Nervous System II
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A set of flashcards based on the key concepts and terminology of the nervous system, highlighting action potentials, synapses, reflexes, and neurotransmitters.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
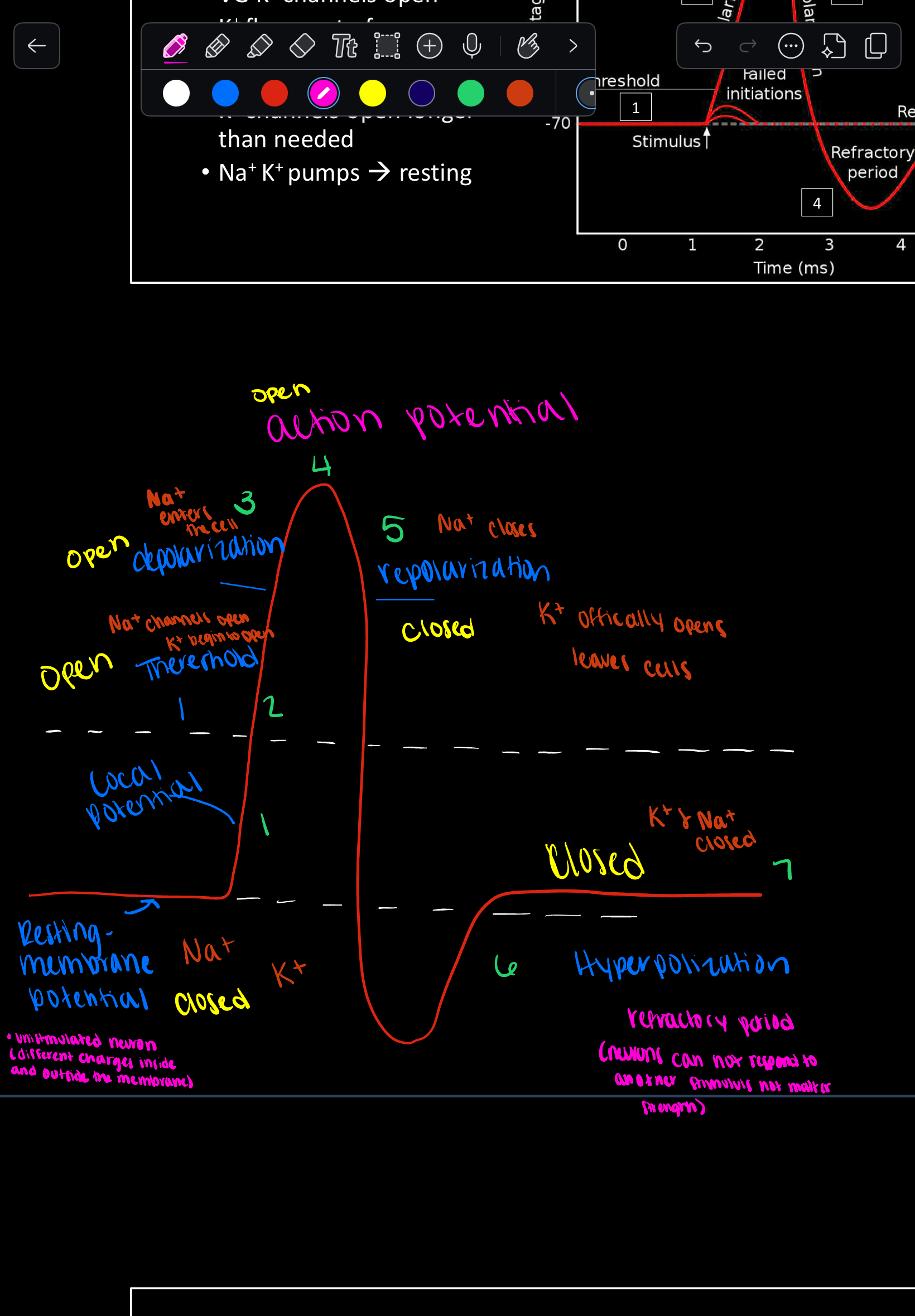
What are the two main types of potential changes in the nervous system?
Graded potential and Action potential.
What is the difference between graded potentials and action potentials?
Graded potentials are temporary, short-range changes with variable strength, while action potentials are long-distance signals with constant strength.
What channels open during the depolarization phase of an action potential?
Voltage-gated Na+ channels.
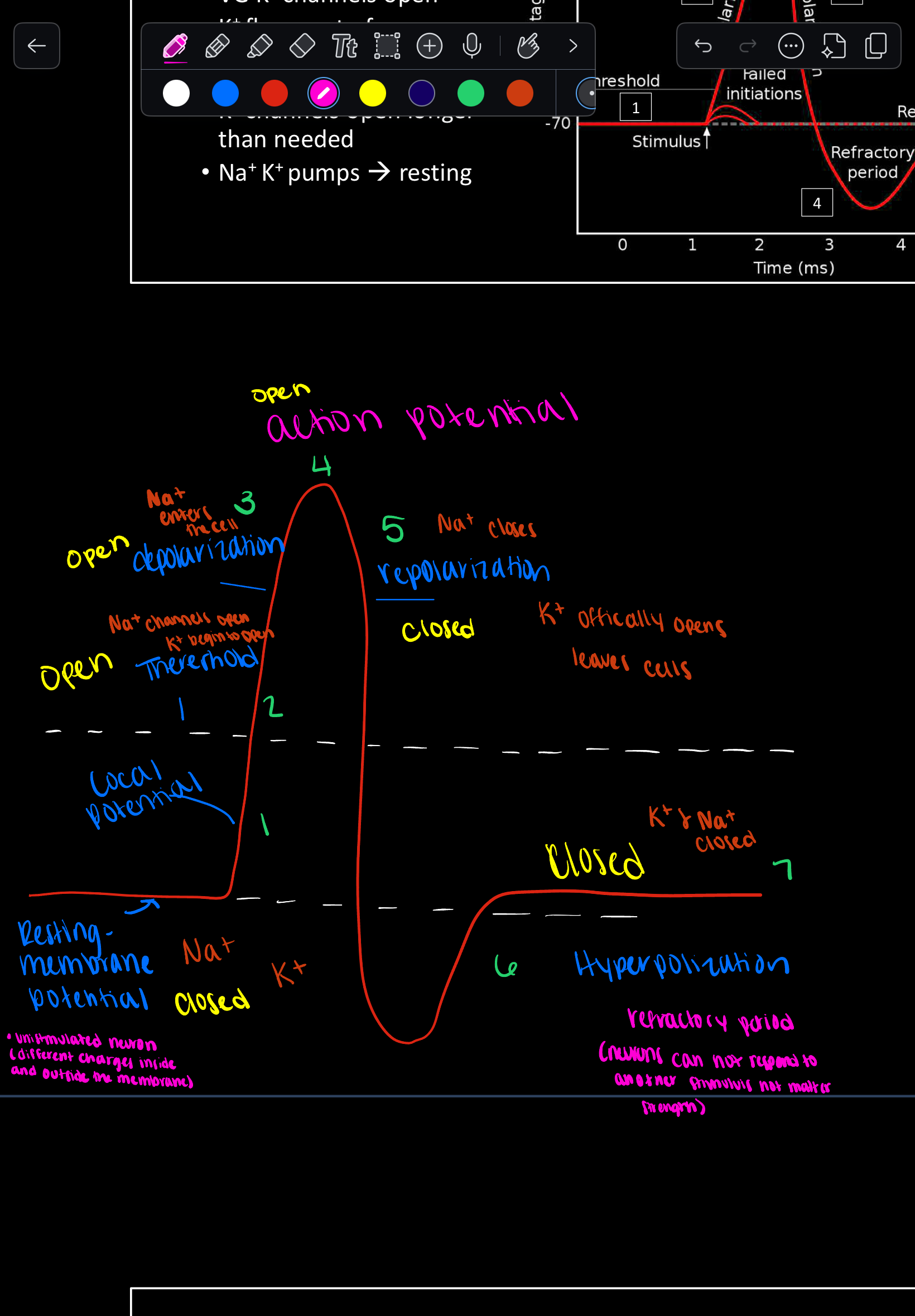
What is the 'all or nothing' principle in action potentials?
An action potential either happens completely or not at all; there is no partial action potential.
What ion primarily flows out during repolarization of an action potential?
K+ (Potassium) ions.
What are synaptic vesicles?
Membrane-bound structures that contain neurotransmitters and release them into the synaptic cleft.
How do excitatory neurotransmitters affect the postsynaptic neuron?
They cause depolarization, making the neuron more likely to fire an action potential.
What is a reflex arc?
A neural pathway that controls a reflex action, consisting of a sensory neuron, interneurons, and a motor neuron.
What are the two types of reflex arcs?
Monosynaptic reflex arcs and polysynaptic reflex arcs.
What type of neuron is a sensory neuron?
A neuron that transmits sensory information to the central nervous system.
In saltatory conduction, where does the action potential regenerate?
At the nodes of Ranvier in myelinated axons.
What is the role of the Na+/K+ pump after hyperpolarization?
To restore resting ion concentrations of sodium and potassium to re-establish resting membrane potential.
What is the absolute refractory period?
A phase during action potential when no new action potential can be generated because Na+ channels are inactivated.
What does the frequency of action potentials generated by a sensory receptor indicate?
The strength of the stimulus.
Conduction Velocity
Axon diameter
Axon myelination
Group A:
-myelinated
-somatic sensory and motor fibers
Group B:
-intermediate
-visceral sensory
Group C:
-non-myelinated
-autonomic fibers
What is the function of neurotransmitters at the synapse?
To transmit signals across the synaptic cleft to the postsynaptic neuron.
What is the purpose of interneurons within reflex arcs?
To integrate signals from sensory neurons and communicate with motor neurons.
What is the role of the spinal cord in reflex actions?
To serve as the integration center where sensory and motor neuron signals connect.
How do electrical synapses differ from chemical synapses?
Electrical synapses are faster and involve direct cell-to-cell connections, while chemical synapses use neurotransmitters and involve synaptic clefts.
What is the function of descending tracts in the spinal cord?
To carry motor signals from the brain down to the spinal cord and muscles.
what is the function of ascending tracts in the spinal cord?
to carry sensory signals from the body to the spinal cord and brain.
What behavior is associated with biogenic amines like dopamine and serotonin?
Emotional behavior and regulation of mood.