2-3: CNS Stimulants
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
what are the 8 common neurotrasmitters?
acetylcholine
norepinephrine
epinephrine
dopamine
seretonin
y-aminobutyric acid (GABA)
histamine
glutamate
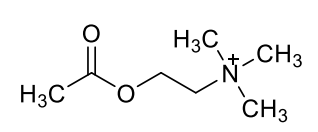
acetylcholine
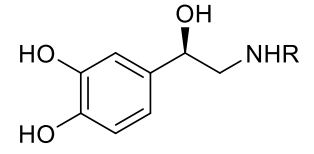
if R = H —> Norepinephrine (aka NE, Noradrenaline)
if R = CH3 —> Epinephrine (aka E, adrenaline)
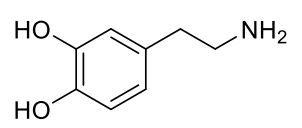
dopamine
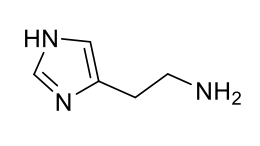
histamine
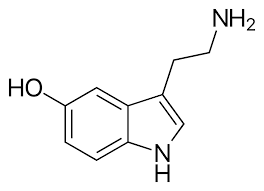
seretonin
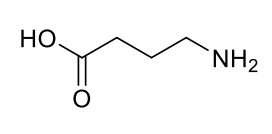
y-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA)
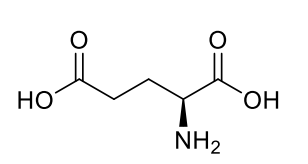
Glutamate
what are the two therapeutic uses of CNS stimulants?
Central Sympathomimetic Agents and Antidepressants
Methylxanthine Alkoids:
What are the 3 MOA?
which is the most important?
moa:
competitively binds to adenosine (adenosine is CNS depressant) - most important!
inhibit phosphodiesterase —> increases cAMP
alter calcium distribution (increase)
what are the 3 uses of Methylxanthine Alkoids?
bronchial asthma
infant apnea
migraine headaches
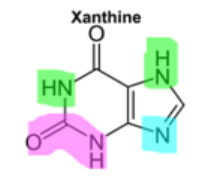
There are many CNS stimulants that are derivatives of Xanthine
which amines are acidic?
which amines are weakly basic?
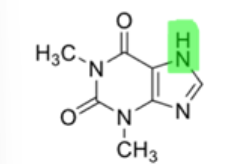
is the functional group in pink acidic or no?
acidic amines = green
weakly basic amines = blue
functional group is NOT acidic
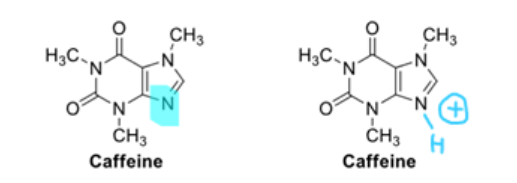
the conjugate acid of caffeine (right) has pka of ____
0.6

which methylxanthine is this? (3 methyls added to xanthine)
what is its moa?
what is the pka of its conjugate acid shown in the picture?
caffeine
inhibit adenosine
inhibit PDE (increase cAMP)
increase calcium
pka = 0.6
which methylxanthine is this? (2 methyls added onto the ring)
what is its moa?
what is its pka?
theophyline
moa:
inhibit adenosine
inhibit PDE (increase cAMP)
increase Ca2+
pka = 9

which methylxanthine is this? (methyl added onto imidazole and the bottom of ring)
what is its moa?
what is its pka?
theobromine
moa
inhibit adenosine
inhibit PDE (increase cAMP)
increase Ca2+
pka = 7.89
do methylxanthines have low or high water solubility (think of caffeine!)
how does impact how the drug is taken?
LOW - which is why caffeine is served hot to increase solubiity
decreases oral bioavailability and ability to be infused
how can you increase water solubility of methylxanthines so they can be used for oral usage and iv infusions?
salt formation: adjust acditiy or basicity of solvent to create salts that will disolve better in H20
add substituents such as OH that will react with water
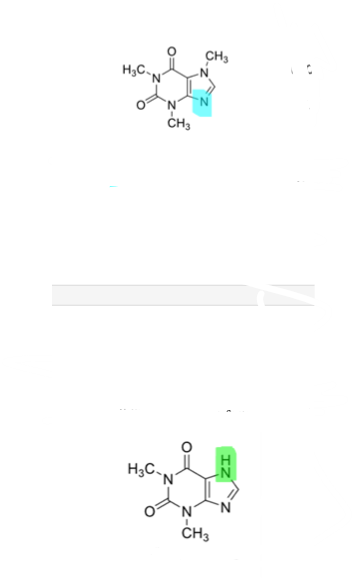
what is caffiene used for?
what is theophyline used for?
which is which?
top = caffeine = infant apnea and migraine headaches
bottom = theophyline = bronchial asthma
what are the three methylxanthine CNS stimulants derived from Xanthine?
caffeine
theophyline
theobromine