environmental air pollution
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
ambient air pollution
According to the WHO, 99% of the global population lives in places where air quality exceeds 2021 WHO guidelines for mean outdoor air pollution for PM10 or PM2.5.
sources of ambient air pollution are principally
Internal combustion engines
Power generation
Domestic biomass and coal burning
In some places, wind-blown dust and wildfire smoke may be significant, but episodic
Fossil fuels may cause about 65% of deaths attribute to air pollution globally
global ambient air pollution and mortality
Ambient air pollution leads to ~6% more deaths in the most polluted than in the least polluted cities. PM2.5 shows greater effect than PM10 for a given increase in concentration. Higher temperatures lead to more deaths.
WHO estimates for causes of premature deaths from outdoor air pollution in 2019
45.7% heart disease
22% stroke
14.2% acute lower respiratory infections e.g. tuberculosis
13.6% chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) - emphysema and bronchitis
4.6% lung and throat cancers
PM2.5
PM2.5 is especially harmful because of very large surface area exposed to alveoli; gases including nitrogen oxides may be very significant too.
mechanisms may include
Greater coagulability of blood
Constriction and inflammation of blood vessels
Disturbances of heart functions
COPD
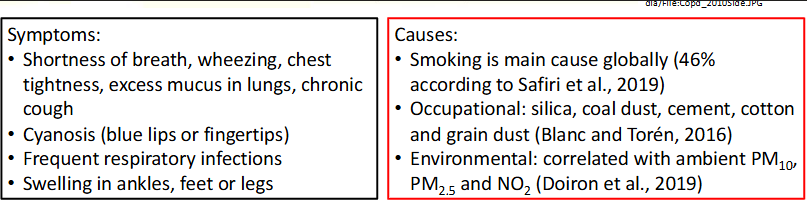
COPD global incidence and mortality 2019
High incidence in many countries, smoking being most important cause in wealthy countries.
COPD mortality is disproportionately high relative to incidence in poorer counties.
overview of airborne particulates - affected populations
