Human Anatomy Exam 3
1/201
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
202 Terms
CNS
central nervous system; brain and spinal cord
PNS
the sensory and motor neurons that connect the CNS to the rest of the body
somatic receptor
Sensory receptors in the skin, muscle, and joints; respond to pain, temp, proprioception (sense of knowing the position of your body without looking)
visceral receptor
Sensory receptors in the internal organs (blood vessels, stomach, heart, lungs); respond to stretch, pressure, oxygen levels, pH
somatic effector
skeletal muscle that produces voluntary movement
visceral effector
cardiac and smooth muscle fibers, glands that produce involuntary movements
afferent pathway
flow from receptor to control center
efferent pathway
flow from control center to effector
neuron
a nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system; workhouse of nervous tissue
cell body of neuron
contains nucleus and organelles; golgi, RER, mitochondria
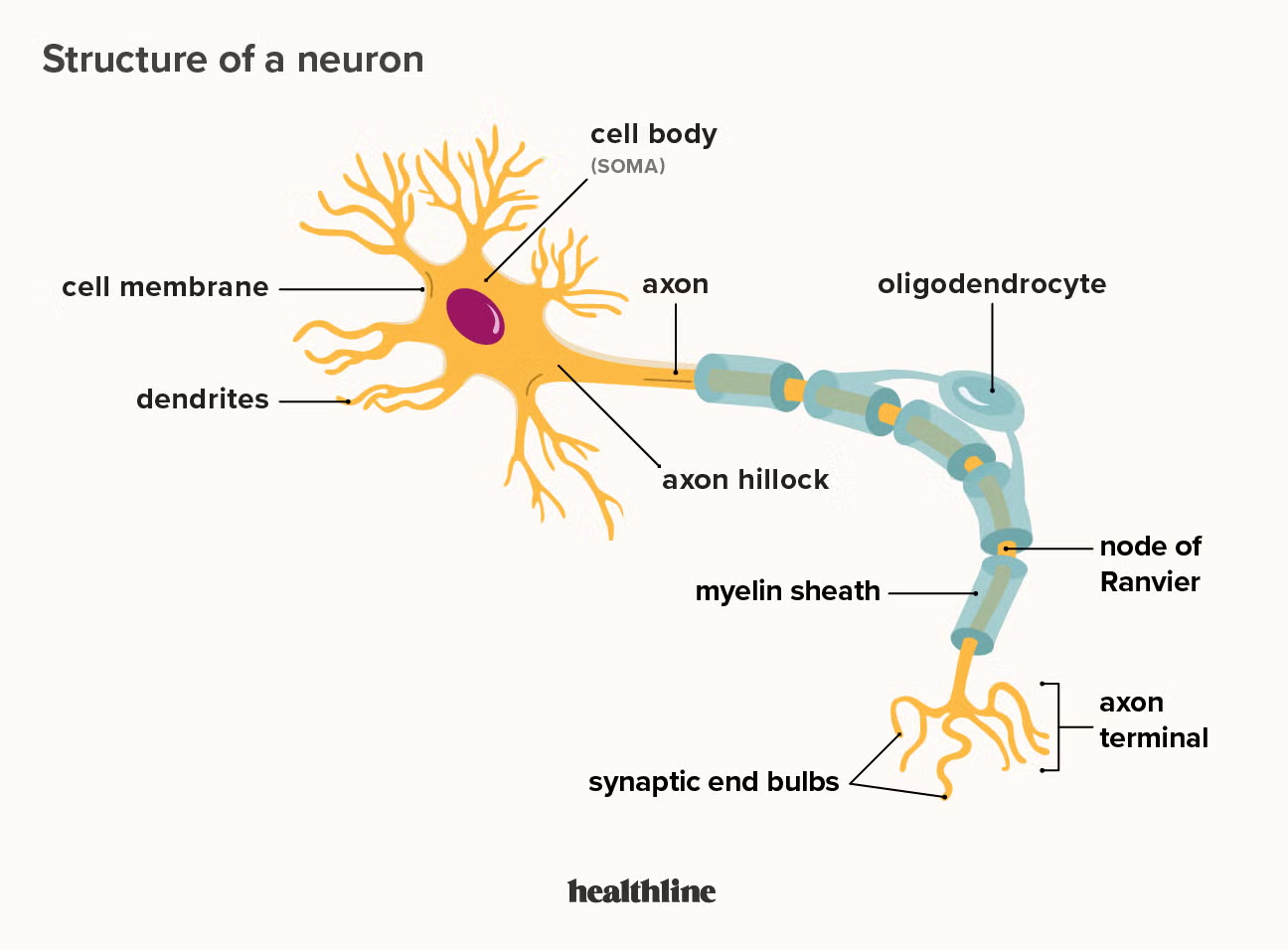
dendrites
Branchlike parts of a neuron that are specialized to receive information.
axon
the extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons or to muscles or glands
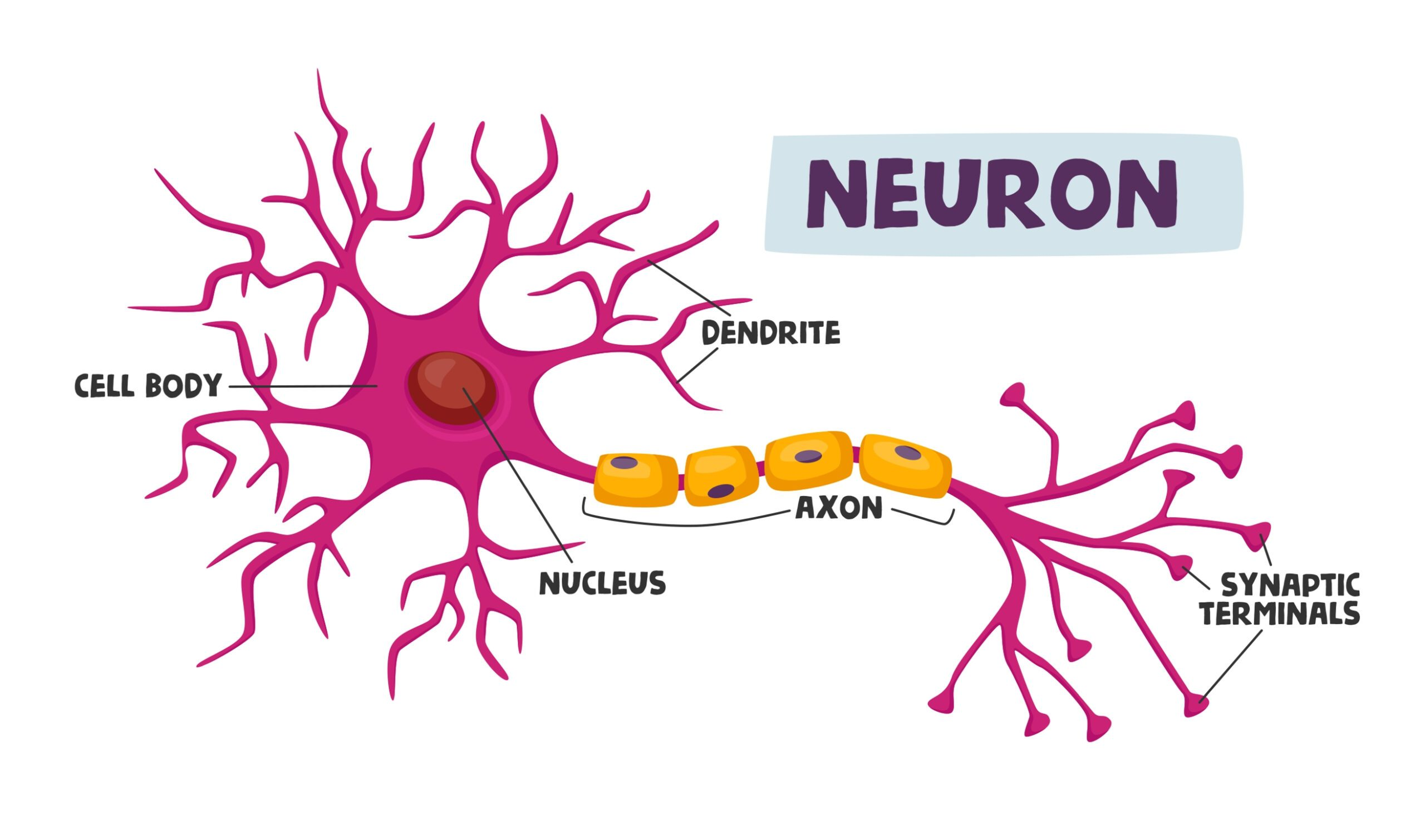
axon terminal
The endpoint of a neuron where neurotransmitters are stored
synaptic vesicles
Membrane-bounded compartments in which synthesized neurotransmitters are kept.
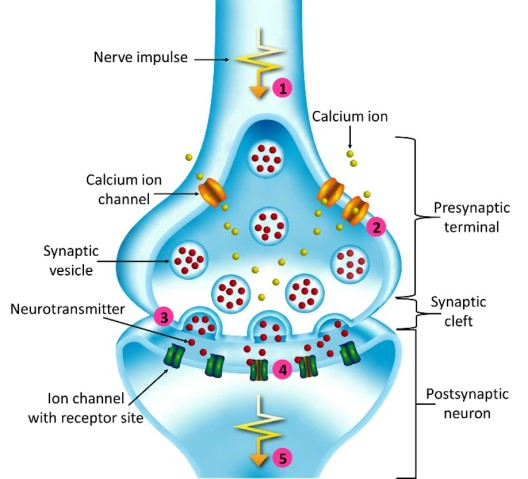
neurotransmitters
chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons
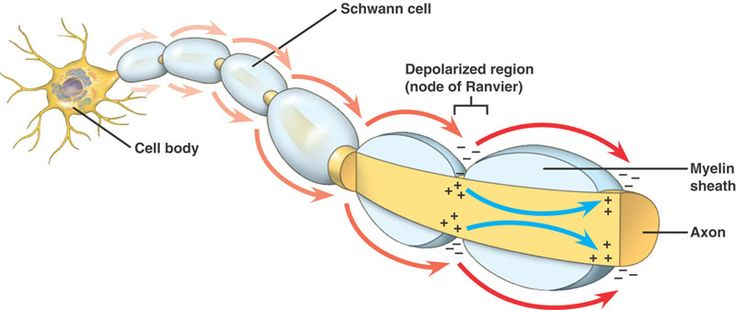
myelin sheath
covers the axon of some neurons and helps speed neural impulses
neurofibril nodes of ranvier
gaps between segments of myelin sheath
they allow the action potential to jump from node to node
synapse
the junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron
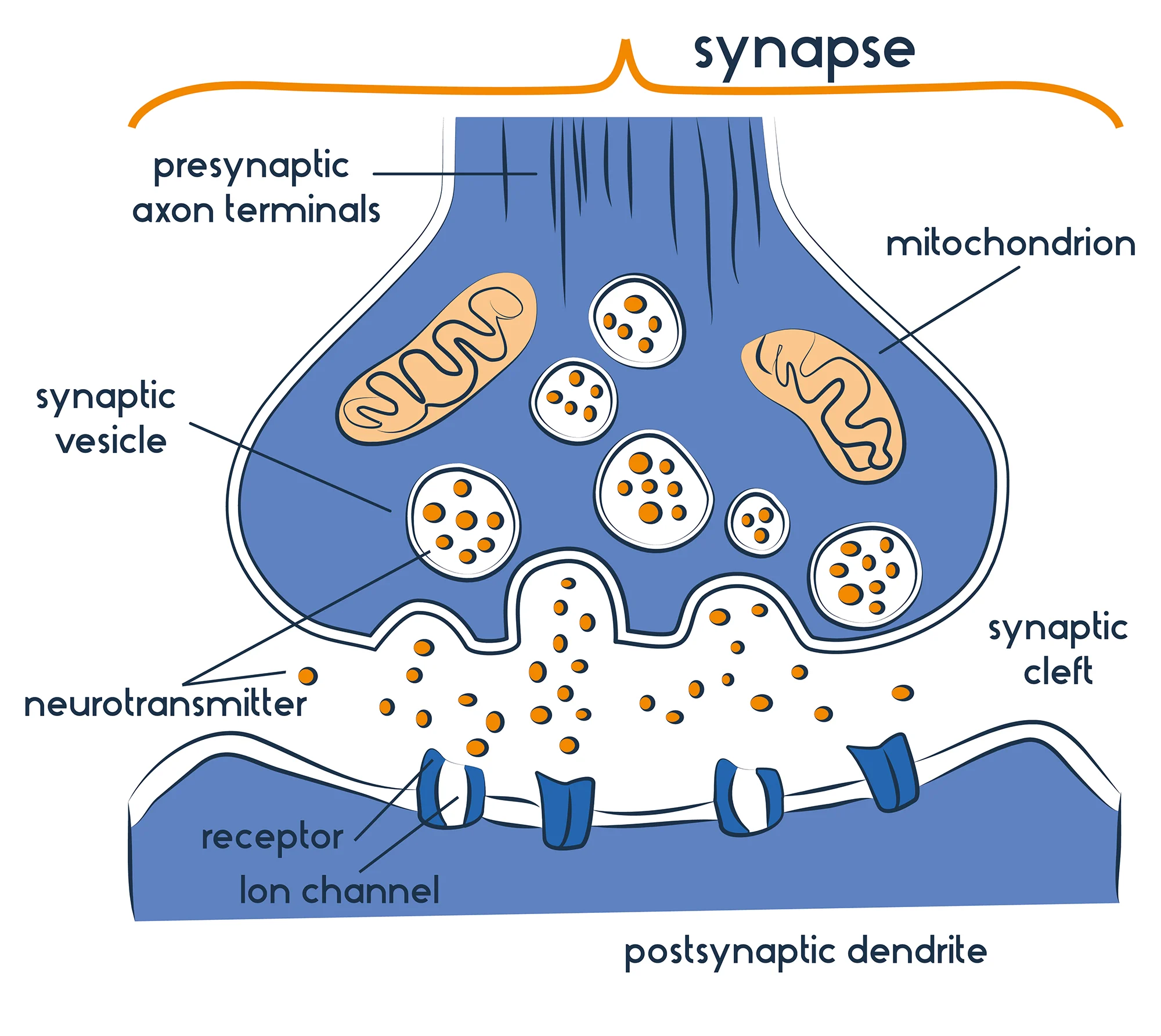
presynaptic neuron
conducts impulses toward the synapse; has neurotransmitters
postsynaptic neuron
transmits impulses away from the synapse; has neurotransmitter receptors
synaptic cleft
The narrow gap that separates the presynaptic neuron from the postsynaptic cell.
action potential
a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon
depolarization
The process during the action potential when sodium is rushing into the cell causing the interior to become more positive; action potential spreads along axon
somatic
conscious control
visceral
part of autonomic nervous system; sympathetic: in control when in fight/flight/fright; parasympathetic: in control in nonstressful situations
local potentials
excitatory and inhibitory potentials
multipolar (motor) neuron
has numerous processes (dendrites) extending from the cell body and a single axon, allowing it to receive many inputs and send signals to effectors
unipolar (sensory) neuron
only one process from the cell body that splits into a central process and a peripheral process(sensory neurons)
neuroglia
all cells of nervous tissue, expect neurons. cells that perform various supportive and protective roles for the neurons
oligodendrocytes (CNS)
forms myelin sheath in CNS
schwann cells
form myelin sheath in PNS
microglia (CNS)
Act as phagocytes, eating damaged cells and bacteria, act as the brains immune system
ependymal cells (CNS)
line the cavities of the brain (ventricles) and spinal cord (central canal) and produce cerebral spinal fluid
astrocytes (CNS)
star-shaped; processes wrap around blood vessels and form the blood brain barrier
grey matter
unmyelinated axons that appear grey because they are not wrapped in fatty myelin; unmyelinated axons carry sensations such as pain
white matter
groups of myelinated axons in the CNS
nerves
bundle of axons in PNS
tracts
bundles of axons in the CNS
neural tube
a groove formed in the top layer of differentiated cells in the embryo that eventually becomes the brain and spinal cord; The tips of the neural folds fuse with each other to form it
primary vesicles
Prosencephalon (forebrain)
Mesencephalon (midbrain)
Rhombencephalon (hindbrain)
secondary vesicles
telencephalon, diencephalon, mesencephalon, metencephalon, myelencephalon
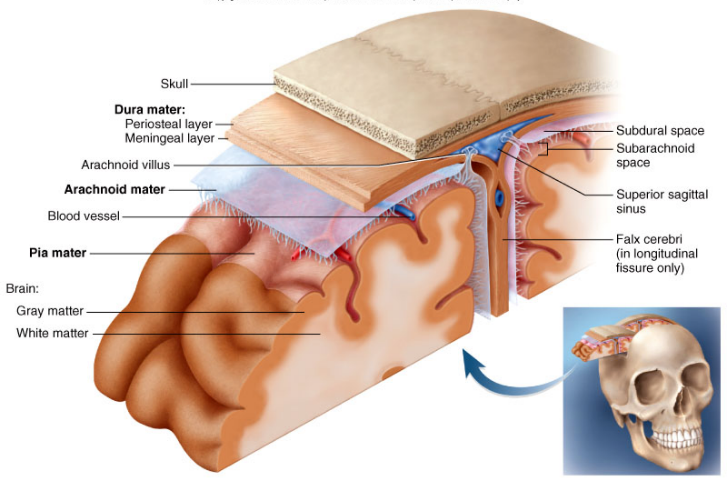
skull
frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital bones all protect brain
vertebral column
protects spinal cord
pia mater
thin, delicate inner membrane of the meninges; ends at L2
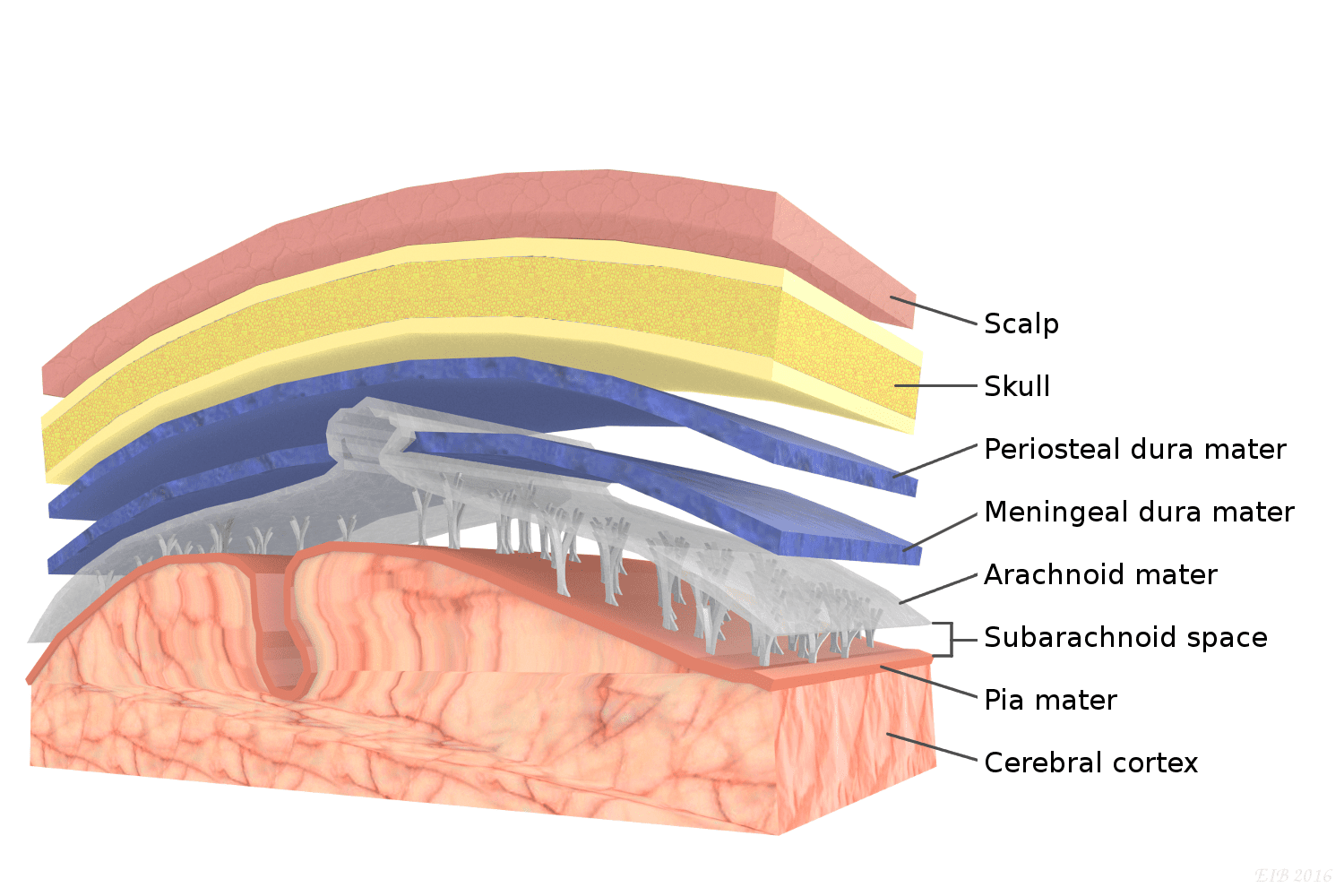
arachnoid mater
middle layer of the meninges; ends at S2
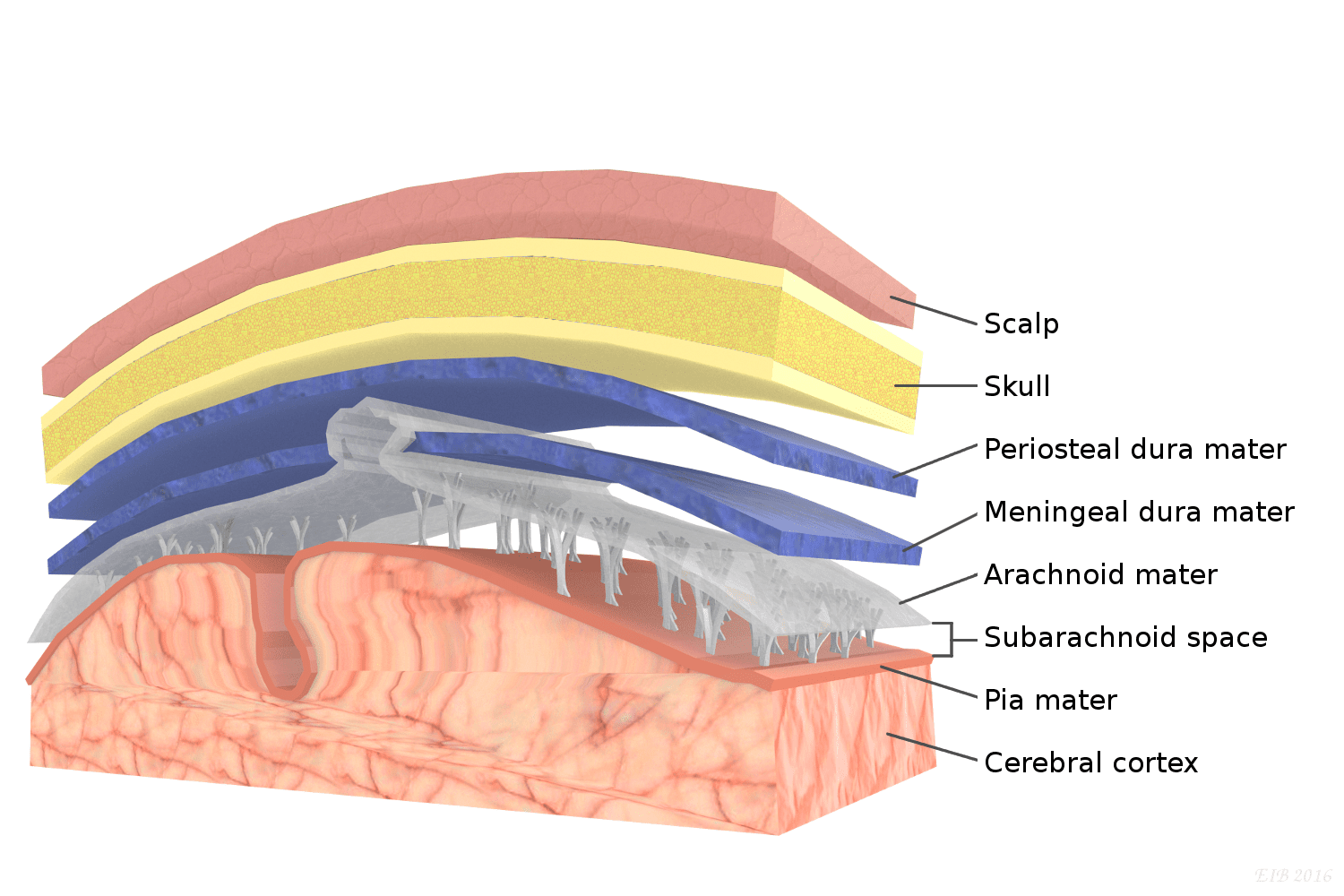
dura mater
thick, outermost layer of the meninges surrounding and protecting the brain and spinal cord; has periosteal (closer to bone) and meningeal layers which are usually fused and if they aren't the form the dural venous sinus which contain venous blood; ends at S2
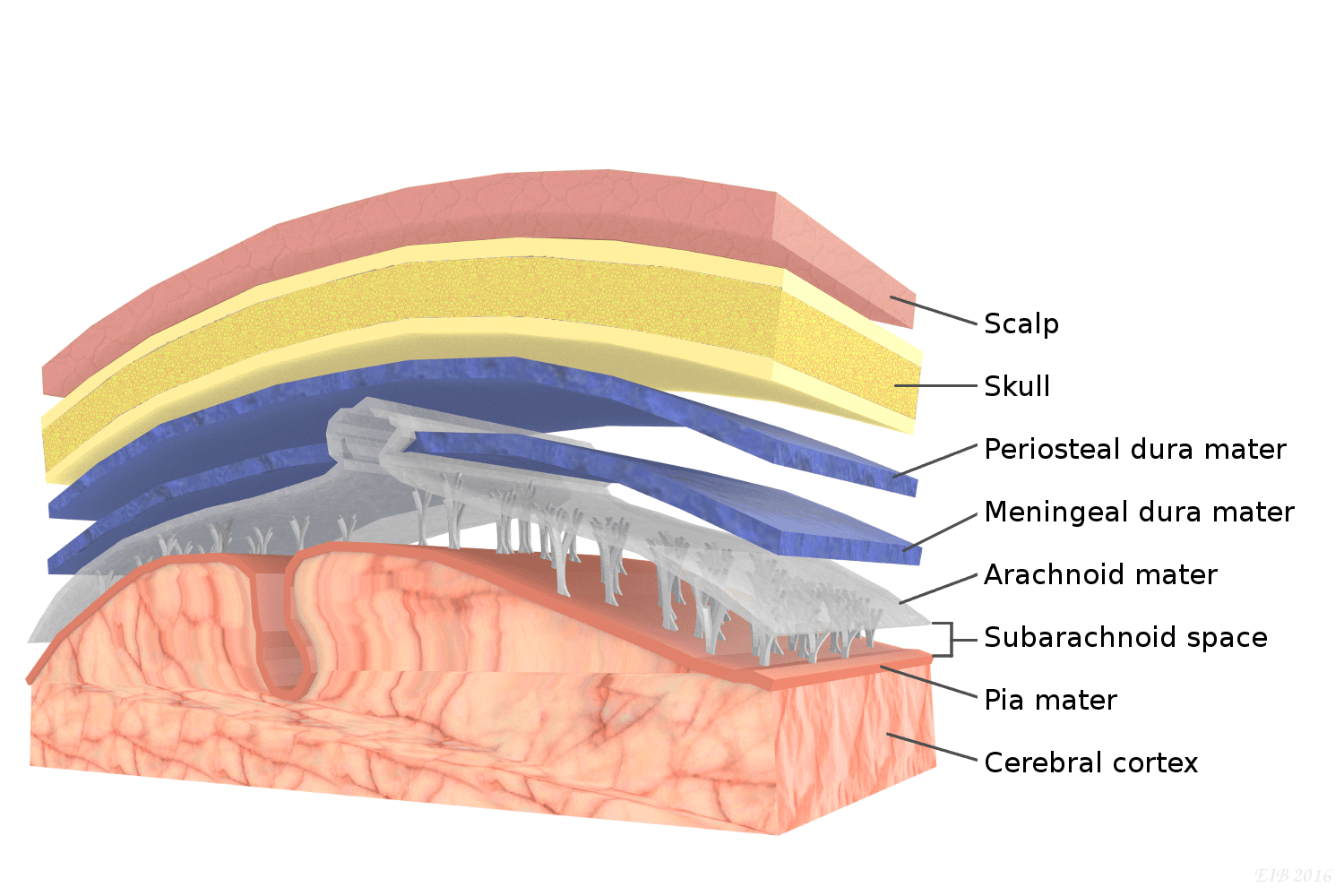
arachnoid villus
get cerebral spinal fluid from subarchanoid space into the dural venous sinus
arachnoid trabeculae
extensions of the arachnoid that occur within the subarachnoid space
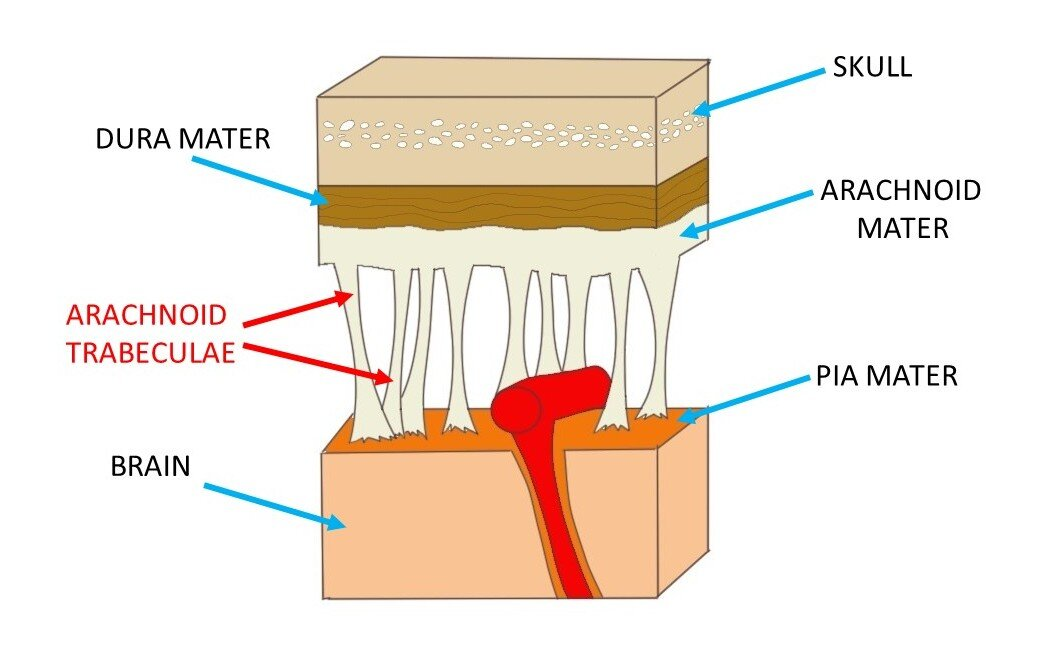
subarachnoid space
gap between pia and arachnoid
rostral neural tube
brain
caudal neural tube
spinal cord
telencephalon becomes
cerebral hemispheres and has lateral ventricle in each
lateral ventricle shape
backwards C with posterior projection
cavity in diencephalon
3rd ventricle--between left and right thalamus
interventricular foramen
connects 3rd ventricle and lateral ventricles
cavity in mesencephalon
cerebral aqueduct (connects 3rd and 4th ventricles)
4th ventricle
partial contributions from metencephalon and myelencephalon; leads into central canal of spinal cord; CSF can get out of 4th ventricle and go to the subarachnoid space through lateral openings
choroid plexus
produces CSF; where ependymal cells in the brain are paired with capillaries and they filter blood and produce CSF
forebrain
cerebrum, thalamus, hypothalamus
cerebrum
largest, L and R hemispheres --derived from telencephalon; surface is all grey matter (cell bodies and dendrites)
diencephalon
thalamus and hypothalamus; important in motor and sensory pathways and ANS
brainstem
midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata; contains nuclei of cranial nerves--these control vital functions (cardiovascular activity, respiratory control)
midbrain
derived from mesencephalon
pons
derived from metencephalon
medulla oblongata
derived from myelencephalon
cerebellum
derived from metencephalon; separated from pons by 4ht ventricle; occupies most of posterior cranial fossa; function: balance and movement
gyrus (gyri)
ridges/bumps on brain
sulcus (sulci)
grooves in brain
nucleus
a cluster of cell bodies of neurons in the CNS
tract
a cluster of axons in the CNS
fissure
deep sulcus
longitudinal fissure
separates cerebral hemispheres
transverse fissure
separates cerebrum from cerebellum
cerebral cortex
The intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells covering the cerebral hemispheres; the body's ultimate control and information-processing center.
white matter of brain
deep to cerebral cortex; has myelinated axons
cerebral nuclei
cluster of cerebral cell bdoes
thalamus
made up of unmyelinated cell bodies; 3rd ventricle is between left and right thalamus; made up of nuclei that have different functions-relates to regions of the cerebrum
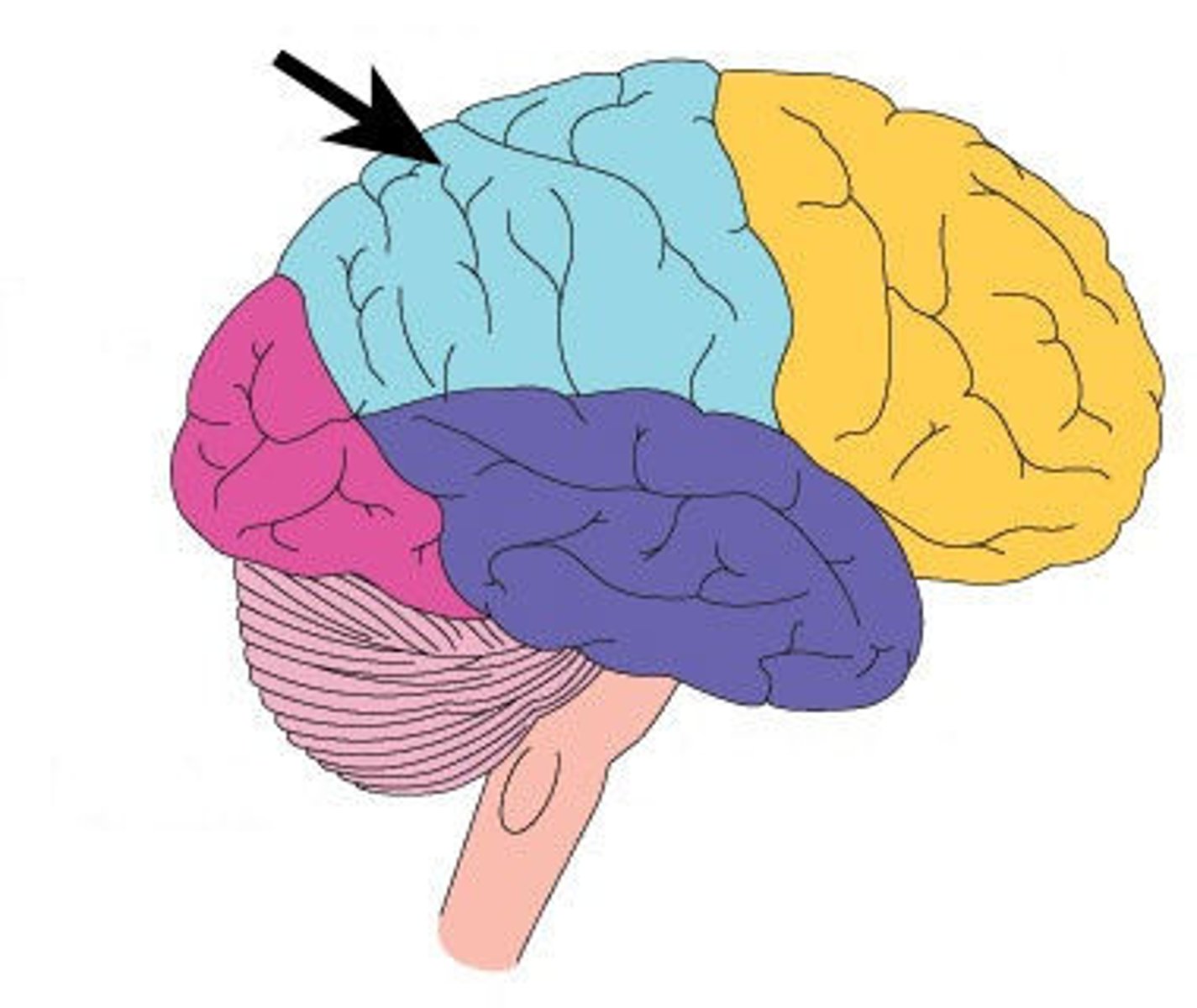
frontal lobe
The lobe at the front of the brain associated with movement, speech, and impulsive behavior; left side contains brocas area
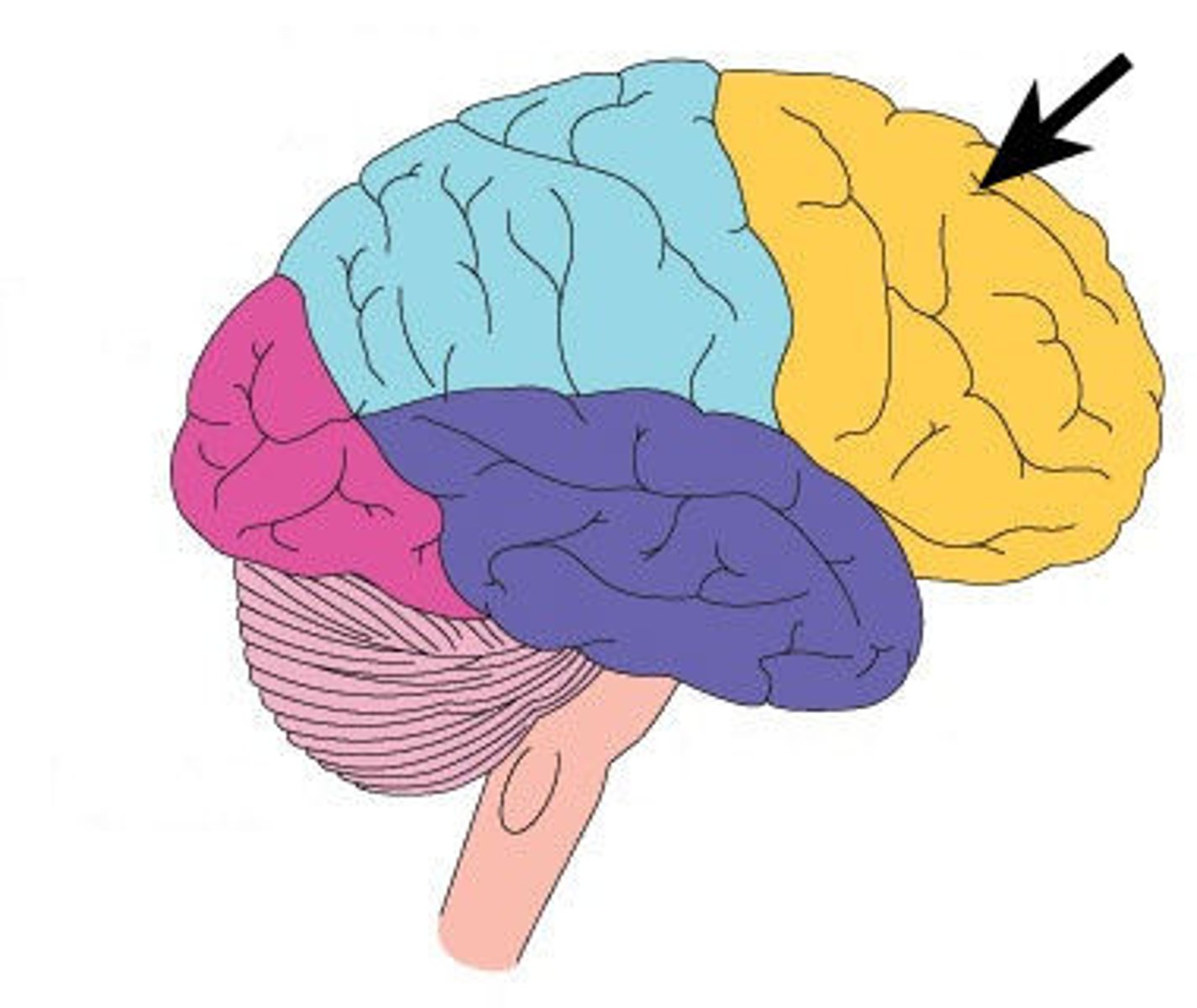
parietal lobe
portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the top of the head and toward the rear; receives sensory input for touch and body position; has Wernicke's area
central sulcus
separates frontal and parietal lobes
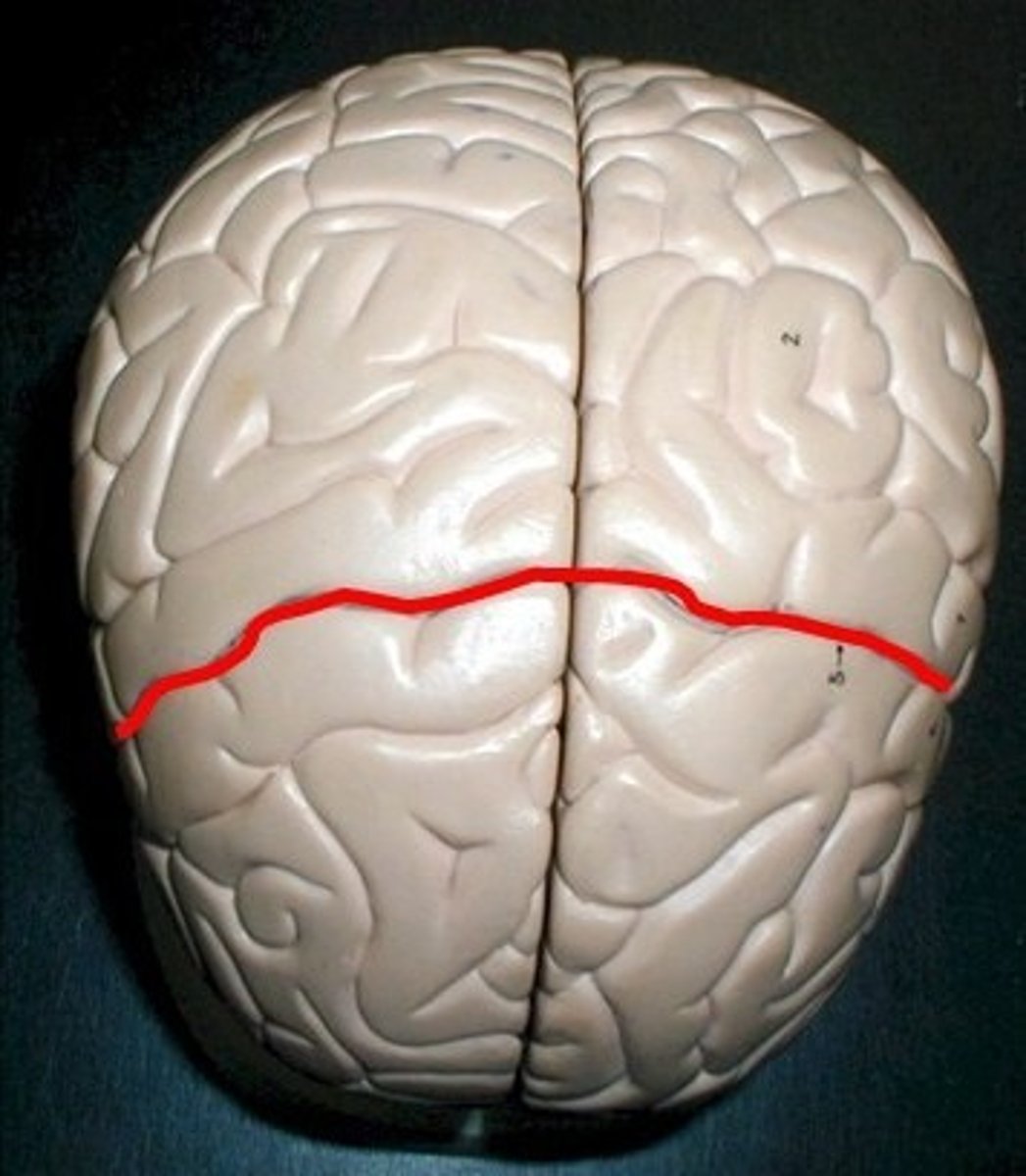
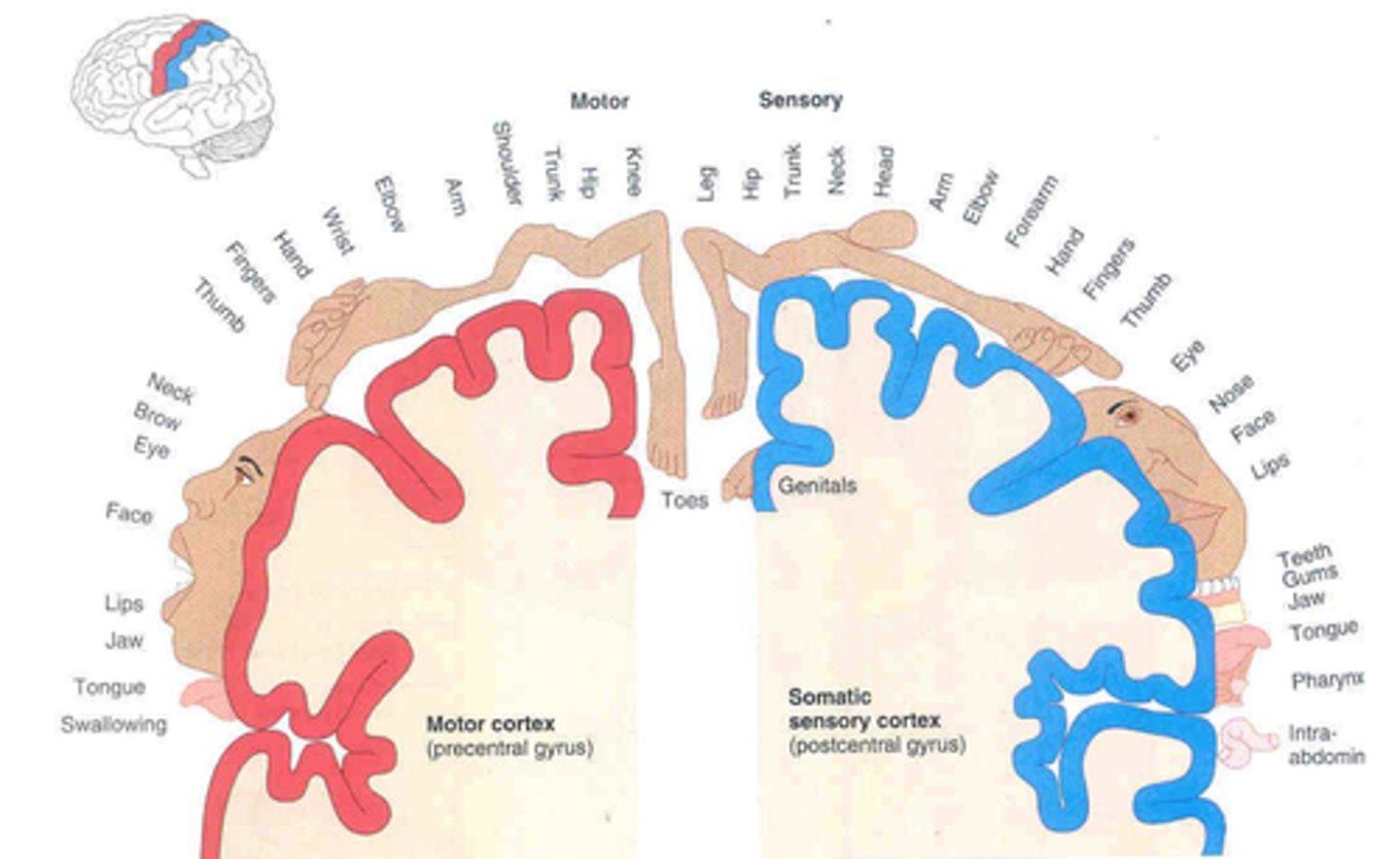
precentral gyrus
motor cortex; GSE pathways begin here
postcentral gyrus
sensory cortex; GSA pathways end here
occipital lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information
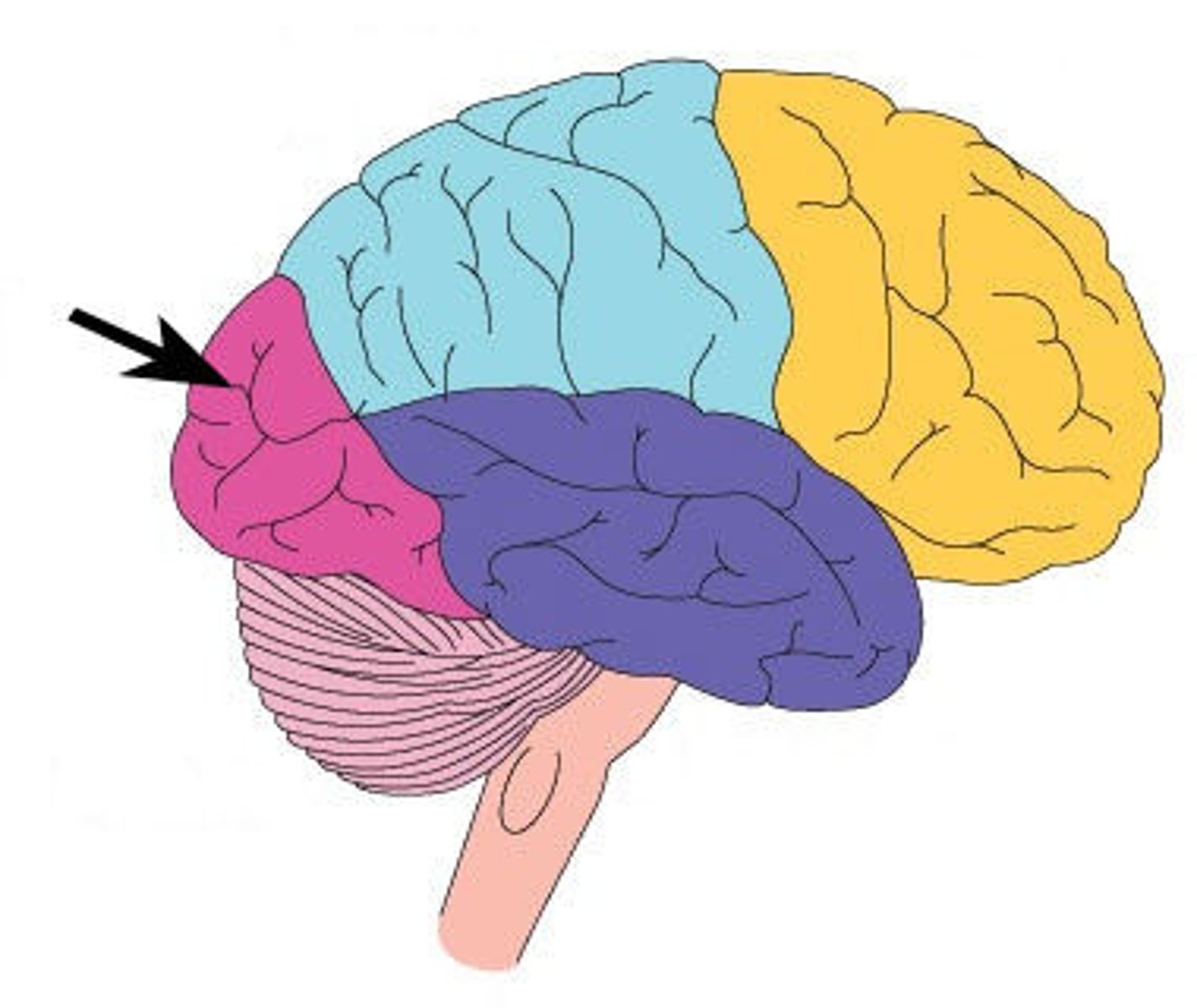
temporal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex responsible for hearing and language; long term memory
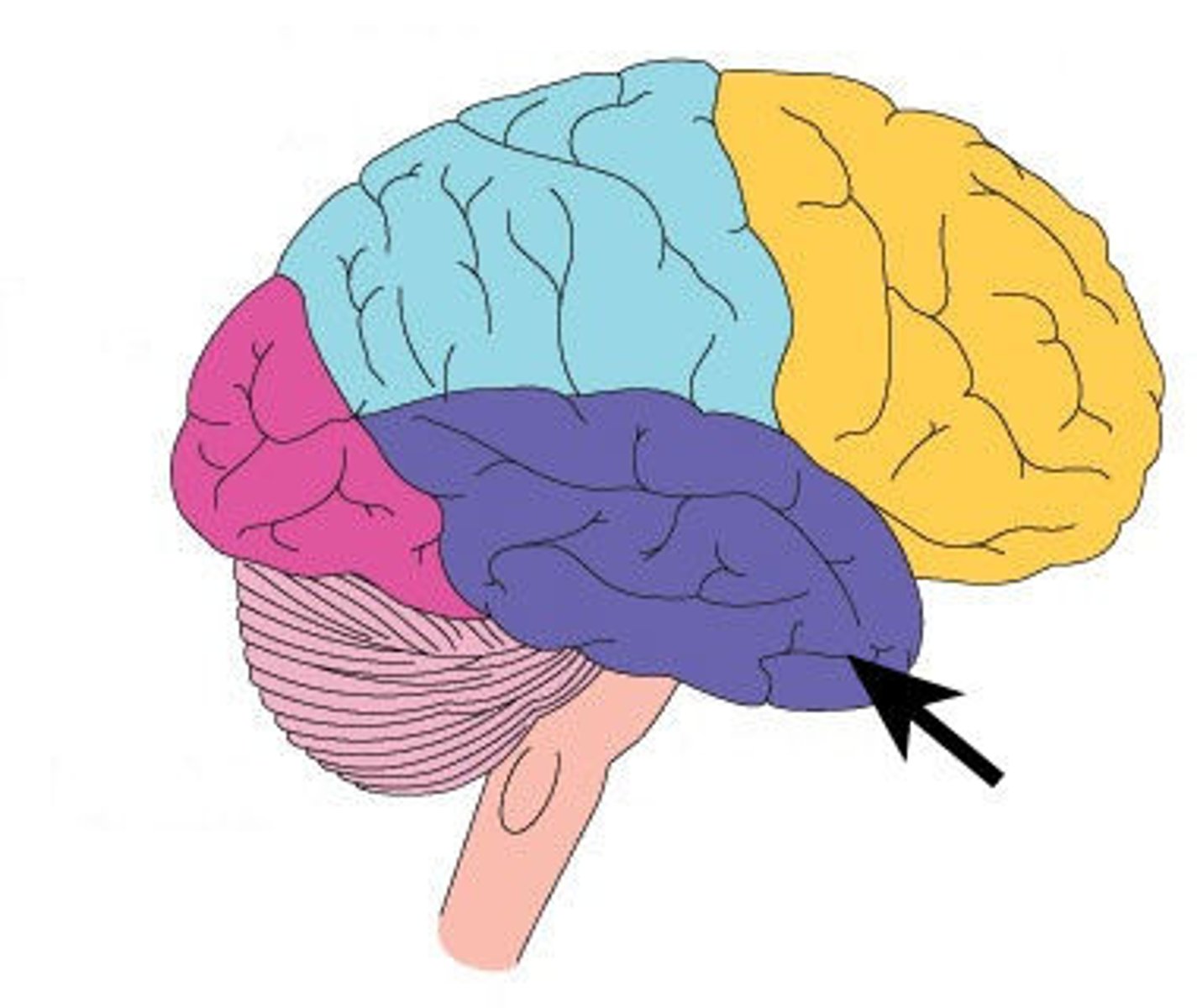
lateral sulcus
Separates temporal lobe from parietal and frontal lobes
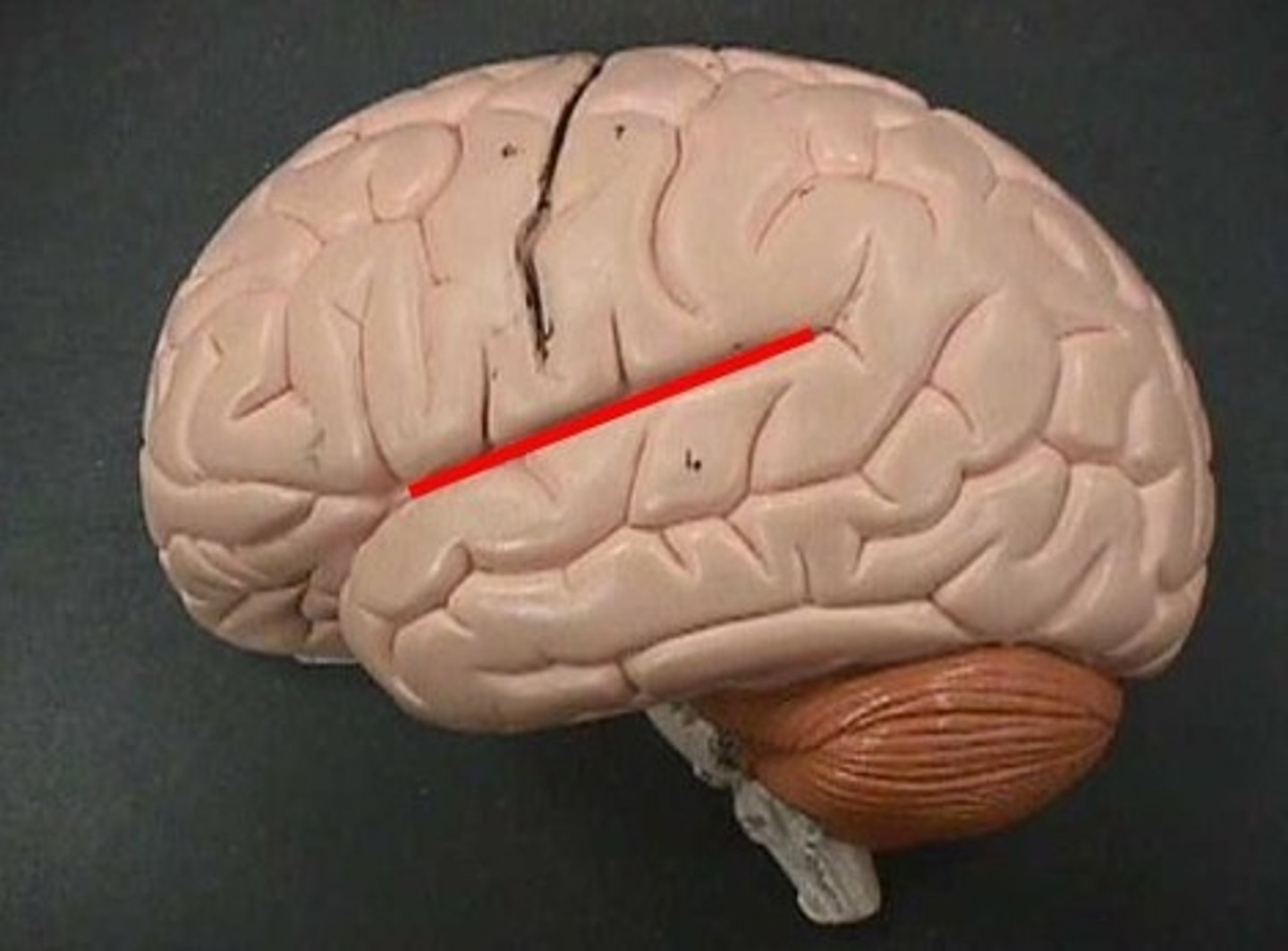
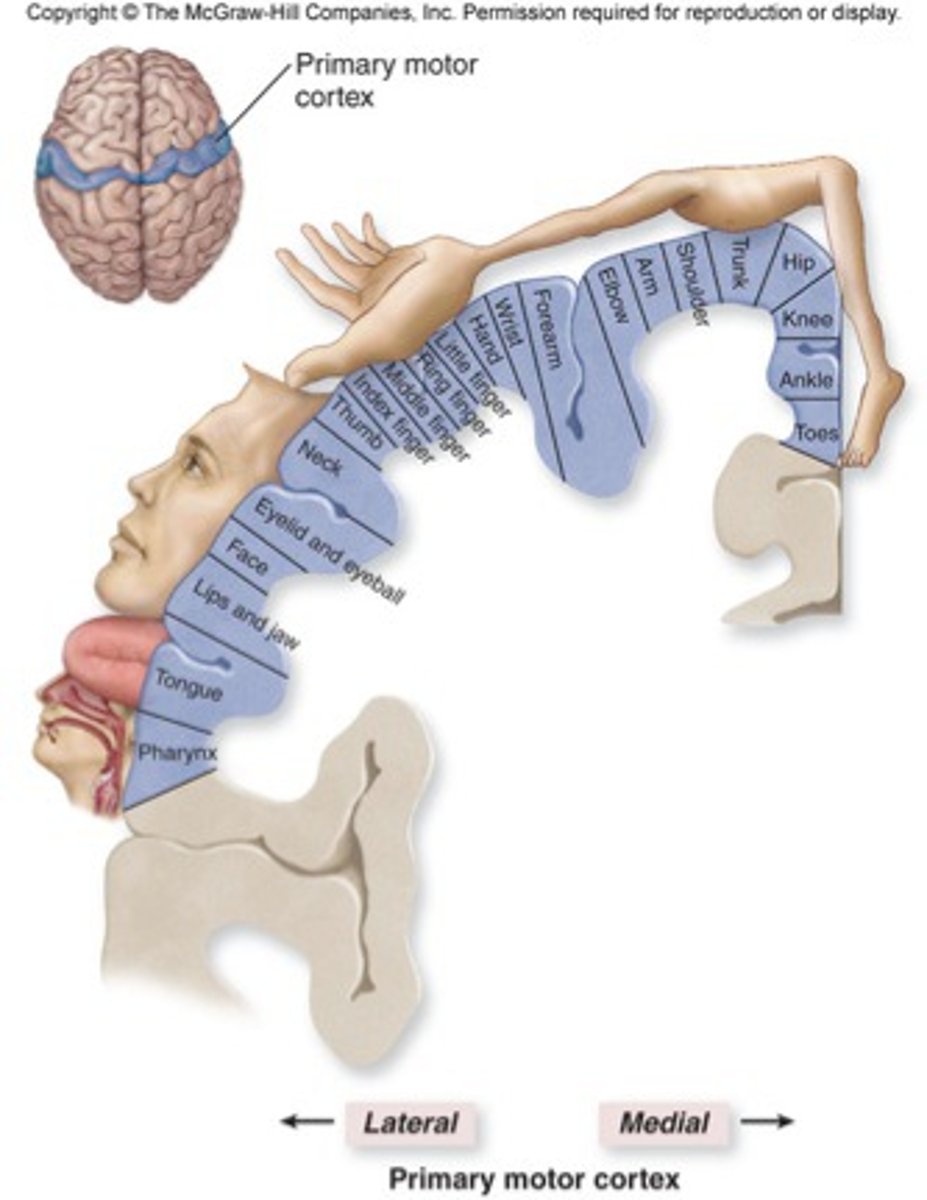
primary motor cortex
the section of the frontal lobe responsible for voluntary movement
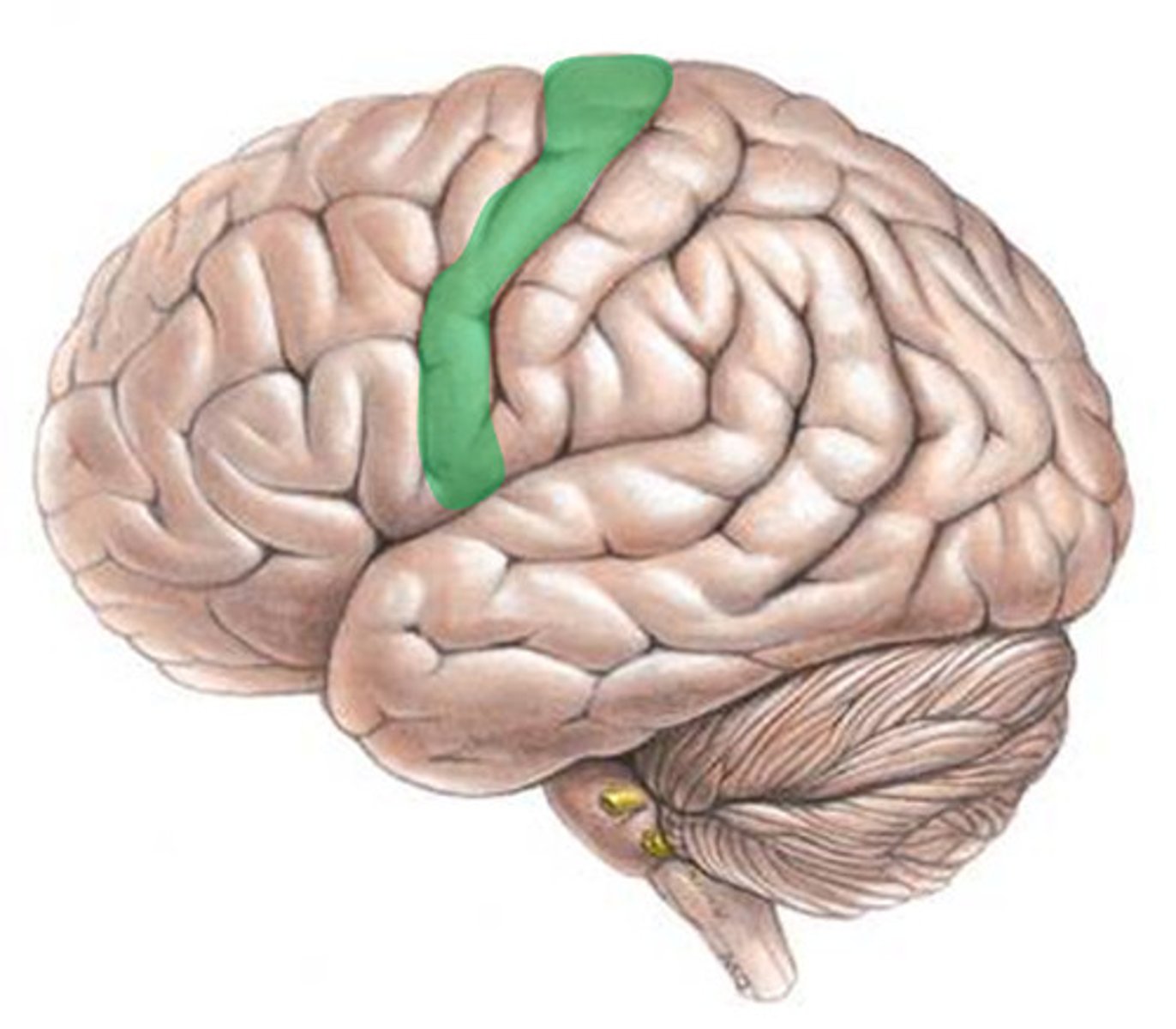
motor homunculus
broad areas of primary motor cortex devoted to controlling movements of different body regions; amount of space a portion of the body makes up relates to how much motor control is needed for that part of the body
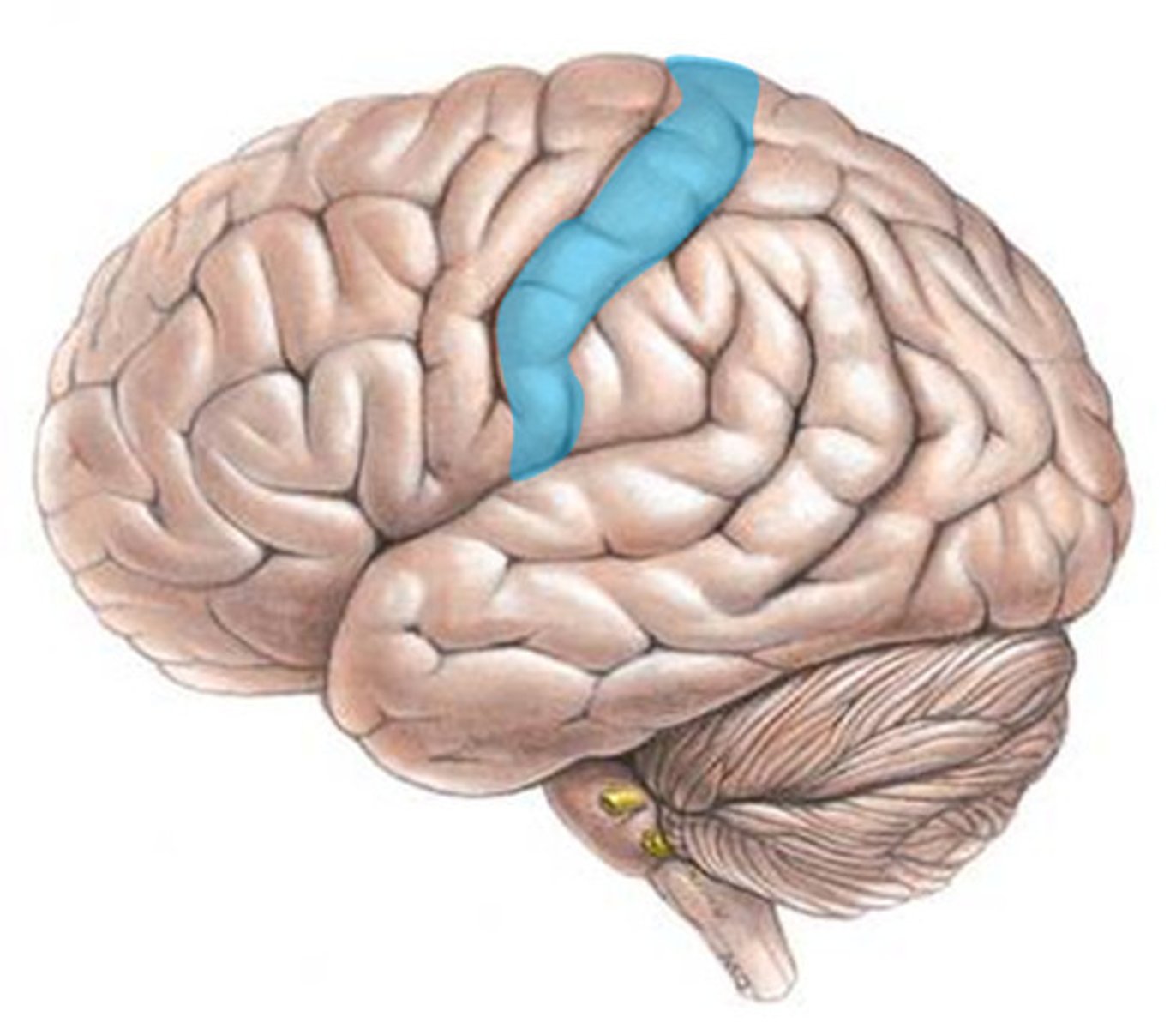
primary somatosensory cortex
the region of the anterior parietal lobe whose primary input is from the somatosensory system
sensory homunculus
Demonstrates that the area of the cortex dedicated to the sensations of various body parts is proportional to how sensitive that part of the body is.
primary visual cortex
the region of the posterior occipital lobe whose primary input is from the visual system
primary auditory cortex
the region of the superior temporal lobe whose primary input is from the auditory system
cerebral white matter
myelinated fibers and their tracts
responsible for communication
commissural fibers
horizontal fibers that connect gray matter of two hemispheres
corpus callosum
the large band of neural fibers connecting the two brain hemispheres and carrying messages between them
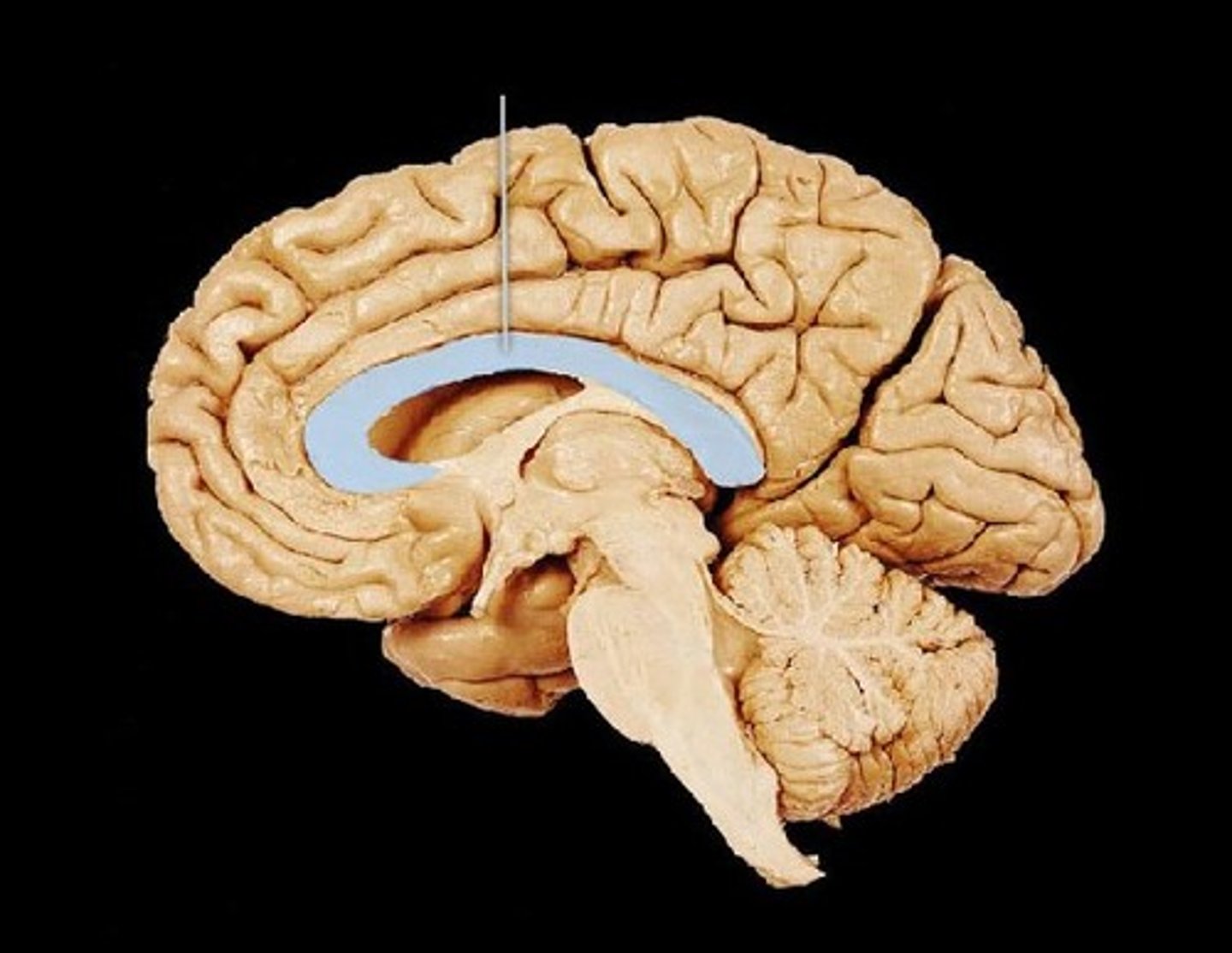
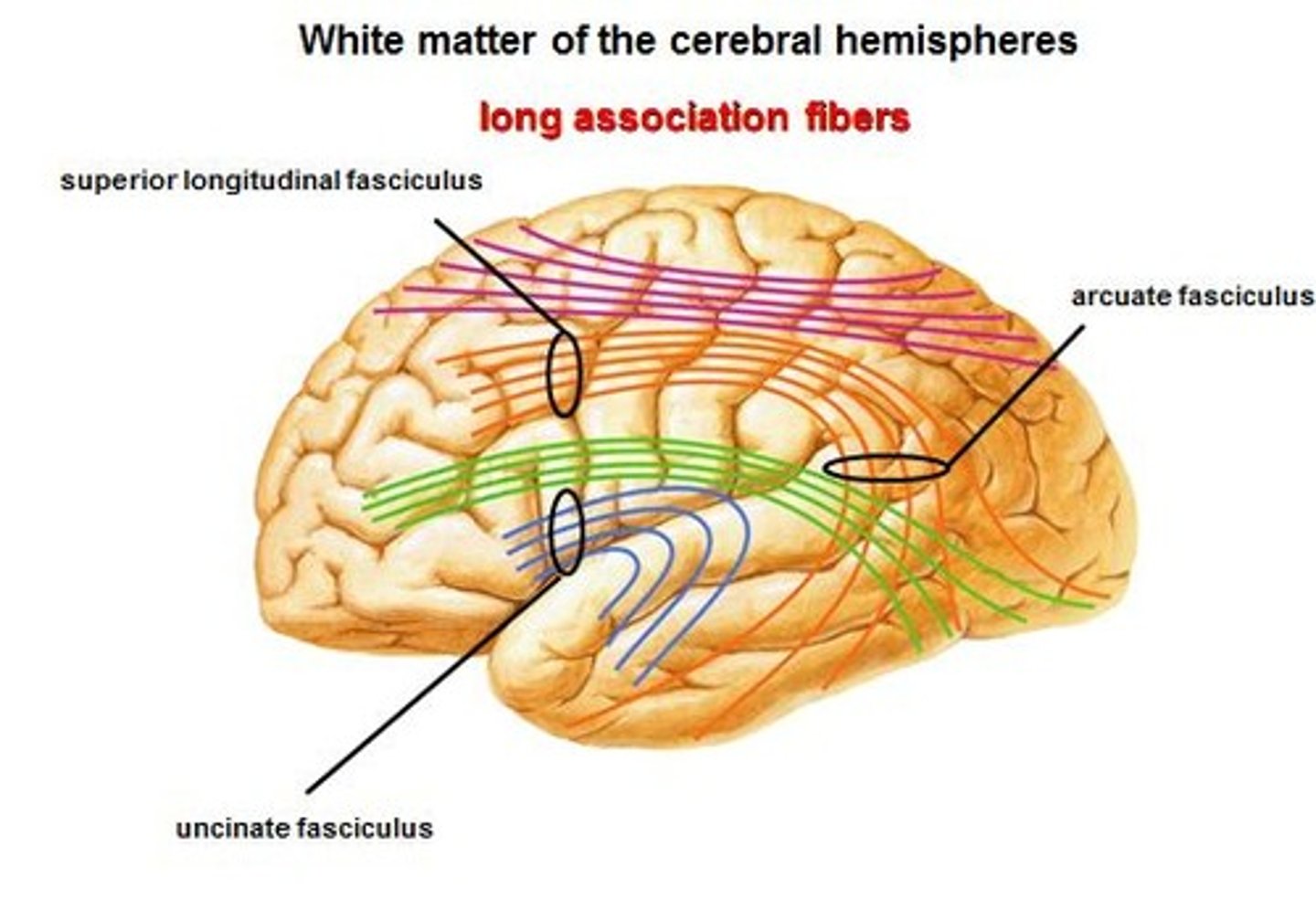
association fibers
connect different parts of the same hemisphere
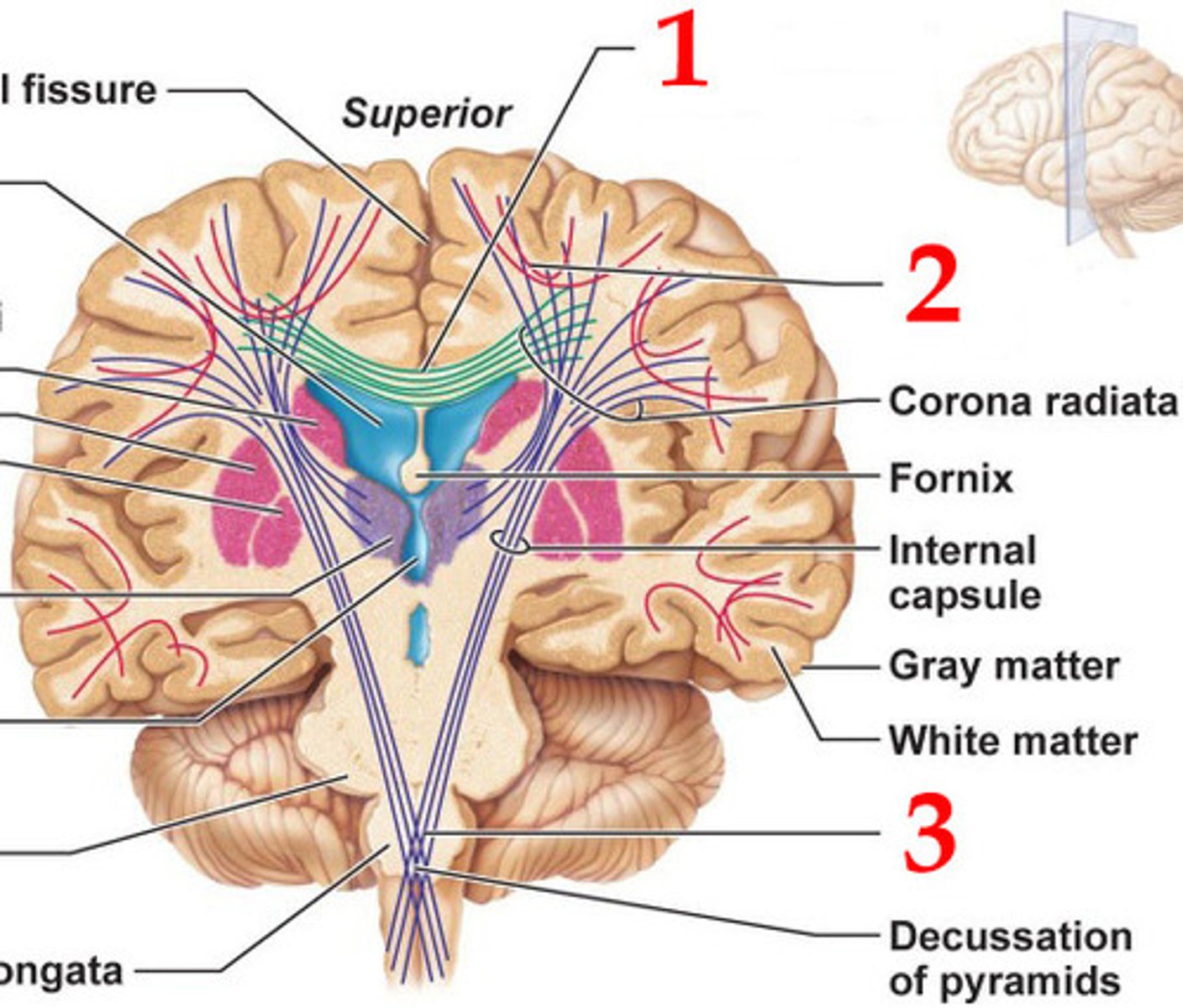
projection fibers
tracts between the cerebrum and other parts of the brain and spinal cord
basal nuclei
islands of gray matter buried within the white matter
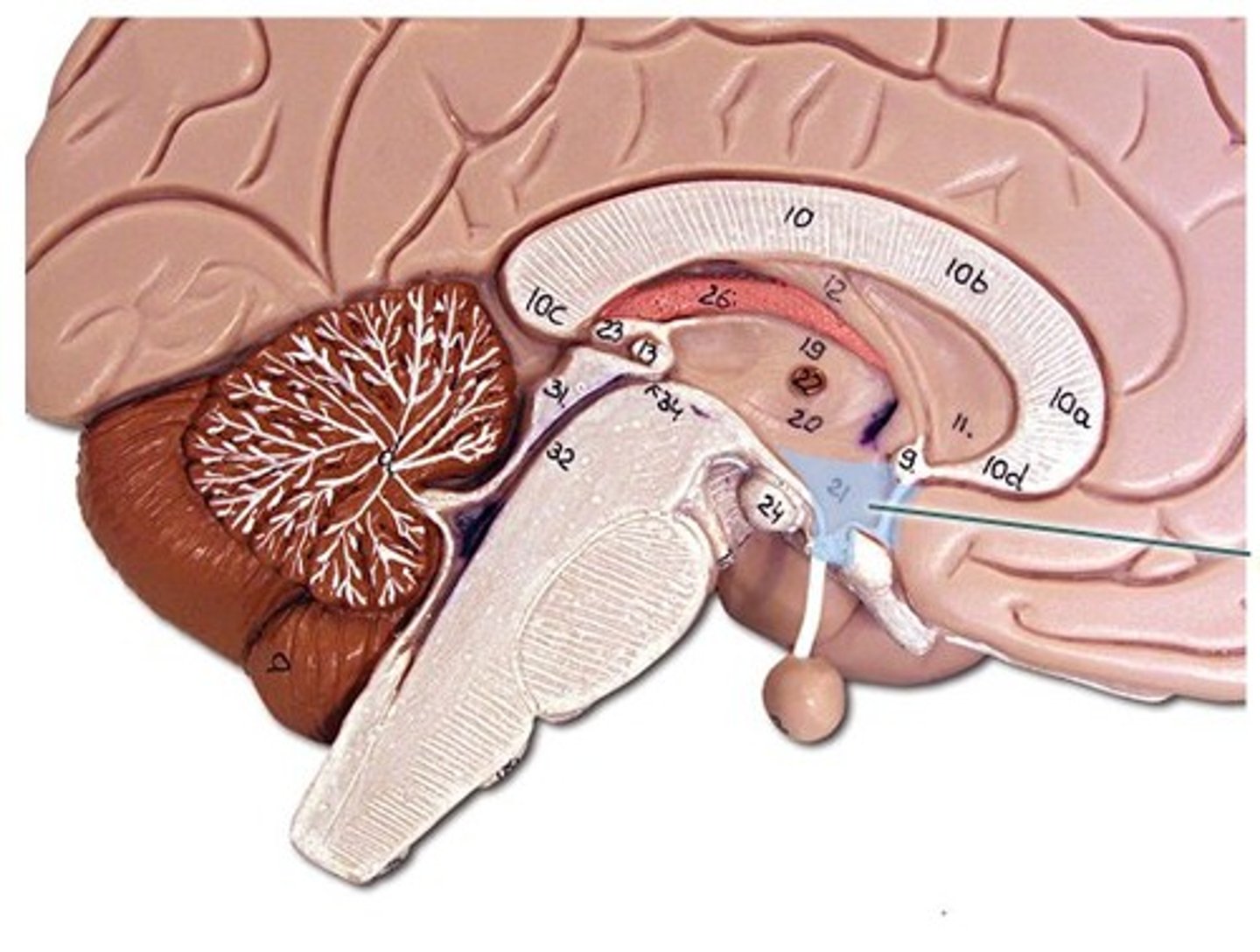
limbic system
A doughnut-shaped system of neural structures at the border of the brainstem and cerebral hemispheres; associated with emotions such as fear and aggression and drives such as those for food and sex. Includes the hippocampus, amygdala, and hypothalamus.
hypothalamus
nuclei control thirst, hunger, rage, sexual, parts of autonomic nervous system; 2 but only one is needed to function
cranial nerves
midbrain: III, IV
pons: V, VI, VII, VIII
medulla: IX, X, XI, XII
-cranial nerves I and II don't have cell bodies in the brainstem
-don't have to be mixed like spinal nerves
-can be motor: cell body in brainstem and axon effector goes to muscle in the head
-GVE (parasympathetic); start in brainstem and stop to synapse onto a second neuron that goes to the smooth muscle or glands of the head (have ganglion in the middle of their pathway)