Exogenic Processes and Depositional Environments
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Depositional environments
The combination of chemical, physical, and biological aspects that dictate what sediments, rock types and landforms are deposited or formed
Erosion
It is a geological process in which earth materials are weathered and transported
Deposition
The accumulation of weathered sediments to create different landforms
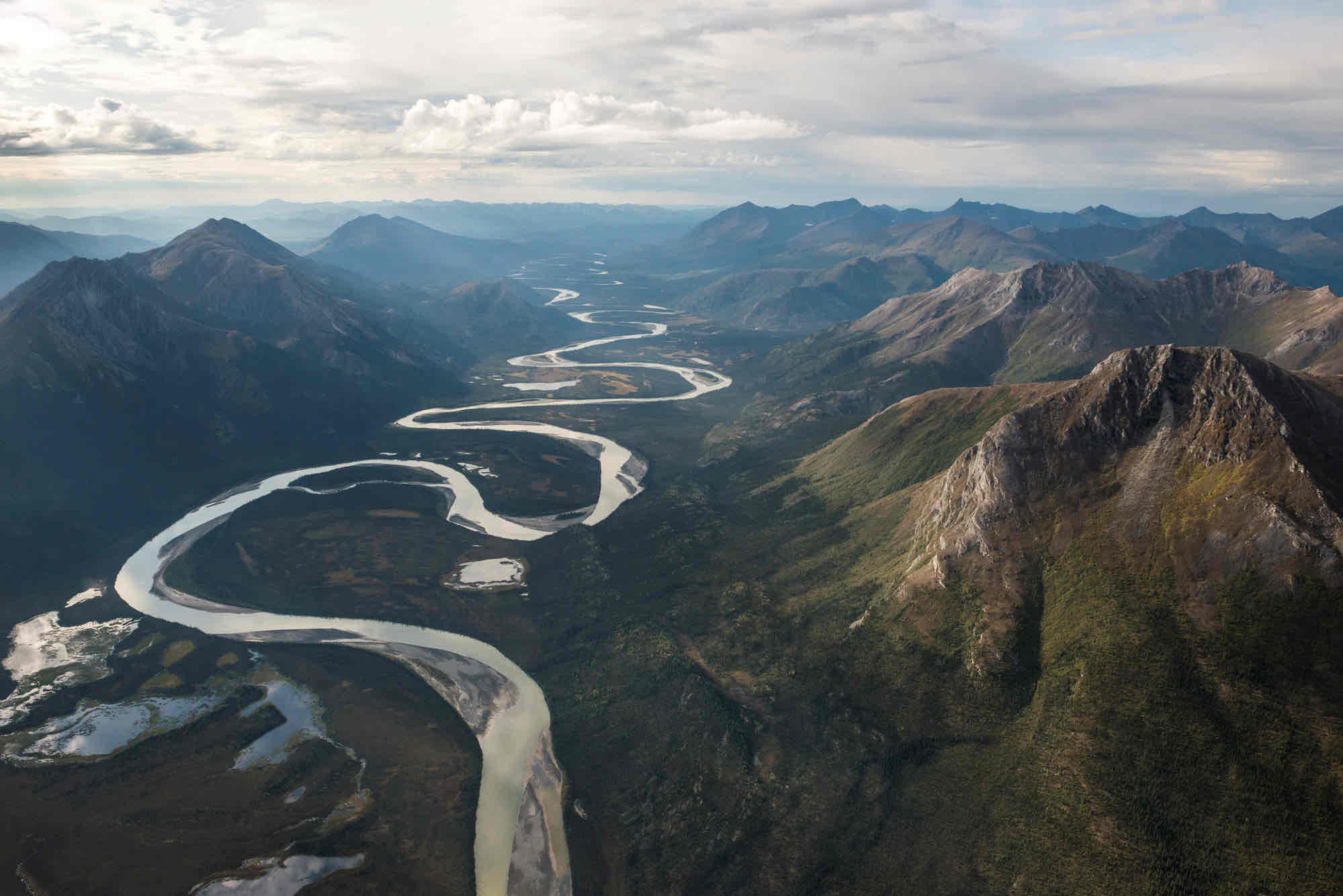
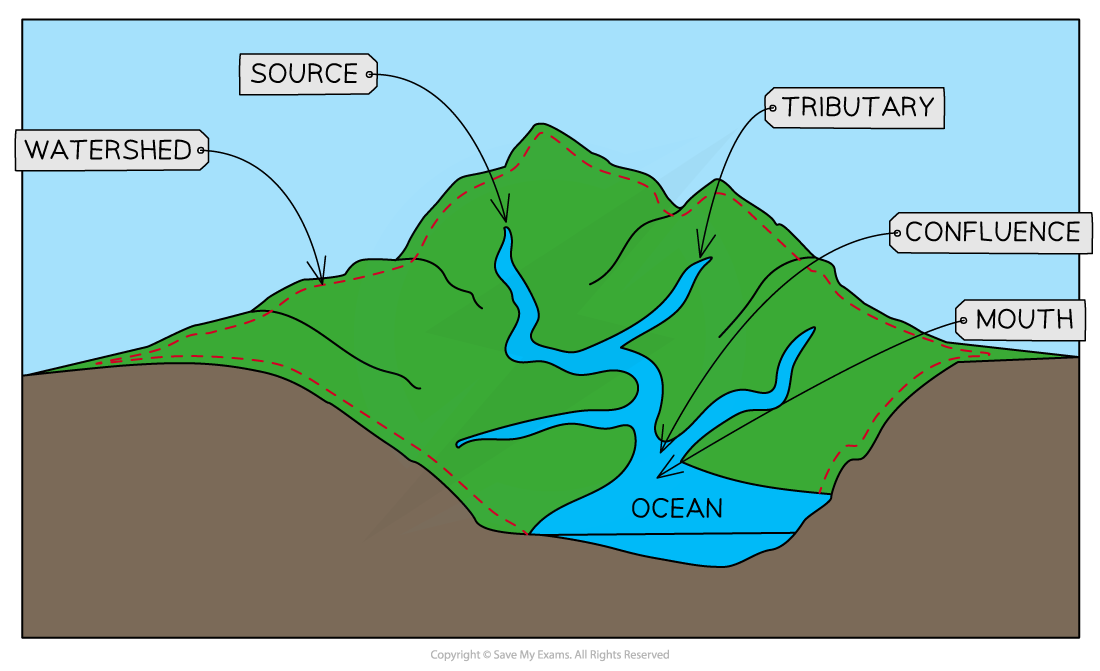
Fluvial
Depositional environment in rivers and streams

Aeolian/eolian
Depositional env. in deserts and arid areas
Alluvium
Material deposit (made up of mixture of loose rocks) of a stream

Alluvial
Mountainous environments
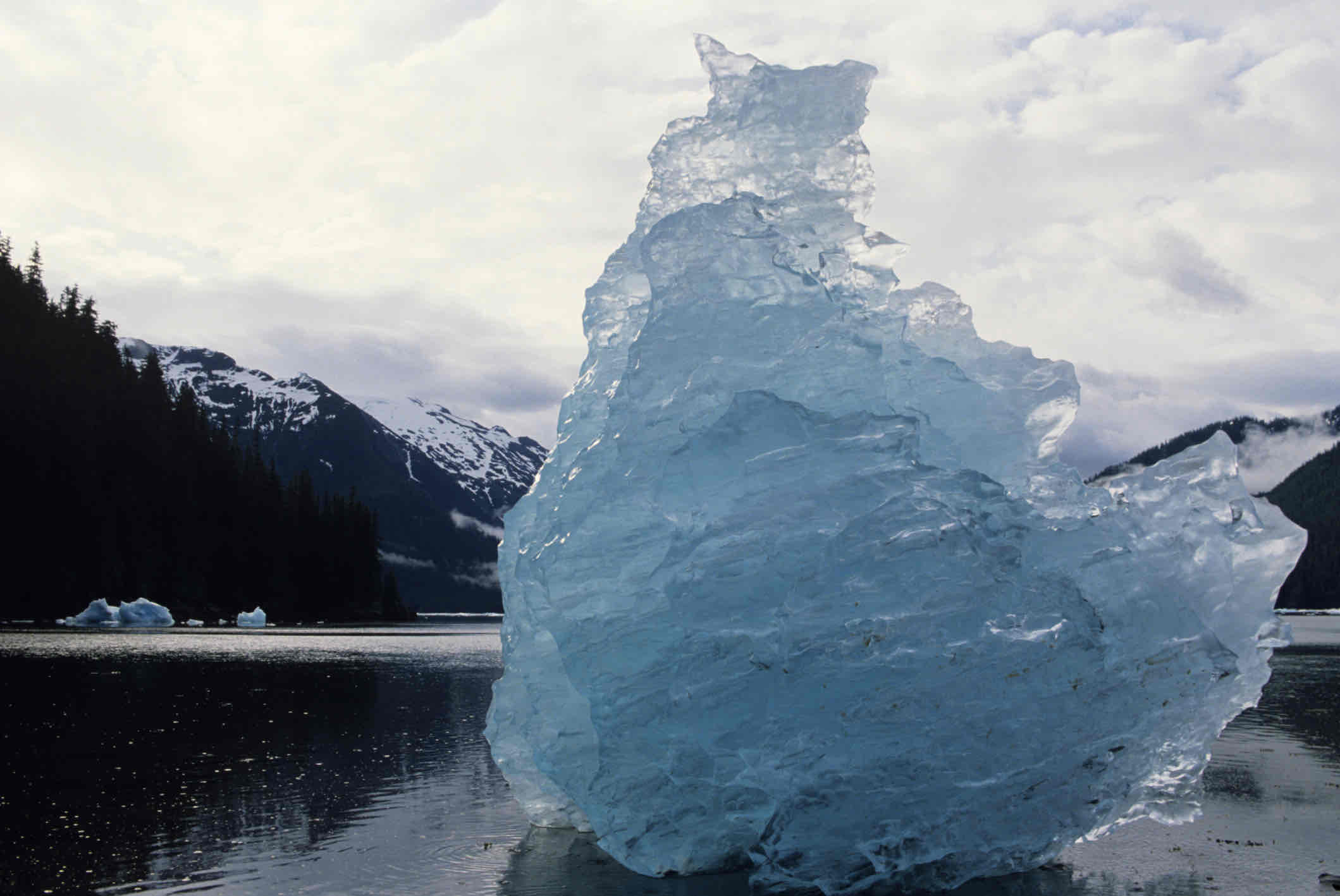
Glacial
Ice cap and glacial areas
Lacustrine
Lake area

Deserts
The most dominant agent of erosion in these areas is running water followed by wind
Glacial environments
The most dominant agent of erosion is ice
Glaciers
Moving ice over land
Ice sheets
Large masses of ice that cover an extensive area of land
Drainage basins
Natural springs from underground
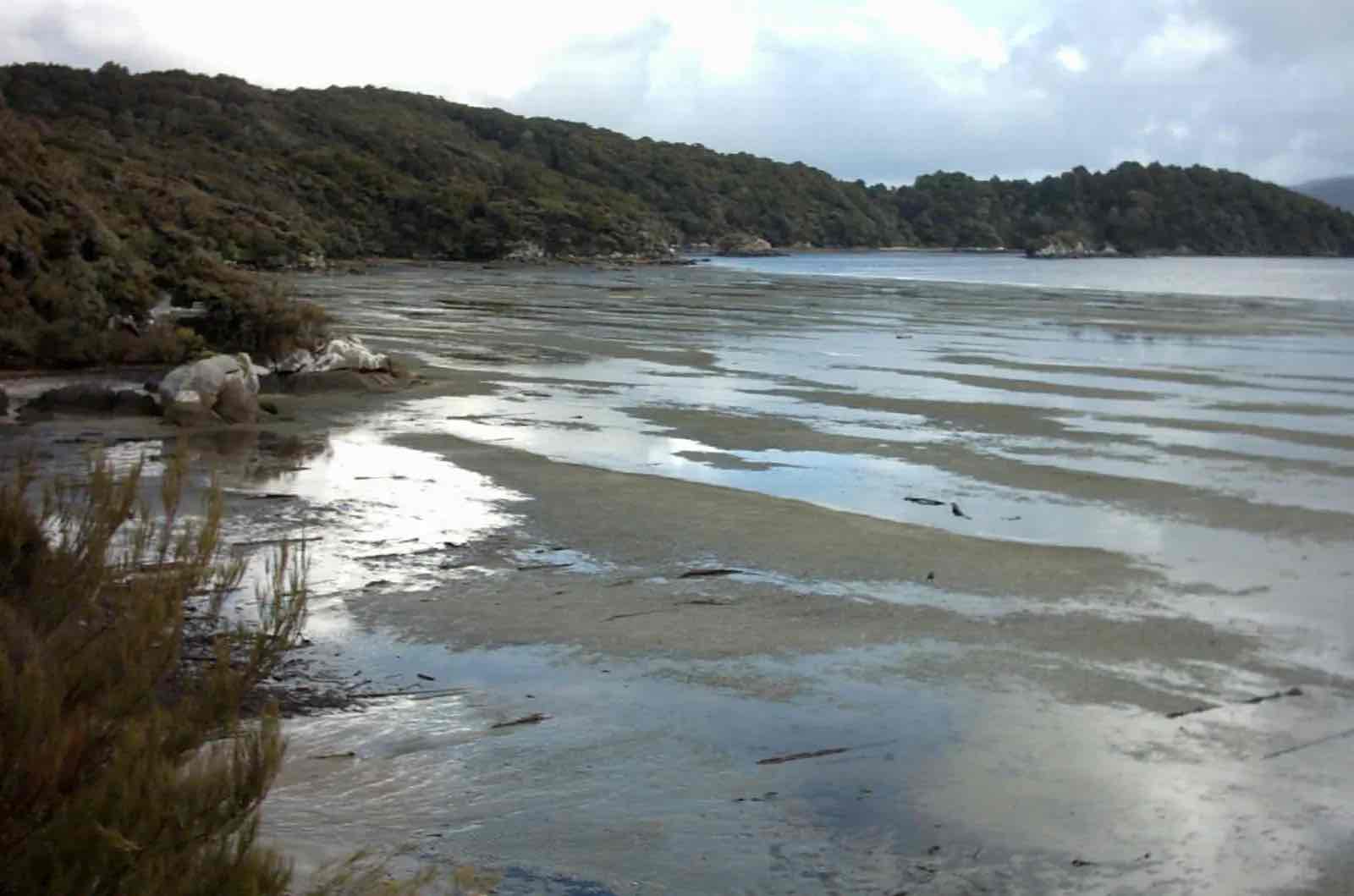
Tidal Flat
Low-lying areas affected by tides

Deltaic
Where the river flows into the sea
Lagoonal
A small body of water closed off from a larger body of water

Deltas
Areas at the end of the mouth of a river where freshwater mixes with seawater

Wetlands
Areas that are near rivers or coastlines where soils are saturated
Marshes
Wetland where moss and soft-stemmed vegetation are most prominent
Swamps
Wetland where trees dominate the plant life
Continental shelf
Extensions of continental crust submerged by water
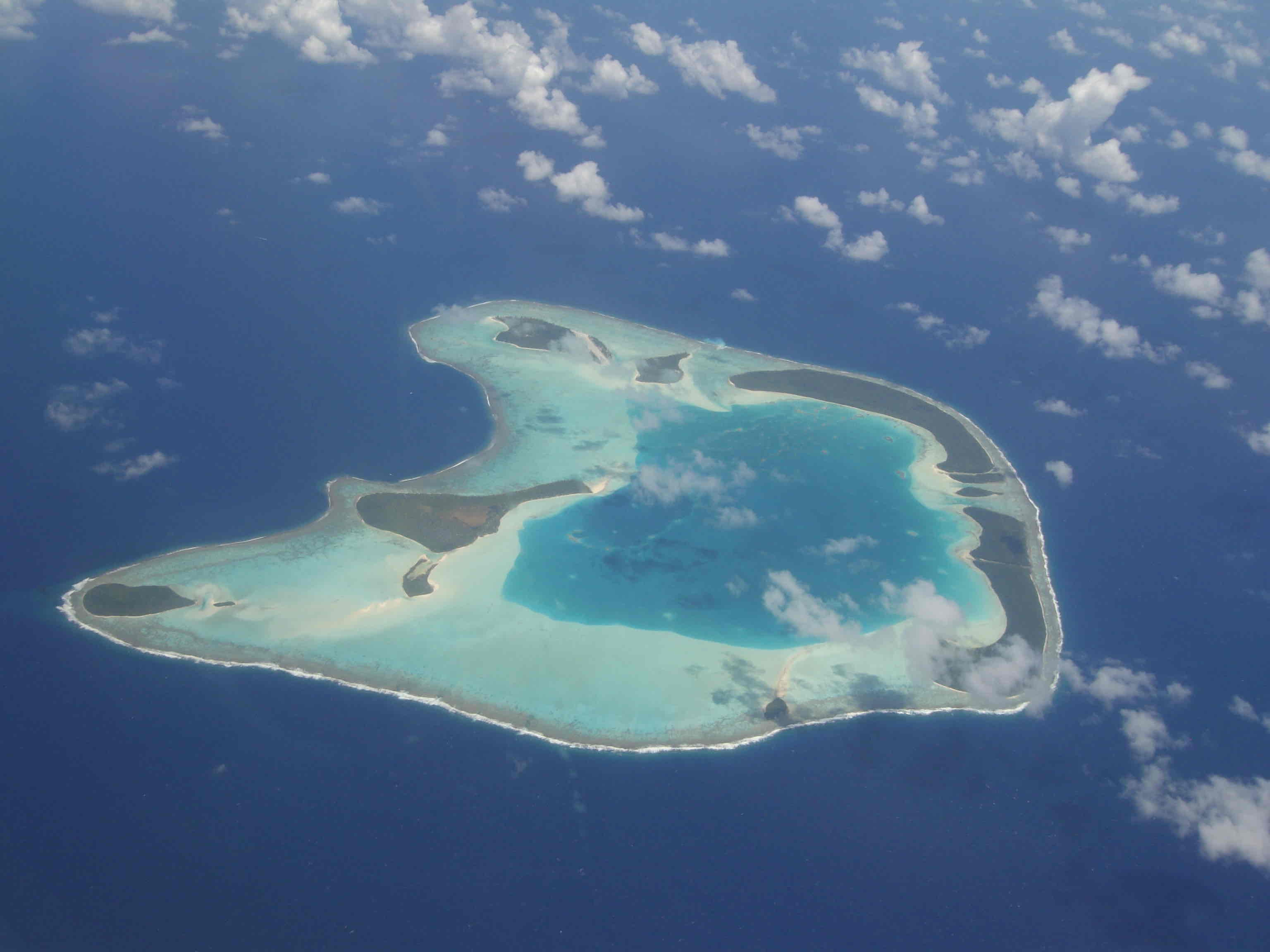
Atoll
Rings or partial rings of coral that usually form around a volcanic island or volcano that has receded or been eroded throughout time

Guyots/Seamounts
Elevated platforms with flat tops formed volcanic activity near the ocean floor. These can be massive and reach heights up to more than 600m
Deltas
It is formed when a river loses energy as it flows to an area of slow-moving water
Distributaries
Parts of a stream that leaves the main flow
Alluvial Fans
Formed when a stream reaches a flat area or gently sloping plain

Flood plain
A flat wide expanse of alluvium covering flat areas prone to flooding

Glacial Till
All unsorted deposits of rock formed directly by the ice

Moraines
Layers or ridges of till
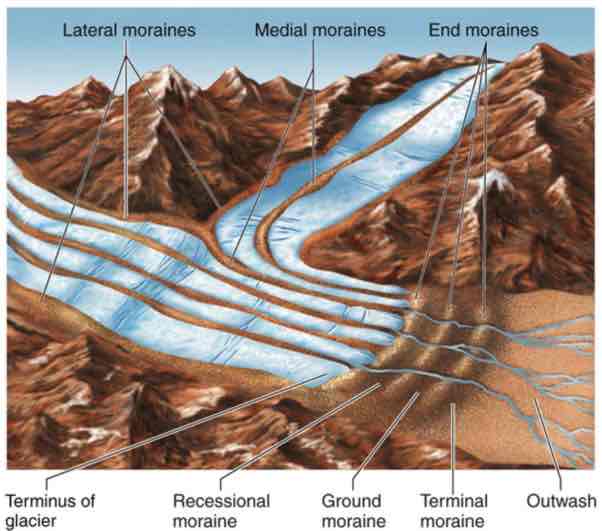
Lateral Moraine
A long pile of rocky material at the edge of a glacier
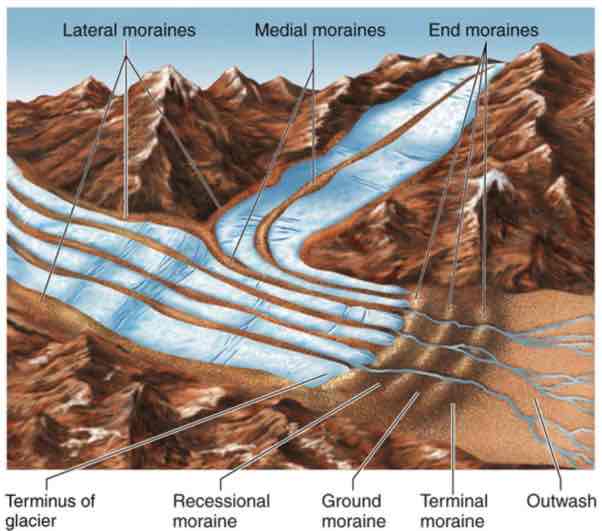
Medial Moraine
A long pile of rocky material at the middle of a glacier
Esker; sand and gravel
Water that forms under a glacier through melting forms a winding ridge called ___ made of ___ and ___
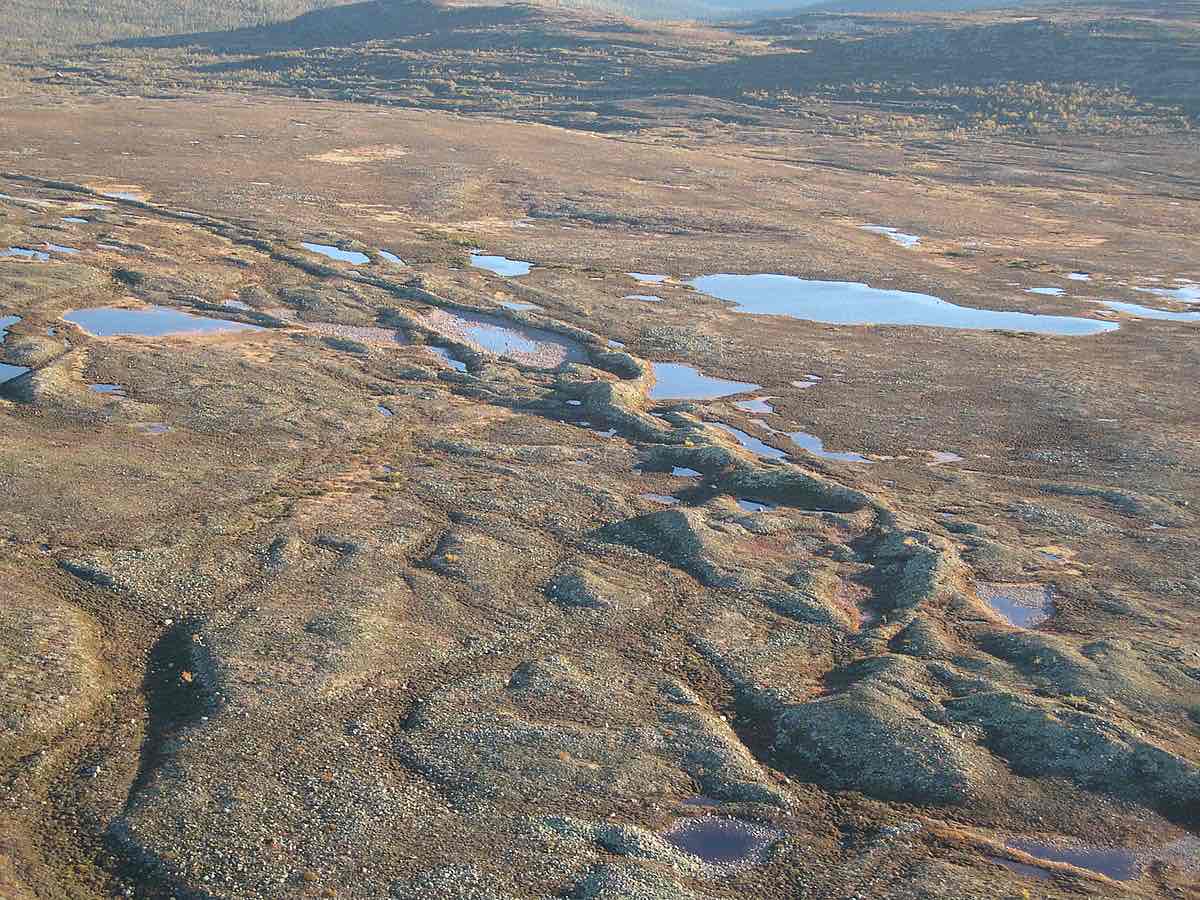

Drumlins
Streamline asymmetrical hills composed of till

Kames
Steep-sided hills

Loess
Accumulated blanket of silt carried by wind in suspension and deposited over any broad areas

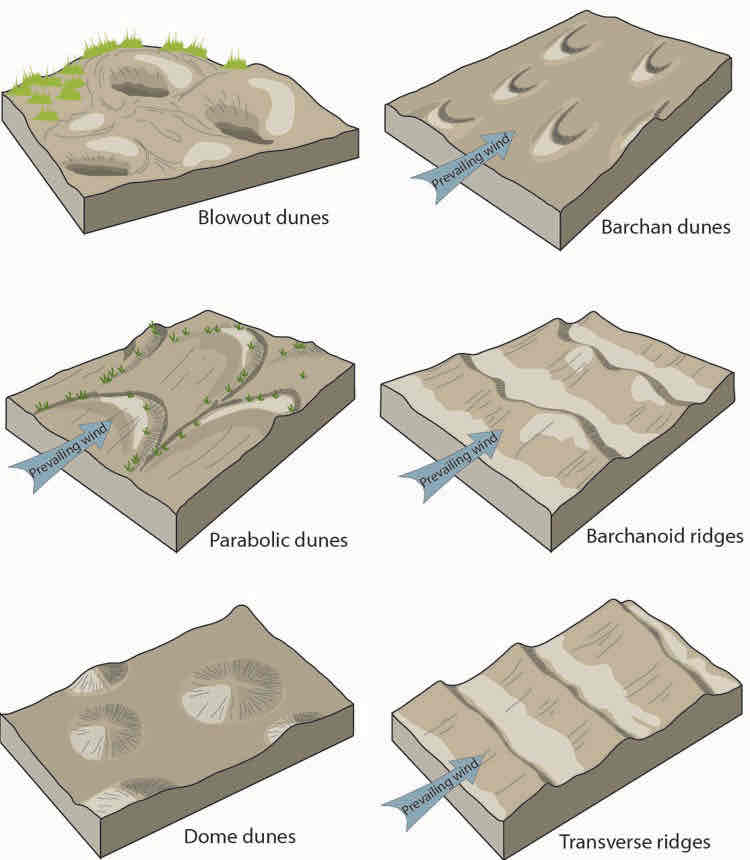
Sand dunes
Deposits of coarse materials in the shape of hills or ridges
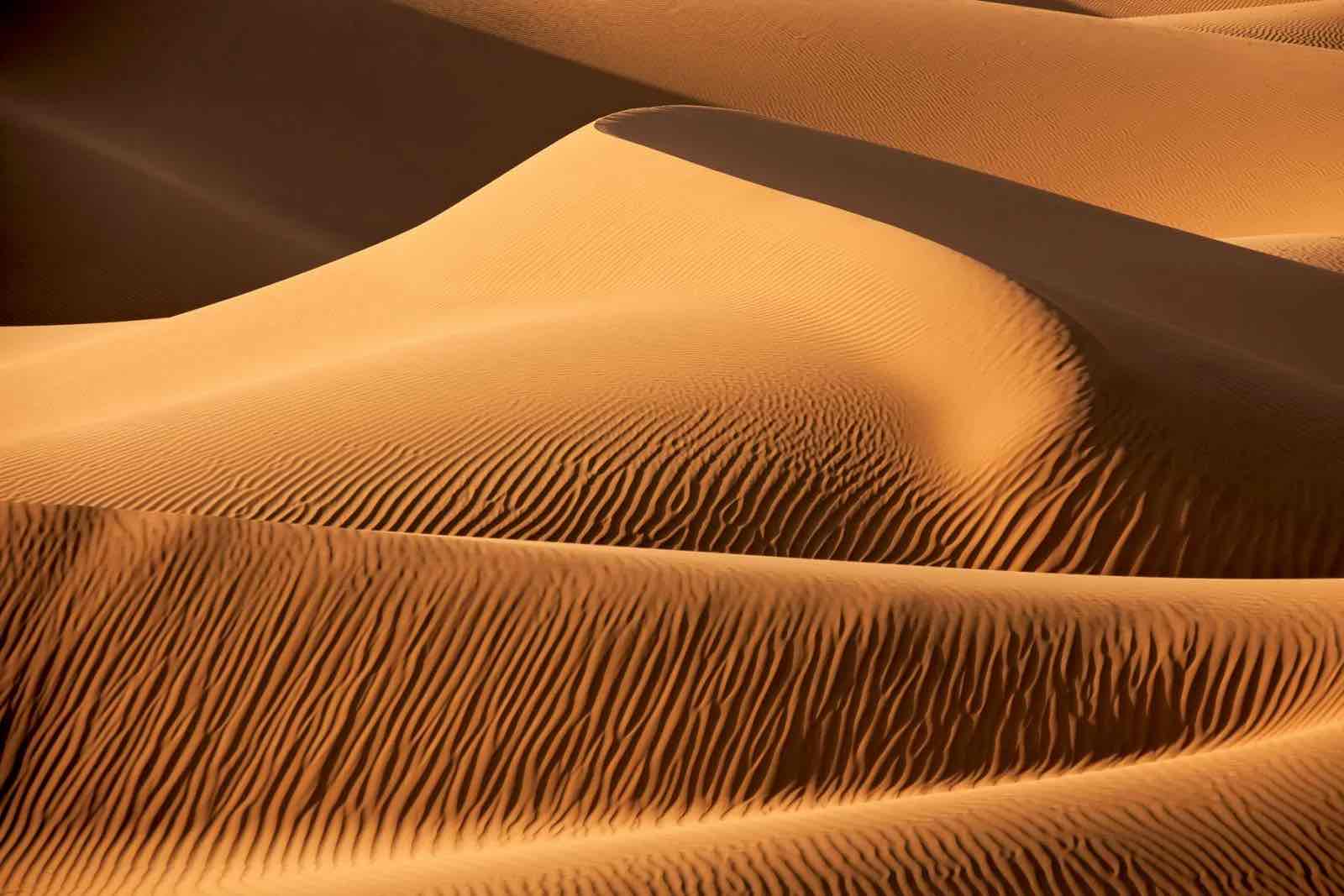

Dune
Any mound or ridge of windblown sand rising to various heights up to 50m
Iron reacts with atmospheric oxygen and moisture and forms iron oxide
Provide one real-life example of oxidation
Water
Glacier
Wind
Transportation
What are the primary agents of Erosion?
Gully erosion
After heavy rain, water flows in narrow channels, eroding ravines into great depth
Carbon dioxide from the soil or atmosphere dissolves in water to form carbonic acid which reacts with minerals in rocks and may gradually dissolve the rock
Provide a real-life example of Carbonation and Solution
Water reacts with a mineral’s chemical structure which can result in the formation of clay minerals, dissolved ions, and silica in solution
Provide a real-life example of Hydrolysis
Daily Temperature Fluctuations: During the day, rocks are exposed to intense solar radiation and expand. At night, rapid cooling and contraction of the rock surfaces occur.
Differential Expansion: Different minerals within a rock expand at contract at varying rates which created internal stresses within the rock.
Exfoliation: Generation of mechanical stresses and the peeling of layers within the rock occurs.
Explain the full process of Thermal stress
Gravity
The driving force of mass wasting
Angle of repose
The steepest angle at which materials remain stable and do not move down slope
Translational slides
The movement of a mass of materials along a well-defined surface
Rotational slides
Occur when the descending materials move en masse along a concave, upward surface
Removal of vegetation
Oversteepening of slopes
Adding moisture
Three Human Activities that may induce mass wasting
Solar energy and Gravity
What are the two driving factors of exogenic processes?