The Cell Cycle, Mitosis, Meiosis
1/85
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
cell division
creates new cells (1—> 2)
asexual reproduction
creating genetically identical offspring
why is asexual reproduction good but bad as well
quick
problematic with a constantly changing environment
sexual reproduction
creating genetically diverse offspring
binary fission
a type of asexual reproduction
used by many bacteria
creates 2 daughter cells from 1 parent
chromatin
loosely wound DNA (scribbles)
chromosome
tightly wound DNA (half of X)
what is the DNA in a chromosome wrapped around
histone proteins
sister chromation
duplicated chromosome held together at centromere (X)
interphase
all of the cell cycle except M
mitosis
nuclear division that maintains chromosome number
how many chromosomes per human
46
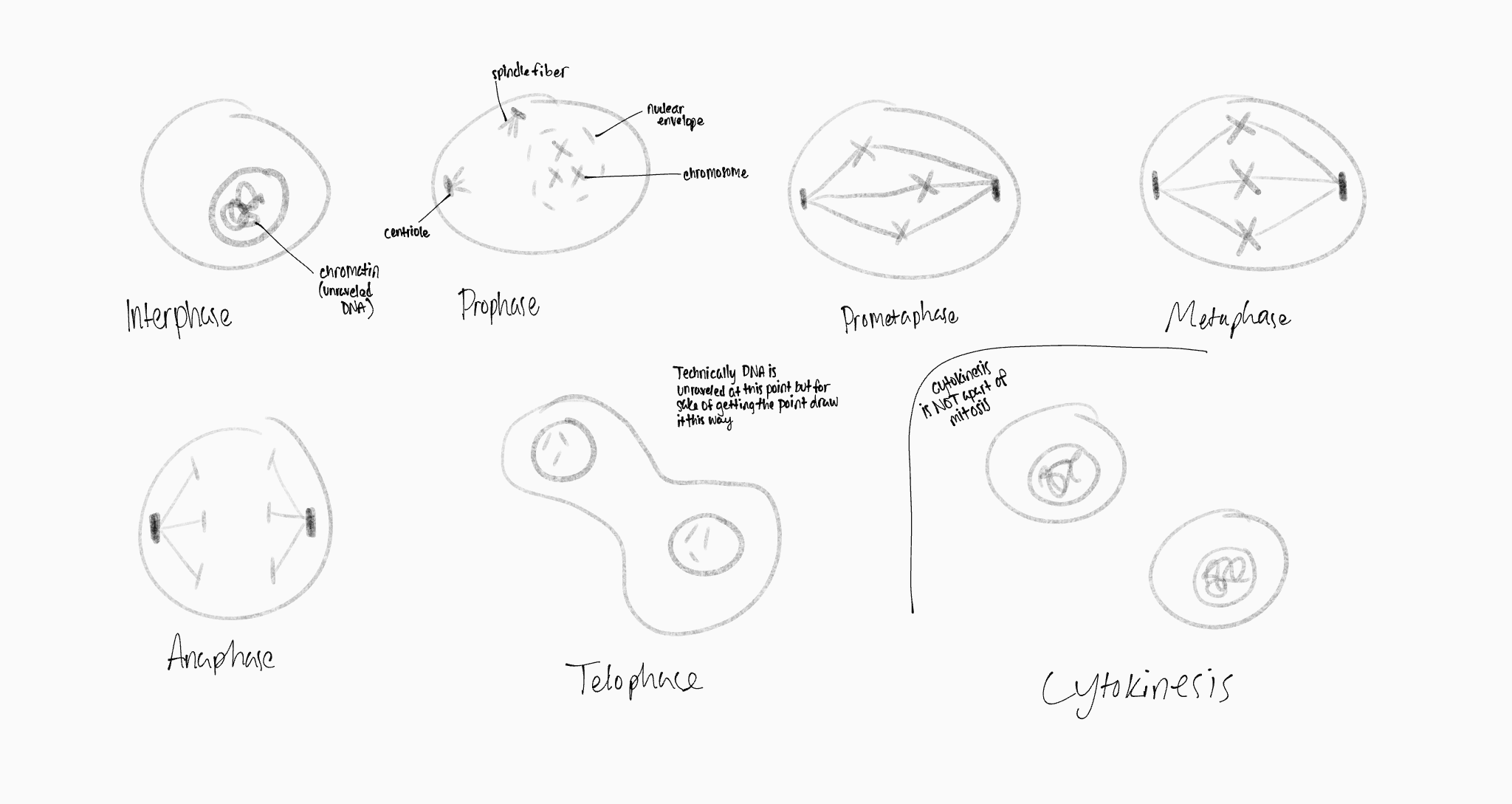
what are the 5 phases of mitosis
prophase
prometaphase
metaphase
anaphase
telophase
what happens in prophase
nucleolus disappears
chromatin condense into chromosomes
separation of centrosomes(centrioles)
formation of spindle fibers
what happens in prometaphase
nuclear envelope disassembles
spindle fibers (microtubules) attach to chromosomes
what happens in metaphase
chromosomes align on the metaphase plane (middle)
what happens in anaphase
chromatids separate towards opposite poles
what happens in telophase
new nuclear envelope forms'
chromosomes unfold back into chromatin
nucleoli reappear
cell continues to enlongate
what is cytokinesis
occurs after mitosis
doesn’t happen to all cells
daughter cells divide
how do plant cells do cell division
form a new cell wall from cell plate
how is a cell plate formed
with vesicles that are lined up
how do animal cells do cell division
they pinch
how do animal cells pinch
they have a cleavage furrow with is a contracting ring of microfilements
what is cancer
uncontrolled cell division
what is a mass of cells called
a tumor
what do most cells need to divide
growth factor (proteins and signals tell them to divide)
why are checkpoints important
to make sure cells are good and correct so they don’t replicate bad cells
what happens if a cell fails a checkpoint
G0 —> try to fix cell—> can’t fix them destroy cell
what is it called whena cell destroys itslef
apoptosis
why is apoptosis good
it prevents cancer and only affects the 1 cell (not like all cells getting damaged)
what do cancer cells do at checkpoints
ignore them
what are the stages of cancer and what do they mean
1- small mass
2- spread in the same area
3+4- spread to other parts of the body
what us it called when cells spread to other parts of the body
metastasis
ploidy
number of sets of chromosomes (not how many chromosomes we have)
haploid
1 set of chromosomes
diploid
2 sets of chromosomes
humans are diploid or haploid
diploid we have 46 chromosomes in 2 sets 1 set from mom and 1 from dad (23 from each)
what is the 23 set of our chromosomes
the sex chromosomes
for every single type of chromosome we have how many sets
2
one of the set of 2 chromosomes is from mom and one from dad
mitosis drawing
Meiosis definition
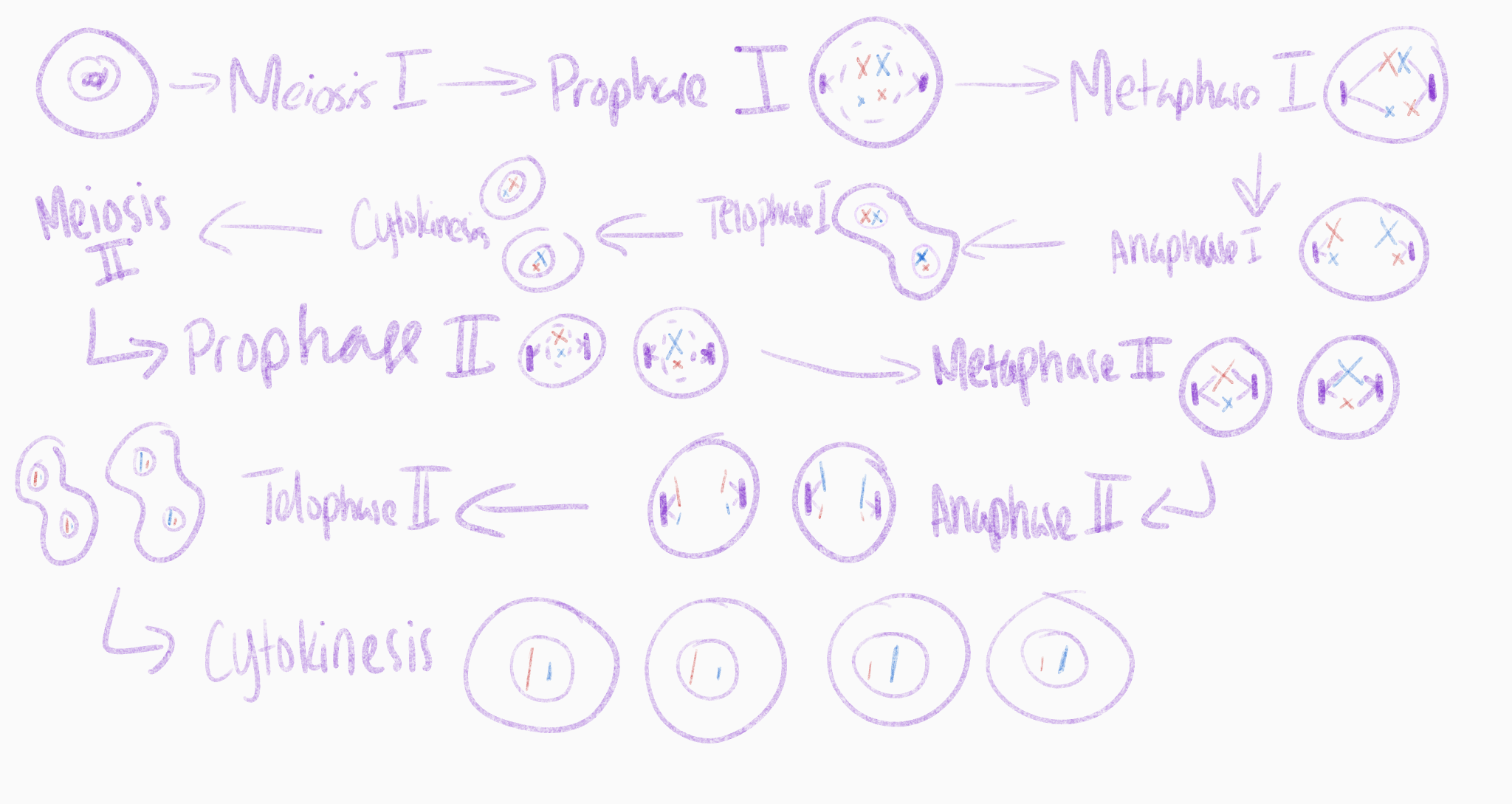
nuclear division that halves chromosome number
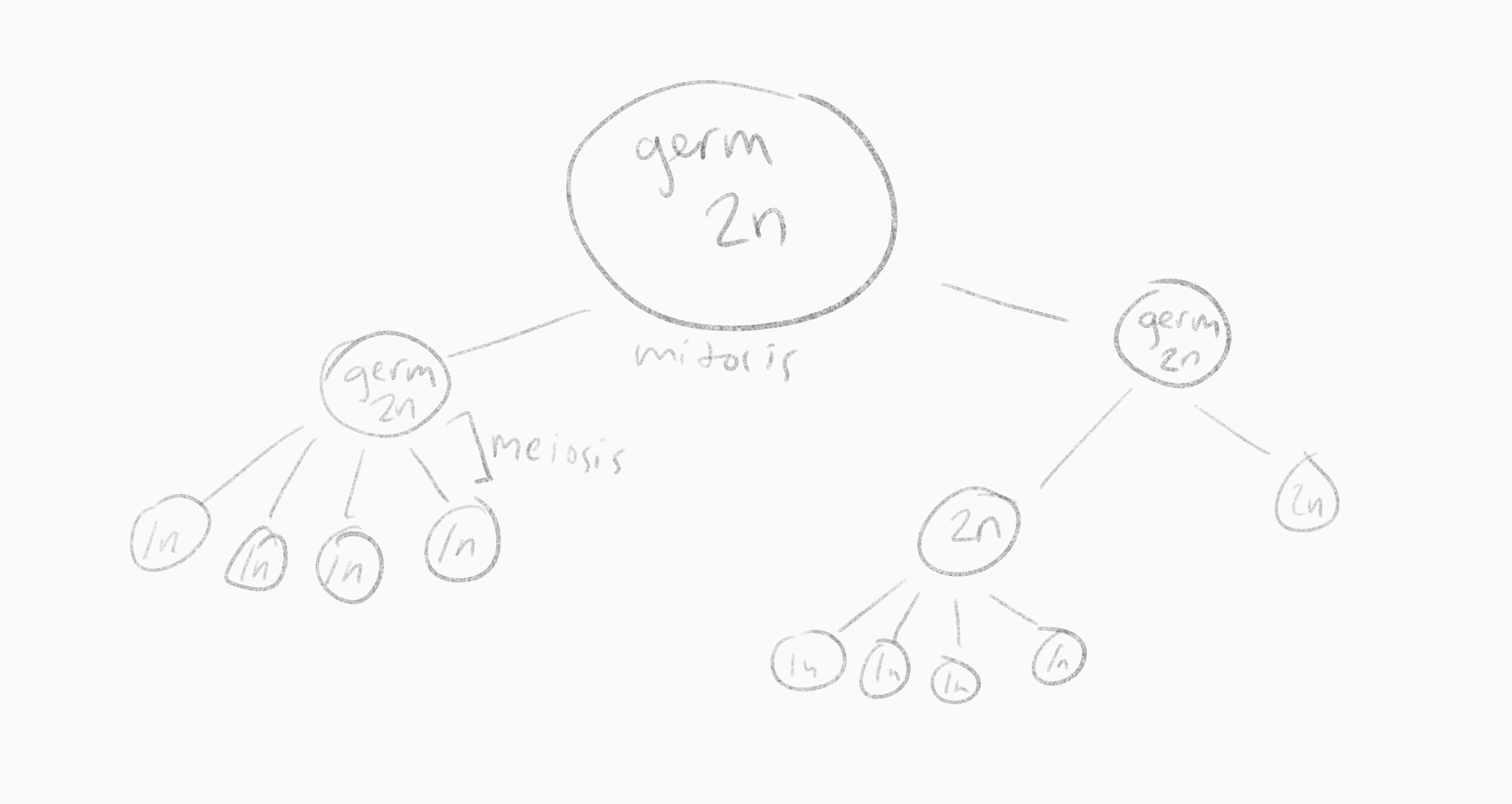
What is the result cell wise of meiosis
it creates 4 haploid cells from 1 diploid cell
haploid shorthand
1n
diploid shorthand
2n
what kind of cells come from meiosis
gametes (sperm and eggs)
what kind of cells are the first cells in meiosis
germ cells
what are germ cells
they are in ovaries and testes and are supposed to make sperm and egg
why don't germ cells just immediately split into four cells
we would run out of germ cells
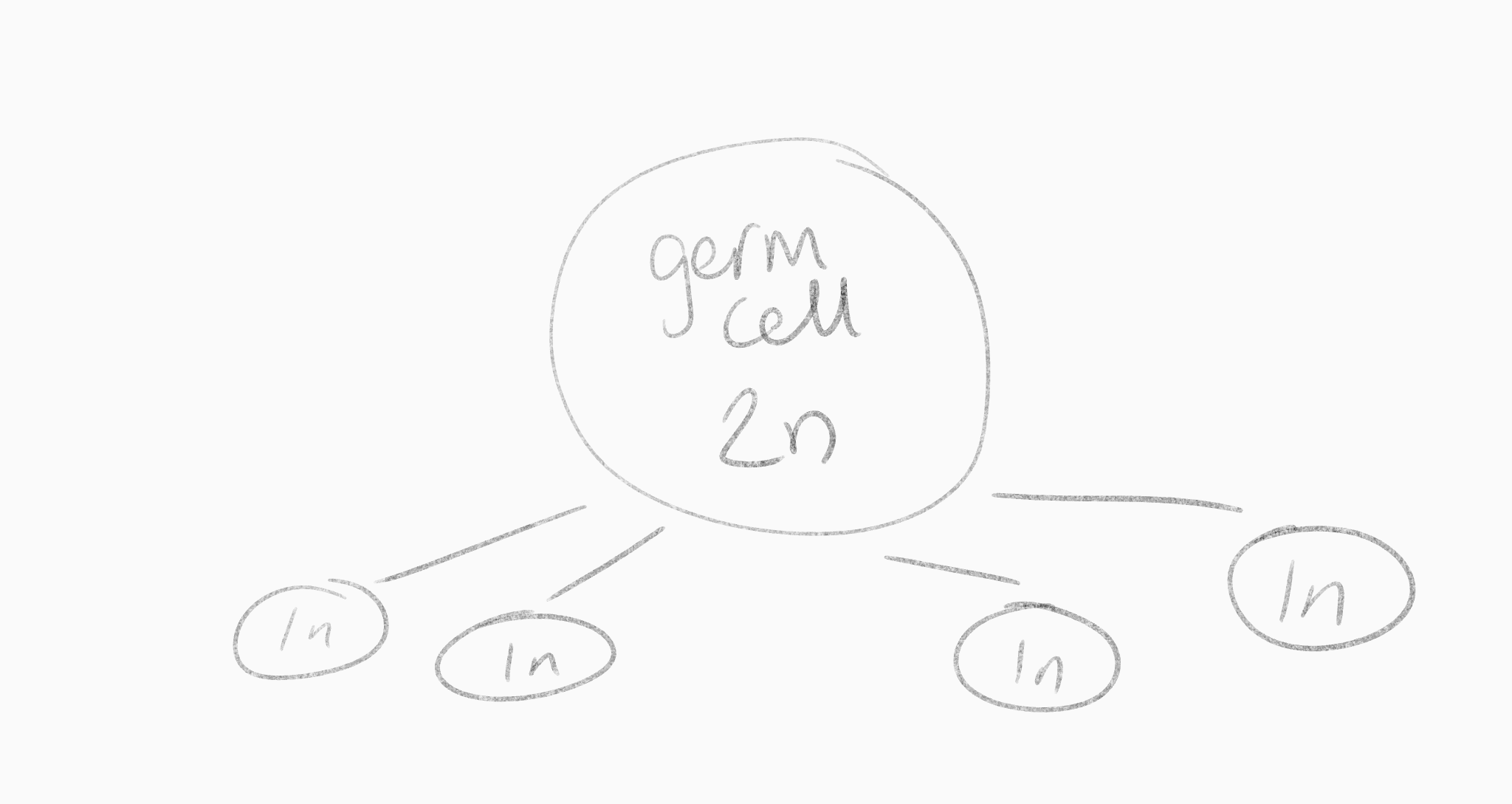
What do the cells do instead to preserve a germ cell
they preform mitosis (which remember preserves chromosome number)
meiosis drawing
what are the 3 ways meiosis increases genetic diversity
independent assortment, crossing over/genetic recombination, random fertilization
what is independent assortment
how they line up all ways are equally likely because it is random
when does independent assortment occur
metaphase 1
what does the diploid shorthand (2^n) mean/determine
n = sets of chromosomes (for example humans have 23)
so 2^n helps determine the number of different combinations or orders of chromosomes
(humans 2²3 = 8,000,000)
what is crossing over/ genetic recombination
when the 2 chromosomes cross over each other and swap some genes
when does crossing over occur
during Prophase 1
when crossing over what has to match for them to be able to cross over
their number (a 1 to a 1, 2 to a 2, etc)
the area that swaps on a chromosome is called
chiasma
what is random fertalization
sperm and egg are random, random sperm fertilizes random egg
what is nondisjunction
when chromosomes don’t separate correctly
how can nondisjunction occur in meiosis 1
this can happen because of the failure of a pair of homologous chromosomes to separate during meiosis 1 (an entire tetrad moves to one side)
how can nondisjunction occur in meiosis 2
the failure of sister chromatids to separate during meiosis 2
what is affected if the mistake occurs in meiosis 1
it will affect all four gametes (sperm or egg)
what is affected of the mistake occurs in meiosis 2
only 2 gametes will be affected
what is a karyotype
a picture of someones chromosomes (a photographic inventory of an individual’s chromosomes)
what are a males sex chromosomes
XY (y is a lot smaller in general)
what are a females sex chromosomes
XX
whta is it called when there is an extra copy of chromosomes 21
down syndrome (trisomy 21)
what is a survival rate of trisomy 21
it is high
do other chromosome number differences usually survive
no
is this a mutation
no a mutation is a change in DNA
what is the biggest risk factor for having a child with trisomy 21
a woman’s age
why is a woman’s age a big risk factor
nondisjunction increases as you age
what is the affect of an abnormal number of sex chromosomes
not usually any affects
doesn’t usually affect survival
but could
health issues sometimes come with what chromosomes (what may be the issue and name)
XXY
Klinefelter syndrome (male)
sterile
usually normal with what chromosomes
XXX (maybe slightly taller than average)
what are autosomes
chromosomes that aren’t the sex chromosomes
what is turner syndrome and what are the symptoms
when only one X chromosome is received (X0)
female
sterile
what is a somatic cell
a cell that is not a gamete, germ , etc cell
what is the cell cycle
G1
S
G2
M
what occurs in G1
growth
what occurs in S
DNA replication
what occurs in G2
growth and prep for mitosis
what is M
mitosis
do cells that do meiosis do the cell cycle
kinda they grow, and they replicate their DNA in the first stage of meiosis
when meiosis 1 is finished what are the 2 cells that are made
haploid