Astronomy 101 final
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
123 Terms
zenith vs nadir
-zenith is the point in the celestial sphere directly above the person- top of dome directly overhead
-Nadir is the point directly below
what is the astronomical unit? AU
distance from center of earth to center of sun-1.496×108 km
used to measure long distances in the galaxy
What is polaris?
The north star, which is located close to the direction of the celestial north pole so can help with directions by letting us know which direction is north
-because it never sets
What is a light-year?
the distance light travels in one year, 9.46 × 10¹² km
is used to measure the distance of things extremely far away because light travels very quickly
what is the geocentreic model?
-A model that represents the universe as earth in the center with all celestial bodies circling it
-almost everyone /ancient people before the renaissance used the celestial sphere to show how everything was just a circle around the earth which made sense to them and was evidence to prove what they were seeing
-was preserved more by the church who was able to remain powerful if there were more people that believed in god/ that god had picked them as the center of the universe, rather than not being in the center.
what is the heliocentric model?
the model that represents the sun being in the centre with us and other planets circling it
-was proposed by Aristarchus, but wasnt fully accepted until 1700s
how are the seasons created?
because the earth does not rotate perfectly vertcle on its axis, but on an angle
23.5 degree angle
-depending on its position around the sun, that angle may be facing away, towards,or adjacent to the sun, which creates the longer days
the difference in heat is caused when the sun is further away or closer to the earth/ at a different angle; and the more sun rays in a smaller angle the more intence that light is, so its more intence in the summer when closer and less so in the winter
what is the celestial sphere?
the idea of a giant circle surrounding earth that rotates around us every night and day; confirms the geocentric idea
-thought that it turns on the axis, instead its earth turning
-can still be helpful idea to mark out the location of things in the sky, just not correct
Aristarchus (of samos)
#2-310-230 BCE
-created one of the first known models where the earth went around the sun (heliocentric model)
-Was rejected; heliocentric model wasn’t accepted until the 17-1800s
Isaac Newton
#12-1643-1727 CE
-Figured out how to explain things in the physical world no one had explained before
-created three laws of motion that determine how everything in the universe moves, including everything off of the earth
explain newton first law
-law of inertia
Every object will continue to be in a state of rest or move at a constant speed in a straight line unless it is compelled to change by an outside force.
explain newton second law
Fnet=ma
-When you apply a (net) force, an object will accelerate!(how quickly a object changes speed or direction) meaning an object will change speed and/or direction
-The change of motion of a body is proportional to and in the direction of the force acting on it
explain newton third law
every single force is created by something, and you need something to push and something to be pushed.
when they interact/ push against each other both things will experience the same amount of force (equal and opposite)
it just depends on the sizes; as although a smaller/ lighter thing will feel the same amount of force as a larger thing, it will be affected more than the larger thing
-like if i push the person next to me by their chest, they might move from the force- i feel the exact same amount of force against my hands when i push.- because a wall is stronger/ more sturdy than a person, when i push it again we both feel the exact amount of force, but because the wall is strong it doesn’t move; and the amount of force i use to try to move the wall might hurt my hand-
affects non-physical force too
when calculating the pull of two objects gravity forces, use grav. constant (6.67×10-11) the mass of the two objects (kg) and the distance between them (meters)
explain aristotle
#1-384-322BCE-first on list
knew that moon was closer than the sun because of solar eclipses where moon passes in front and blocks all the light
-Believed the earth was round because the shape of the shadow on the moon after solar eclipse was round, and if it were flat then it would show as a straight line sometimes
-also because the stars change wherever you travel, and if the earth was flat you would see the same stars all the time
eratosthenese
#3- 276-194 BCE
-Figured out earth’s size/ circumference and proved is not flat because of his study of the two cities
because sun was at different angles at the same time of the day for each place, he found the angle they made and used it in comparison to 360 degree measurement
hipparcus
4th-190-120 BCE
-Discovered that location of north star had changed overtime; direction of rotation of sky changes slowly but continuously. (precession-earth rotating and moving: like a top)
-Collected list of around 850 examples of stars and their locations in the sky, and categorised by their brightness(apparent magnitudes)
Ptolemy
#5-100-170 CE
-Created a geometric (earth in the middle) representation of the solar system that predicted positions of planets at any date and time; left data for the intention of future generations to build off
-Created book with massive amount of astronomical knowledge-Almagest (the greatest); how have have gained the knowledge of greek astronomers, especially hipparchus
scientific notation/ exponents; what did we learn in class?
-Makes really big and small numbers easier to understand
-move the decimal place of the number to the front, and use “ten to the power of”; represents how many numbers aren’t being shown-
104 =10×10×10×10
5.0×104 means that the 5 is in the hundred thousandths place
depending on the unit we can move what place that first digit is in-
-when adding scientific notation #s, add the digits that are in the same spot
List the names and order of the astronomers for this section-16 total
1-Aristotle-384-322 BCE
2-Aristarchus-310-230 BCE
3-Eratosthenes -276-194 BCE
4-Hipparchus- 190-120 BCE
year zero
5-Ptolemy- 100-170
6-Copernicus:1473-1543
7-Tycho Brahe:1546-1601
8-Kepler:1571-1630
9-Galileo:1564-1642
10-Cassini-1625-1712
11-Huygens: 1629-1695
12-Newton- 1643- 1727
13-Herschel-1738-1822
14-Henrietta Swan Leavitt:1886-1921
15-Kuiper:1905-1973
16-Nancy Grace Roman:1925-2018
what is the synodic day
24 hours-
earth rotation relevant to the sun, because since its also orbiting sun it has to turn a bit extra each day to have the sun at the same angle- has to go 361 degrees
what is the sidereal day
23 hour, 56 minute, 4 seconds
earth rotation relevant to distant stars
-they are so far away that its just the actual full time it takes for the full 360 degree rotation
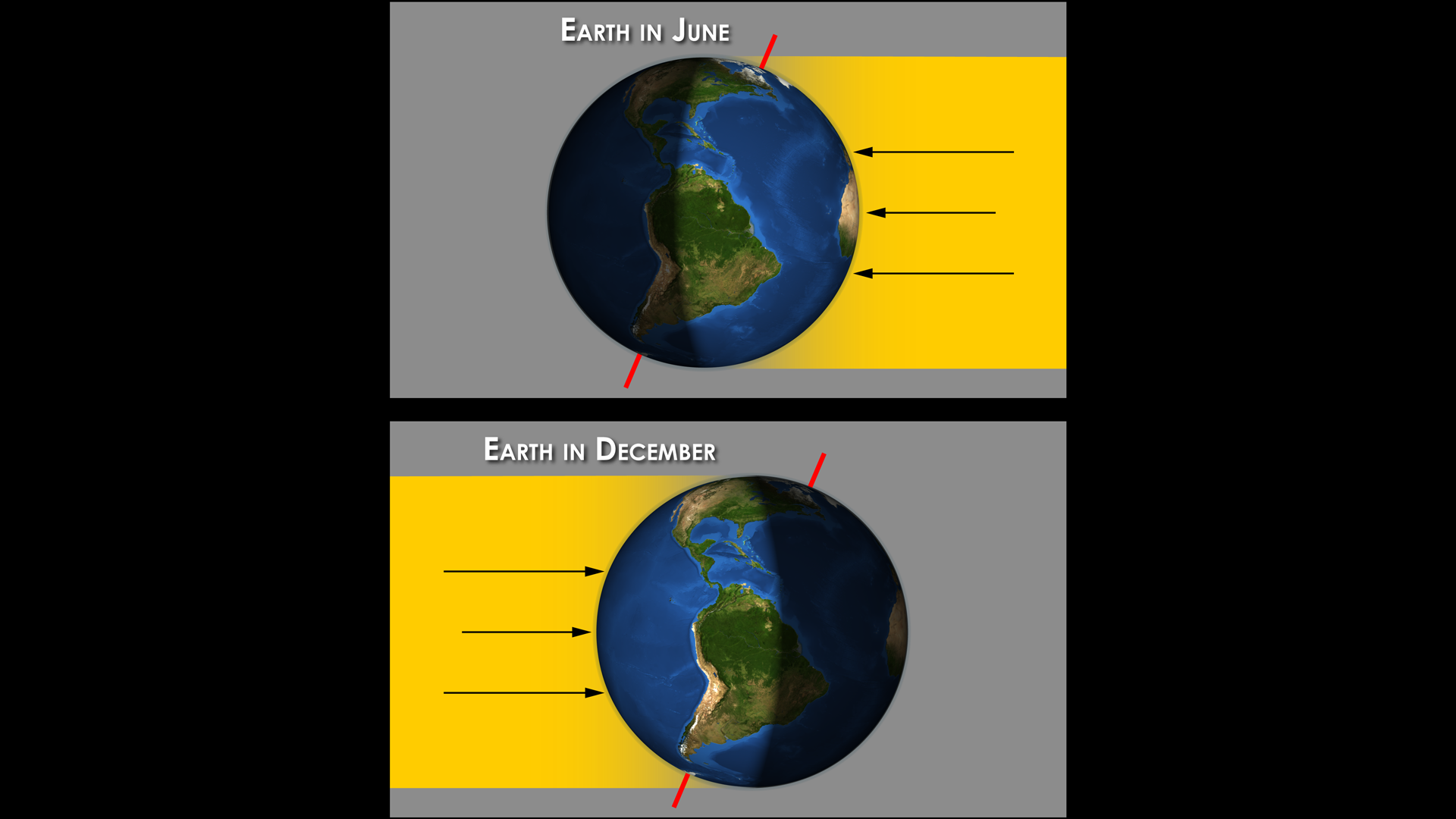
what makes it hotter in the summer
In the summertime the earth is angled towards the sun differently so that the ground has more rays concentrated in a specific spot. The more intense rays causes the rise in temperature with the side tilted closer. when compared to the same amount of light being spread over a greater distance in the wintertime, its colder, tilting away
what is a comets tail made of? what directon does it alwasy point?
-Is made from particales of dust/ ice
-unlike popular belief, tail isnt showing the direction of comet, as tail always points away from the sun. the tail is just stuff being blown off the comet by the force from the sun
difference between a comet and a meteor
meteor- small, space dust burning up in our atmosphere
comet-Bigger icy object orbiting the sun; the tail always points away from the sun as it travels
difference between precision and accuracy
Accurate means something is correct-
Precise is how specific you are with something-
-i am between 3 and 6 feet tall: accurate because correct, but very wide range/ vague so not precise
-i am 5’9”.3678364: precis because very specific number, but not accurate because i am not 5’9”
-precise and accurate= i am 5’3”.4563
list the planets in order from the sun
mercury,
venus,
earth,
mars,
Jupiter,
saturn,
uranus
neptune
what is net force?
when the sum of all forces acting on an object are more than zero.
we all have gravitational force, and other force like the ground on us or when sitting in a chair affect us at all times; and these forces equal less than zero (negative) so thats why we can stay seated without falling or moving around (the chair pushes back on us to keep us sitting still)
but if another force is applied that causes the sum of all those forces on us to be more than zero, we move. like a push on the shoulder causes the value of your net force to become more than zero. we experience the opposite force back, and maybe move in the direction the push came from. Cause us to accelerate (even if just a little)
vector indicates which force is stronger than the others and determines what direction we will be pushed in/ move
what is vector?
a quantity that has both magnitude (size) and direction- something that is going some way-
-Velocity is a type of vector
shown as the arrow that represents the amount of force (based on length) and directing, based on the direction the arrow is pointing
what is the difference between speed and velocity?
-speed is how fast something is going
-velocity is how fast and in what direction/ has vector
define acceleration-
how quickly you change speed and/or direction; from slowing down or speeding up
sun sets in the- and rises in the-
sets in the west
rises in the east
What is a newton?
a unit of force-
the force required to accelerate a mass- one kilogram by one meter per second squared
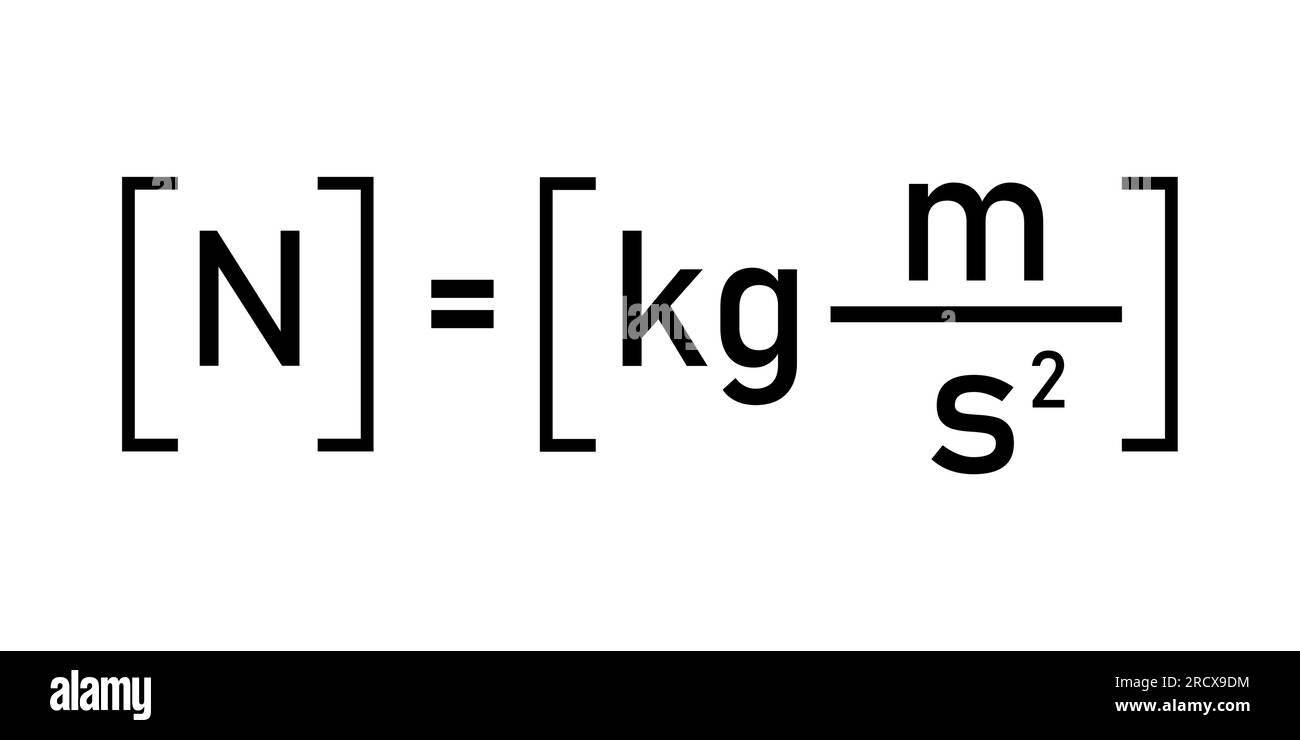
definition of mass,
Mass-how much matter makes up an object; how much it contains
what is the (newtons) universal gravitational constant? (number and explanation)
6.67×10-11 —— unit is N2/Kg2
newtons squared by kg squared
symbol is capital G!
Quantifies the strength of gravity in our universe/ lets us turn the force into a measurable number
differcnce between mass and weight?
Weigh is the force of gravity by something on an object. that’s why you weigh less on the moon. the moon is a smaller mass and therefore has a smaller gravity, so its gravitational force pulls less on you, in comparison to how much the earth pulls on you, making you weigh less
mass is the amount of matter an object contains. like you there were 7×1027 atoms, always make up about that may atoms no matter which planet you’re on. however those atoms do weigh less on the moon because of the moons lighter gravity force
definition of density
Density- how tightly material that makes up an object is packed (a brick is more dense than cotton candy)
definition of volume
volume- how much space an object takes up (car has more volume than a balloon)
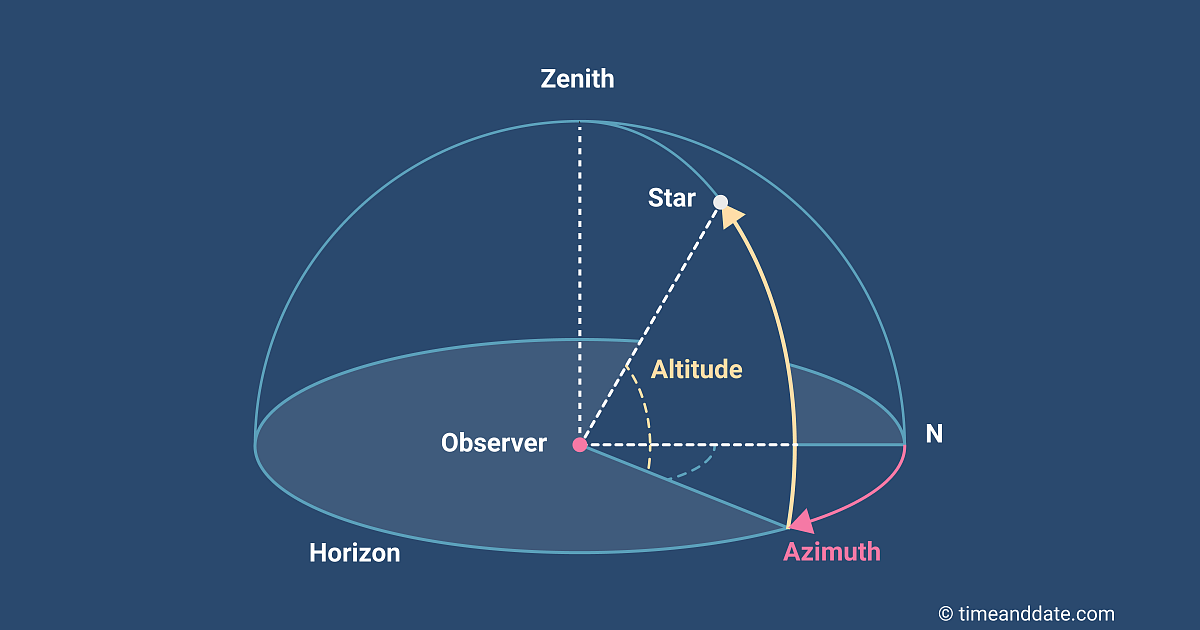
What are the two main systems for locating celestial objects?
Horizonal-local
Equatorial- global
Explain horizonal location system
-Local, depends on specific location to measure objects in sky; uses zenith and north as starting points to move from, as you determine the distance of the starts by measuring the distance from these points.
-To find star’s height/altitude in the sky(horizontal!): use zenith as the starting point directly above you, and measure the angle from the top of the sky to your object to find the height
-To find star’s vertical location in sky/ azimuth: Measure using north direction as starting point, and going clockwise measure the angle/ distance of the star compared to north
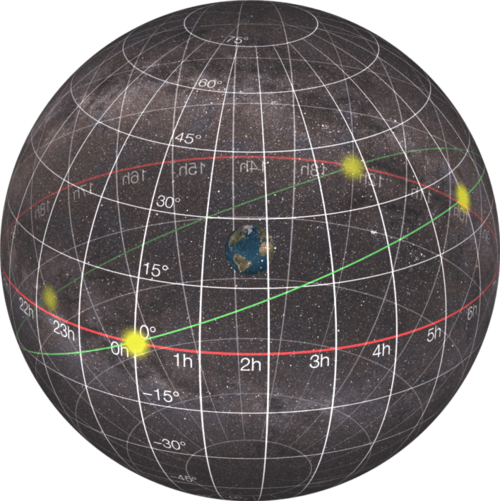
Explain equatorial location system
-The planet is broken up into measurements and lines, with north pole being 90 degrees and south pole being -90 degrees, equator is zero
-use the celestial sphere to mark on the globe directly where the stars meet us, not just how we see it; use coordinates to find
what equation do you use to calculate the force of gravity between two objects
Fg= GMm divided by R2

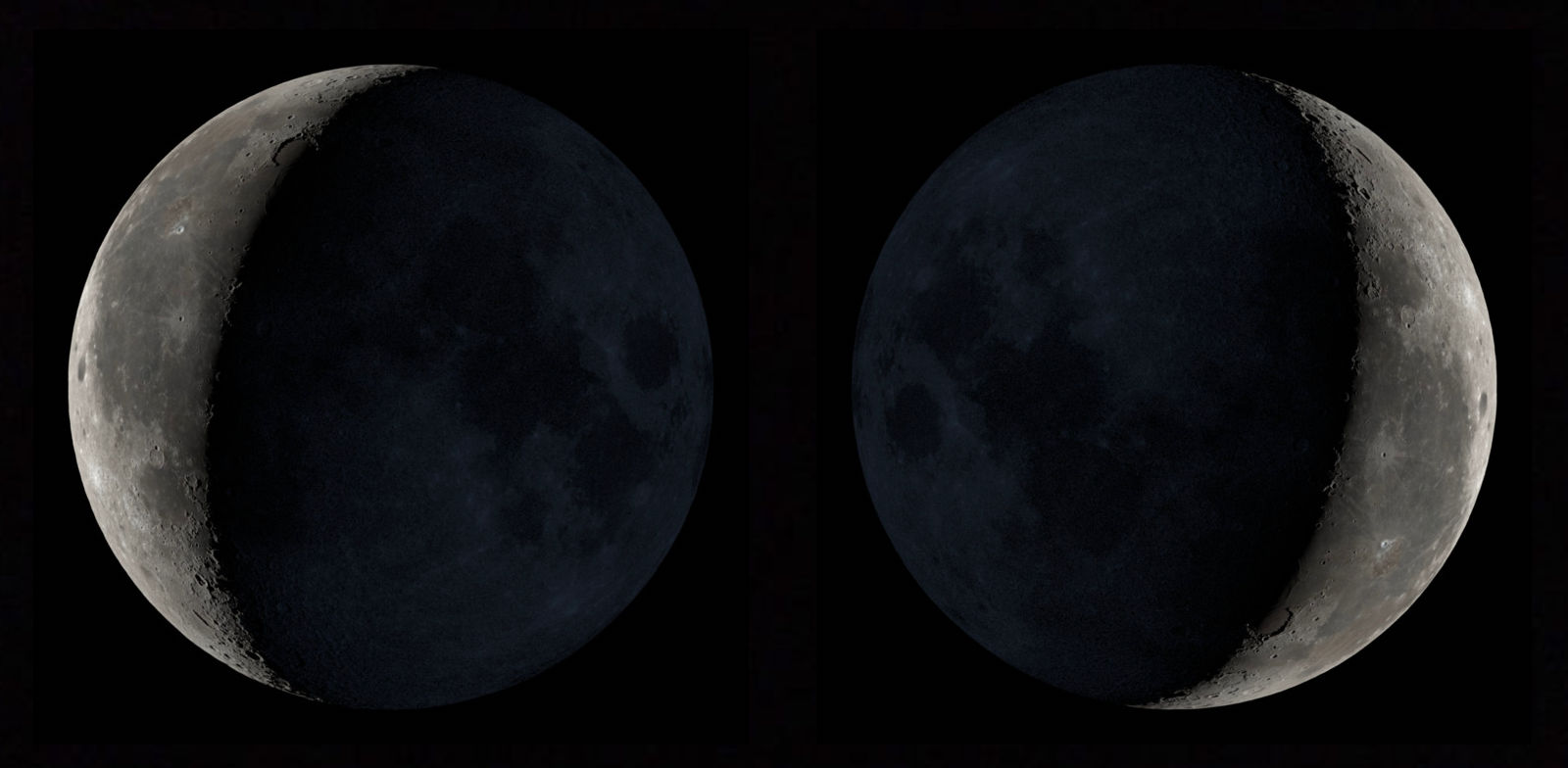
where would you see the moon facing this direction? why?
-From the equator!
-they see our moon “sideways”
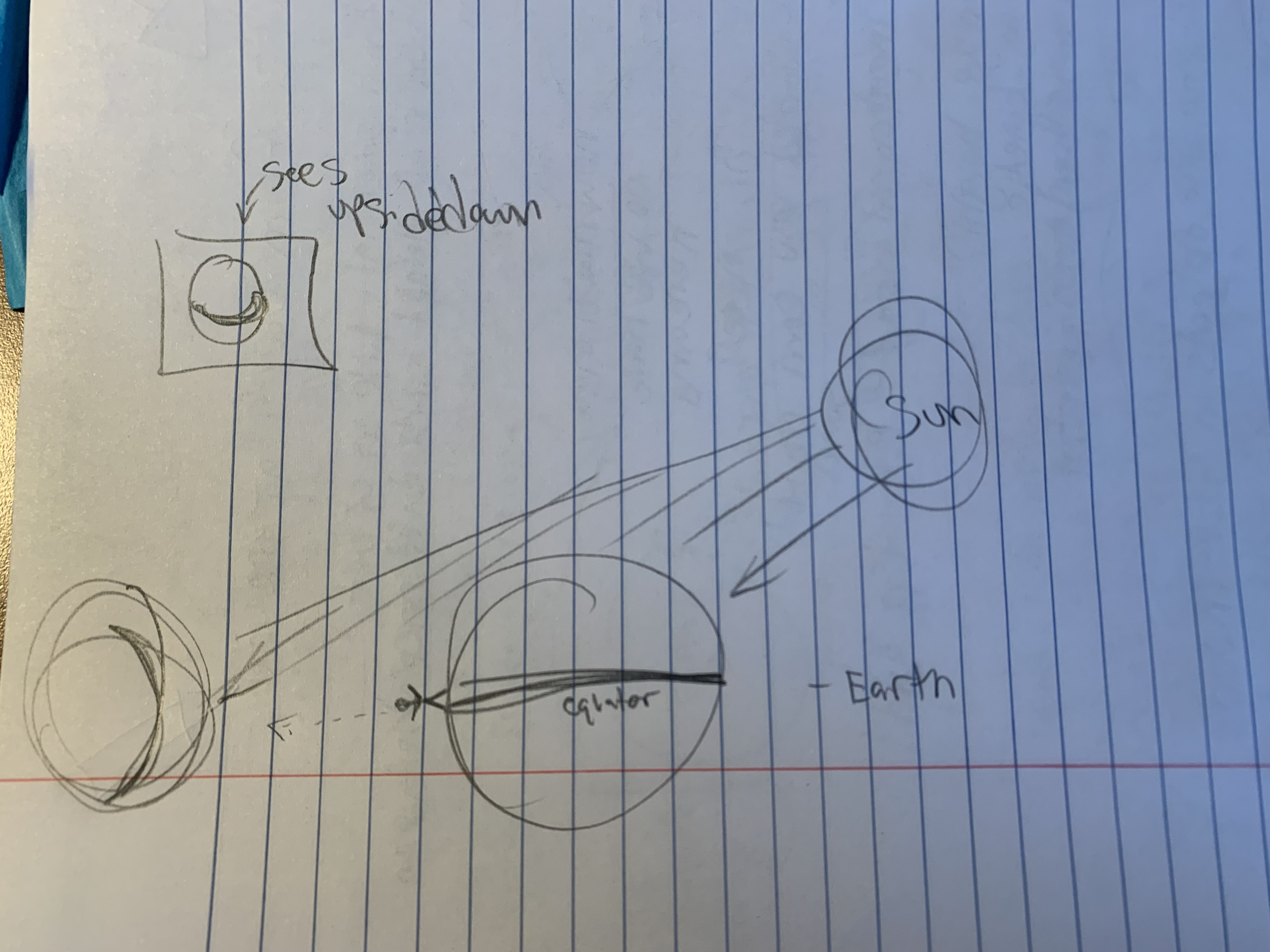

where would you see the moon facing this direction? why?
from northern or southern side
-changes angles so they eventually see the same thing, but it is flipped
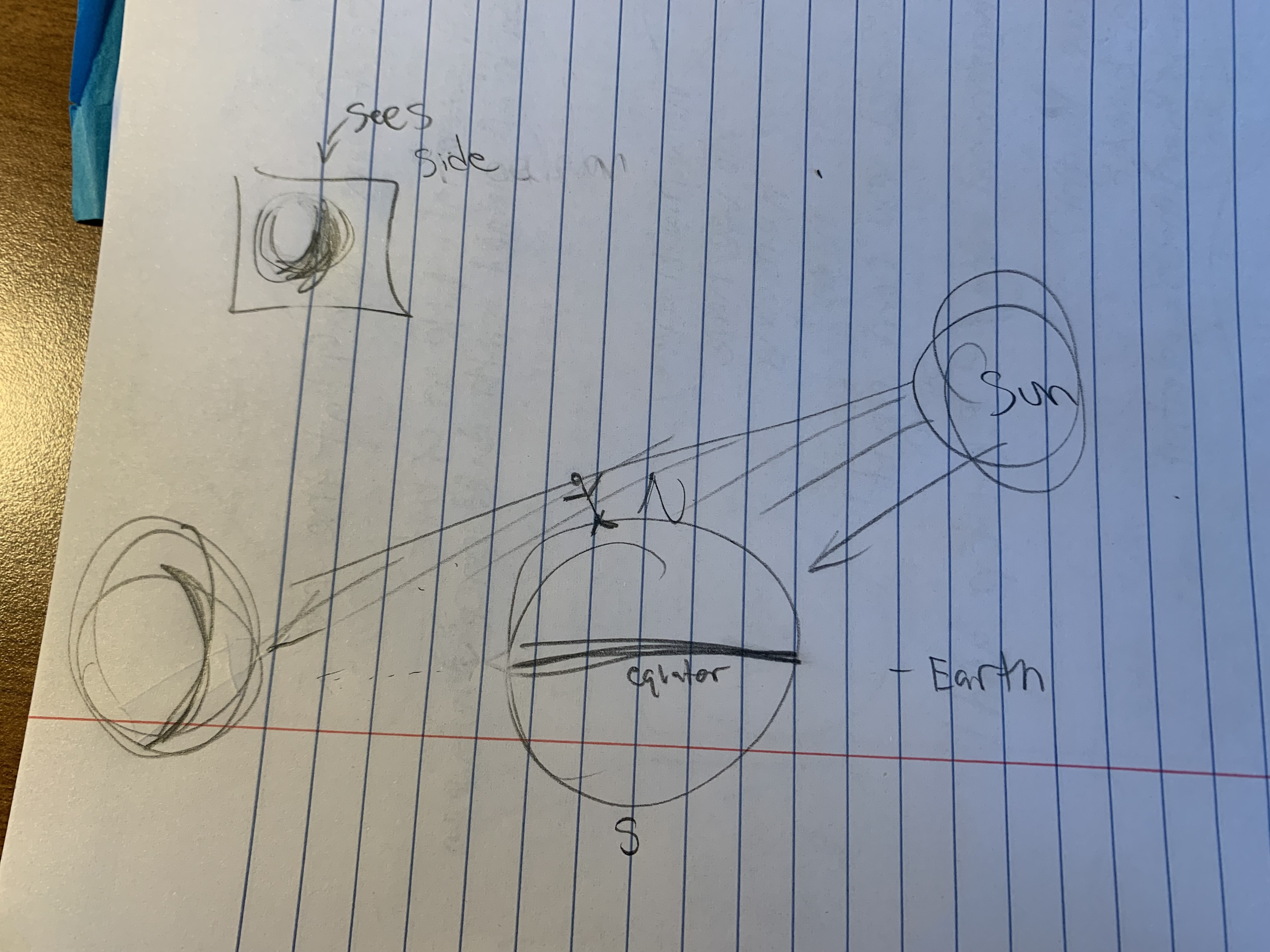
what did we learn in class about place value? explain
look at the units and spot of number; number is irrelevant unless you know units
What is keplers first law?
-planets orbit in ellipses, not circles
-the big object causing the planet to orbit (sun) is at one focus point of two spots within the center of the ellipse
what is keplers second law?
-as a planet are moving around a mass, it sweeps out/ travels equal distances at equal times. even when moving more slowly
-when far away= move slowly, the slice of pie is really narrow but long
-when close by= move really fast, the slice of pie is short and thick
If both examples took the same amount of time to travel, it means their distance/ area is the same
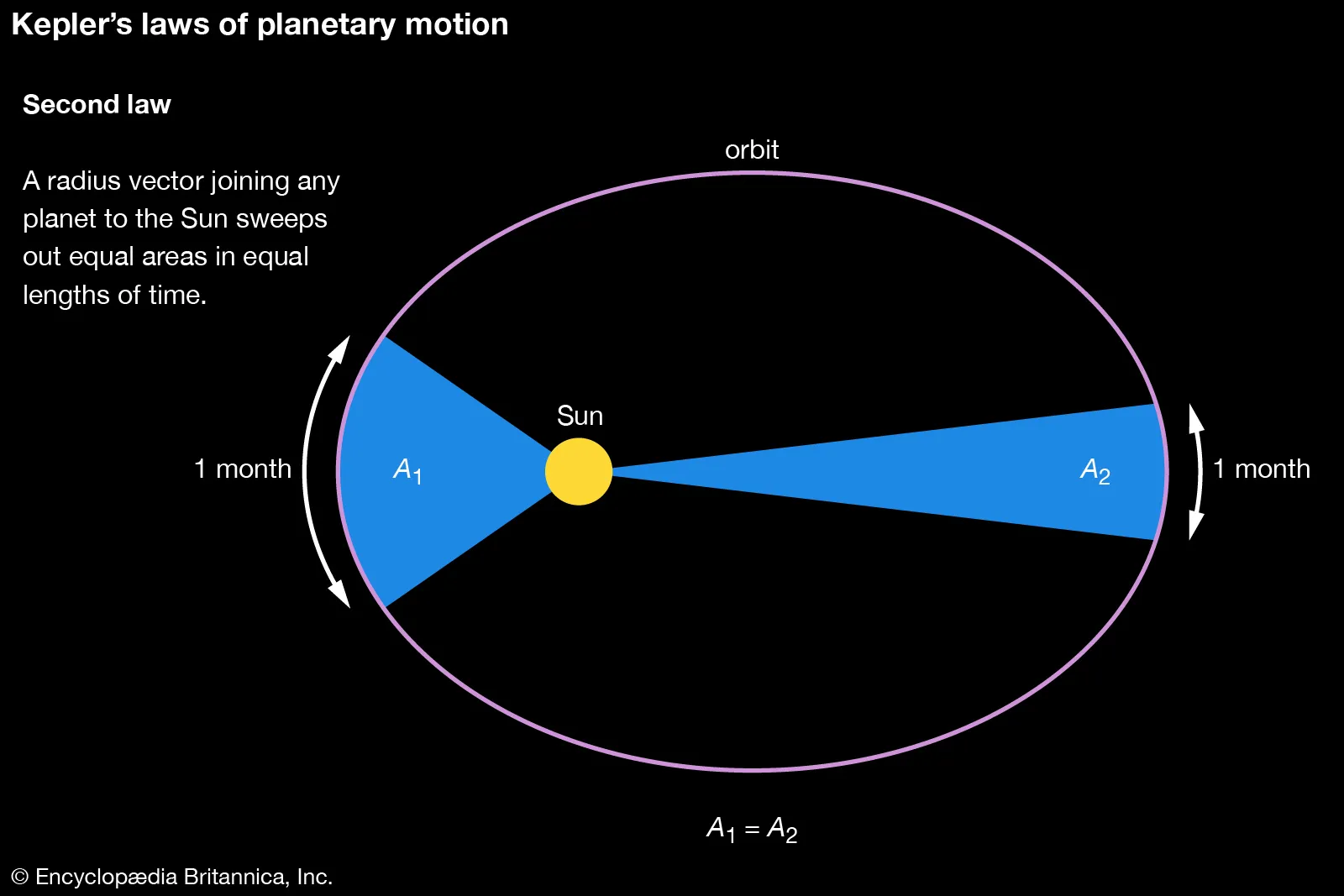
what is keplers third law?
-The period and radii(radius orbit) of a planet are related by the equation T2=a3
-related in earth years
-Time squared equals the semi major axis cubed
-explain newtons addition to keplers law
Newton added M1+M2 to Keplers equation T2=a3
this is not keplers law anymore!
-Addition explains that the equation can be used outside of the solar system as well when they discovered our solar system was a separate thing from the whole universe
-”both bodies orbit their common center of mass, and their total mass (𝑚1+𝑚2) determines the orbital period and distance
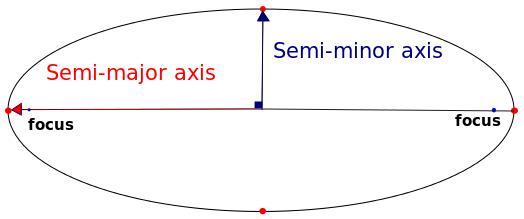
what is an ellipse/ how does it work?
-Planet usually dont orbit in perfect circles, but ellipses. the force of gravity from other objects on something orbiting pulls it in a different direction from the thing being orbited
-there are the two foci (singlular focus) within the ellipse, with the orbitee at one of the two points.
-If an ellipse is circular enough, the foci are both in the center and become one point; if not they make an oval. has major and minor axis
what is momentum?
-A quantity that describes an objects tenancy to keep going or slow down.
-Depends on velocity/ speed, and mass
-The bigger and faster an object the harder it is to stop/ the more momentum it has
what does conservation of angular momentum mean? explain
whatever momentum you have, you keep
-have to loose something to gain something, either speed or mass
-like the ice skater: when their arms are stretched out while spinning they go slower, but when they tuck their arms in they actually loose mass! have less surface area which makes less air friction, and gain more speed= same momentum but different form. a slow moving heavy thing is just as difficult to stop as a fast moving light thing
-When running and crashing into something= loose momentum because of loosing speed
what is the difference between momentum and angular momentum?
Momentum- an objects linear motion
Angular momentum- an objects rotational motion
What is meant with the equation T2=a3?
the equation for kepler’s third law
-depending on which info you have, can help you find a planets semi major axis/ a distance, or the time it takes to orbit once around the sun; measured in earth years
T=time in earth years
a= means axis, or semi major axis/ the distance from the center of the ellipse to the widest part of the ellipse- measured in astronomical units
What are the two main types of energy?
Potential
Kinetic
what are the three things that determine how much potential energy something has?
1-Gravity field/ big mass- more gravity=stronger pull/ falls faster
2-Its mass
3-How far it will fall; how far from the ground it is
-Like if you held a baseball that weighs 150 grams 10 feet above the ground on earth-
=has a lot less potential energy than if you held a bowling ball 20 feet above the ground on bigger planet with a stronger force of gravity
what is the conservation of momentum and angular momentum?
-the total momentum of an isolated system remains constant
-similar to conservation of angular momentum, but angular momentum is special because its just for spinning objects; and explains how things that pull inward as they spin arent changing energy amount but mass
what is meant by eccentricity?
-helps describe the shape of an elliptical
-depending on how close it is to a circle
-circular elliptical is value of 0, while more extreme or oblong elliptical is closer to 1.0 (like a 0.7, or 0.9)
e=foci separation
major axis
how do you find the eccentricity value, or ε?
use equation-
ε=foci separation, divided by the major axis (on equation sheet)
foci separation- how far apart the two main points of the ellipse are; the farther apart the more oblong
major axis- the length of the ellipse hot dog style/ long way; the longer the more oblong
what is uniform circular motion?
-Movement of an object along a circular path
-has change in acceleration because of constant change in direction, but not speed
what does the equation 𝐹𝑛𝑒𝑡=𝑚𝑎 mean?
Newtons 2nd law; when you apply a net force an object will accelerate
-Used to find an object’s net force when you have its mass or acceleration, or the other way around
What do you use the equation 𝑣=√𝐺𝑀/𝑟 for?
-to calculate the orbital speed of an object in a stable circular orbit around a larger mass!
-using the gravitational constant, the mass of the thing being orbited, and the orbital radius (usual distance of altitude and radius of big mass), can find how fast moon is moving around
How do you find an orbital radius? or r
use the altitude provided and then add the radius of the thing creating the gravity
make sure they are in the same units! m or km?
-x or divide 1000/ X103
how do you find the orbital period of something?
use T2=a3 (Kepler third law)
how do you find the semi major axis of something?
use T2=a3
-Orbital periods of planets are listed on the sheet
whats the difference between zero potential energy on earth vs in space?
on earth- zero is the ground/ where ever you make it; a place to fall to
-in space- a place infinitely far away, meaning you always have negative potential energy
what is the equation for escape velocity/ all its parts?
V= velocity, with the small e specifying escape
big G=grav constant/6.67×10-11
Mass= of the big mass- the thing with the gravity
R- distance between objects; to the bigger planets center
2- double than the energy of orbital velocity, what is needed to leave atmosphere and never slow down/ come back!

what is the difference between the orbital velocity and escape velocity equation?
the 2! Escape velocity had a two added
-because the equation without the two is the amount of energy to “stay in orbit”, while doubling that amount of energy is what is needed not not only surpass the gravity but to keep going forever and ever
what is the equation to find potential energy?/ meaning?
E= -GMM /R
Energy: potential=
G-grav constant
Mass1- of puller
Mass2- of thing being pulled
R-big mass radius+ any distance it and the object has
Negative because 0 is very far away! everything negative (to get to escape velocity/ reach zero need to multiply by two to get to zero potential energy)
Copernicus
#6-1473-1543
-Discovered that earth’s axis isnt completely vertical but is tilted on an angle, discovered this tilt and how it affects the intensity of sunlight is the cause of our seasons; and not a large amount of change in distance from the sun
-also proposed an early heliocentric model, but didnt make it known until right before he died to avoid getting into trouble with church (unlike Galileo)
Galileo
9#-1564-1642
-Discovered/ confirmed 4 moons of Jupiter, proving that not everything in the universe has to circle around the earth; going against church
-also phases of venus did not make sense if he imagined it circling us, but made sense with going around the sun
-was put on house arrest for 20 years for his findings because they did not like it
Tycho Brahe
#7-1546-1601
-Designed better/ more precise measuring equipment
-got to build the first large observatory in Christian Europe
Kepler
#8-1571-1630
-created three laws of planetary motion
was tycho brahe’s assistant, continued on work, brahe was scared that he would take all credit
Nancy Grace Roman
-16th- 1925-2018
-first woman to hold an executive position at NASA
-Important for planning and development of hubble space telescope
Kuiper
15#-1905-1973
-suggested the belt of ice material objects past neptune and around our solar system, a lot bigger than asteroid belt
turned out to be true so was named after him- kuiper belt
-explains solar blast/ left over particles that didnt get to be apart of developing planetary embryos
Henrietta Swan Leavitt
-#14-1868-1921
-Discovered more than 2,400 variable stars, which brightness’s change overtime
-created a law connected to pulsating stars, and how their brightness can be used to measure their distance to us and other things; helped us learn that the universe is a lot bigger than we thought
Cassini
#10-1625-1712
-Discovered four of saturns moons
-Discovered the gap in saturns ring; cassini division
Mercury info
1st-
smallest planet and closest to the sun
-rotation is 59 earth days;
Venus info
2nd-
hottest planet! had water, but because of greenhouse gas effect it evaporated and continued to heat up the planet and evaporate more to create a heating cycle
-very high atmosphere pressure!
-spins retrograde, turned upside down rotating very slowly; 243 day rotation
mars info
4th
has largest volcano in solar system, shield volcano Olympus mons, taller than mount Everest but very wide; under hot spot but no moving plate so it just kept growing!
-has lots of evidence of previously having liquid water, but since its gone and mars has no ozone layer to protect life, it couldnt happen
Jupiter info
5th-
largest planet!
-has a giant red storm with fast moving wind!
-closest jovian/ gas planet to the sun
saturn info
6th-
has the most moons
has the most definite/ visible rings
-is the least dense planet (obvious because on the sheet)
-has shortest day/ rotation, 10.5 hours
uranus info
7th-
first of the ice giants
-has 98 degree tilt, rotating on side!
discovered by herschel
neptune info!
8th
furthest from the sun!
-has 40 year long seasons
what are the two types of volcanos?
Shield
stratovolcano
explain shield volcano
-A broad and flat volcano! happens in the middle of a tectonic plate over a hot spot (patch of extra intense heat) that causes the earth to bulge and grow with magma and open up over time.
-as the plate slides along the surface, the hot spot moves over a new spot of ground causing a new volcano/ forms a line of volcanos that marks the movement of the plate

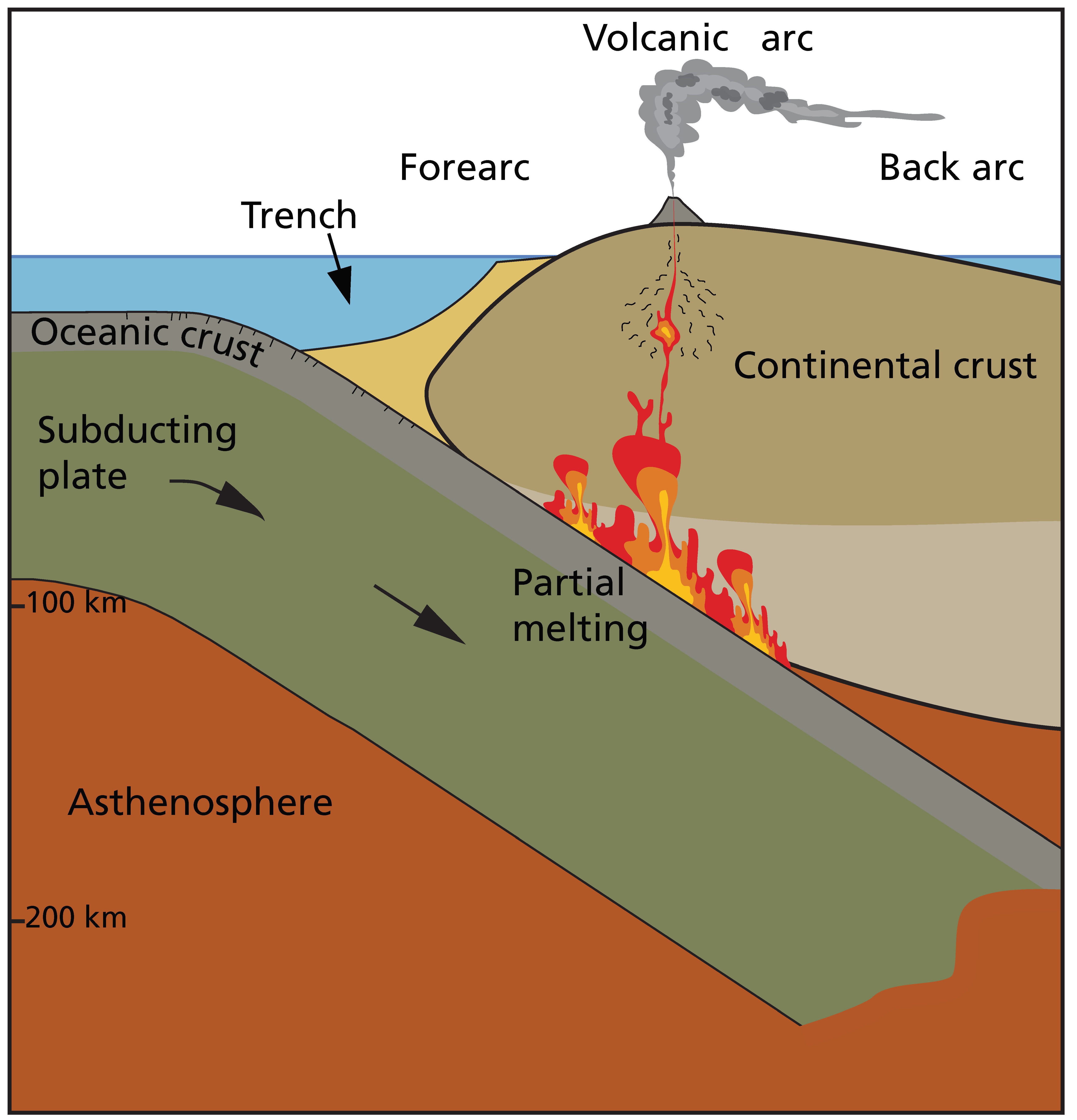
explain strato volcano
-Steep, narrow volcano! results from subduction zone (where two tectonic plates collide) as one dense oceanic plate pushes into the lighter continental plate from the bottom/side and forces the ground up. as lava comes up it also grows that way
-as the oceanic crust pushes down into the manel the friction melts it, which creates gases that rise up out of volcano. magma from underneath comes up and is released as lava
-”stato” means layers, which happen as lava and ash pile up and create distinct layers that form/ grow overtime! :33
-oceanic wants to go underneath because it is more dense and heavy, is usually underwater, and continental plates are higher up
what is the difference between an absolute and a relative date in regards to rocks?
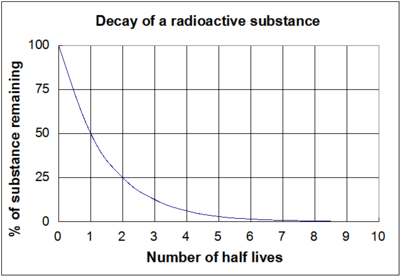
absolute age-A specific numerical age of rock; determined using the half-life chart
relative age- knowing something is younger/ older than something else because of how it is covering or being covered; relative age in relation to other things, not a number
what is an index fossil?
-a fossil that you can tell the very specific age of compared to other fossils!
-Since they are only found in a specific layer/ age of rock and nowhere else and had a short lifespan as a species, we can tell by the age of the rock they are in!
how is a magnetic field created within a planet?
-Liquid, like molten rock/ metal moving around inside the planet
-sometimes if that metal cools, it will harden with a line design that basically creates a giant magnet; so can have small magnetic field without any more moving material
what are the two main types of crusts/ tectonic plates?
oceanic
continental
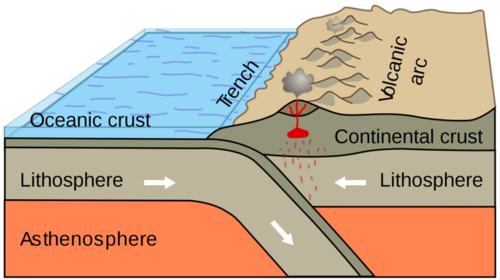
Oceanic tectonic plate info
-the dense, basaltic plates forming Earth's ocean floors,
-thinner but heavier than continental plates, constantly moving,
Continental tectonic plate info
-plates made up of Earth's lithosphere (crust + upper mantle) that carry continents, are thicker and less dense (granitic) than oceanic plates,
-constantly move, floating on the semi-fluid asthenosphere,
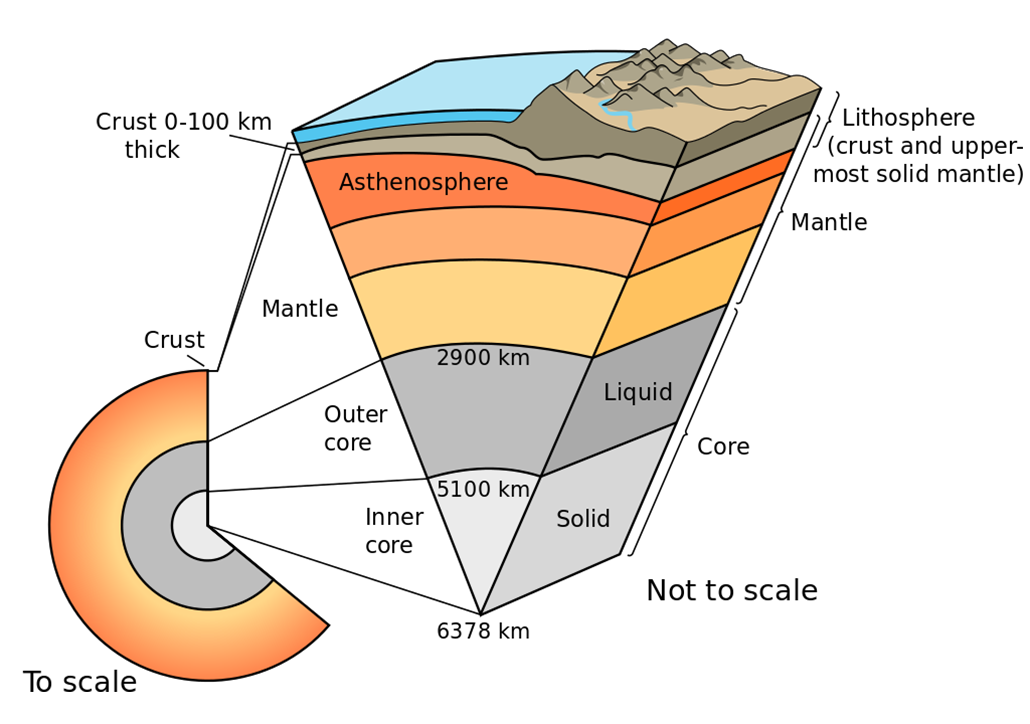
what are the main layers of the earth?
crust-3 to 50km thick
mantel- 2,900km thick
outer core-2,200km thick
inner core-1,300km thick
what is the isotope of an atom?
-The same element that has different number of neutrons
-the number of proton dictates what element it is, so it doesnt matter how many neutrons the atom has. there are just more commonly seen amounts of neutrons for specific atoms
what is the late heavy bombardment era?!!!!!
-the kuiper belt was a lot closer around us, and during solar system development was affected by neptune and jupiter pushed them around, a lot went near earth and other terrestrial planets, and things went into the orbital path of planets
-belt had smallish pieces of debris that could have become small planets, but instead they went crashing into the planets as asteriods
-made a lot of dents in planets and moons, small and big
what is a maria?
-A big flat section on a celestial object caused by getting hit really hard. lava flows out like a wound and eventually cools and hardens and leaves a flat mark on the surface.

what is beta decay
-A weak nuclear force causes radioactivity, can cause a proton to turn into a neutron and a neutron to a proton, which leads to the change of an element overtime
-Acts very slowly
draw a half-life chart!! :33
huzzah!
first draw the two lines, with number of half lives at the bottom and the percentage/ amount of stuff remaining on the side. then draw the round line
Herschel info!
#13-
-discovered uranus!
-Experimented with light prism and discovered infrared radiation; used for looking at things in space and seeing past dust ext
Huygens info
#11-
-Discovered/ accurately described saturns rings
-accurately estimated the length of a day on mars