Intro to ID
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
What were three things that changed from 1900 to now that led to fewer deaths from infectious diseases?
Sanitation, vaccination, antibiotics
What are some unintended consequences of overuse of antibiotics?
Antibiotic resistance, alterations in the microbiome leading to things such as c diff
What is a hallmark sign of infection?
Fever (>100.4F)
What can create a false positive for a fever?
Malignancy, drug fever, blood transfusions, recent surgery
What can create a false negative fever?
Use of antipyretics, antimicrobial therapy, overwhelming infection
What lab value is generally a confirmation of infection?
Elevated white blood cell count (>10,000)
What is a way to zero in on where an infection may be in the body?
Where pain and inflammation is occuring
What should we do before beginning antimicrobial therapy?
Start efforts to identify the pathogen- microscopy, culture, or molecular tests
What is an issue with selecting antimicrobial therapy when it comes to pre-marketing data?
Lack of comparative trials, extremely ill patients were excluded, generally all organisms are susceptible to antibiotics
If a culture is gram postive, how will it appear under a microscope?
Blue
If a culture is gram negative, how will it appear under a microscope?
Red or pink
Define MIC
Lowest concentration of antimicrobial that prevents visible growth performed with a broth dilution
Define MBC
Lowest concentration of antibiotic that kills a bacterium
What are some situations where we should determine an MIC?
Severe infection (especially when the MIC is expected to be low), unusual resistance, uncommon organisms, unexpected treatment failure, usage of a new antibiotic that isn’t normally in a culture panel
Define antibiogram
A chart made to describe susceptibility of bacteria to antibiotics for a local population (such as a hospital), used to make empiric decisions to treat infection
What’s an important thing to consider with antibiotics in terms of protein binding?
Only free drug is active
Where do most pathogens typically live if an infection is in tissue?
Extracellular fluid
How does the free drug concentration in the blood compare to the extracellular fluid concentration?
Equal
True or false. Renally eliminated antibiotics can be used to treat UTIs
False
Define bactericidal agent
An agent that kills 99% of the organism within 24 hours
Describe concentration dependent bactericidal activity
A direct relationship between antibiotic concentration and bactericidal effect
Describe time dependent bactericidal activity
Maximum suppression of an organism is achieved as long as antibiotic concentrations remain above the MIC
Define bacteriostatic
An antimicrobial that kills <99% of an organism in 24 hours; kills enough to keep growth in check
What is the practical difference between bactericidal and bacteriostatic agents?
None
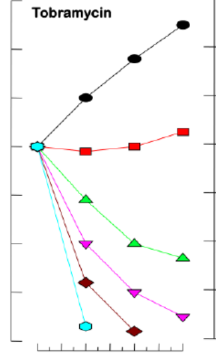
What type of MIC relationship is displayed here?
Dose dependent
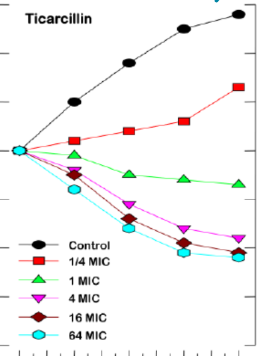
What type of MIC relationship is displayed here?
Time dependent
What are some major offenders for drug interactions with antibiotics?
Rifampin, HIV drugs, fluoroquinolones with antiarrhythmics, warfarin
In general, how do we manage drug interactions when it comes to antibiotics?
Weigh the potential benefit of the antibiotic and recognize the antibiotic is generally temporary
What are some factors of the patient that can affect antibiotic selection?
Age, genetic and metabolic abnormalities, pregnancy, renal and hepatic function, site of infection
What are some things to assess when you see a sick patient in an outpatient setting?
How sick are they, do they need to be stepped up in care, is this viral, have they had any other antibiotics, do they have any infectious history, do they have any real allergies, is there a diagnosis
When is the best time to obtain cultures?
Before antibiotics have been given
EM is in your hospital and has been for the last 5 weeks after a routine surgery was complicated by a wound infection. He is currently in the ICU, intubated and sedated. Today he has spiked a fever to 102.2 and his WBC is 19.1. The wound appears unchanged from previous exams, it is not erythematous and isn’t warm to the touch. His urine and bowel output is stable. What is the most likely source of new infection in this patient?
Urine
Antibiotic associated colitis (c diff infection)
Lung (pneumonia)
Surgical wound
3
A patient presents to the ED with S/S suggestive of infection including fever to 103.1, WBC 23.4, BP 97/61. Which of the following is the best course of action?
Initiate empiric antibiotics immediately, then take a sample for culture
Get a sample for culture immediately and then start empiric antibiotics right after
Get a sample for culture and wait to start antibiotics until culture results come back
2
In general how should you think about antibiotics?
Spectrum of gram positive and gram negative coverage along with aerobes and anaerobes
Is it better to overdose or underdose antibiotics?
Overdose- who cares if the SCr increases we want to kill the infection
What is the number one way we should follow up on when administering antibiotics?
See if cultures came back to more directly target therapy and limit collateral damage
What are Dr. Leonard’s three fundamental skills of ID?
Understand the usual microbiology of various infections, be able to make an appropriate empiric recommendation based on knowledge of usual microbiology and available data and guidelines, appropriately narrow antimicrobial therapy in response to susceptibility data