Overview of Artificial Intelligence and Its Applications
1/95
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
is the field of computer science that focuses on creating machines that can think and learn like humans.

History of AI
AI has a rich history that dates back to the 1950s, when the term 'artificial intelligence' was first coined.
Applications of AI in Healthcare
AI can help doctors and healthcare professionals make more accurate diagnoses, develop personalized treatment plans, and discover new drugs.
Applications of AI in Finance
AI can help banks and financial institutions detect fraudulent activities, make investment decisions, and automate routine tasks.
Applications of AI in Manufacturing
AI can help optimize production processes, improve quality control, and reduce costs.
Applications of AI in Transportation
AI can help develop autonomous vehicles, optimize traffic flows, and improve logistics.
Applications of AI in Retail
AI can help retailers analyze customer data, develop personalized marketing campaigns, and improve customer service.
Applications of AI in Education
AI can help personalize learning, provide real-time feedback to students, and identify areas where students may need additional support.
Machine Learning
is a subfield of AI that focuses on creating algorithms that can learn from data.
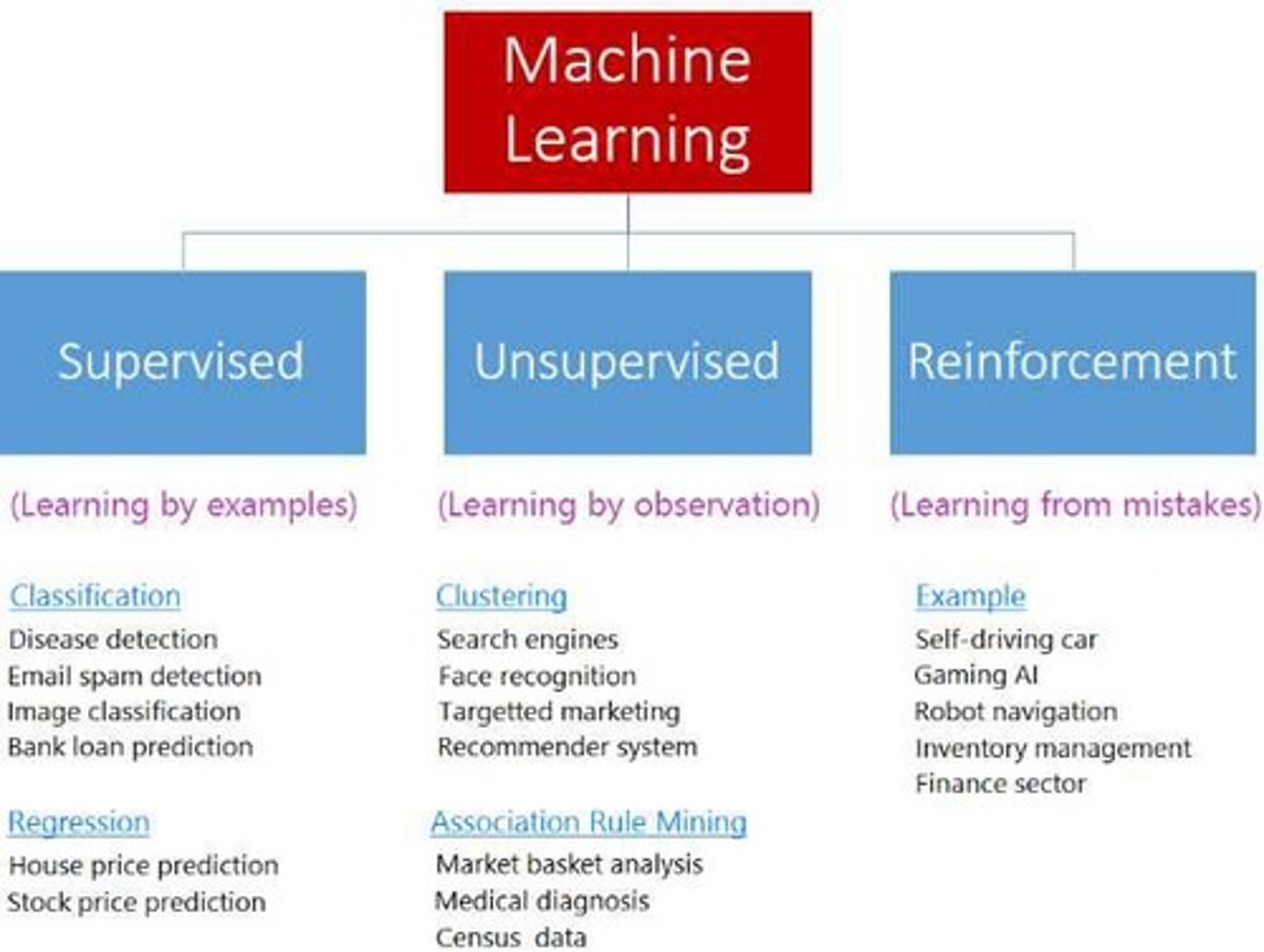
Supervised Learning
In supervised learning, the algorithm is given a set of labeled examples to learn from.
Unsupervised Learning
In unsupervised learning, the algorithm is given a set of unlabeled examples to learn from.
Reinforcement Learning
In reinforcement learning, the algorithm learns by interacting with an environment and receiving feedback in the form of rewards or punishments.
Applications of Supervised Learning
Common applications include image classification, speech recognition, and predicting stock prices.
Applications of Unsupervised Learning
Common applications include clustering, anomaly detection, and dimensionality reduction.
Applications of Reinforcement Learning
Common applications include robotics, game playing, and optimizing industrial processes.
Recommender Systems
Recommender systems use machine learning algorithms to suggest products or services to users based on their past behavior or preferences.
Fraud Detection
Machine learning algorithms can be used to detect fraudulent activities in financial transactions, such as credit card fraud.
Speech Recognition
Machine learning algorithms can be used to recognize speech and convert it into text, which can be used in applications like virtual assistants or transcription services.
Image recognition
Machine learning algorithms can be used to identify objects in images and videos, which can be used in applications like self-driving cars or security systems.
Natural language processing (NLP)
A subfield of AI that focuses on the interaction between computers and human language.
Tokenization
Breaking a text into individual words or phrases (tokens).
Part-of-speech tagging
Identifying the part of speech (noun, verb, adjective, etc.) of each word in a sentence.
Named entity recognition
Identifying and classifying named entities (such as people, organizations, and locations) in a text.
Sentiment analysis
Determining the sentiment (positive, negative, or neutral) expressed in a text.
Language translation
Converting text from one language to another.
Ambiguity in NLP
Human language is often ambiguous, and it can be challenging for computers to understand the intended meaning of a sentence.
Context in NLP
The meaning of a sentence can depend on the context in which it is used, making it difficult for computers to accurately interpret text.
Nuances in human language
Human language contains many nuances and subtle variations, such as sarcasm, irony, and metaphor, that can be difficult for computers to understand.
Data quality in NLP
NLP models require large amounts of high-quality data to train effectively, but obtaining and cleaning this data can be time-consuming and expensive.
Multimodal learning
Combining text with other modalities, such as images and video, to create more comprehensive and accurate models.
Transfer learning
Using pre-trained models to improve the performance of NLP tasks, particularly in low-resource settings.
Explainability in NLP
Developing NLP models that are more transparent and explainable, allowing users to understand how the model arrived at its predictions.
Contextual understanding in NLP
Improving the ability of NLP models to understand context, including social and cultural context, to improve accuracy and reduce bias.
Computer vision
A subfield of AI that focuses on enabling machines to interpret and understand visual data from the world around them.
Object recognition
Identifying and localizing objects within an image or video.
Image classification
Assigning a label or category to an image based on its content.
Face detection
Locating and identifying faces within an image or video.
Tracking in computer vision
Following an object or multiple objects over time within an image or video.
Segmentation
Dividing an image into regions or segments based on common characteristics.
Pose estimation
Determining the position and orientation of objects within an image or video.
Self-driving cars
Computer vision is used to detect and track objects on the road, such as other vehicles, pedestrians, and traffic signals.
Security systems
Computer vision is used to monitor and detect suspicious behavior, such as unauthorized entry or theft.
Medical imaging
Computer vision is used to analyze medical images, such as X-rays and MRI scans, to aid in diagnosis and treatment planning.
Robotics
Computer vision is used to enable robots to perceive and interact with their environment, such as picking up and manipulating objects.
Augmented reality
Computer vision is used to overlay digital information onto the real world, such as in smartphone apps that recognize and label objects.
Variability in computer vision
Objects and scenes can vary in appearance due to changes in lighting, angle, and occlusion, making it challenging for machines to recognize and identify them accurately.
Scale in computer vision
Computer vision models must be able to handle images and videos of different sizes and resolutions.
Data quality in computer vision
Computer vision models require large amounts of high-quality data to train effectively, but obtaining and cleaning this data can be time-consuming and expensive.
Ethical concerns in computer vision
The use of computer vision in areas such as surveillance and facial recognition has raised ethical concerns around privacy and bias.
Bias in AI
AI systems are only as good as the data they are trained on. If the data is biased or incomplete, it can lead to biased decisions and perpetuate discrimination.
Privacy concerns in AI
AI systems often rely on large amounts of data, including personal information, raising concerns about privacy and data protection.
Impact of AI on the workforce
As AI becomes more prevalent, it has the potential to disrupt industries and lead to job displacement.
Accountability and transparency in AI
It is important to ensure that AI systems are transparent and accountable, with understandable decision-making processes and a clear chain of responsibility.
Fairness and justice in AI
AI systems have the potential to exacerbate existing inequalities and injustices, making it important to ensure that AI promotes fairness and justice.
Trust and transparency in AI
Ethical considerations in AI include issues such as bias, privacy, and the impact on the workforce.
Five areas of ethical considerations in AI
Fairness and bias, trust and transparency, accountability, social benefit, and privacy and security.
Deep learning
A subset of machine learning that involves neural networks with many layers.
Applications of Deep Learning
Deep learning has a wide range of applications across industries, such as detecting cancer in healthcare, fraud detection in finance, and object detection in autonomous driving.
Challenges of Deep Learning
Deep learning is complex and computationally intensive, requiring large amounts of data for training, facing issues like overfitting, and lacking interpretability.
Future of Deep Learning
Despite challenges, deep learning is rapidly advancing, with potential to solve complex problems and transform industries, while raising ethical concerns about bias and discrimination.
Robotics
The combination of AI, machine learning, and engineering to create intelligent machines that can interact with the physical world.
Types of Robotics
Different types of robots include industrial robots for manufacturing, service robots for healthcare, and autonomous robots for transportation.
Robotics Applications
Robots are used in manufacturing for welding, painting, and assembly, in healthcare for surgery and patient care, and in transportation for autonomous vehicles and drones.
Challenges of Robotics
Robotics faces challenges such as the need for robust hardware, development of algorithms for perception and decision-making, and ensuring ethical use of technologies.
Reinforcement Learning
A type of machine learning that focuses on teaching machines how to learn by trial and error.
Neural networks
Computational models inspired by the human brain, consisting of interconnected nodes (neurons) that process data.
Computational power
The capacity of a computer to process data and perform calculations, often measured in FLOPS (floating-point operations per second).
Overfitting
A modeling error that occurs when a machine learning model learns the training data too well, failing to generalize to new data.
Interpretability
The degree to which a human can understand the cause of a decision made by a machine learning model.
Artificial neural networks
Computational networks that mimic the way human brains operate, used in deep learning to recognize patterns and make decisions.
Healthcare applications of deep learning
Using deep learning to detect cancer and other diseases from medical images.
Finance applications of deep learning
Using deep learning for fraud detection and risk assessment.
Retail applications of deep learning
Using deep learning for demand forecasting and personalized recommendations.
Autonomous driving applications of deep learning
Using deep learning for object detection and recognition in self-driving cars.
Service robots
Robots designed to assist humans in tasks such as healthcare and hospitality.
Industrial robots
Robots used in manufacturing for tasks like welding, painting, and assembly.
Drones
Unmanned aerial vehicles used for various applications including surveillance and delivery.
Ethical implications of deep learning
Concerns regarding bias and discrimination in decision-making processes influenced by deep learning technologies.
Agent
An entity that interacts with an environment and learns to take actions that maximize a reward signal.
Environment
The context within which an agent operates and takes actions.
Reward Signal
Feedback received by the agent based on the outcome of its actions.
Model-based Reinforcement Learning
A type of reinforcement learning that involves building a model of the environment to make predictions about the outcomes of actions.
Model-free Reinforcement Learning
A type of reinforcement learning that learns directly from experience without relying on a model.
Applications of Reinforcement Learning
Includes robotics, game playing, and recommendation systems.
Robotics
In reinforcement learning, it is used to train robots to perform tasks such as grasping objects and navigating environments.
Game Playing
Reinforcement learning has been used to train agents to play games such as Go and chess.
Recommendation Systems
Reinforcement learning is used to personalize recommendations for users.
Challenges of Reinforcement Learning
Includes the need for large amounts of data, exploration of the environment, and balancing exploration and exploitation.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
A technology transforming the business world by automating processes, gaining insights into customer behavior, and improving decision-making.
Benefits of AI in Business
Includes increased efficiency, improved accuracy, reduced costs, and improved customer service.
AI in Customer Service
AI-powered chatbots can handle routine customer inquiries and support requests.
AI in Marketing
AI can analyze customer data and personalize marketing campaigns.
AI in Supply Chain Management
AI can optimize inventory levels, improve demand forecasting, and reduce logistics costs.
AI in Finance
AI can detect fraud, analyze financial data, and automate tasks such as loan processing and risk assessment.
Challenges of AI in Business
Includes the need for significant investment in technology and infrastructure, skilled personnel, and the potential for bias and discrimination.
Future of AI
AI is likely to become increasingly integrated into daily lives, transforming the way we live and work.