turner unit 2 science test
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/59
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
1
New cards
define: a barrier that maintains the internal and external environments of the cell.
cell membrane
2
New cards
define: only certain molecules can pass through the cell membrane
semi-permeable
3
New cards
what type of molecules are allowed to pass though the cell membrane?
small and nonpolar
4
New cards
define: molecules moving from high to low concentration
simple diffusion
5
New cards
what molecules need a transport protein to pass through the cell membrane?
large and polar
6
New cards
what is it called when molecules use a transport protein to pass through the cell membrane?
facilitated diffusion
7
New cards
what is the cell membrane composed of?
a phospholipid bilayer
8
New cards
define: being half hydrophilic and half hydrophobic
amphipathic
9
New cards
which part of the phospholipid orients itself to the outside?
the head
10
New cards
which part of the phospholipid orients itself to the inside?
the tail
11
New cards
which part of the phospholipid is hydrophobic?
the tail
12
New cards
which part of the phospholipid is hydrophylic?
the head
13
New cards
define: a model that describes the movement and composition of the cell membrane
fluid mosaic model
14
New cards
define: proteins are used by molecules (especially large and polar molecules) to enter/leave the cell
molecular transport
15
New cards
define: to catalyze a reaction (speed up)
enzymes
16
New cards
define: proteins on two cells that can attach and send signals to each other
cell communication/recognition
17
New cards
define: act to receive hormones or other signaling molecules that circulate in the blood or interstitial fluids
signal receptors
18
New cards
define: some proteins act as attachment points for the cytoskeleton and flagella/cilia
attachment points
19
New cards
define: the ability for a single cell to stick to another cell or extracellular matrix
cell to cell attachment
20
New cards
define: runs completely through the cell membrane. usually used in molecular transport and to maintain integrity of cell membrane
integral protein
21
New cards
define: has a channel through the protein for molecular transport
channel protein
22
New cards
define: spiral shaped protein used for molecular transport
alpha helix protein
23
New cards
define: large protein with receptor sites to recognize and transport certain molecules
globular protein
24
New cards
define: act as reception sites for cell signals. act as enzymes/catalysts for reactions
peripheral proteins
25
New cards
define: found on inner or outer of cell membrane; do not penetrate into cell membrane
surface proteins
26
New cards
define: extend about halfway through the membrane; does not extend through membrane
peripheral proteins
27
New cards
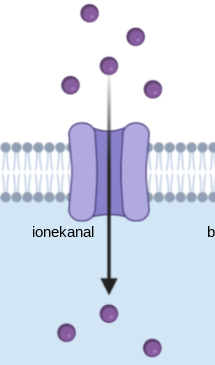
WHAT IS THIS???
channel protein
28
New cards
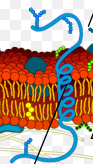
tell me what this is or ill shoot
alpha helix protein
29
New cards

__ is my favorite snack
globular protein
30
New cards

whats this???
surface protein
31
New cards

who is this man
peripheral protein
32
New cards
define: a lipid molecule embedded in the cell membrane that keeps the membrane flexible and fluid. also helps keep the proteins embedded in the membrane
cholesterol
33
New cards

name him
cholesterol
34
New cards
define: a sugar chain attached to either a protein or a lipid on the cell membrane
carbohydrate chain
35
New cards
define: a protein with a carbohydrate attached to it. usually the carbohydrate attachment functions in cell communication-cells able to recognize each other
glycoprotein
36
New cards
define: a phospholipid with a carbohydrate attached to it. usually the carbohydrate attachment functions in cell communication-cells able to recognize each other
glycolipid
37
New cards
define: the movement of molecules through the cell membrane so that the cell can maintain homeostasis
cellular transport
38
New cards
define: does not require energy from the cell to move the molecule through the cell membrane
passive transport
39
New cards
define: molecules move from high to low concentration through the cell membrane without using energy
passive transport
40
New cards
define: movement of molecules from high to low concentration through the membrane. defined accordingly to solutes dissolved in water.
osmosis
41
New cards
define: molecules move from high to low concentration through the cell membrane using a channel protein. cellular energy is not used
facilitated diffusion
42
New cards
define: high concentration of water outside of cell/low concentration of water inside the cell water moves into the cell causing the cell to swell
hypotonic
43
New cards
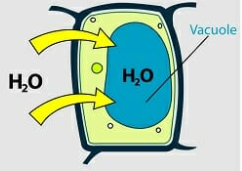
whats this
hypotonic
44
New cards
define: high concentration of water inside the cell/low concentration of water outside of cell. causes cell to shrink
hypertonic
45
New cards
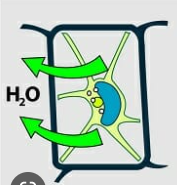
whats this??
hypertonic
46
New cards
define: water concentration is equal inside and outside of cell. no change in size
isotonic
47
New cards
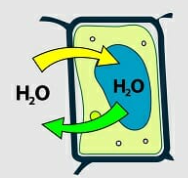
whats this
isotonic
48
New cards
define: when molecules enter/leave cell but cellular energy is required. usually the energy is supplied by ATP
active transport
49
New cards
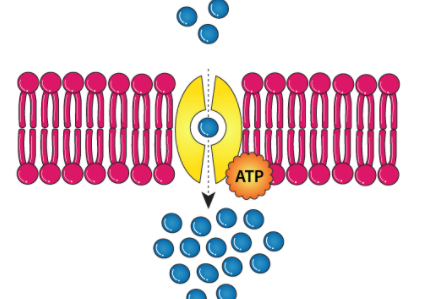
who is this man
active transport
50
New cards
define: process of moving very large molecules out of cell. they are too large to use a transport so the golgi body forms a vesicle around the molecule
exocytosis
51
New cards
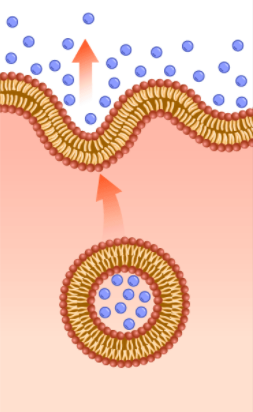
whats this
exocytosis
52
New cards
define: process of moving very large molecules into the cell. they are too large to use a transport protein so cell membrane engulfs the molecule and forms a vesicle around the molecule
endocytosis
53
New cards
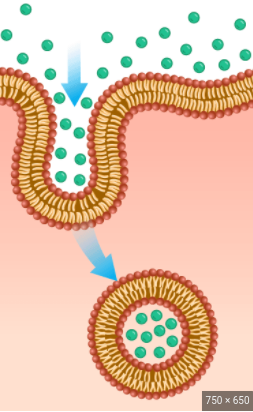
whats this
endocytosis
54
New cards
define: bringing in a liquid using endocytosis
pinocytosis
55
New cards
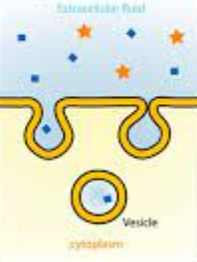
whats this
pinocytosis
56
New cards
define: bringing in a solid using endocytosis
phagocytosis
57
New cards
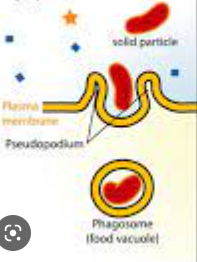
whats this
phagocytosis
58
New cards
define: receptor cites are located on the cell membrane; for a molecule to be accepted it has to fit the shape of the receptor
receptor-mediated endocytosis
59
New cards
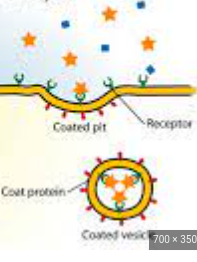
whats this
receptor-mediated endocytosis
60
New cards
what is used for energy in active transport?
ATP