[CRS 101] LYMPHATIC SYSTEM - TRANSES
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
lymph
IDENTIFICATION
interstitial fluid filtered by the blood that entered lymphatic vessels
contracts
FILL IN THE BLANK
Smooth muscle in lymphatic vessel walls _______, pushing lymph forward
contract
FILL IN THE BLANK
When surrounding skeletal muscles ______, they compress lymphatic vessels, pushing lymph to move
TRUE
TRUE OR FALSE
During inspiration, the pressure in the chest decreases, causing lymphatic vessels to expand and draw in lymph, while expiration increases chest pressure, compressing the vessels to push lymph forward.
lymphatic vessels
IDENTIFICATION
it helps keep the right amount of fluid in our tissues
lymphatic capillaries
FILL IN THE BLANKS
lymphatic vessels start as tiny, closed-off tubes called ______ ______ that collect excess fluid from tissues
E.
IDENTIFICATION
Which of the following areas of the body contain lymphatic vessels?
A) Central Nervous System (CNS)
B) Bone marrow
C) Tissues without blood vessels
D) Cartilage, epidermis, cornea
E) Digestive tract
inner
IDENTIFICATION
[inner/middle/outer]
layer of the lymphatic vessel that is made up of endothilium surrounded by an elastic membrane
middle
IDENTIFICATION
[inner/middle/outer]
layer of the lymphatic vessel that is made up of smooth muscles and elastic fibers
outer
IDENTIFICATION
[inner/middle/outer]
layer of the lymphatic vessel that is made up of fibrous connective tissue
one-way
IDENTIFICATION
the lymphatic vessel contains a [one-way / two-way] valve that prevents the backward movement of lymph
lymph nodes
IDENTIFICATION
a round, oval, or bean-shaped bodies distributed along the various lymphatic vessels that filters the lymph
lymphatic trunk
IDENTIFICATION
these are larger vessels that drains lymph from a major portion of the body
jugular trunk
IDENTIFICATION
what lymphatic trunk drains lymph from the ff:
Head & neck
subclavian trunk
IDENTIFICATION
what lymphatic trunk drains lymph from the ff:
Upper limbs, superficial thoracic wall, mammary glands
bronchomediastinal trunk
IDENTIFICATION
what lymphatic trunk drains lymph from the ff:
Thoracic organs & deep thoracic wall
intestinal trunk
IDENTIFICATION
what lymphatic trunk drains lymph from the ff:
Abdominal organs: intestine, stomach, pancreas, spleen, liver
lumbar trunk
IDENTIFICATION
what lymphatic trunk drains lymph from the ff:
Lower limbs:, pelvic & abdominal walls, pelvic organs, ovaries/testes, kidneys, adrenal glands
lymphatic ducts
IDENTIFICATION
this structure connects lymphatic trunks to large veins
right lymphatic duct
IDENTIFICATION
this is where Jugular, subclavian, and bronchomediastinal trunks often connect separately and drain lymph from the right side of the head, right arm, and right chest
thoracic duct
IDENTIFICATION
largest lymphatic vessel that drains lymph from the right side of the body inferior to the thorax & the entire left side of the body
cisterna chyli
an enlarged pouch on the thoracic duct that serves as a storage area for lymph moving toward its point of entry into the venous system; sac that is formed by the lymphatic trunks
lymphocytes, reticular fibers
FILL IN THE BLANKS
lymphatic organs contain lymphatic tissues which consists of ______ and ______
lymphocytes
IDENTIFICATION
Part of the immune response that destroys microorganisms and foreign substances and originates from the red bone marrow
reticular fibers
IDENTIFICATION
produced by the reticular cell, this traps microorganisms and other particles; filters fluid
connective tissue capsule
FILL IN THE BLANK
Lymphatic tissue of the body may or may not be separated from other tissues by a ______ ______ ______
mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue
IDENTIFICATION
a group of nonencapsulated lymphatic tissues found in and just below the mucous membranes; it catch and stop harmful microorganisms as they try to enter the body through these systems
lymphatic nodules
IDENTIFICATION
found within lymph nodes and the spleen, this is a denser arrangement of lymphatic tissue and is usually referred to as lymphatic follicles
peyer patches
IDENTIFICATION
a group of lymphatic nodules in the distal half of the small intestine
tonsils
IDENTIFICATION
large groups of lymphatic nodules and diffuse lymphatic tissue that protects against bacteria and other potentially harmful material entering the pharynx from the nasal or oral cavity
palatine tonsil
IDENTIFICATION
type of tonsils
relatively large, oval, lymphatic masses on each side of the junction between the oral cavity and the pharynx
pharyngeal tonsils
IDENTIFICATION
type of tonsils
collection of somewhat closely aggregated lymphatic nodules near the junction between the nasal cavity and the pharynx
adenoids
IDENTIFICATION
enlarged pharyngeal tonsil which interferes with normal breathing
lingual tonsils
IDENTIFICATION
type of tonsils
loosely associated collection of lymphatic nodules on the posterior surface of the tongue
TRUE
TRUE OR FALSE
In adults, the tonsils decrease in size and eventually may disappear
1 multiple choice option
lingual
FILL IN THE BLANK
______ tonsils become infected less often than the other tonsils and are more difficult to remove
lymph nodes
IDENTIFICATION
distributed along the course of the lymphatic vessels; this filter the lymph, removing bacteria and other materials
450
Approximately there are how many lymph nodes found in the body?
dafuq
INFORMATION
type "dafuq" when answring
number of lymph nodes
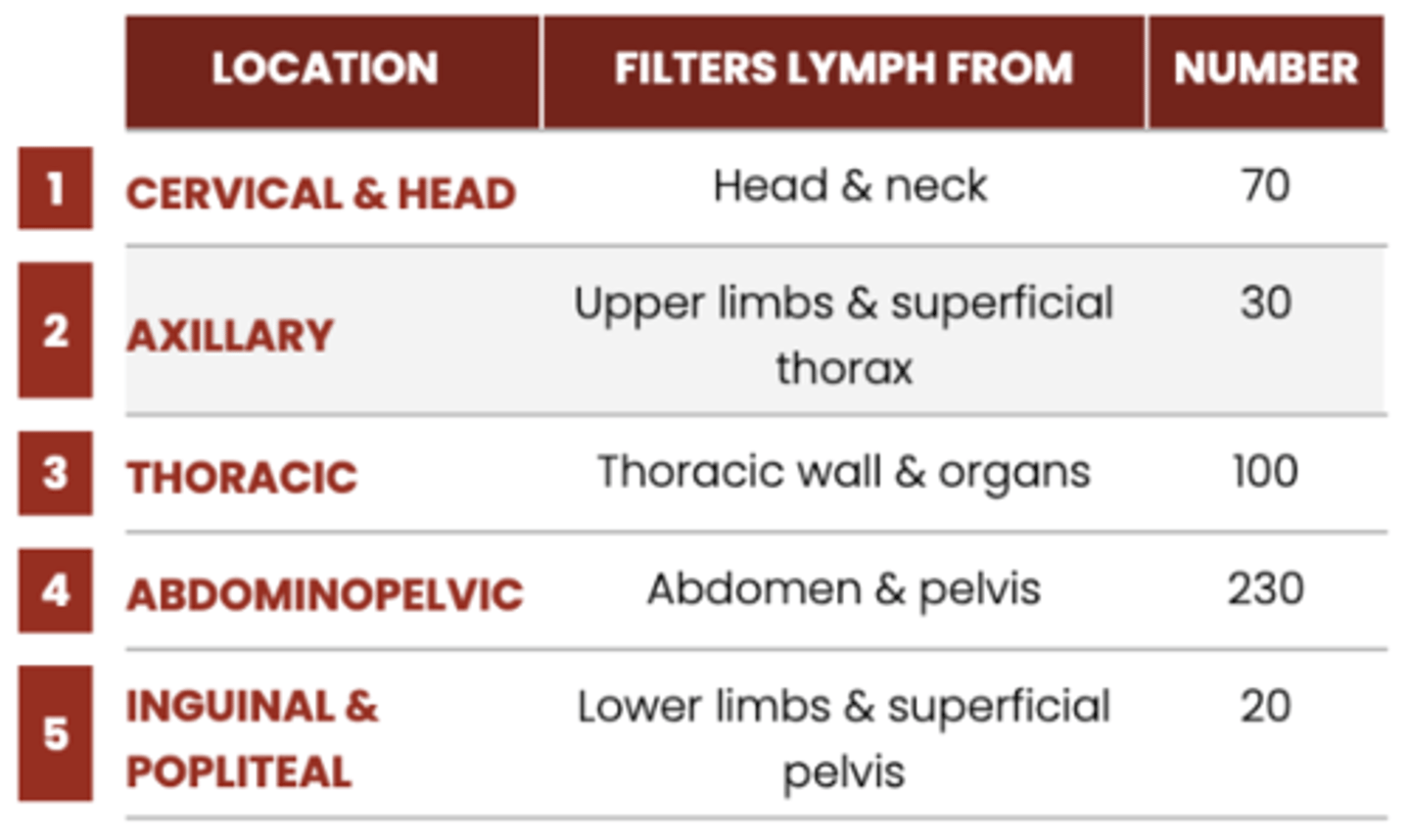
capsule
IDENTIFICATION
structures in the lymph nodes
surrounds each lymph node
trabeculae
IDENTIFICATION
structures in the lymph nodes
extensions of the capsule; form the internal skeleton of the lymph node
reticular fibers
IDENTIFICATION
structures in the lymph nodes
extend from the capsule and trabeculae; from a fibrous network throughout the lymph node
lymphocytes & macrophages
IDENTIFICATION
structures in the lymph nodes
Packed around the reticular fibers; Form lymphatic tissue
lymphatic sinuses
IDENTIFICATION
structures in the lymph nodes
open spaces
outer cortex
IDENTIFICATION
layers of the lymph node
this layer contains the Subcapsular Sinus and Cortical Sinuses
inner medulla
IDENTIFICATION
layers of the lymph node
this layer contains the Medullary Cords and Medullary Sinuses
lymph nodes
IDENTIFICATION
these are the only structures that filter lymph
afferent lymph nodes
IDENTIFICATION
type of lymphatic vessel that carry lymph to the lymph nodes
efferent lymph nodes
IDENTIFICATION
type of lymphatic vessel that carry lymph away from the lymph node
spleen
IDENTIFICATION
located on the left, superior part of the abdominal cavity; this structure destroys defective red blood cells, dects and responds to foreign substances in the blood, and acts as a blood reservoir
outer capsule
IDENTIFICATION
structures in the spleen
Dense connective tissue and a bit of smooth muscle
trabeculae
IDENTIFICATION
structures in the spleen
extensions of the capsule that divides the spleen into compartments
white pulp
IDENTIFICATION
structures in the spleen
lymphatic tissue surrounding the arteries within the spleen
red pulp
IDENTIFICATION
structures in the spleen
associated with veins within the spleen
outer capsule
IDENTIFICATION
structures in the thymus
thin connective tissue capsule
trabeculae
IDENTIFICATION
structures in the thymus
extensions of the capsule; divides it into lobules
epithelial cells
IDENTIFICATION
the thymus is made up of what type of cells?
cortex
IDENTIFICATION
[cortex/medulla] of the thymus
Dark-staining area with many lymphocytes
medulla
IDENTIFICATION
[cortex/medulla] of the thymus
Lighter-staining has fewer lymphocytes and thymic corpuscles, which help in developing regulatory T cells
thymosin
IDENTIFICATION
the thymus produces this hormone that aids in T-cell development