Micro Rotation
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
Production of beta lactamase is inducible in which organisms
haemophilus influenza and staph aureus
Which of the following is NOT consistent with strep pneumoniae
Catalase Negative
Bile solubility +
Bile esculin hydrolysis +
Alpha hemolysis on sheep blood agar
Bile esculin hydrolysis +
What test can differentiate Viridans strep from group D strep and enterococcus
Bile esculin (viridans neg)
Optimal temp for Yersinia
25C
PYR: colorimetric method to ID _____and _____
enterococci and Group A strep
Bacitracin: used to ID ________ and differentiate from other beta-hemolytic streptococci
group A beta-hemolytic strep (S)
Optochin: Used to ID __________
Streptococcus pneumoniae (S)
Novobiocin: Used to ID _____from other coag neg staph
S. saprophyticus (R)
Cefinase: Used to isolate beta-lactamase producing colonies of:
Staph
Haemophilus
Enterococci
Anaerobes
Neisseria gonorrhoea
LAP: Used to ID___________. Specifically_______ from _______, ______
catalase negative gram positive cocci
Aerococcus from Streptococcus, Enterococcus (+)
MCAT (butyrate esterase): Used to ID______
Moraxella catarrhalis (+)
AST for coliforms should routinely include which antibiotic?
Gentamicin
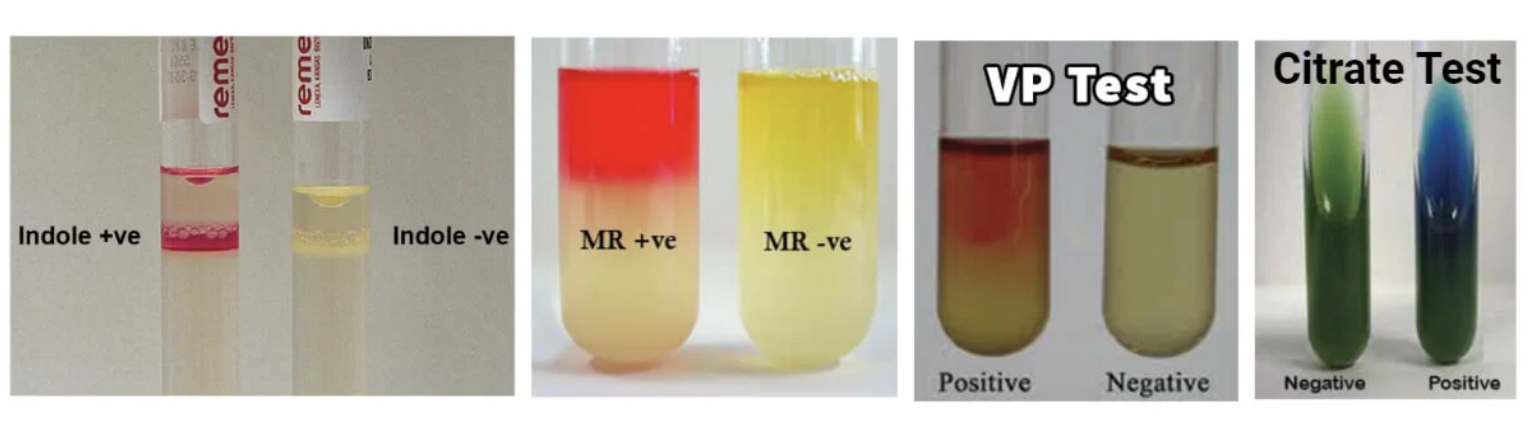
Know what IMVC tests look like

How to perform Nitrate test?
Detect nitrate reductase (NO3 reduction)
Procedure:
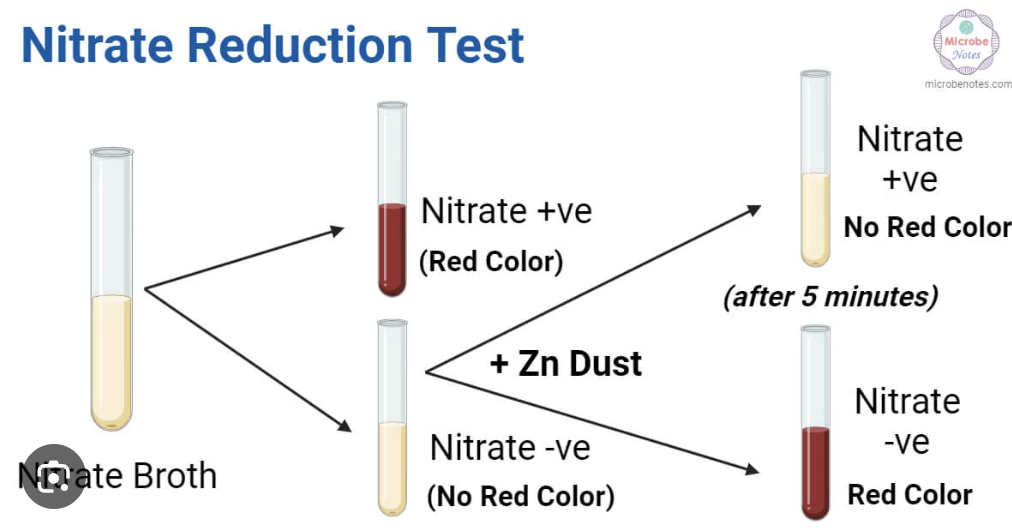
How to perform Sodium Hippurate?
Detects hippuricase (hippurate—> glycine and benzoic acid)
Procedure:

How to perform VP?
Detects acetyl methyl carbonyl production (from glucose fermentations)
Procedure: Add reagent A and B after incubation and observe for color change
How to perform MR?
Detects acid production (pH<4.5) during glucose fermentation
Procedure: add methyl red indicator at the end of incubation
IMVIC is used to ID organisms in the _______group
coliform (GNR, aerobic/facultative anaerobic, and produces gas from lactose within 48 hrs)
IMViC for important organisms
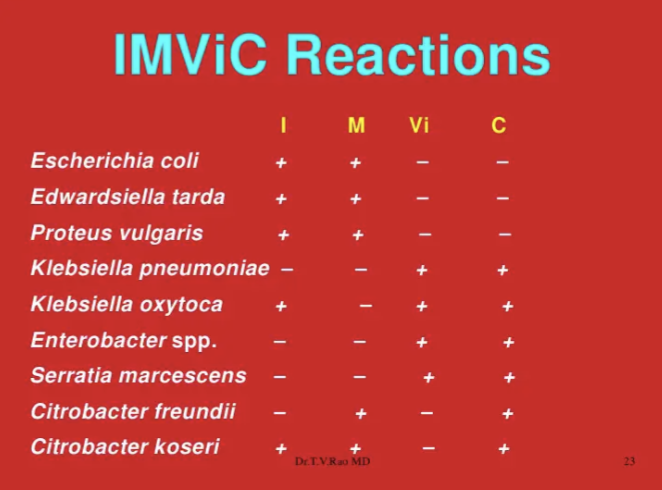
What 4 things are needed to classify Enterobacteriaceae?
Nitrate reducer
Motile (except Shigella, Kleb, and sometimes Yersinia)
Oxidase (-)
Glucose Fermentor
Agents of Bioterrorism
Y. pestis
Route: Fleas

Agents of Bioterrorism
B. Anthraces
Route: Farm Animals (woolsorters!)

Agents of Bioterrorism
B. Anthraces can present as:
_____(most common)
_____(most deadly)
_____
cutaneous (most common)
pulmonary
gastrointestinal
Agents of Bioterrorism
F. tularensis “rabbit fever”

Agents of Bioterrorism
Brucella
Route: contaminated animal products

Agents of Bioterrorism
Brucella can cause _____fever
undulant
Agents of Bioterrorism
B. Pseudomallei
Route: contaminated water and soil

List the 4 main organisms under Food Bioterrorism
Salmonella
Shigella
E.coli O157
Vibrio
Strep Chart (in reference book-only common ones)
A=Bactiracin
P=Optochin
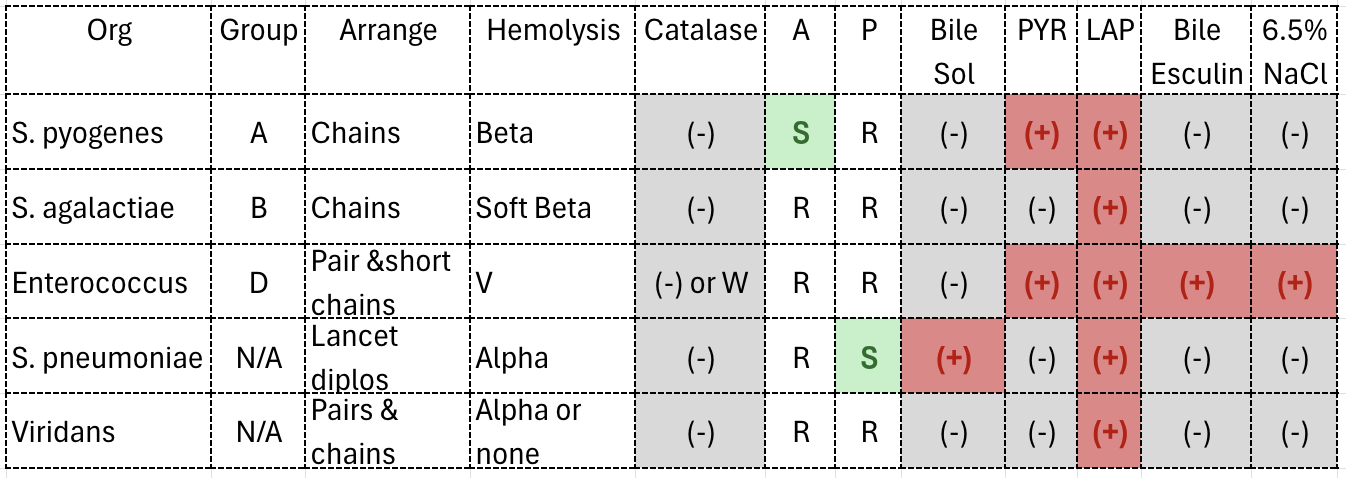
What organisms can satellite around other colonies on SBA?
Haemophilus sp. and anything fastidious
Can MALDI be used to ID Shigella?
NO; use Vitek
What are the screening disks and diameters for ESBL?
CAZ <22mm
CRO <25mm
What is the follow up fo ran ESBL screen?
(CAZ/CLA) - CAZ
(CRO/CLA) - CRO
5mm difference of either = (+)
What organisms get an ESBL screen?
E.coli
Kleb
Proteus mirabilis
How is the KB zone size determined?
CLSI
Minimum Inhibitory Concentration
conc. that prevents organism from growing
Minimum Bactericidal Concentration
conc. that completely kills organism
List 4 Beta lactamase antibiotics
Penicillins
Cephalosporins
Carbapenems
Monobactams
Colony counts using a calibrated loop of 1 uL:
0-10=
10-99=
100+=
0-10= 103
10-99= 104
100+ = 105
Colony counts using a calibrated loop of 10uL:
0-10=
10-99=
100+=
0-10= 102
10-99= 103
100+= 104
What causes a D zone?
Inducible penicillin resistance between Clindamycin and Erythromycin
How to test for penicillin on S. viridans?
E test or 1ug OX disc
How to test for penicillin on Strep pneumo?
E test or 1ug OX disc on MH w/ 5% blood
Orgs found in blood cultures that are associated with colon cancer
Clostridium septicum
Streptococcus bovis
Clostridium septicum ID
Smoothly swarming
Beta hemolysis
Thin rods w/ subterminal spores
Indole (-)
Streptococcus bovis ID
PYR (-)
6.5% NaCl (-)
Bile esculin (+)
Group D
What is the common cause of sepsis in neonates and how do we test for it?
Group B strep ( Strep agalactiae)
Testing: Carrot broth, Detect agar, lance field antigen test
What are the primary & secondary diseases caused by Group A strep?
Primary (during infection):
Scarlet Fever
Secondary (after infection):
Rheumatic Fever
Post-Streptococcal glomerulonephritis
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae
Source: piggy’s and common in occupational exposure handling animal products
Characteristics:
Gram (+) : rods in chains or V shape
Catalase (-)
H2S (+)
Non motile
Resistant to VANCO
What internal ailment can Enterotoxin by staph aureus cause?
Food poisoning
What external ailment can Enterotoxin by staph aureus cause?
Scalded Skin Syndrome (Ritter’s Disease)
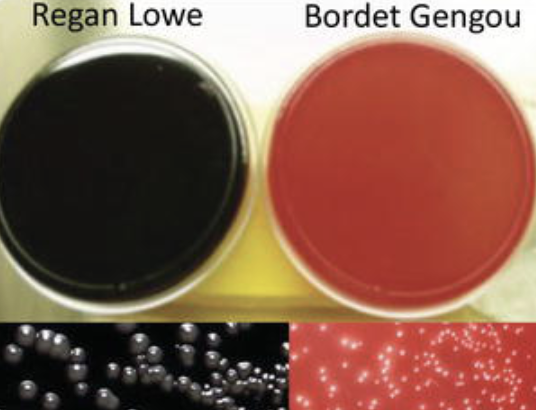
Incubation requirements for Pertussis
Temp: 35-37C
Media: Bordet-gengou or Regan-Lower
Appearance: Mercury Droplets

Incubation requirements for Legionella
Temp: 35C
Media: BCYE

What is permease deficiency and ONPG used for?
determine the ability of an organism to produce β-galactoside enzyme
used on enterobacteriaciae (yellow = + )
What causes Gastric ulcers and how is it identified?
H. pylori
Testing: Tissue biopsy and Urea breath test
Bacillus ____decolorizes easily
over
Bacillus can be ____hemolytic
beta
What can cause a pseudomembrane in the throat?
Corynebacterium diphtheria
What media is used for C. diphtheria and how does it appear?
Media: Tellurite media
Appearance: black
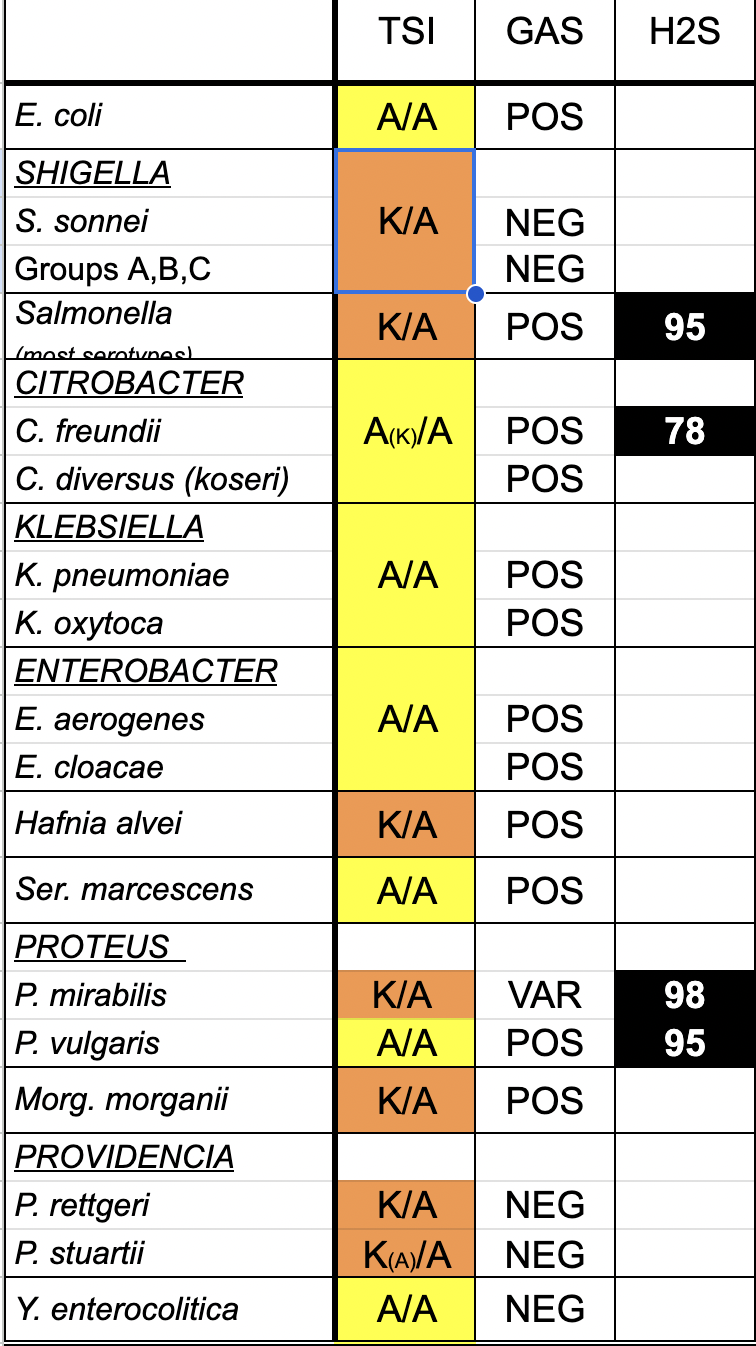
What is in a TSI?
Slant: Lactose and Sucrose
Butt: Glucose
Indicator: Phenol Red (Yellow = acid; Red = alkaline)
What are all the possible TSI reactions?
(Glucose: Lactose: Sucrose—> 1: 10: 10)
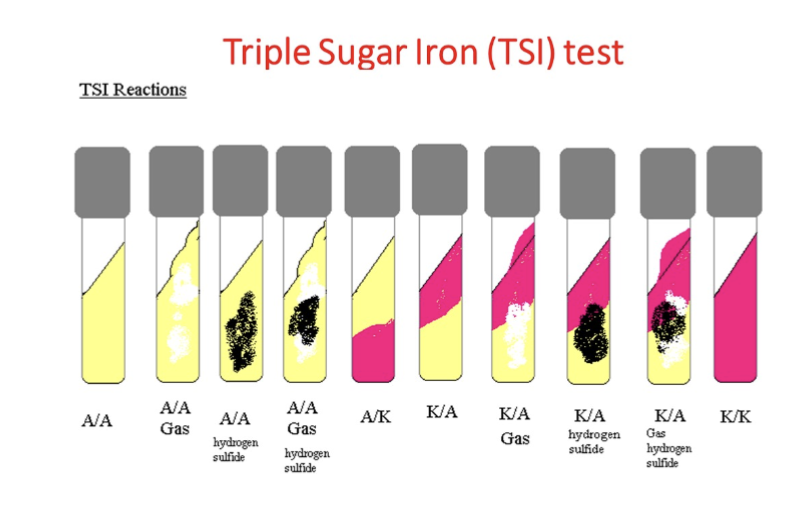
Know TSI for Enterobacteriaceae
Due to their lack of cell wall Mycoplasma are inherently resistant to ____
β-lactams
TCBS Agar and vibrio organisms
yellow=sucrose utilization

OFPBL Agar is used to select for ______especially in ____patients
Burkholderia cepacia; CF
How does OFPBL Agar inhibit other organisms?
selective agents:
polymyxin B (Gram -)
bacitracin (Gram +)
Standard MH Requirements
pH: 7.2-7.4
Specific cation conc.
Depth: 4mm
Temp: 35C
Incolum: 0.5 McFarland with fresh colonies (16-24 hrs)
AST can be read at 16-18 hours except for ____and ______
Staph and Enterococcus ( must be 24 hours)
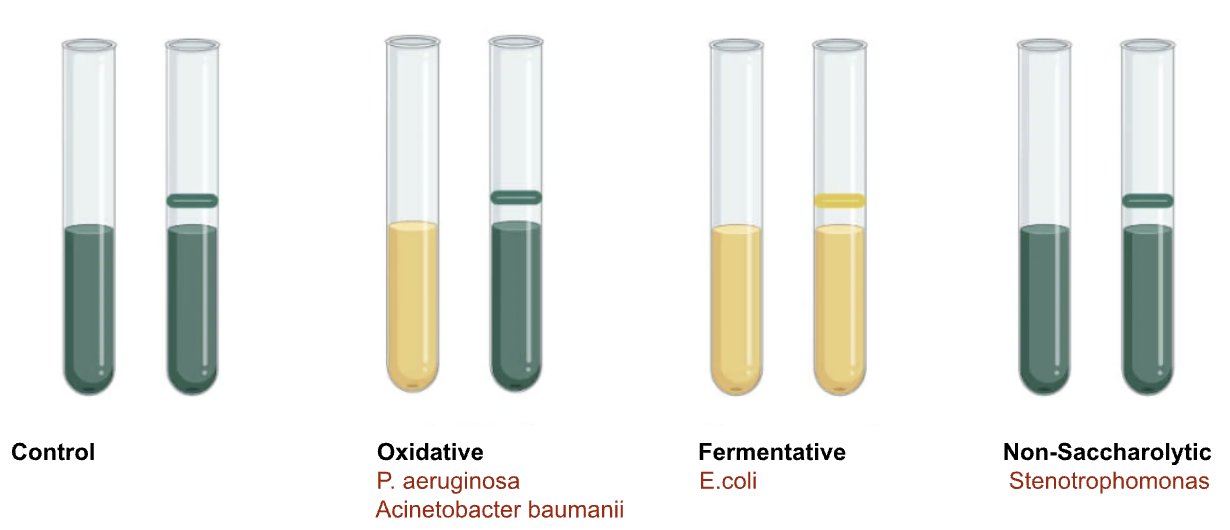
Top 3 clinically sig Non Fermenters
Psued
Acinetobacter
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia
Non Fermenters
Pseudomonas
GNR
NLF
OX (+)
TSI: K/K
Grapes
motile
Non Fermenters
Acinetobacter baumanii
GNR
NLF
OX-
OF glucose: yellow/green
non motile
Non Fermenters
Stenotrophomonas
GNR
NLF
OX-
OF glucose: green/green
Alk Phos +
motile
OF glucose test
Spirochetes
Borrelia
Disease:
Source:
Disease: Lyme disease
Source: Hard ticks
Spirochetes
Leptospira
Disease:
Source:
Disease: Leptospirosis
Source: urine of animals (Hawaii 70% of infections )
Spirochetes
Treponemes pallidum
Disease:
Source:
Disease: Syphilis !!
Source: Sexual Contact
What is the MCAT disc used for?
Detects butyrate esterase to ID Moraxella catarrhalis
Tests for Syphilis
VDRL -screen; can also be used on CSF
RPR - rapid
What is Pseudomonas intrinsically resistant to?
SXT
What is Kleb intrinsically resistant to?
ampicillin
MTM ingredients
SXT (trimethoprim): inhibits Proteus
Colliston: inhibits GN
Vancomycin: inhibits GP
Nystatin: inhibits yeast/mold
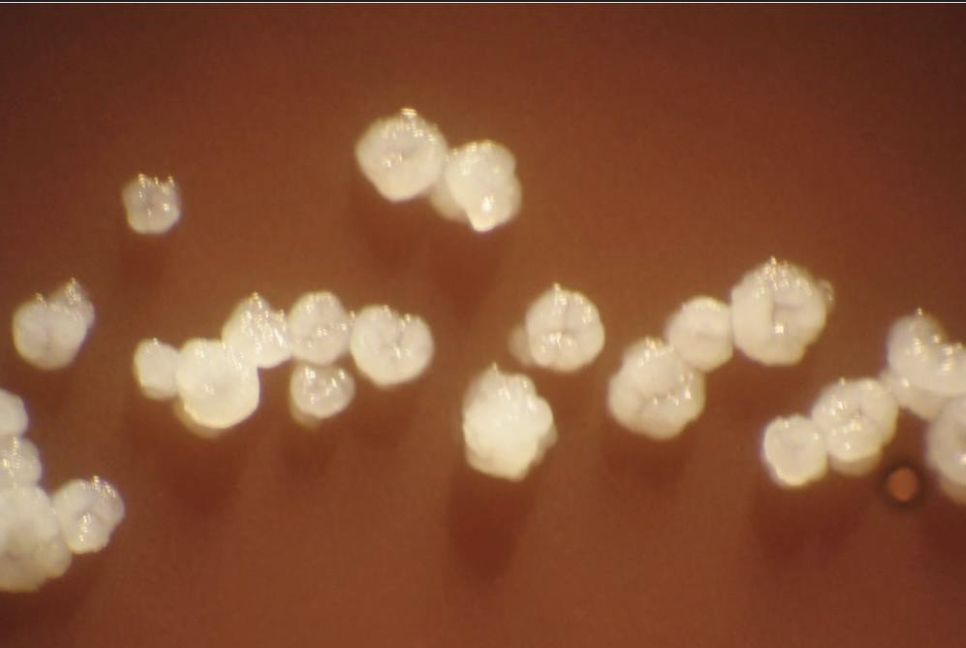
“molar tooth”
Actinomyces
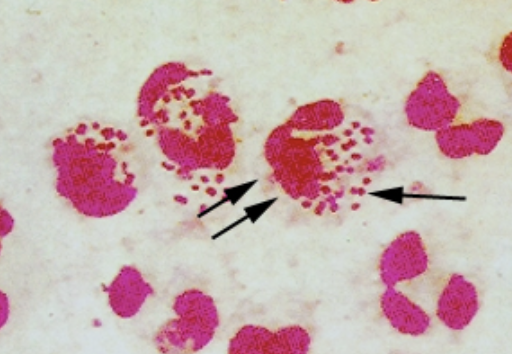
What does this suggest in males? females?
males: Neisseria gonorrhoeae
females: can’t say; females have GNC so must culture
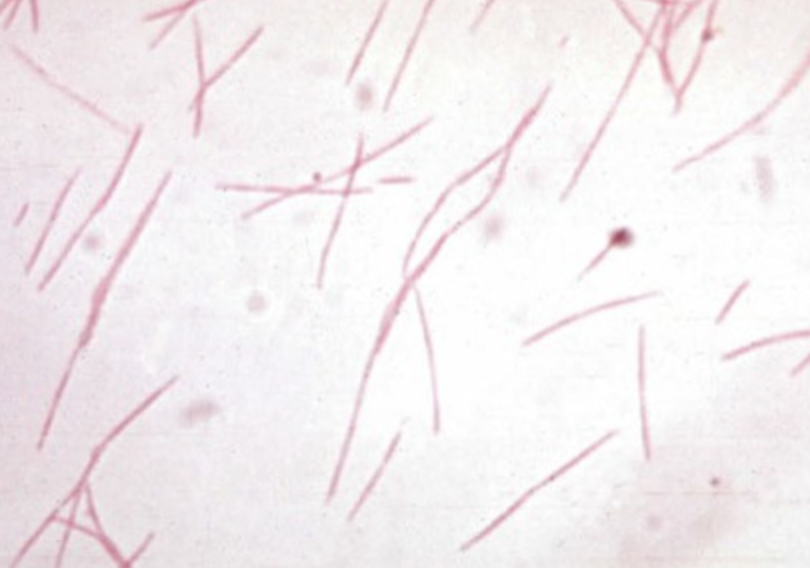
culture looked like “bread crumbs”
Fusobacterium nucleatum
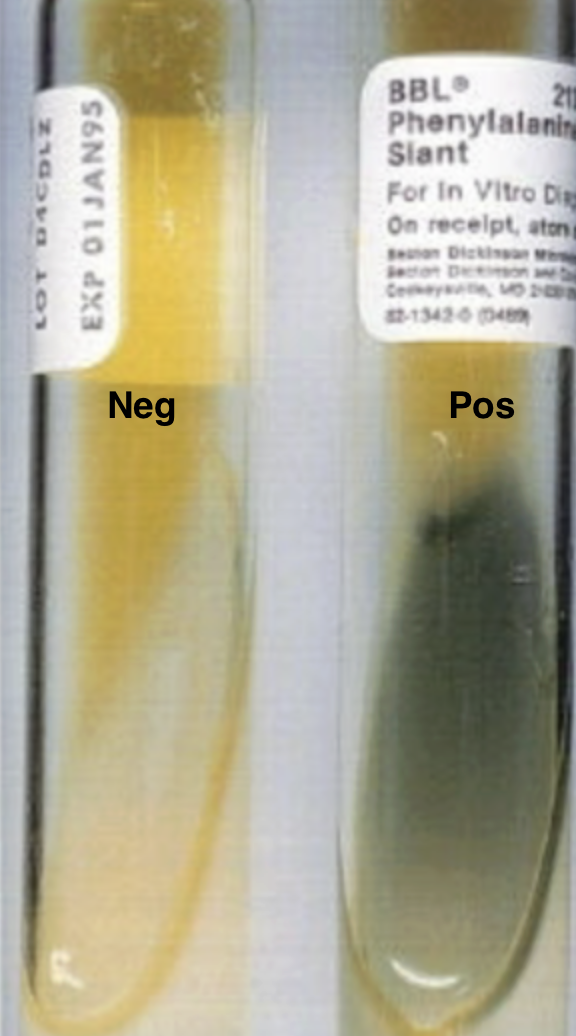
What bacteria genera are PAD (phenylalanine deaminase) positive
Proteus
Morganella
Providencia

If strep pneumo is suspected, what is a quick test that can be performed?
bile solubility (+)
Neisseria carb ferm test

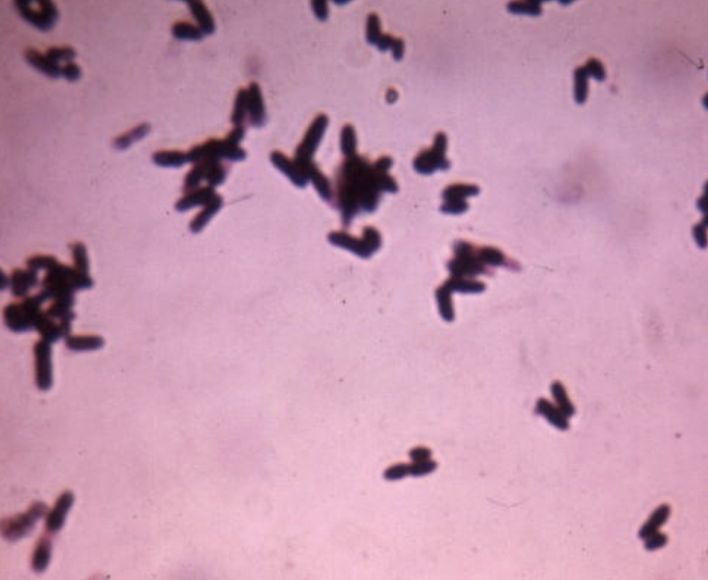
“ chinese/oriental letters” or palisades
Corynebacterium species
What org is incubated in microaerophilic conditions at 42C?
Campy
What orgs require CO2 incubarion
Neisseria
Haemophilus
Strep pneumo
Capnocytophaga
Can specimens for micro be transported on ice?
No, everything is at RT
What does a Q-score of 0 indicate?
lots of epi’s so poor quality and most likely contamination
What does a Q-score of 3 indicate?
high quality and abundant neutrophils, indicating infection
What organisms are resistant to
Ampicillin
Cefazolin
Augmentin
Enterobacter
Citrobacter
Hafnia
Serratia
For which antibiotic should you interpret where there is an 80% reduction of growth?
SXT (Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole)
What is used to quench excess stain in Truants stain ( for acid fast bacteria)?
potassium pergmanganate
What is the only non fermenter that is h2s pos
shewanella putrefaciens
What drug is used to rule out MRSA?
FOX (R)
only OX and CZ reported as (R)
X factor is also known as _____
V factor is also known as_____
X= hemin
V=NAD
Which organism requires
X and V:
only V:
X and V: Haemophilus influenzae
only V: Para influenzae