Comprehensive Review of Oral Biology and Pathophysiology for Clinical Lectures
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
leukedema features, risk factors, and tx
features = increased glycogen
risk = dark skinned races and smokers
tx = none
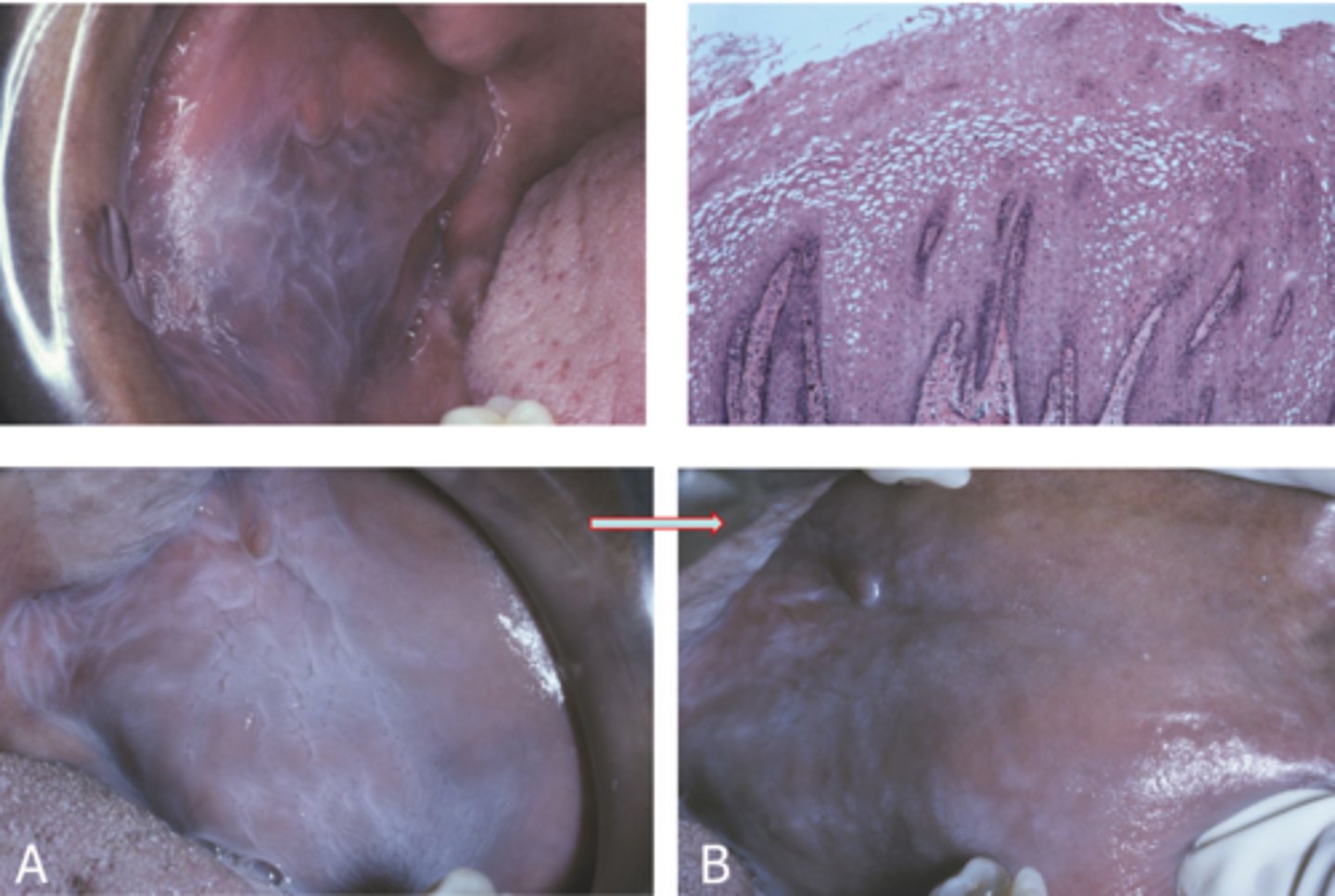
leukoplakia cause, presentation, risk factors
cause = excess keratinization of epithelium
presentation = white plaques
risk = 50+ males, tobacco use
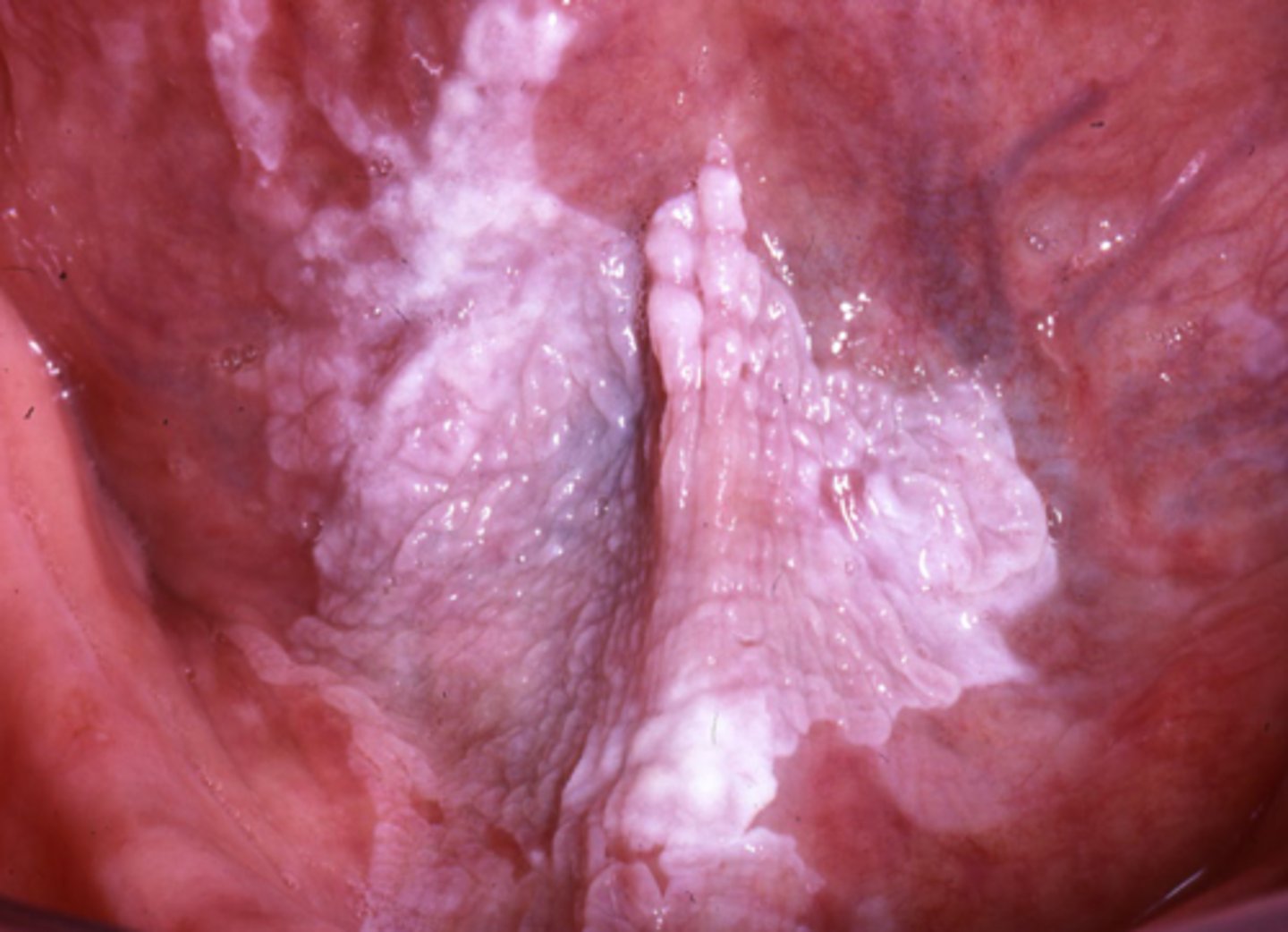
leukoplakia significance
PRECANCER
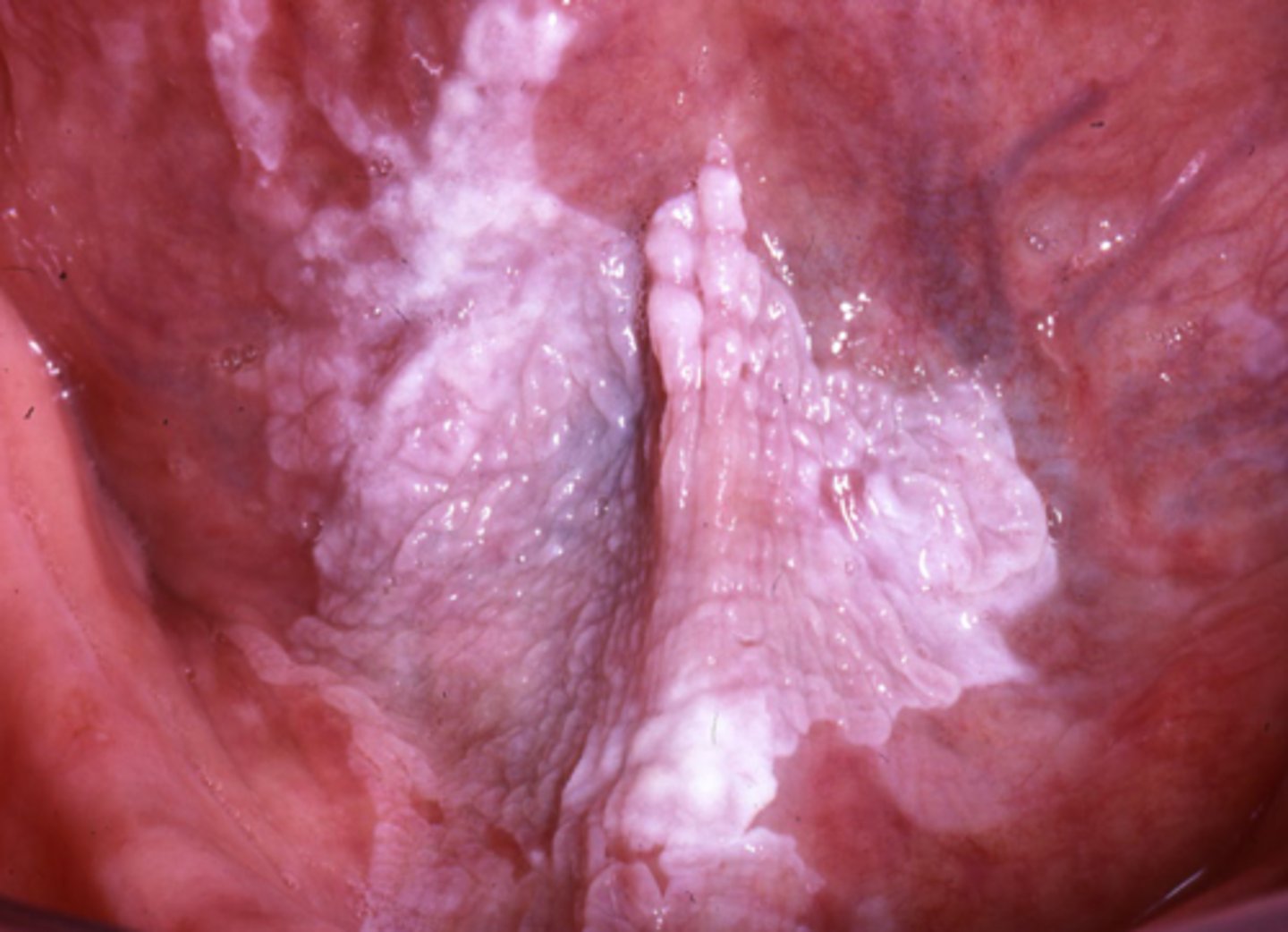
dysplasia indicates
precancer
hallmark sign of squamous carcinoma
basement membrane invasion
causes of squamous cell carcinoma
75-80% from tobacco w/ or w/out alcohol
also sun and HPV
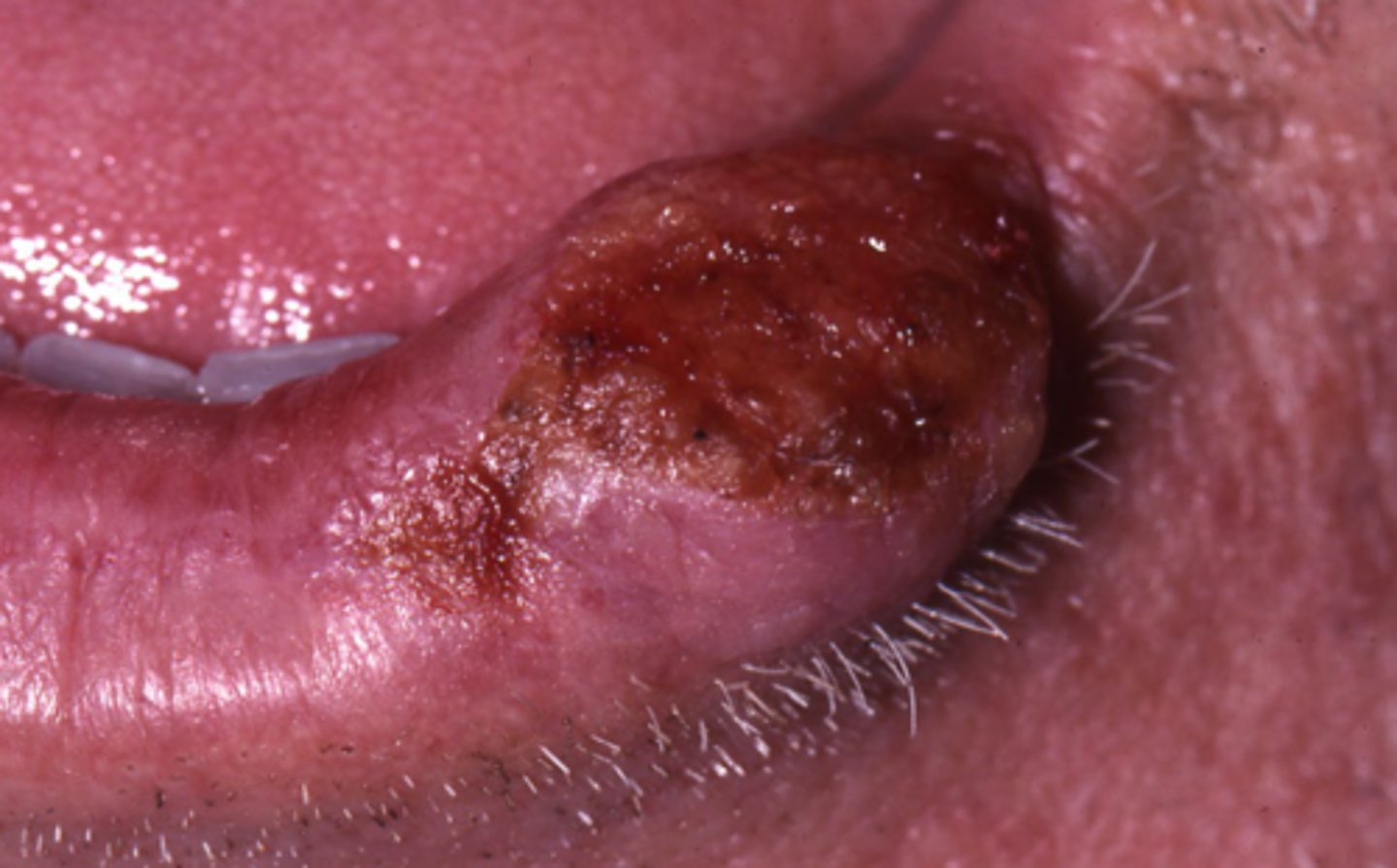
ankyloglossia
short lingual frenum
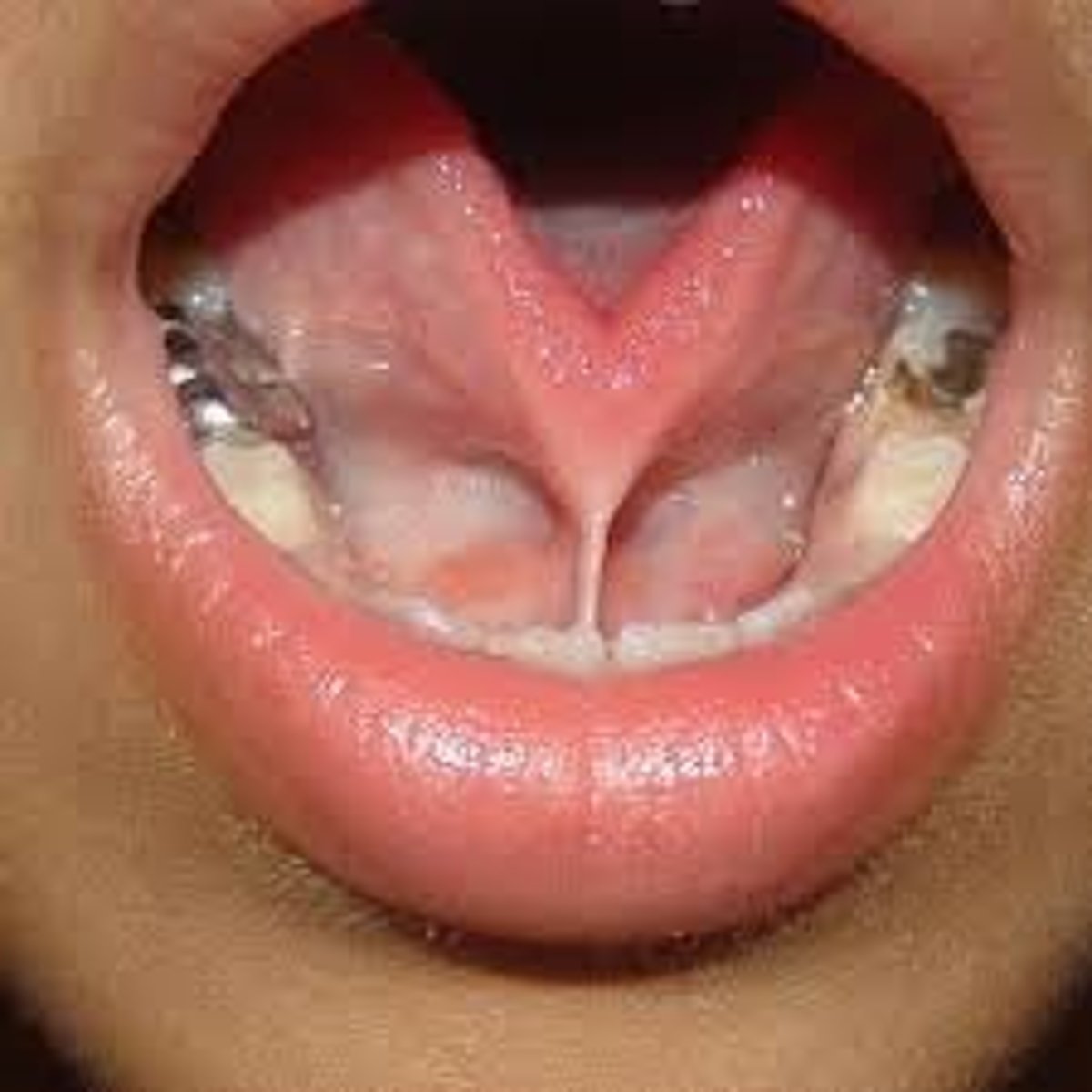
lingual thyroid cause, effect, and tx
cause = hypertrophy of thyroid tissue @ foramen cecum
effect = dysphagia, dyspnea, dysphonia
tx = do NOT remove, TH hormones
melanoma makes up ___% of skin cancers but accounts for ___% of deaths due to skin cancer
5
65
acral lentiginous melanoma impacts what body parts and is common for which group
palms, soles, oral mucosa
most common melanoma for POC
acral lentiginous melanoma prognosis
poor- 15%
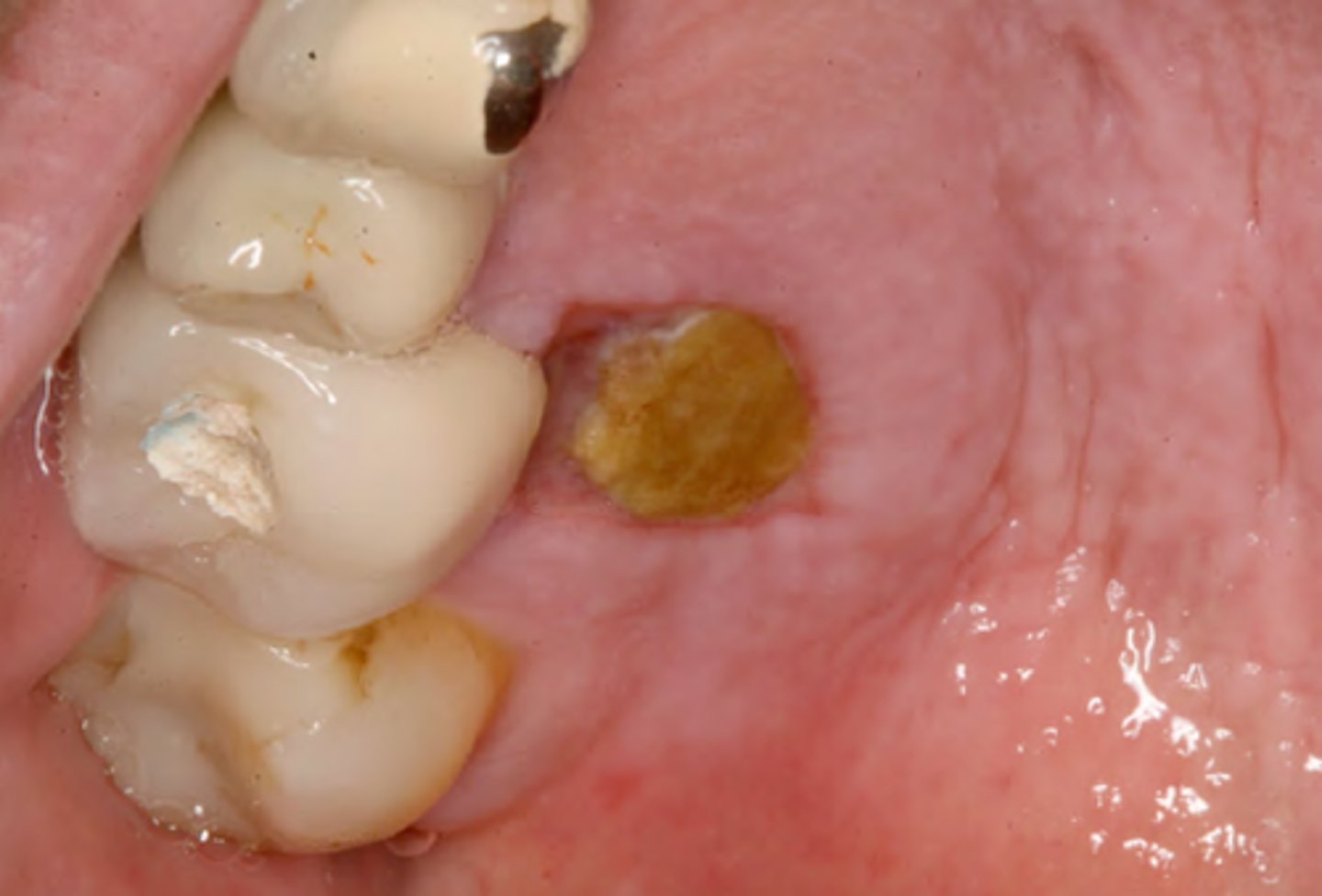
anesthetic necrosis cause and effect
cause = poor local anesthesia technique
effect = necrosis
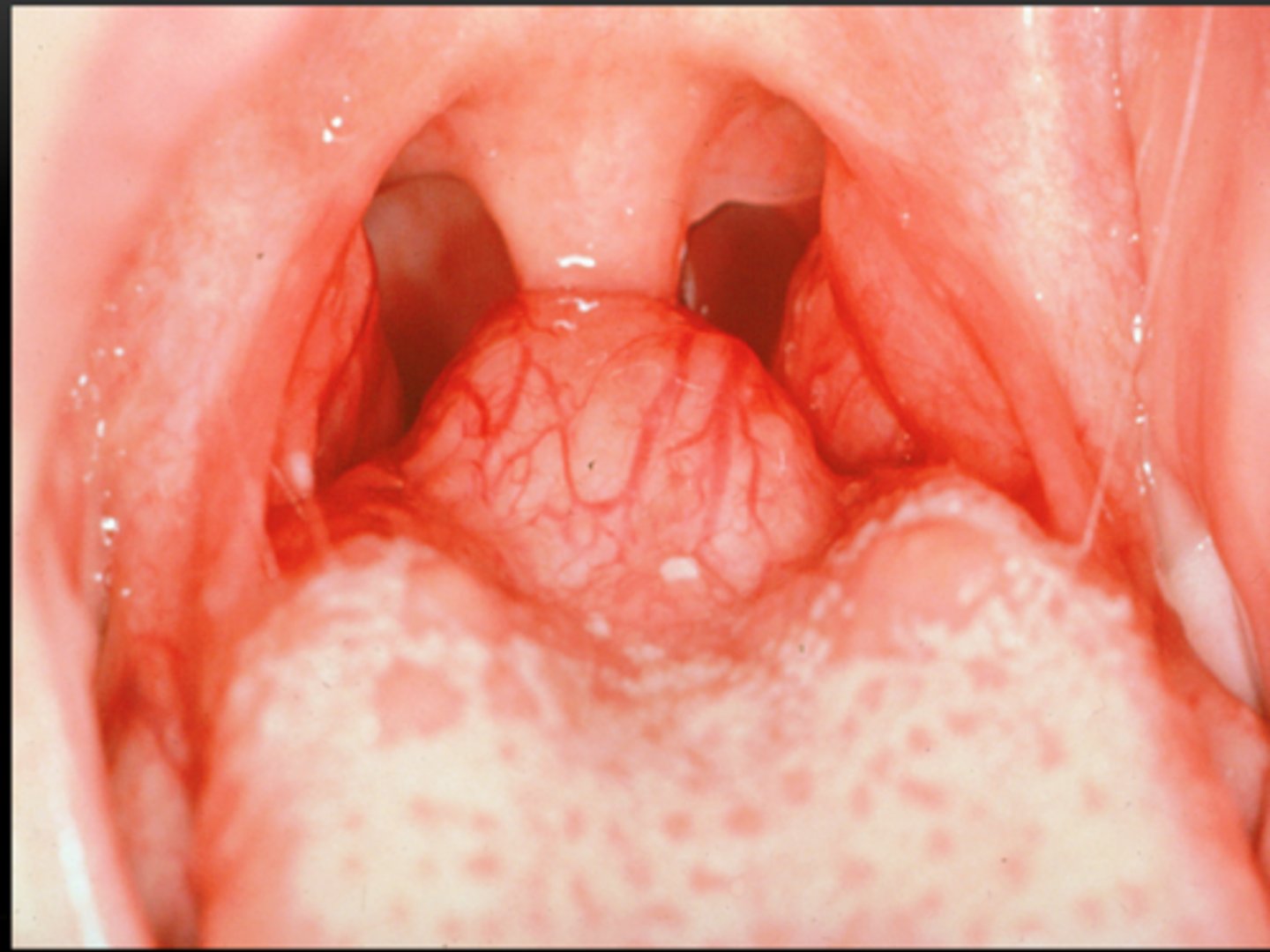
oral lymphoepithelial cyst is ___, occurs in ___, and is treated with ___
keratin filled cyst
palatine and lingual tonsils (lymphoid rich)
excision
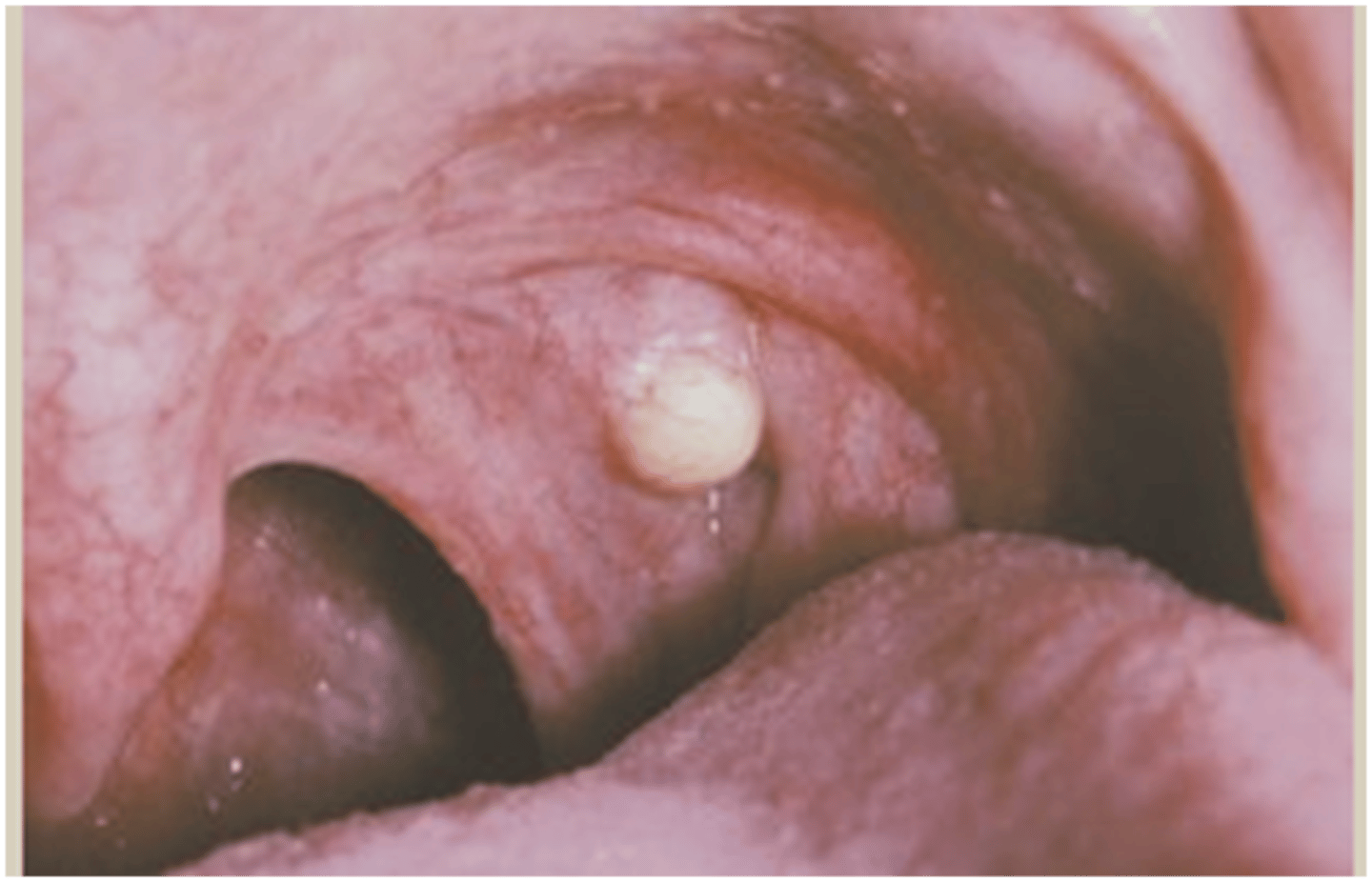
tonsillar concretions and tonsillolithiasis
tonsillar crypts filled w/ debris (surrounding tissues is uninflamed)
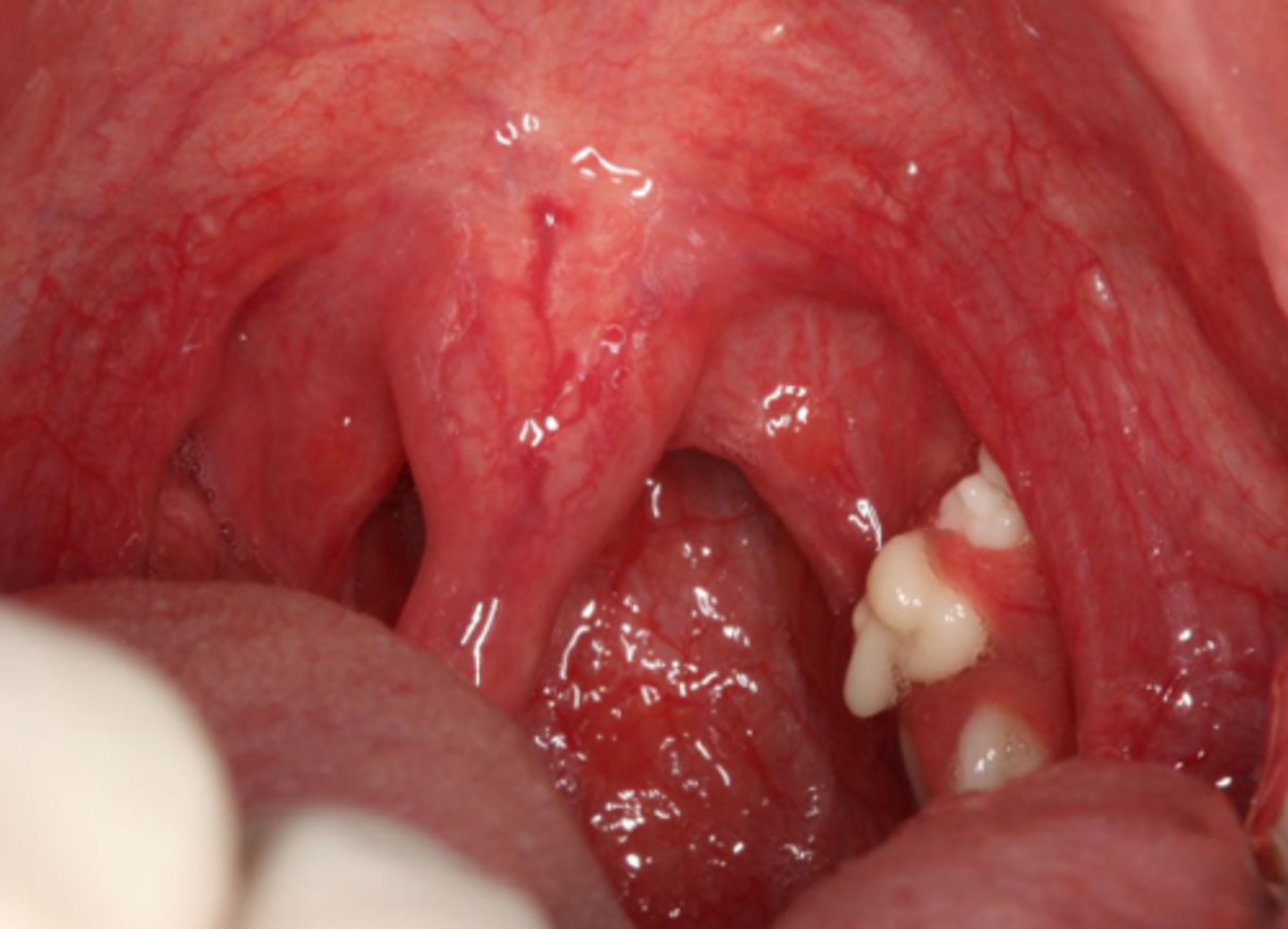
tonsillar concretions and tonsillolithiasis tx
waterpik, lasers, tonsil resection
NOT sharp instruments/ fingernails
bacterial infection of lymph nodes
TB, syphilis, cat-scratch disease
viral infection of lymph nodes
HIV, mono, herpes, measles
protozoal infections of lymph nodes
toxoplasmosis
sjogrens is an ___ disease that impacts ___ glands and will cause ___ symptoms
autoimmune
salivary and lacrimal
dry mouth/ eyes, rampant caries
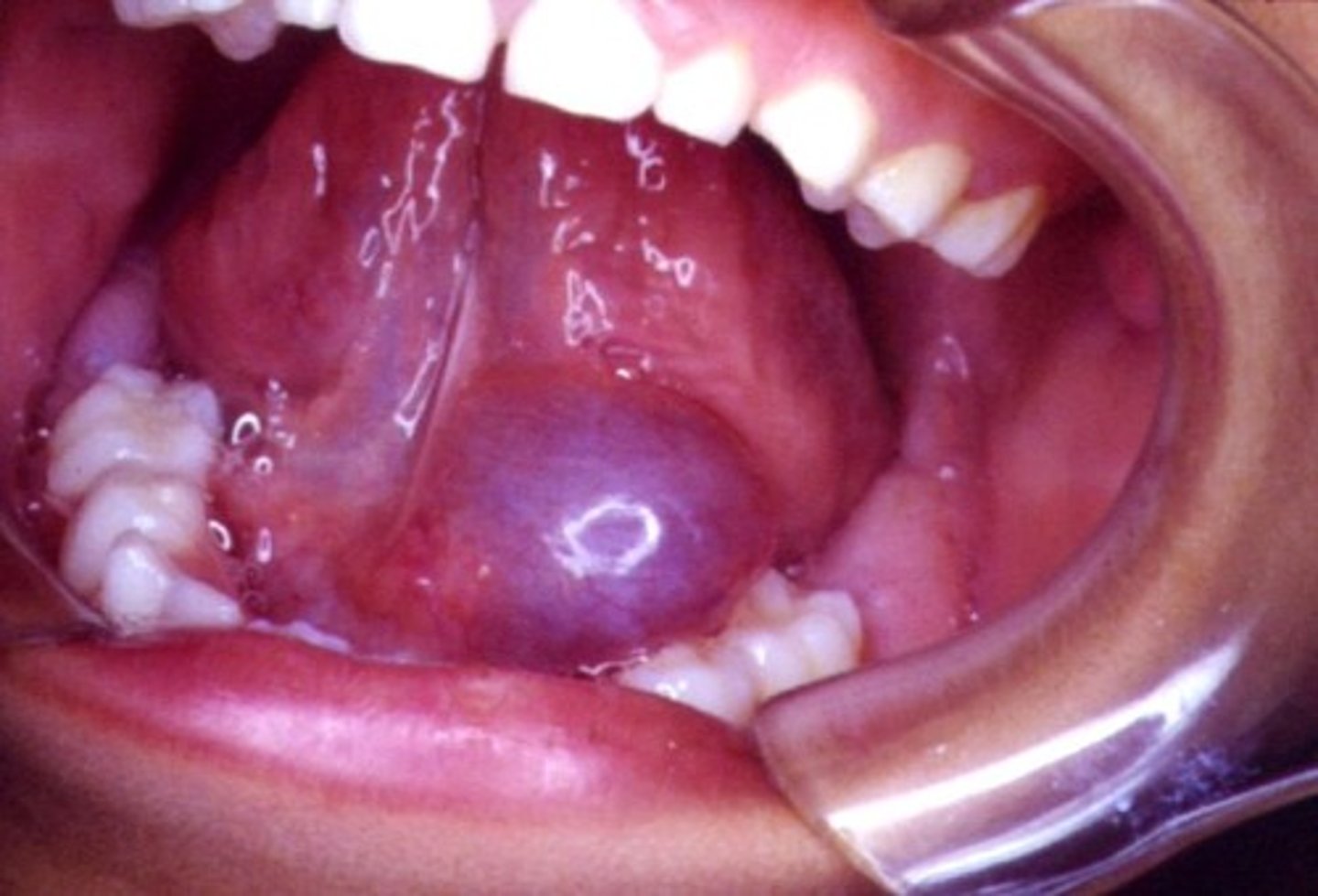
mucocele/ ranula
oral mucosal swelling, not tender
salivary gland tumor involvement
parotid = 64-80%
minor = 9-23%
submandibular = 6-11%
sublingual = <1%
minor salivary gland tumor sites of involvement
palate = 50%
lips = 20%
buccal mucosa = 15%
what cancer makes it feel like being on a descending plane?
deep lobe pleomorphic adenoma
most tumors are parotid gland are
pleomorphic adenoma (50-77%)
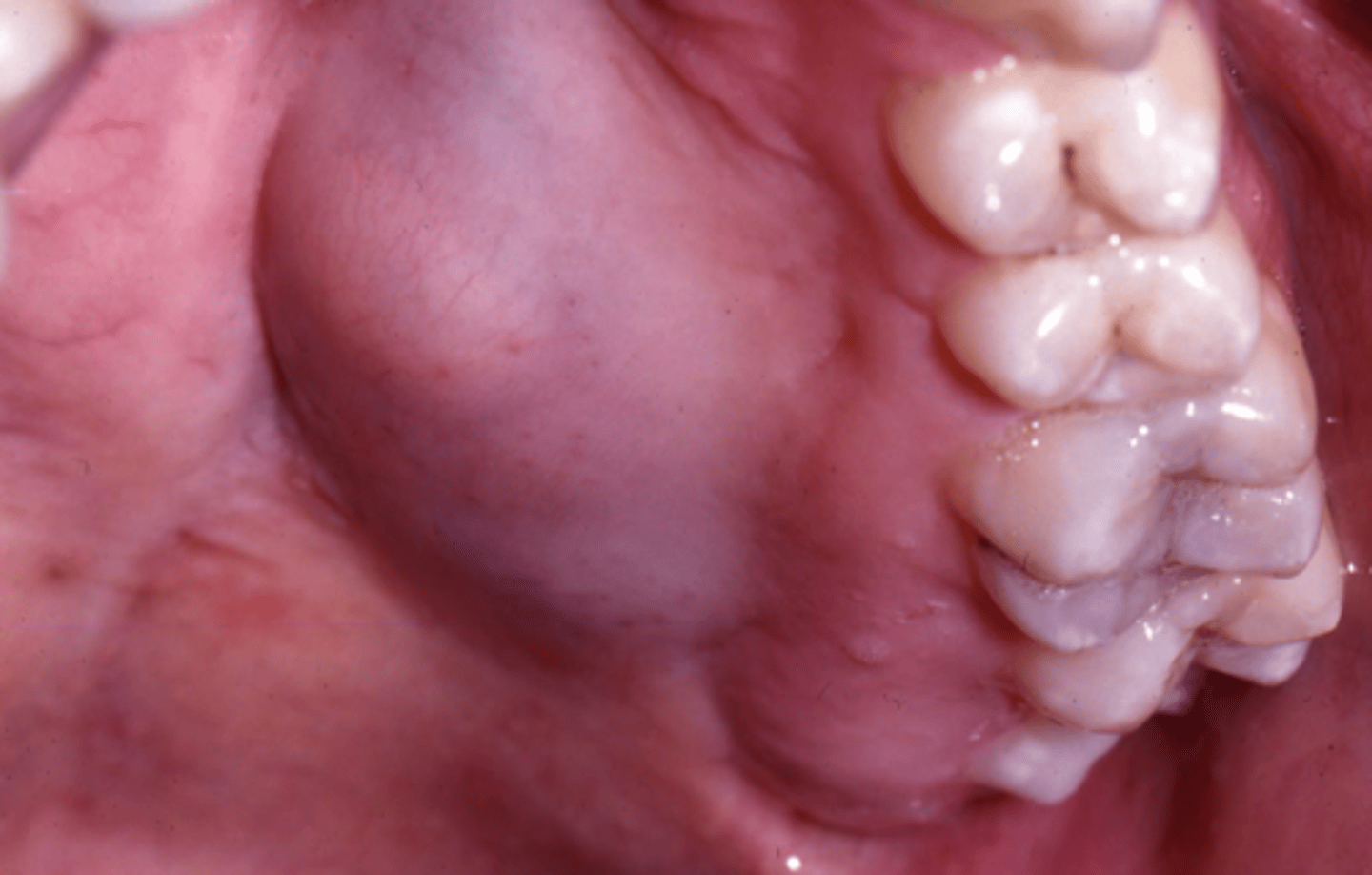
minor gland benign tumors
- slow growing
- painless
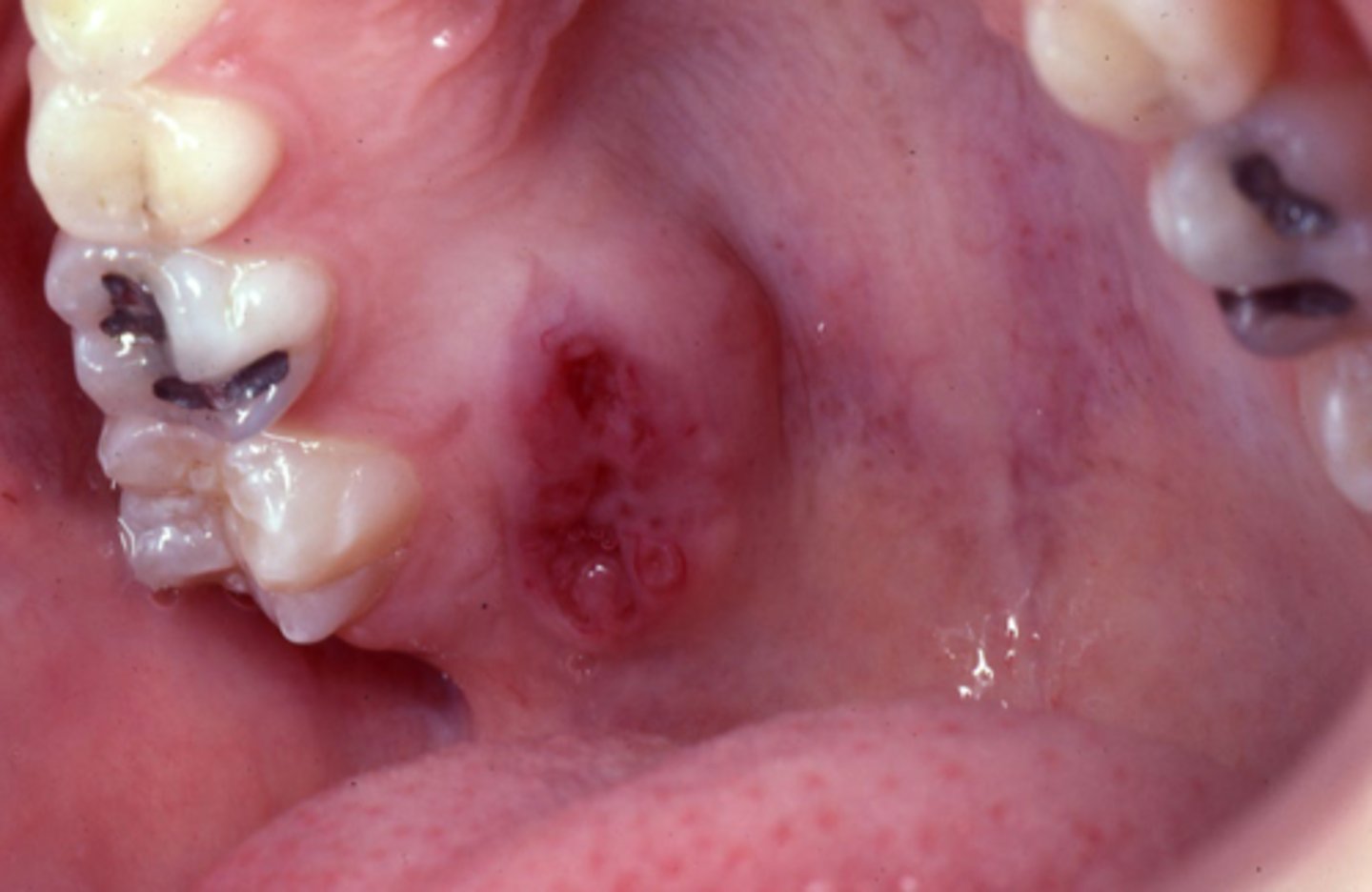
minor gland malignant tumors
- rapid growth
- variable pain
- ulcers
- increased vasculature
What is Dysplasia? (4)
What type of epithelial changes are there?
Abnormal nuclear cell size/shape
Lots of nuclei
Hyperchromatic nuclei
Precancer changes seen in leukopakia
***Basal to squamous cells
What is Acute Sialadenitis? What does it cause? (3)
Xerostomia
Diffuse and painful swelling
Purulent exudate from parotid papilla
Where are salivary gland stones most often found? When do they swell?
Submandibular glands
Swelling of glands before or during meals
Where is a Mucocele found? What is a Ranula? What pt pop? What is the tx?
Lower lip (75%), buccal mucosa, ventral tongue, FOM
Ranula = FOM
Tx: deep biopsy to take out glands or else it will come back
Pts: children
What are the pharyngeal space tumors? What is most common? How do you image?
Pleomorphic adenoma: 50-77% of tumors of the parotid gland
Found in the prestyloid compartment
Imaging occurs prior to biopsy