6.4 Nuclear and Particle Physics
1/69
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
What is nuclear size?
R=r0A1/3
What is r0?
1.2 fm
How do you find density of a nucleus?
use density=m/V, volume is given by 4piR3/3, R is given by other equation, mass is proportional to A
How is density independent of nucleon number?
mass is proportional to A, volume is proportional to A, it cancels out
What is an isotope?
atoms of the same element with differing numbers of neutrons and so they can undergo the same chemical reactions but will undergo different nuclear reactions - their electronic configurations being identical however the stability of their nuclei may differ greatly
What is the quark model of a proton?
uud
What is the quark model of a neutron?
udd
What is the charge of an up quark?
+2/3 e
What is the charge of a down quark?
-1/3 e
What is the charge of an up antiquark?
-2/3 e
What is the charge of a down antiquark?
+1/3 e
What is the charge of a strange quark?
-1/3 e
What is the charge of a strange antiquark?
+1/3 e
When does beta minus decay happen?
when there are too many neutrons in the nucleus compared to protons
When does beta plus decay happen?
when there are too many protons in the nucleus compared to neutrons
What causes beta decay?
thye weak nuclear force causes quarks to mutate, e.g. an up turns into a down
What is the equation for beta-minus decay?
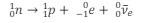
What is the equation in terms of quarks for beta-minus decay?
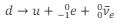
What is the equation for beta-plus decay?
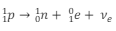
What is the equation in terms of quarks for beta-plus decay?
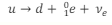
What happens during beta-minus decay?
the weak force mutates a down quark into an up quark within a neutron, transforming it into a proton - this releases energy in the form of a beta-minus particle (high speed electron) and an antineutrino is created to conserve lepton number
What happens during beta-plus decay?
the weak force mutates an up quark into a down quark in a proton, changing it to a neutron - this releases energy in the form of a beta-plus particle (high speed positron) and a neutrino is created to conserve lepton number
What is the nature of radioactive decay?
random and spontaneous
Describe the nature, penetration and range of alpha particles
they are heavy and slow, have a charge of positive 2, and have high ionising ability, but low penetrating power, stopped by paper
Describe the nature, penetration and range of beta particles
they have a charge of positive or negative 1, they are not heavy and fast, they have medium ionising ability and medium penetrating power, stopped by 5mm aluminium
Describe the nature, penetration and range of gamma rays
they have no mass or charge, they are as fast as the speed of light, they have no ionising ability and high penetrating power, stopped (mostly) by 5cm lead
Describe an experiment to investigate the absorption of alpha, beta and gamma particles
What is activity?
rate of decay of a radioactive source, number of decays per unit time
What is the activity equation?
product of decay constant and number of particles
What is the decay constant?
the probability of decay of a single nucleus per second
How does activity or number of atoms decrease?
exponentially
What is the derivation half life of an isotope?
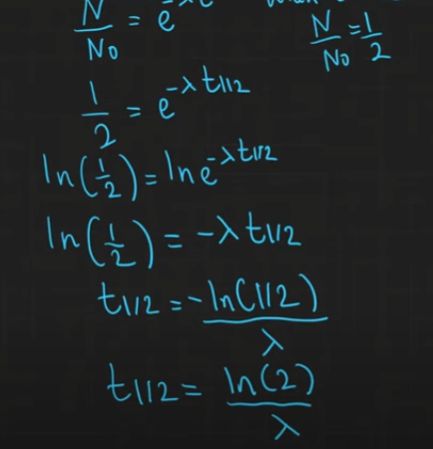
Describe an experiment to determine the half lfie of an isotope
How can you use carbon dating to tell the age of a dead organism?
the ratio of C12, C13 and C14 in the atmosphere is a known constant, organism will absorb C14 during their lifetimes, maximum at death, C14 has a half life of 5700 years, so by measuring the ratio of C12 to C14 and comparing this to the atmospheric ratio, estimation for the time since death can be calculated
What is the frequency of one photon released by annihilation of an electron positron pair?
hfx2=mc2, 2×9.11×10-31xc2 =hfx2
9.11×10-31xc2 =hf
find frequency
What is binding energy?
energy required to completely separate a nucleus into its constituents
What is mass defect?
the difference between the mass of a completely seperated nucleus and the nucleus itself
What is binding energy per nucleon?
minimum energy required to remove a nucleon from the nucleus
What is nuclear fusion?
two lighter nuclei combine to produce a heavy nucleus
What is nuclear fission?
a heavy nucleus splits into two lighter nuclei
What is required for nuclear fusion?
extremely high temperature and pressure to overcome electrostatic repulsion between nuclei
What does a binding energy per nucleon against nucleon number graph look like?
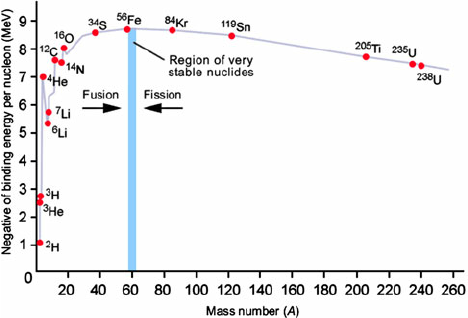
How can Einstein’s mass-energy equation be applied?
energy/mass is released or absorbed in simple nuclear reactions
What is a chain reaction?
in nuclear fission, more reactions are caused by products (neutrons) from previous reactions
How can you cause nuclear fission?
fire a neutron at an unstable nucleus
What are the components of a nuclear fission reactor?
fuel rods contain the uranium fuel, controls rods absorb some neutrons to control the rate of nuclear reaction so only one neutron is a product so only one reaction is caused per reaction so power output is constant, moderator slows down the fast moving neutrons to create thermal neutrons e.g. water
What is the environmental impact of nuclear waste?
products of fission are usually radioactive, known as toxic waste and may have high half lives so remains hazardous for millenia - it may have to be buried deep underground and these sites must be safe from attack and protected against earthquakes