar canal
Mental foramen
Lingual canal
Genial tubercles
List all the anatomical structures you’d find in the TMJ & Temporal Bone
Mandibular condyle
Glenoid fossa
Articular eminence
Styloid process
Mastoid process
Mastoid air cells
External auditory canal
List all the anatomical structures you’d find in the Maxilla
Tuberosity
Hard palate
Nasopalatine canal
Incisive foramen
Anterior nasal spine
Zygomatic process of maxilla
Zygomatic arch (zygomatic & temporal bones)
List all the anatomical structures you’d find in the nasal cavity
Nasal concha (inferior, middle, superior)
Nasal septum
Nasal bones
Nasolacrimal duc
List all the anatomical structures you’d find in the paranasal sinuses
Maxillary sinus
Ostium
Uncinate process
Sphenoid sinus
Frontal sinus
Ethmoid air cells
List all the anatomical structures you’d find in related to orbits
Orbit
Infraorbital foramen (maxillary bone)
Optic canal (sphenoid bone)
Superior orbital fissure
Inferior orbital fissure
List all the anatomical structures you’d find in soft tissues and airway
Nasopharynx
Oropharynx
Soft palate
Tongue
Palatine tonsils
Epiglottis
List all the anatomical structures you’d find in cervical spine and other
Anterior arch of C1
Dens of C2
Pterygoid plates (medial, lateral)
Pterygopalatine fossa
Pterygomaxillary fissure
Hyoid
Sella turcica