Exercise Physiology Final
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
What is the highest arterial pressure measured after left ventricular contraction?
Systolic blood pressure
Where do parts of the atria become prematurely electrically active and depolarize spontaneously prior to S-A node excitation?
Premature atrial contraction (PAC)
Which 2 neurotransmitters can lead to tachycardia during sympathetic stimulation?
Epinephrine and norepinephrine
Which brain area is associated with cardiovascular control?
Medulla
What is cardiovascular drift?
Gradual time-dependent shift in several cardiovascular responses during prolonged exercise that can lead to increases in heart rate?
What principle is when individuals do not respond similarly to a training stimulus?
Individual differences principle
Aerobic training response occurs with physical activity performed at least how many days per week?
3 days per week for at least 6 weeks
What are ways aerobic intensity of exercise can be monitored?
Energy expended per unit time, absolute power output, relative metabolic level, activity below, at, or above LT or OBLA, activity HR or %HRmax, multiples of RMR, or RPE scale
What is interval training?
specific spacing of high-intensity activity and rest periods
What are psychological benefits of aerobic training?
Reduced anxiety state, decreased mild to moderate depression, reduced neuroticism as a long-term conditioning effect, adjunct to professional treatment of severe depression, improved mood, self-esteem, self-concept, and reduced indices of stress
Does less complex movements have a lower or higher ratio of muscle fibers to motor nerves?
Higher
What receives impulses through spinal cord connections and conduct them toward the cell body?
Dendrites
How does force of muscle action vary from slight to max?
Increasing number of recruited motor units and increasing frequency of motor unit discharge
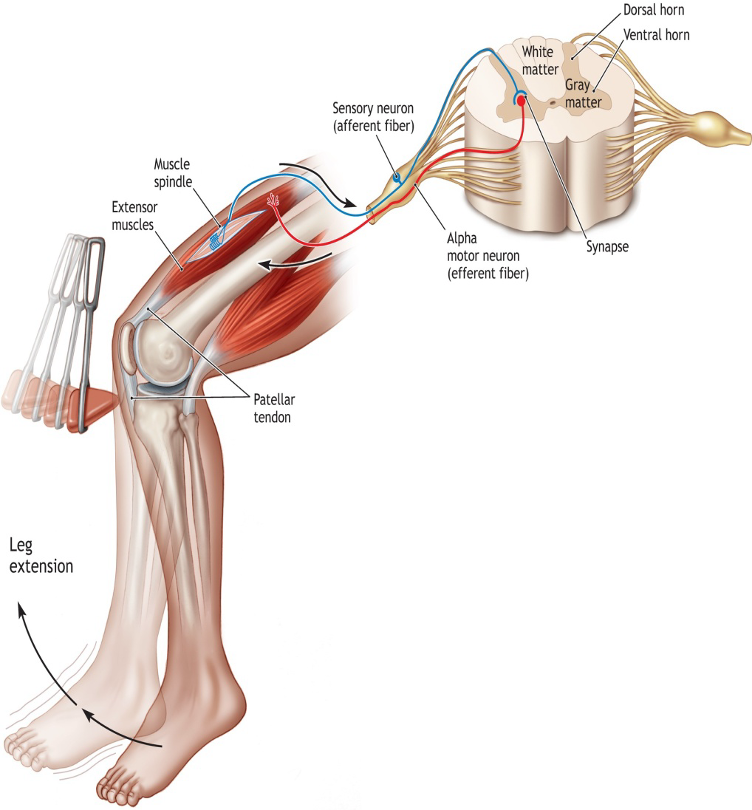
Which proprioceptor is activated in this?
Muscle spindle
What is a bundle of muscle fibers called?
Fasciculus
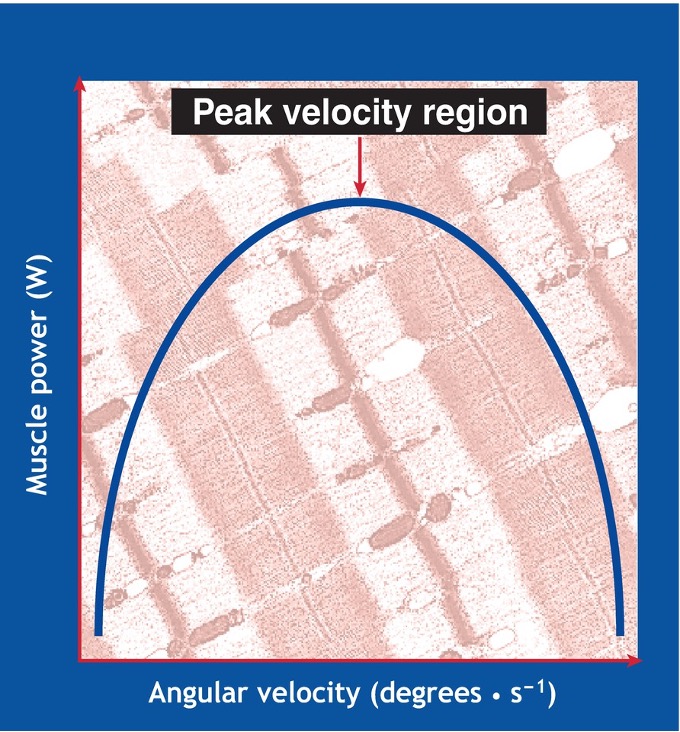
This figure defines what relationship?
Power velocity relationship
What interrelated systems develop muscle strength?
Isometric training, dynamic constant external resistance training, variable resistance training, isokinetic training, and plyometric training
What is held constant in isokinetic training?
Velocity of movement
What is periodization?
Varying training intensity and volume to ensure peak performance to coincide with major competition
What central nervous system factors occur in the early phase of resistance training for neural adaptations?
Increased CNS activation, improved motor unit synchronization, and lower neural inhibitory reflexes
What is the formula for body mass index?
Kg x m²
What does DXA stand for?
Dual energy X-ray absorptiometry
What type of skin fold is the thigh skin fold?
Vertical
Where is the thigh skin fold?
On the front of the thigh midway between the iliac crest and the top of the patella
Which body composition assessment uses ionizing radiation?
DEXA
What is spot reduction?
Belief that an increase in a muscle’s metabolic activity stimulates relatively greater fat mobilization from the adipose tissue in proximity to the active muscle
Which valve separates the right atrium and ventricle?
Tricuspid valve
What is diastolic blood pressure?
The lowest arterial pressure measured during left ventricular relaxation
What is the formula for RPP?
Systolic blood pressure x heart rate
What is RPP an estimate of?
Myocardial work
Which cardiac structure spontaneously depolarizes and depolarizes to provide an innate heart stimulus?
Sinoatrial (SA) node
What is ejection fraction (%)?
The percent of blood pumped from left ventricle relative to its end-diastolic volume
What does the SAID principle stand for?
Specific adaptations to imposed demands
Adaptations to aerobic training includes an increase and reduction in what?
Increases in heart mass, volume, left ventricular size, plasma volume, stroke volume at rest and during physical activity, and cardiac output. A decrease in heart rate during submax and rest
What direction is the lactate threshold pushed to improve performance in a sprint athlete?
To the right
What percentage of VO2max or heart rate is needed for cardiovascular improvements?
50-55% of VO2 max or 70% of heart rate
How many weeks after undertaking a program does positive adaptations with training in cardiorespiratory fitness and aerobic capacity?
2-3 weeks
Which neurotransmitters are released from the neuron across the synaptic cleft?
Acetylcholine
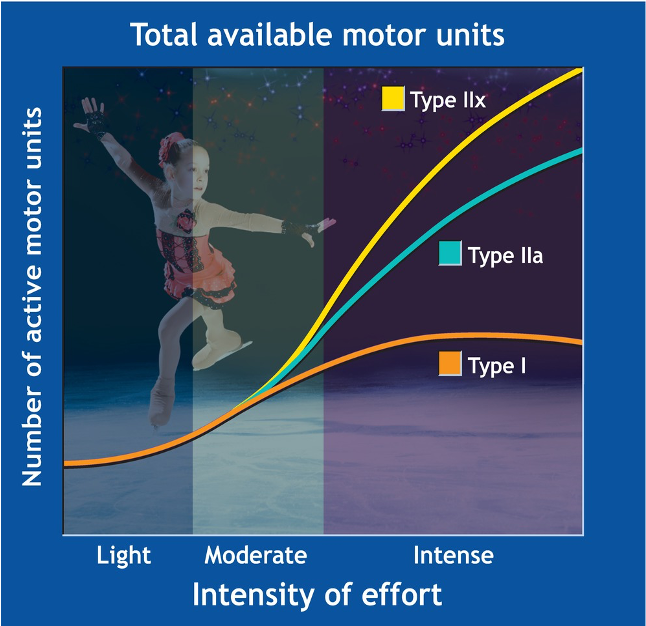
What principle is being demonstrated with this figure?
Size principle
What proprioceptor protects muscle and its connective tissue harness from injury by sudden, excessive load or stretch?
Golgi tendon organ
Which muscle myofilament has a binding site for calcium?
Troponin
What happens to calcium when muscle contraction stops?
It is pumped back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum
What type of muscle action requires tension to be developed while the muscle lengthens?
Eccentric
What is a isokinetic dynamometer?
A tool/machine that uses electromechanical accommodating resistance instrument with a speed-controlling mechanism, accelerates to a preset, constant velocity with applied force regardless of the force exerted on the movement arm
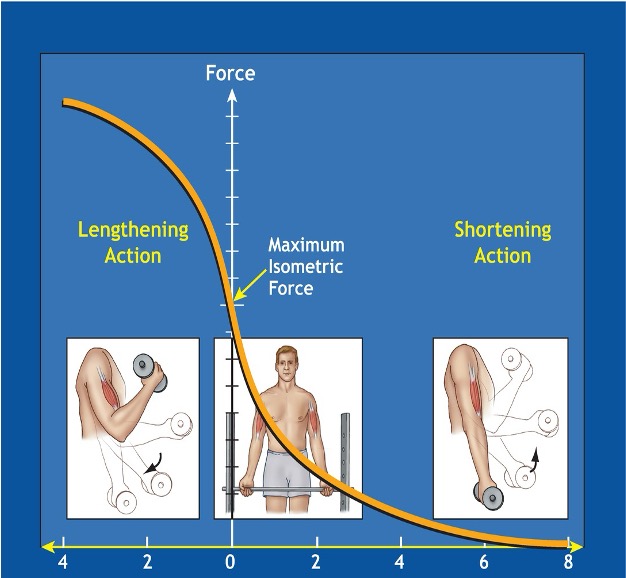
What relationship is depicted by this?
Force-velocity relationship
What is dynamic constant external resistance (DCER) training?
Alters external resistance to movement with a lever arm, irregularly shaped metal cam, air, hydraulics, or pulley to match increases and decreases in force capacity related to joint angle throughout ROM
What cells are important for muscle cell remodeling through migration, proliferation, and differentiation?
Satellite cells
What is the Archimide’s principle?
States that an objects loss of weight in water equals the weight of the volume of water it displaces
What is the Siri equation?
%body fat = 495 ÷ body density - 450
What technique does the BODPOD use to estimate body density?
Air displacement plethysmography
Which skin fold site uses an oblique fold just above the hip bone following the natural diagonal fold?
Suprailiac (iliac crest)
What is bioelectrical impedance?
Uses a small, alternating current between 2 electrodes that passes more rapidly through hydrated fat-free tissues and extracellular water compared with fat or bone because of less impedance from FFM
What is the only artery that carries deoxygenated blood?
Pulmonary
The heart’s valves provide for what?
One-way blood flow
What is the largest constituent of skeletal muscle on a weight basis?
Water
What is the repeating unit between 2 Z lines called?
The sarcomere
What is the major function of tropomyosin?
To inhibit actin and myosin interaction
When a muscle is no longer stimulated, the flow of calcium decreased and what else happens?
Troponin inhibits actin-myosin interaction
What are dynamic measures of muscular strength?
1-RM method, spring-steel dynamometer, and cable tensiometer
Overload occurs by what?
Increasing resistance (load), increases repetition number, and increasing speed of muscle action
What does muscle strength depend on?
Size and type of muscle fibers, anatomic-lever arrangement of bone and muscle, and level of CNS activation
What is concentric muscle action?
It occurs in dynamic activity, joint movement occurs as tension develops, and an example is curling a dumbbell from the extended elbow to flexed elbow position
What do DEXA, CT, MRI, and BIA estimate?
Body composition
What does the Siri equation estimate?
Body fat percentage
What are limitations of using skin folds to predict body fat?
The tester must be experienced taking the measurements, for obese people the thickness of the skin fold often exceeds the caliper’s jaws, a particular camper may contribute to measurement error, and different prediction equations contribute to error