chem final- lipids
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
sphingomyelin
sphingosine, a fatty acid, and phosphate, and choline
lecithin
glycerol, fatty acid 1, fatty acid 2, phosphate and choline
cephalin
simple tiacylglycerols
Glycerol with 3 fatty acids
phospholipids
saturated fats
solid at room temp
single bond, no double bond
unsaturated fat
liquid at room temp
one or more double bonds
what converts oils into soild fats
hydrogenation
glycolipids
sphingolipids
phospholipids
lipids
all biological compounds that are not soluble in water
but are soluble in organic solvents
functions of lipids
1. lipids function as part of the structure of cell membranes,
2. as energy storage molecules for the cell,
3. and the starting material for the synthesis of vitamins and hormones.
lipid storage
storage is an important function of lipids. Energy stored in the fats in our body is more important than the glycogen storage. The burning of fats produces twice as much
energy as the burning of carbohydrates
lipid membrane components
➢ Lipids form the membranes around body cells and around small structures inside the cell.
➢ The purpose of these lipids is to separate cells from the external environment and provide selective transport for nutrients and waste products.
lipid chemical messengers
Cholesterol is the starting material for the synthesis of steroid hormones.
State the components of cell membranes and the fluid mosaic model
phospholipids, proteins, cholesterol, and carbohydrates. The fluid mosaic model describes the membrane as a dynamic structure where these components are free to move within the bilayer, creating a fluid-like mosaic
steroid
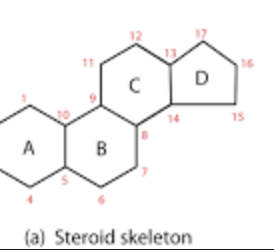
Know the properties of cholesterol
waxy, fat-like substance essential for various bodily functions, including cell membrane structure, hormone synthesis, and vitamin D production. It's a sterol, a type of lipid, and exhibits both hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties due to its unique structure. It's primarily found in animal tissues and is also produced by the liver
Be able to identify the components of the lipid bilayer