PL SC 324 Lecture 3: Stress Responses & Phenotypic Plasticity
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Stress
Is any phenomena that limits the biomass production of plants
Disturbance
Any phenomena that removes or destroys plant biomass
Resistance
Is the ability of a plant to withstand a stress
Resilience
Is the ability of a plant to recover from stress
Draw the Time Scale of Plant Response
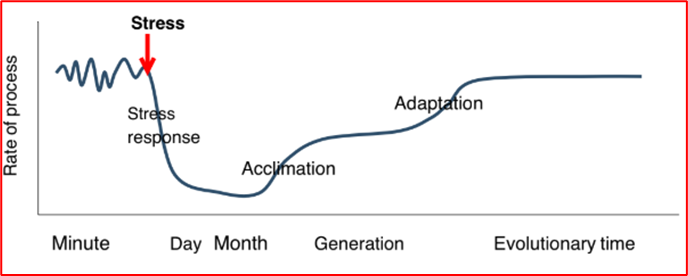
Stress Response
Immediate detrimental effect of stress on a plant process (Photosynthesis, growth, etc.)
Acclimation
Morphological and physiological adjustment by individual plants to compensate for the decline in performance due to a stress (ex: Synthesis of new proteins).
Adaptation
Evolutionary response that results from genetic changes in populations leading to morphological and physiological compensation (genetic changes in populations).
Population
All of the individuals of the same species and living in the same area
Adaptation is the result of
natural selection (or selective breeding)
Long-term stress will lead to selection of — survival strategies as opposed to — strategies
Phenotypic Plasticity:
Ability of a single genotype to produce more than one phenotype. We can demonstrate this by examining genetically similar individuals grown in different environments.
Genotype
The genes of an individual, or the particular alleles of a gene.
Phenotype
The observable characteristics of an individual.
T/F Plasticity can happen in virtually any plant trait
True
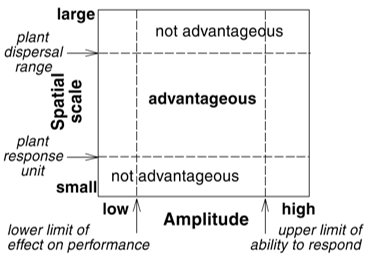
Plasticity may thus be advantageous when the environment varies on an intermediate scale, between scales somewhat larger than the size of the response unit and somewhat smaller than the dispersal range of offspring. Amplitude: the degree to which an environmental factor varies over a given distant. Plasticity is likely to be advantageous over an intermediate rage of amplitude in heterogenicity. With a small amplitude, the environmental variation has no effect on performance, plasticity will have no advantage. When the amplitude of environment is so great that plasticity cannot enable a genotype to survive in more than one environment, plasticity should have no advantage.
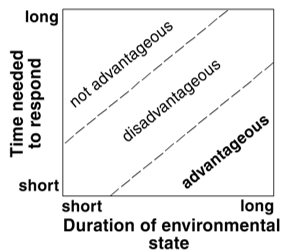
Plasticity is expected to be advantageous only in a trait that responds quickly relative to the duration of environmental states. When the ability to change matches the duration of the environmental state, there will be a lag.
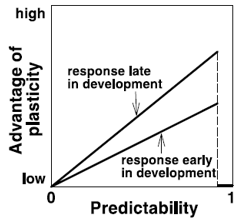
Plasticity may be more advantageous when the environment is more predictable, expect that plasticity should have no advantage when the environment is completely predictable.