Weathering and Soil
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
weathering
wearing away of rocks into smaller pieces
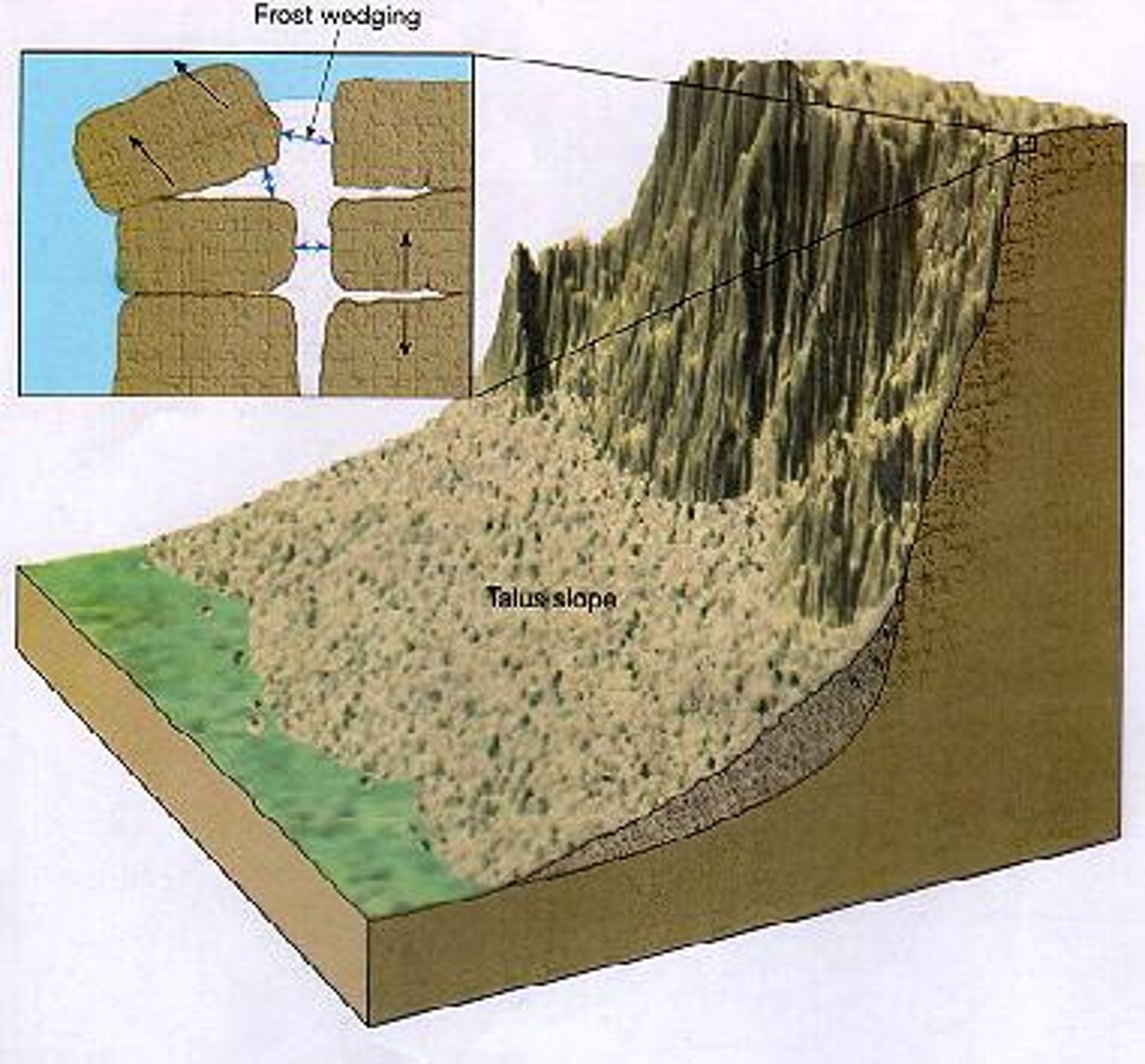
physical weathering
the mechanical breakdown of rocks and minerals
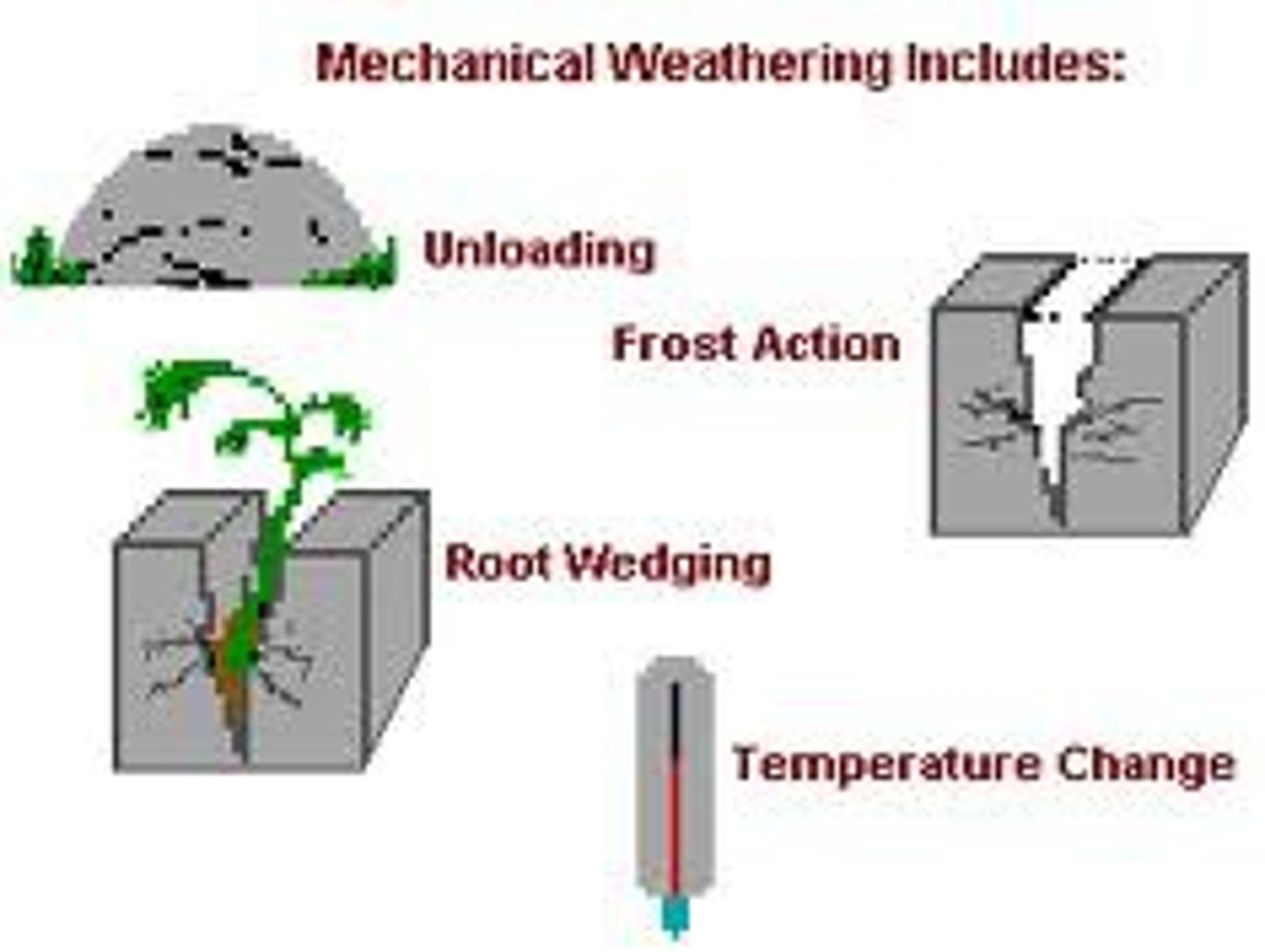
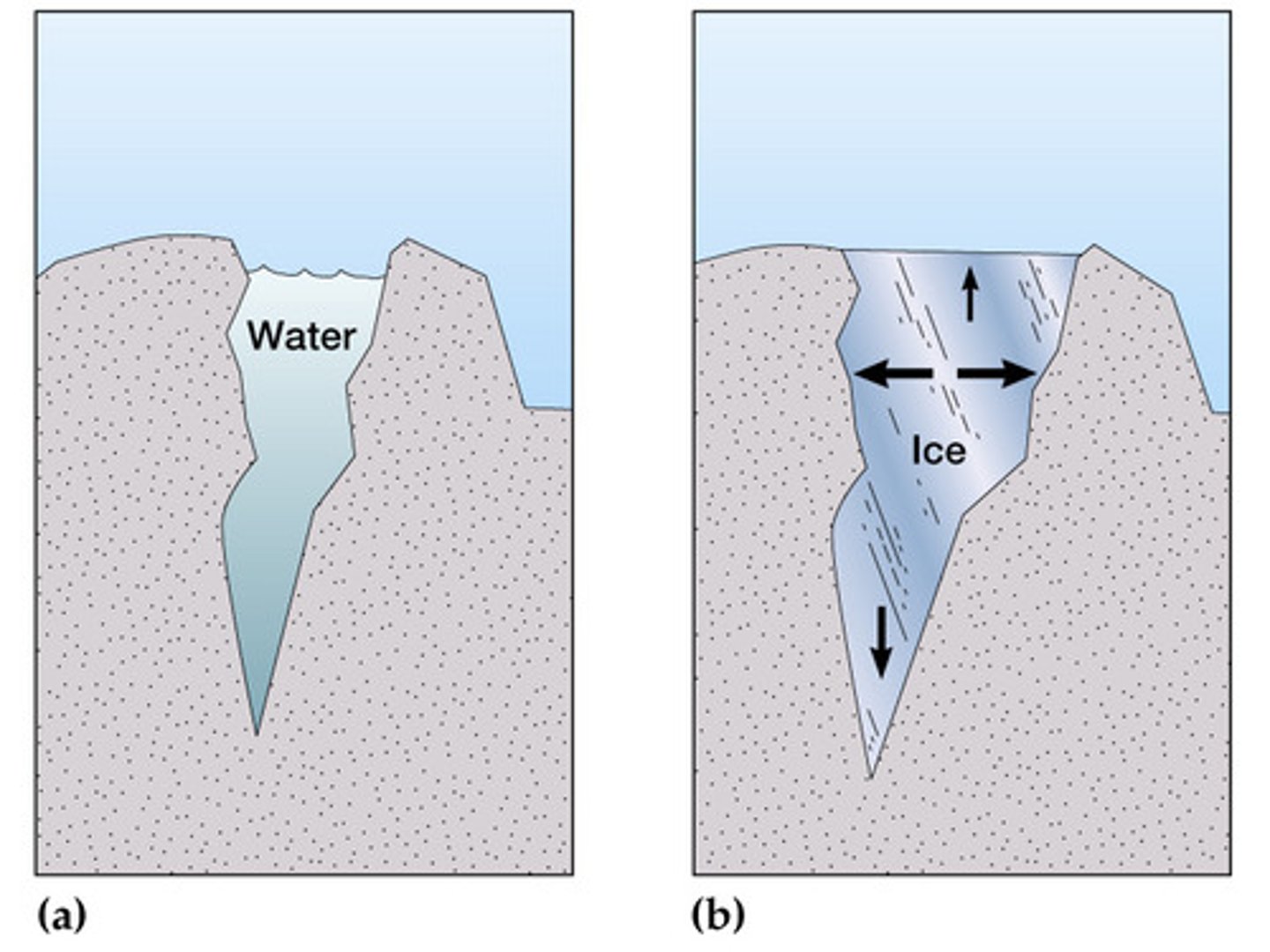
frost action
the weathering of rock by repeated freezing and melting of water
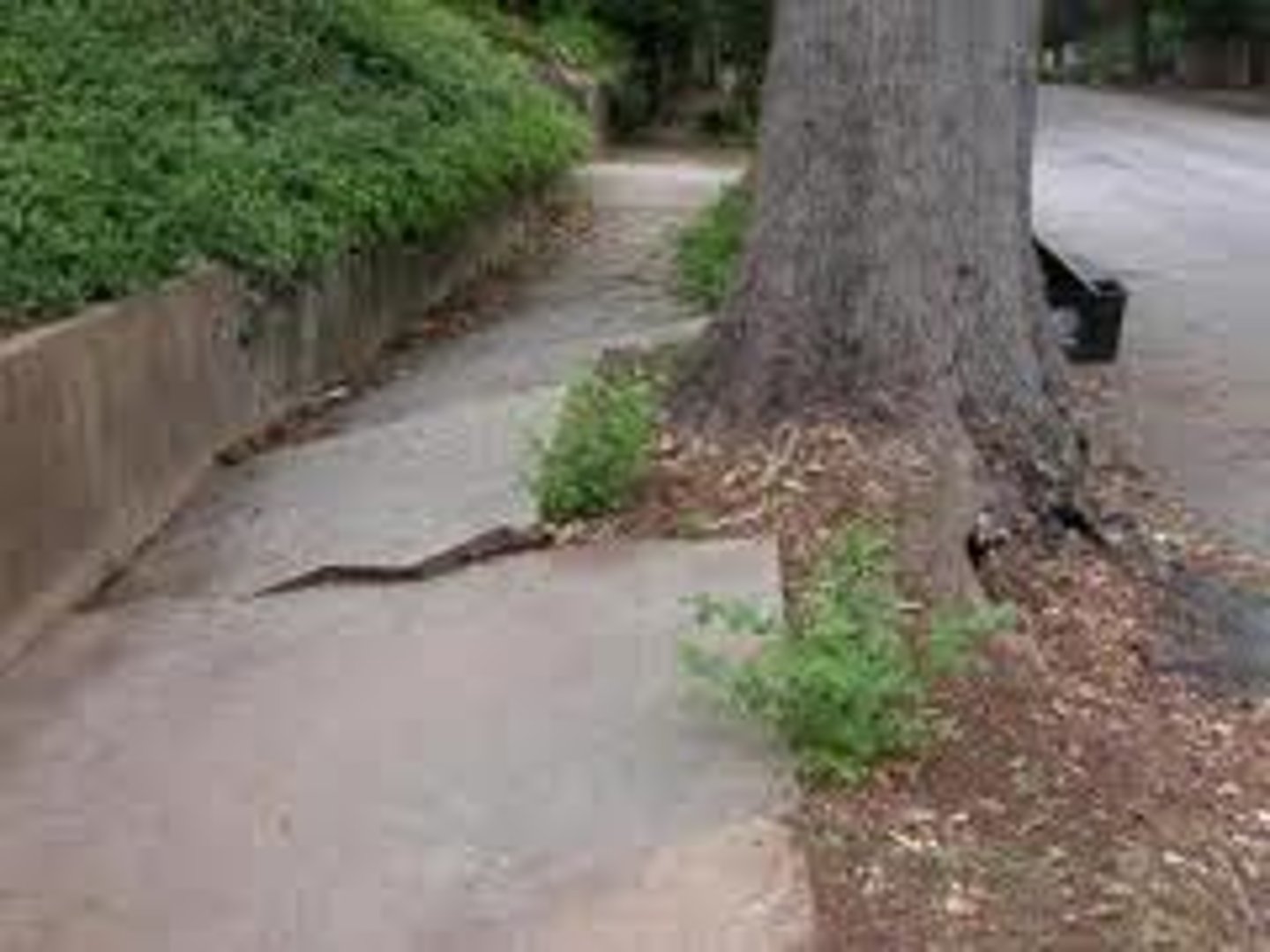
root wedging
when the roots of plants grow and search for minerals and water in rock fractures, exerting pressure on the rocks and driving them apart

abrasion
The grinding away of rock by other rock particles carried in water, ice, or wind
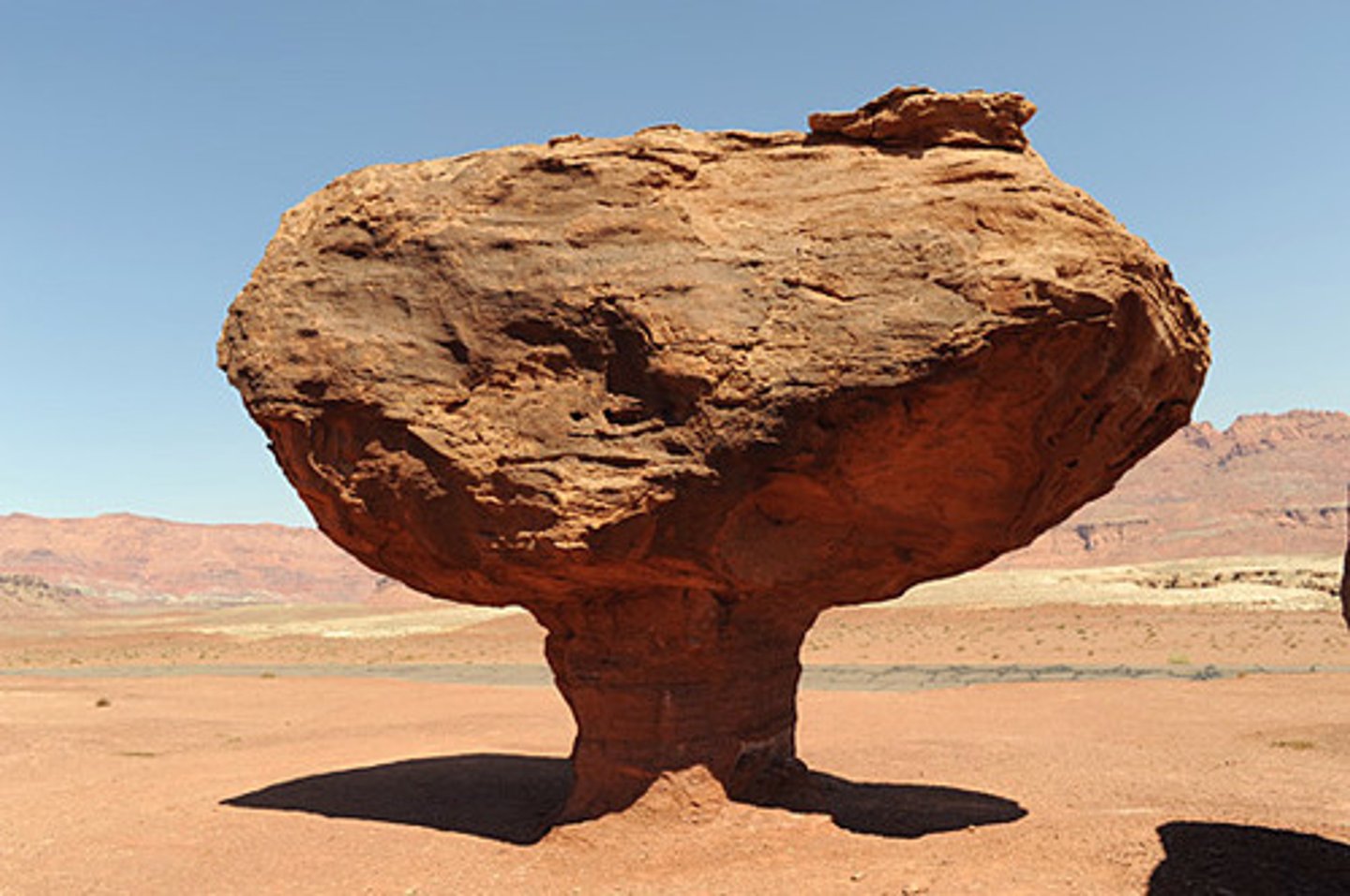

oxidation
A chemical change in which a substance combines with oxygen, as when iron oxidizes, forming rust
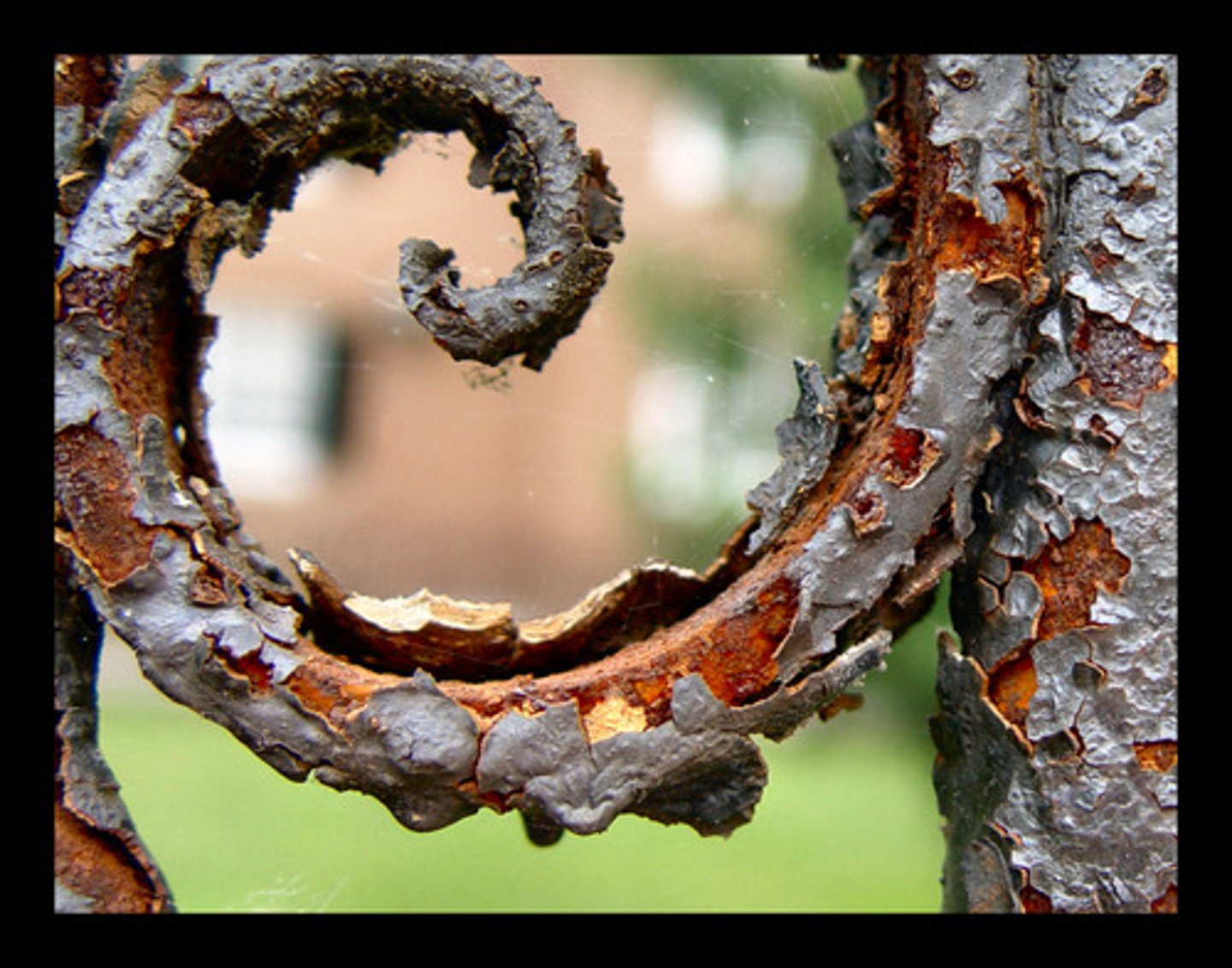

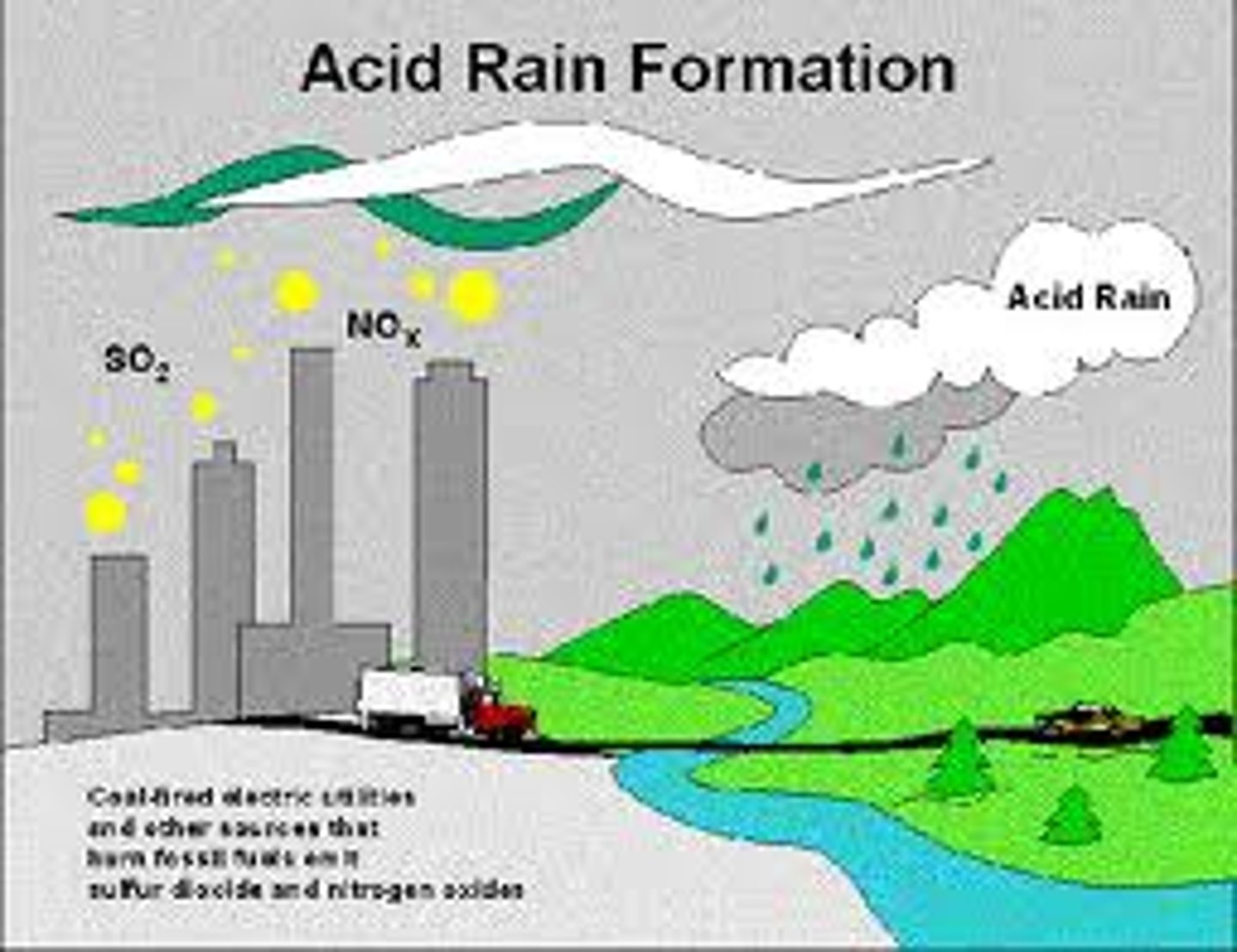
acid rain
Rain containing acids that form in the atmosphere when industrial gas emissions (especially sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides) combine with water.
Hydrolysis
Breaking down complex molecules by the chemical addition of water

soil horizon
The layer of soil that differs in color and texture from the layers above or below it.
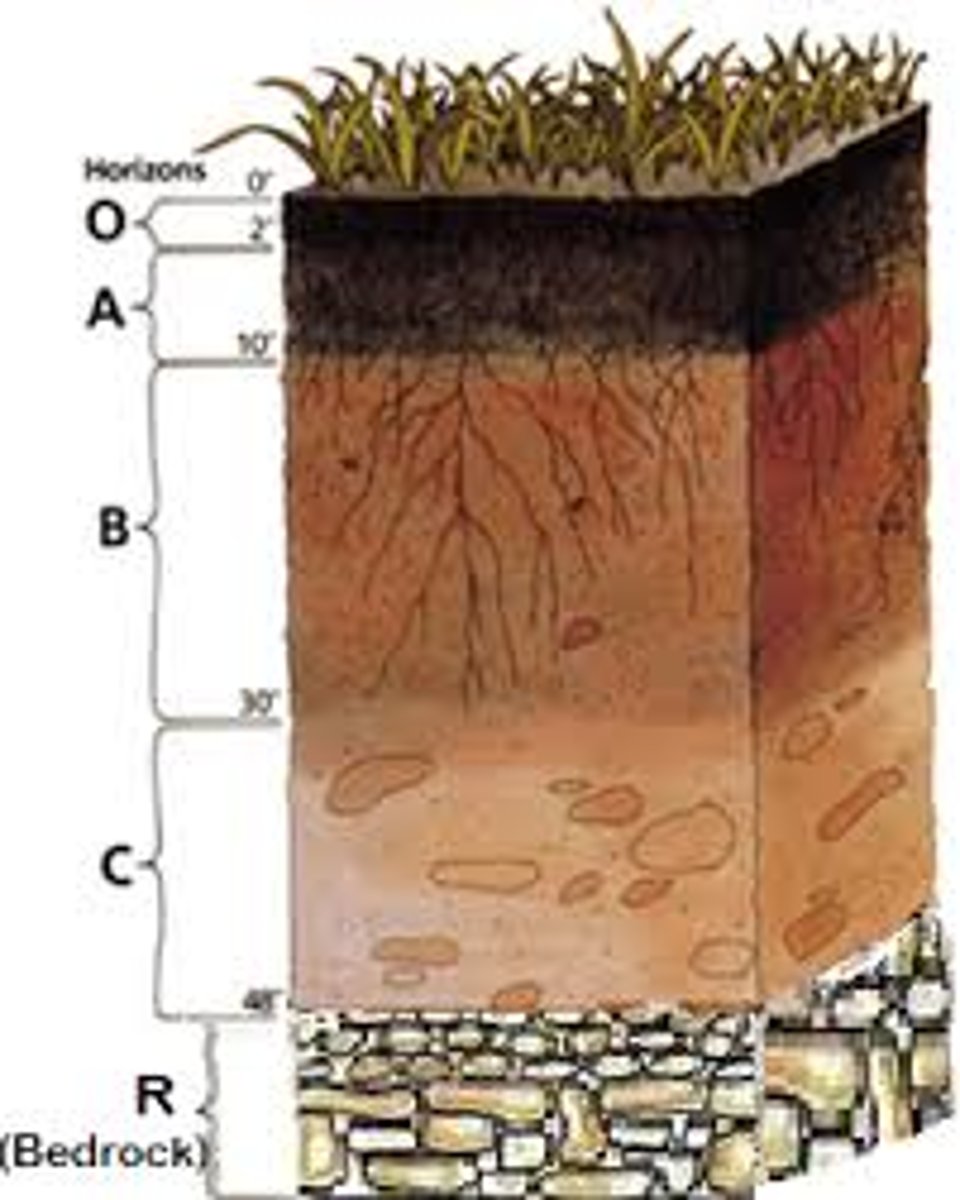
soil profile
All the vertical layers or horizons that make up a soil in a particular place
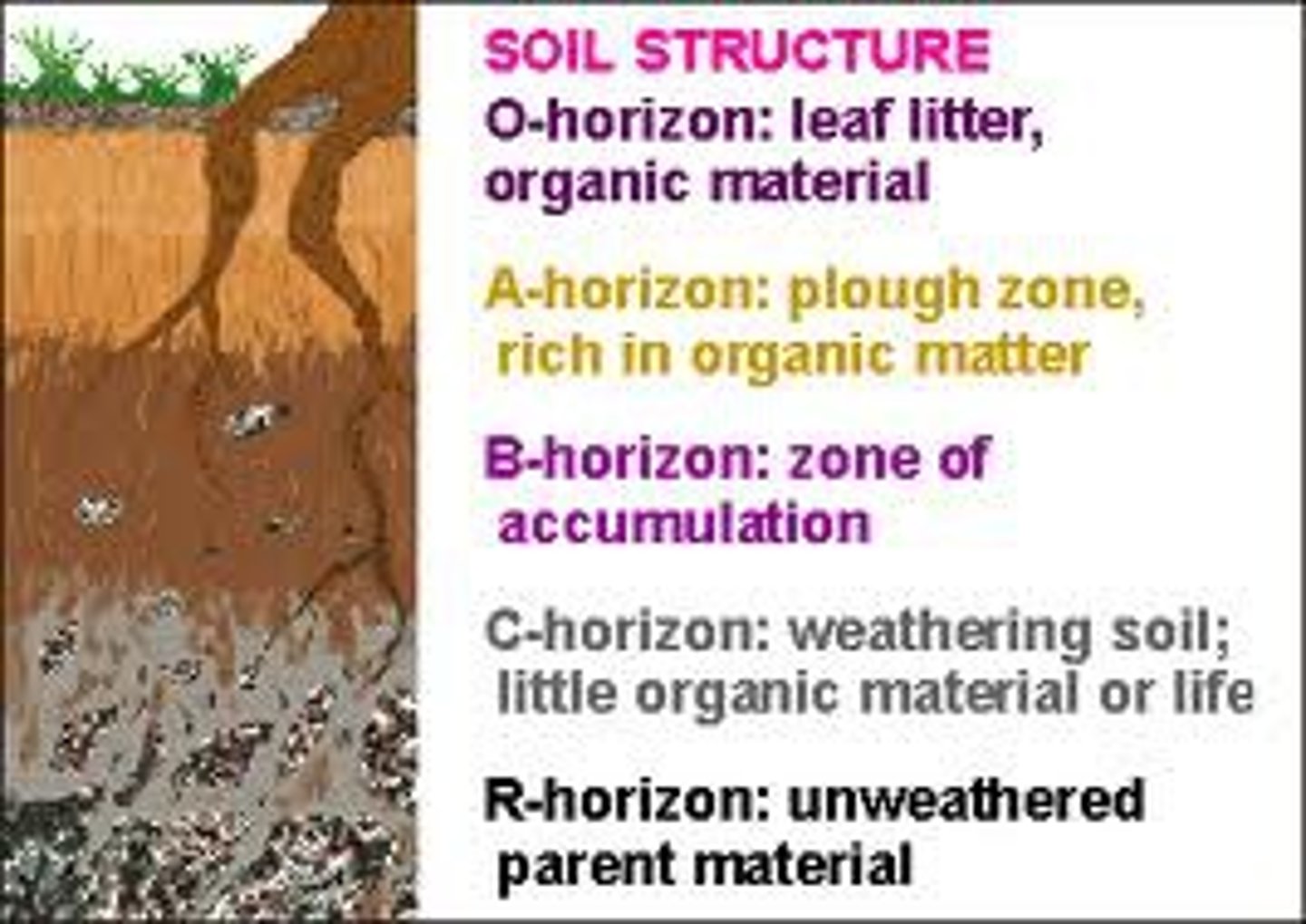
A-horizon
topsoil
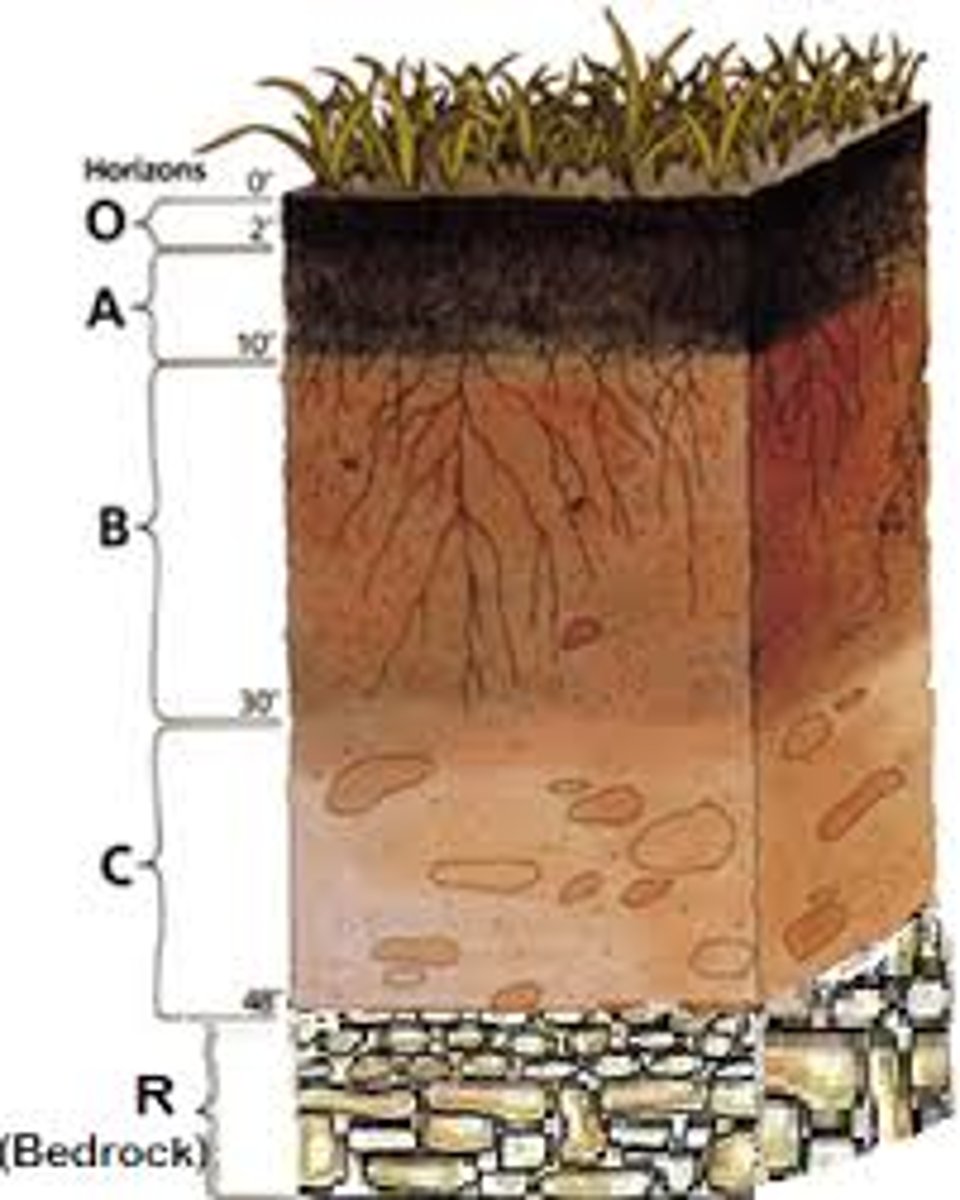
B-horizon
A soil horizon composed primarily of mineral material with very little organic matter
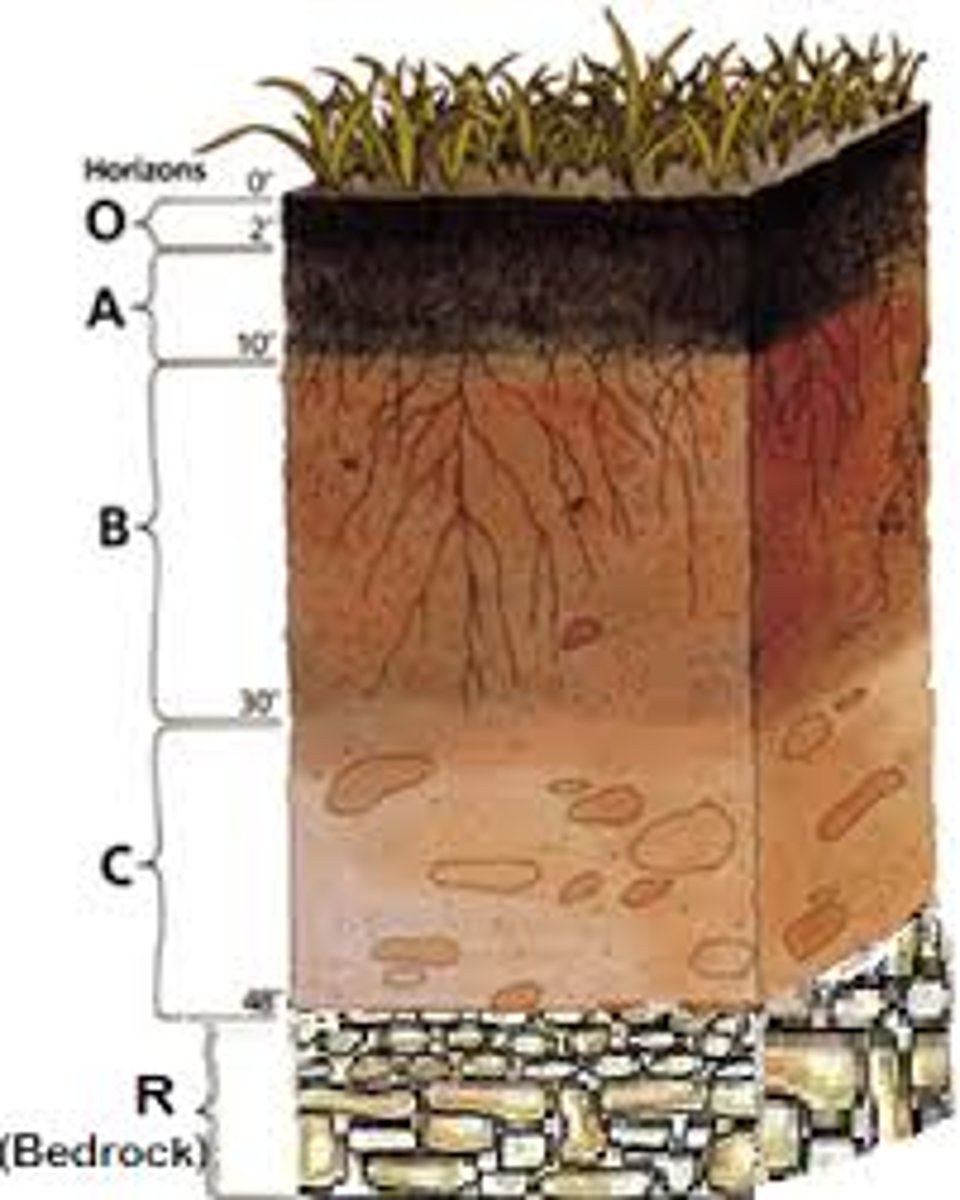
C-horizon
The least-weathered soil horizon, which always occurs beneath the B horizon and is similar to the parent material.
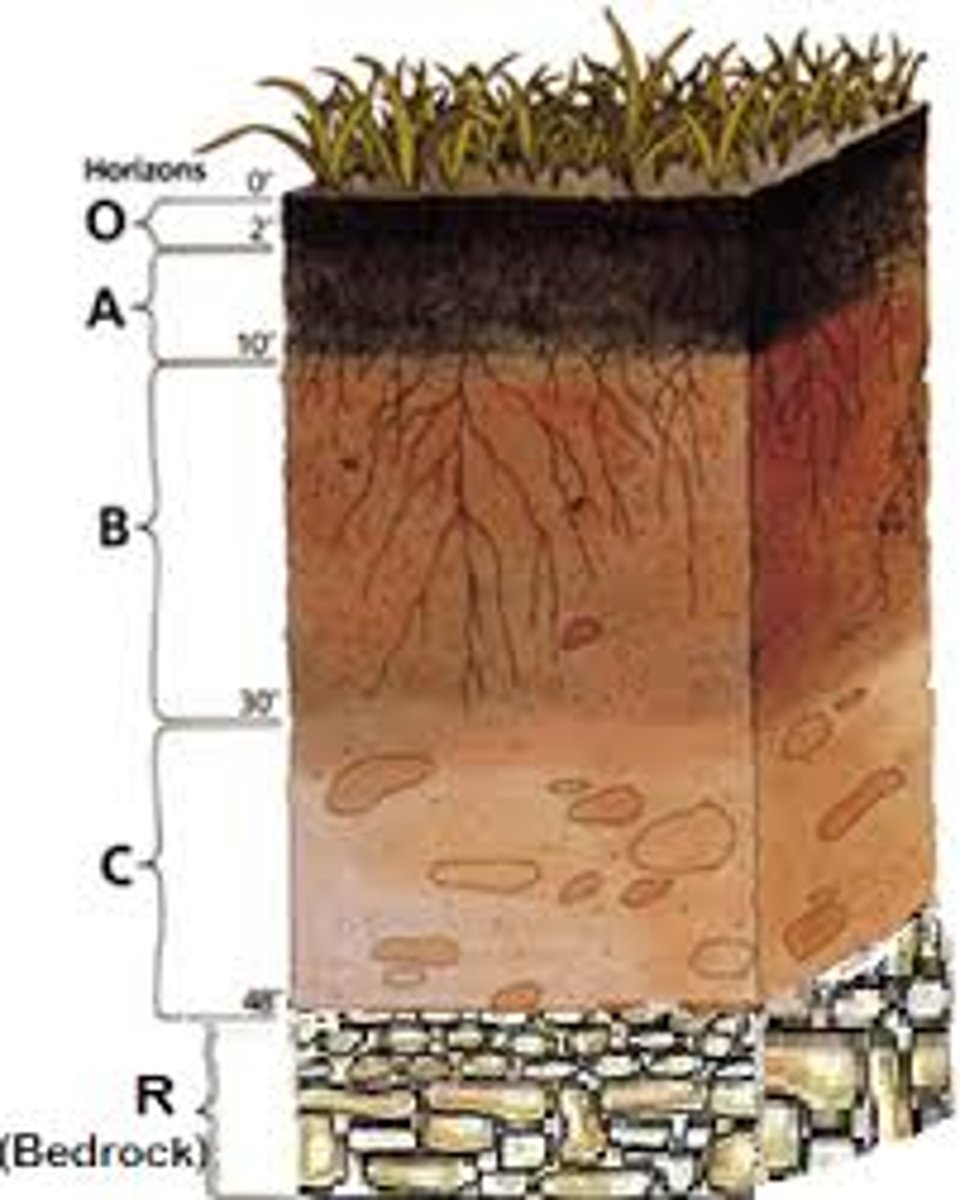
humus
material formed from decaying leaves and other organic matter
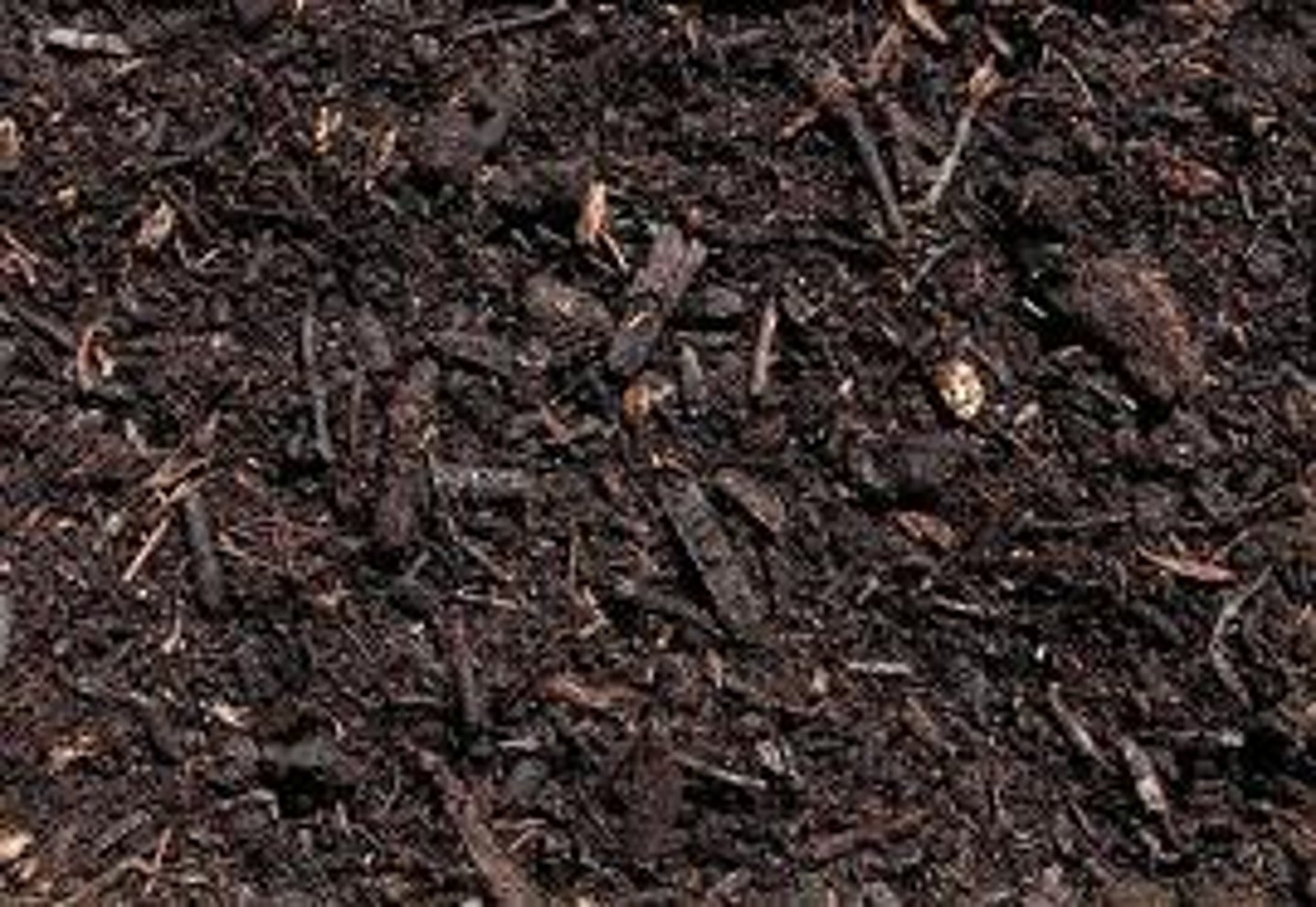

soil
A loose mixture of rock fragments, organic material, water, and air that can support the growth of vegetation
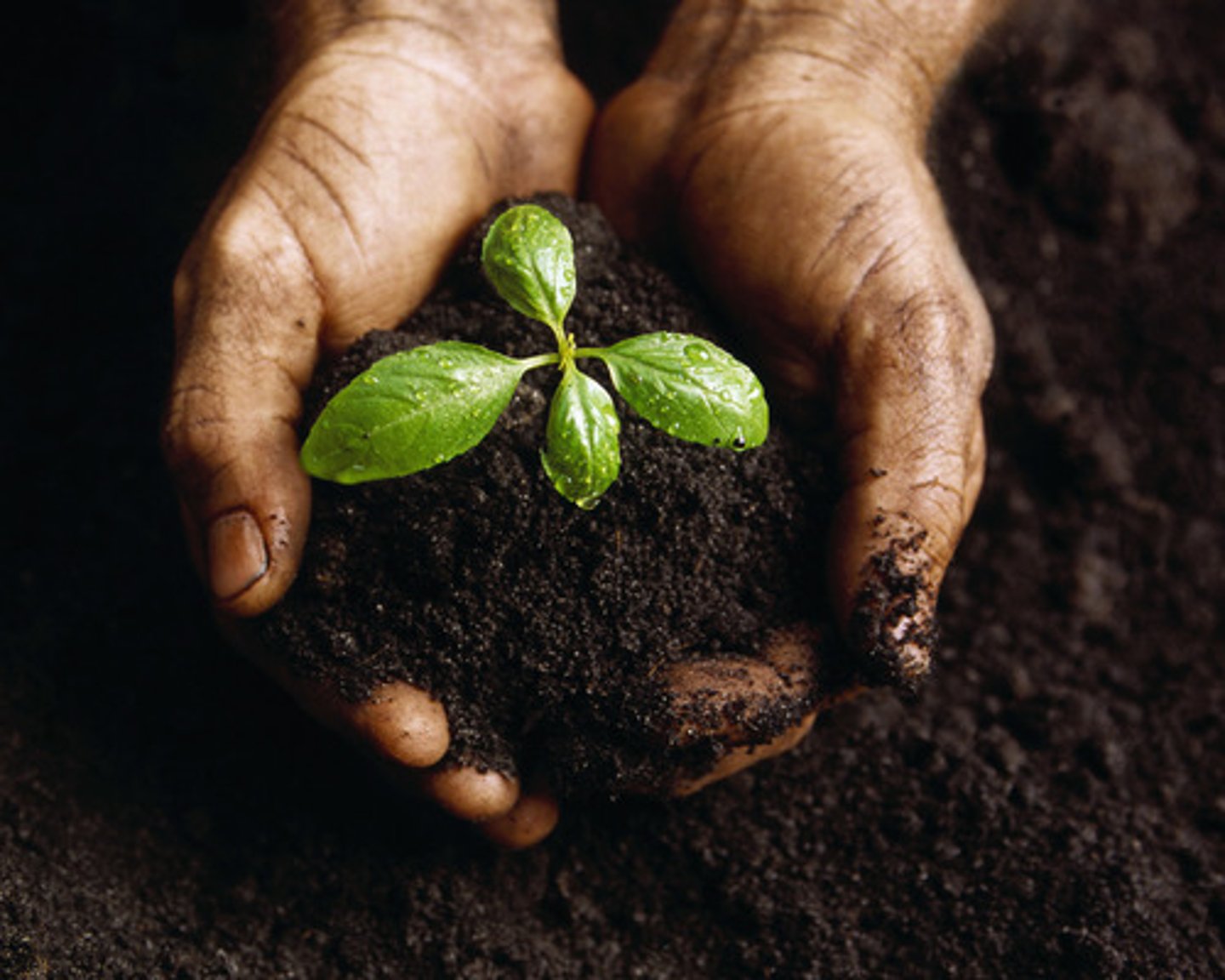

soil formation
Soil forms as rock is broken down by weathering and mixes with other materials on the surface.
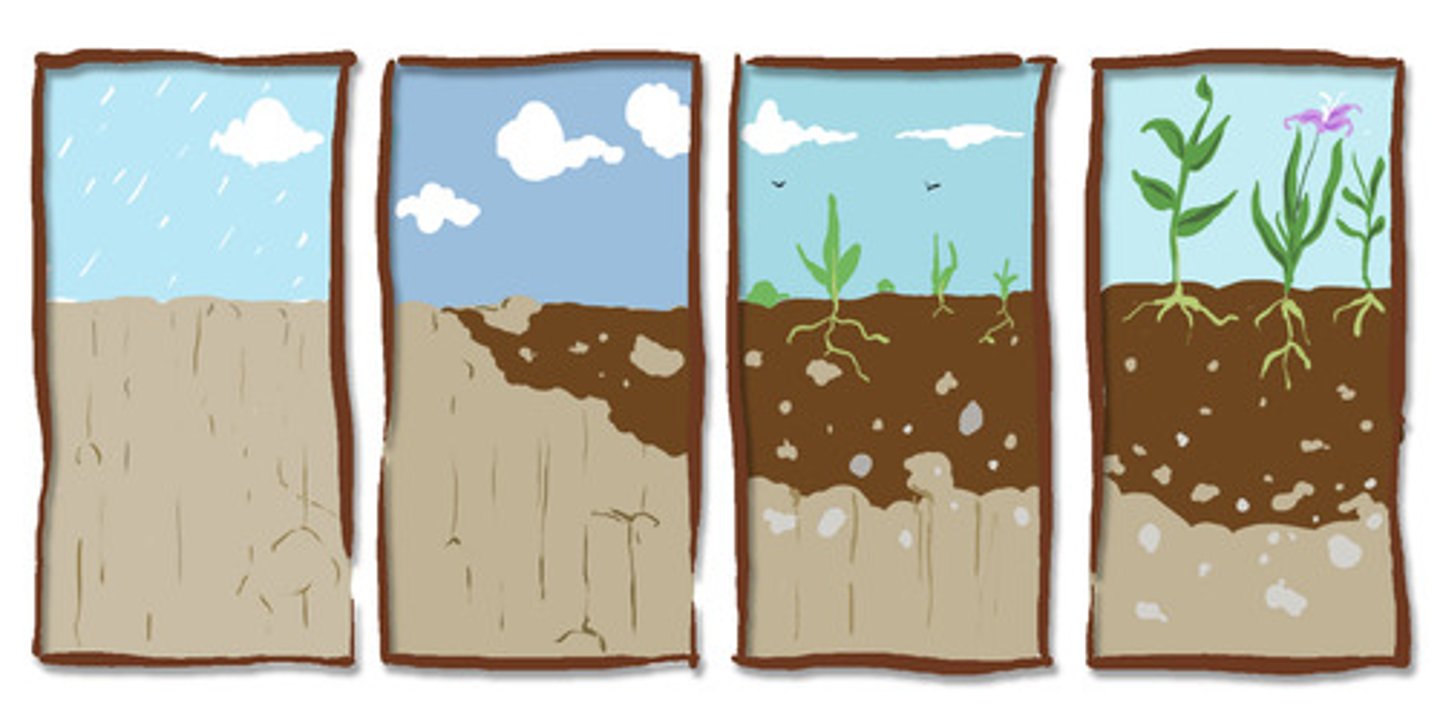

parent material
the rock material from which the inorganic components of a soil are derived
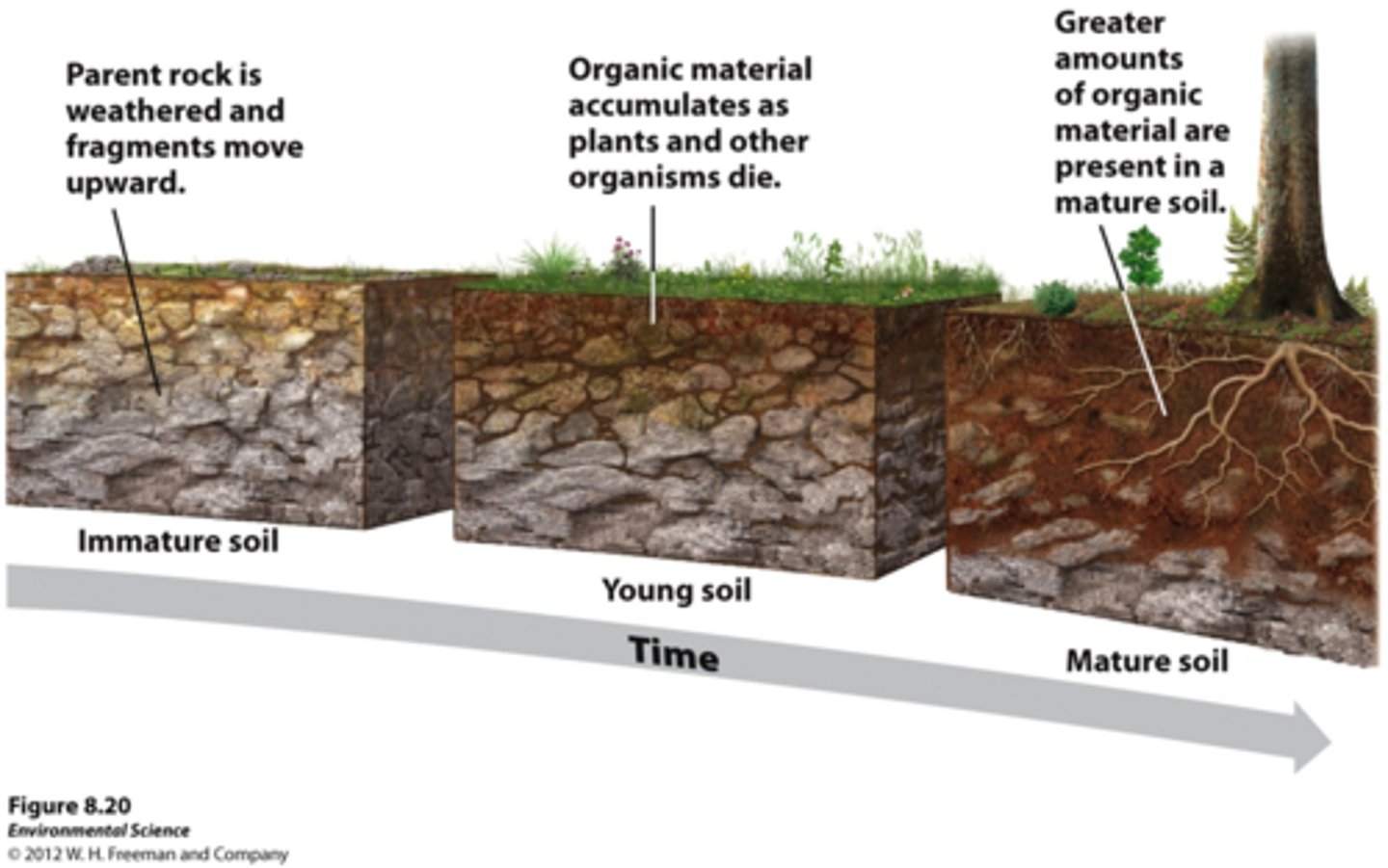
residual soil
Soil that remains above its parent rock

transported soil
Soil that has been moved away from its parent material by water, wind, or a glacier.

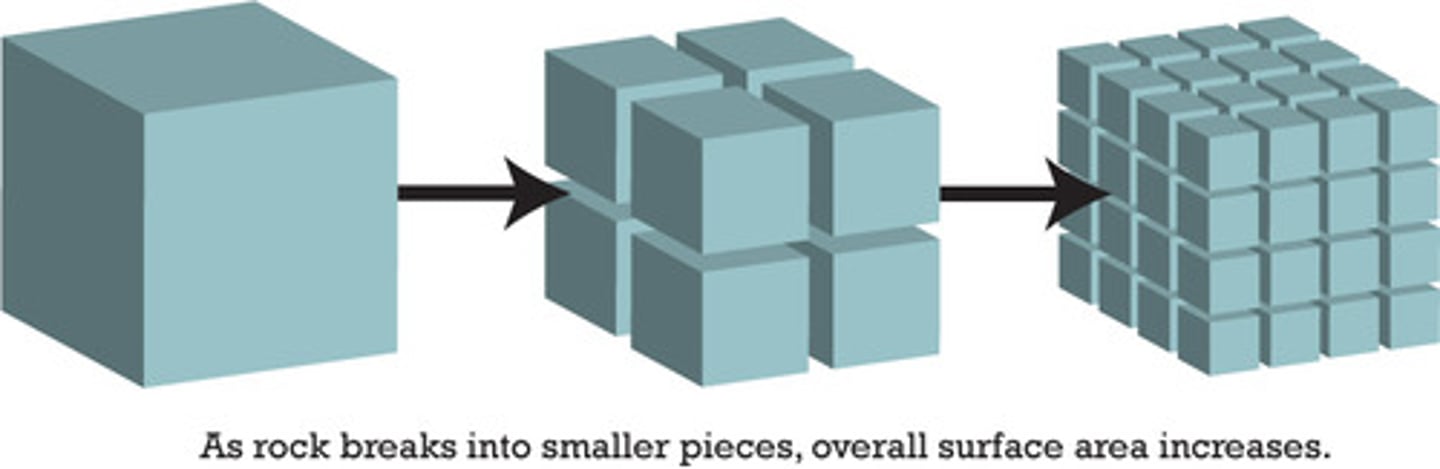
particle size
the smaller the particle the faster the chemical reaction
climate
The average weather conditions in an area over a long period of time
