Clin Med Infectious Disease 1
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
infection
The process in which an organism has a parasitic relationship with a host
Prions
Corrupted proteins that are folded abnormally
What happens when prions and normal proteins come in contact?
Normal folded proteins (PrPc), prion causes a chain reaction of abnormally folded proteins (PrPsc).
Abnormal folded chain of proteins leads to dysfunction
What do Prions cause?
Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathies
Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathies
Uncurable, fatal chronic degenerative disease of brain
Examples of Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathies
Cruetzfeldt-Jakob Disease and Kuru
How are prions transmitted
Coming into contact with infected tissue
What would be examples of infected tissue causing prions?
Ingesting animal brain, blood products, or contaminated surgical instruments
Are viruses living or non-living?
Non-living
Viruses characteristics
Subcellular, made of only nucleic acids and proteins, and they are obligate intracellular parasites (can only replicate in a host)
Viruses spread
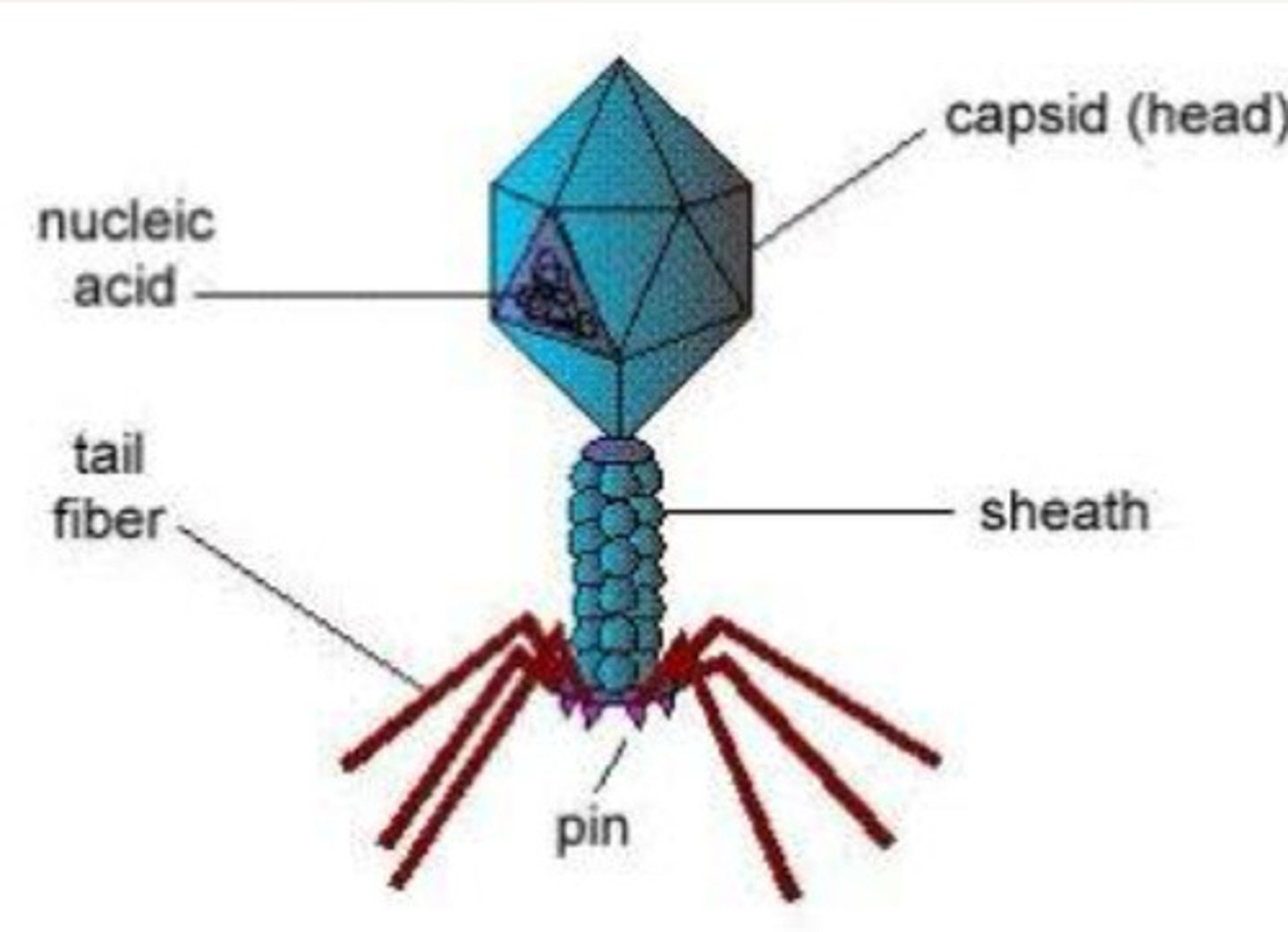
Inject the contents through the tails. Causing infection and dysfunction.
Virus
Do we typically use traditional antibiotics for a virus? If not, what do we use?
No, we use anti-virals
Bacteria characteristics
Single celled, cell wall, grow independently (most of the time), grown on a culture medium (most), contain both RNA and DNA. They have no nucleus.
Bacteria is classified by
Morphology - shapes
Colony types
Gram staining (+/-) - be able to see with stain
Aerobic/anaerobic
Facultative - anaerobic without oxygen
Obligate - harmed by oxygen
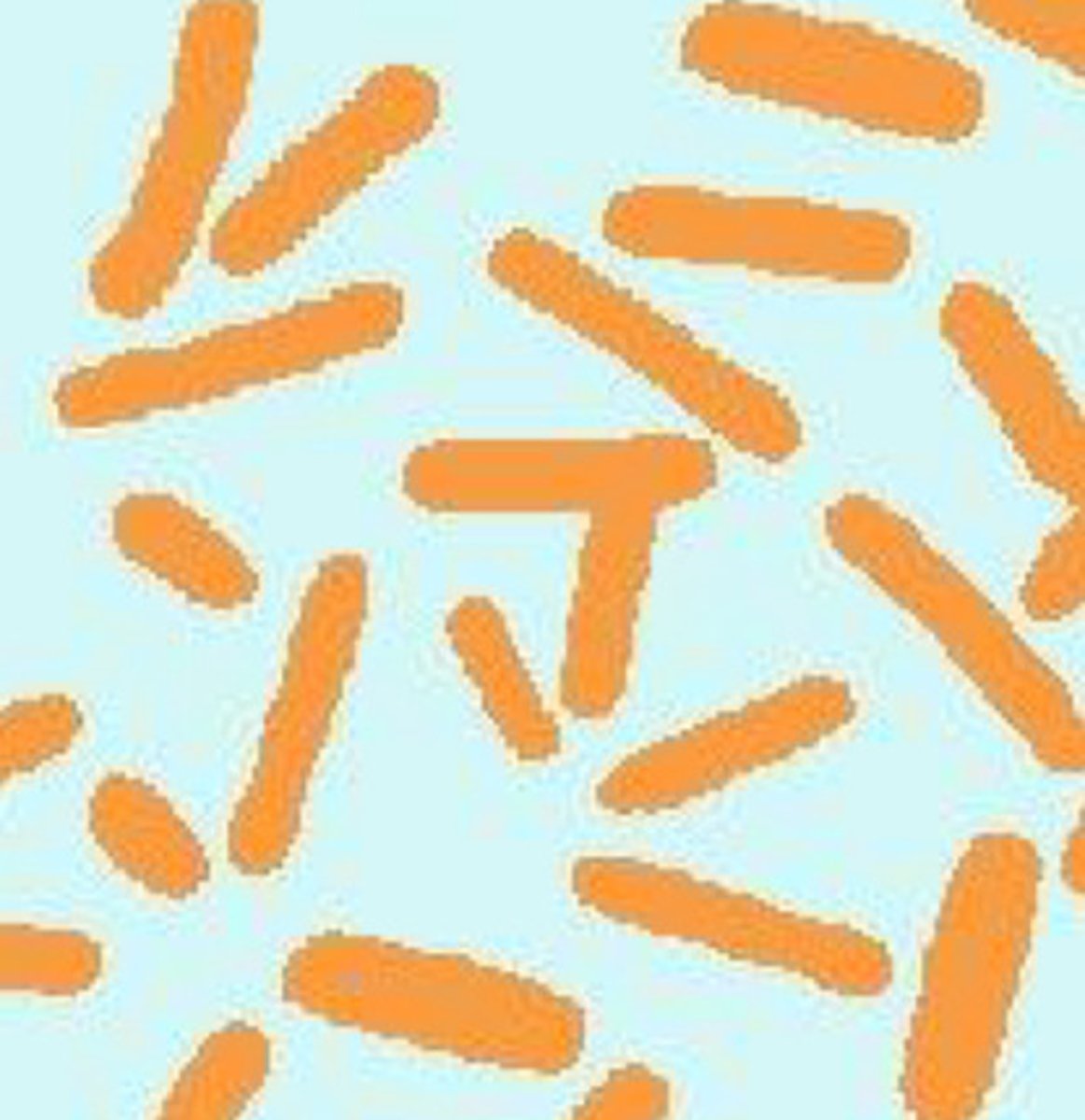
Shape of bacilli
Long, oblong, look like Cheeto puffs
Bacilli
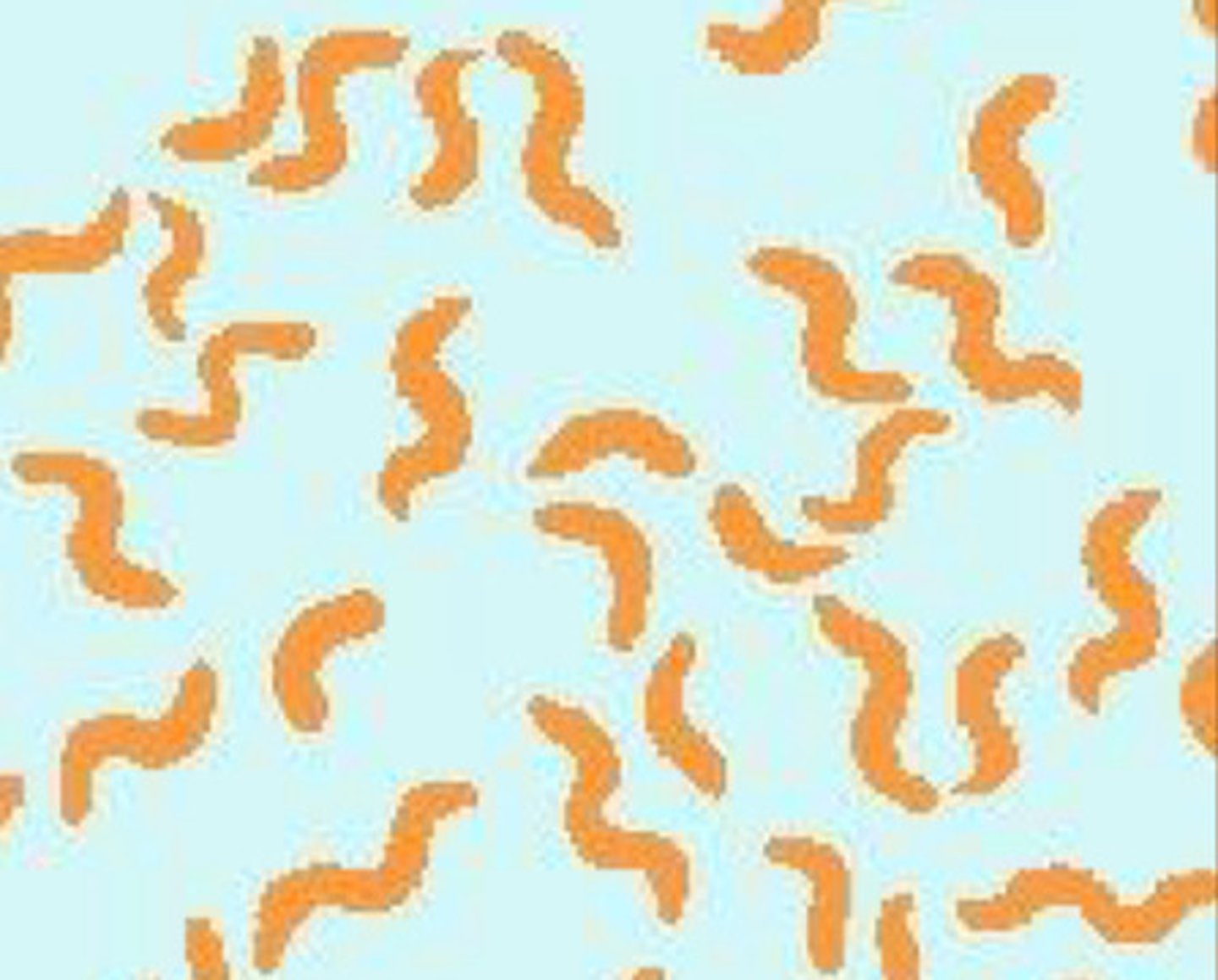
Shape of spirochetes
Spiral-like or worm
Spirochetes
Shape of cocci
Sphere or circle
Colonization
The grouping together
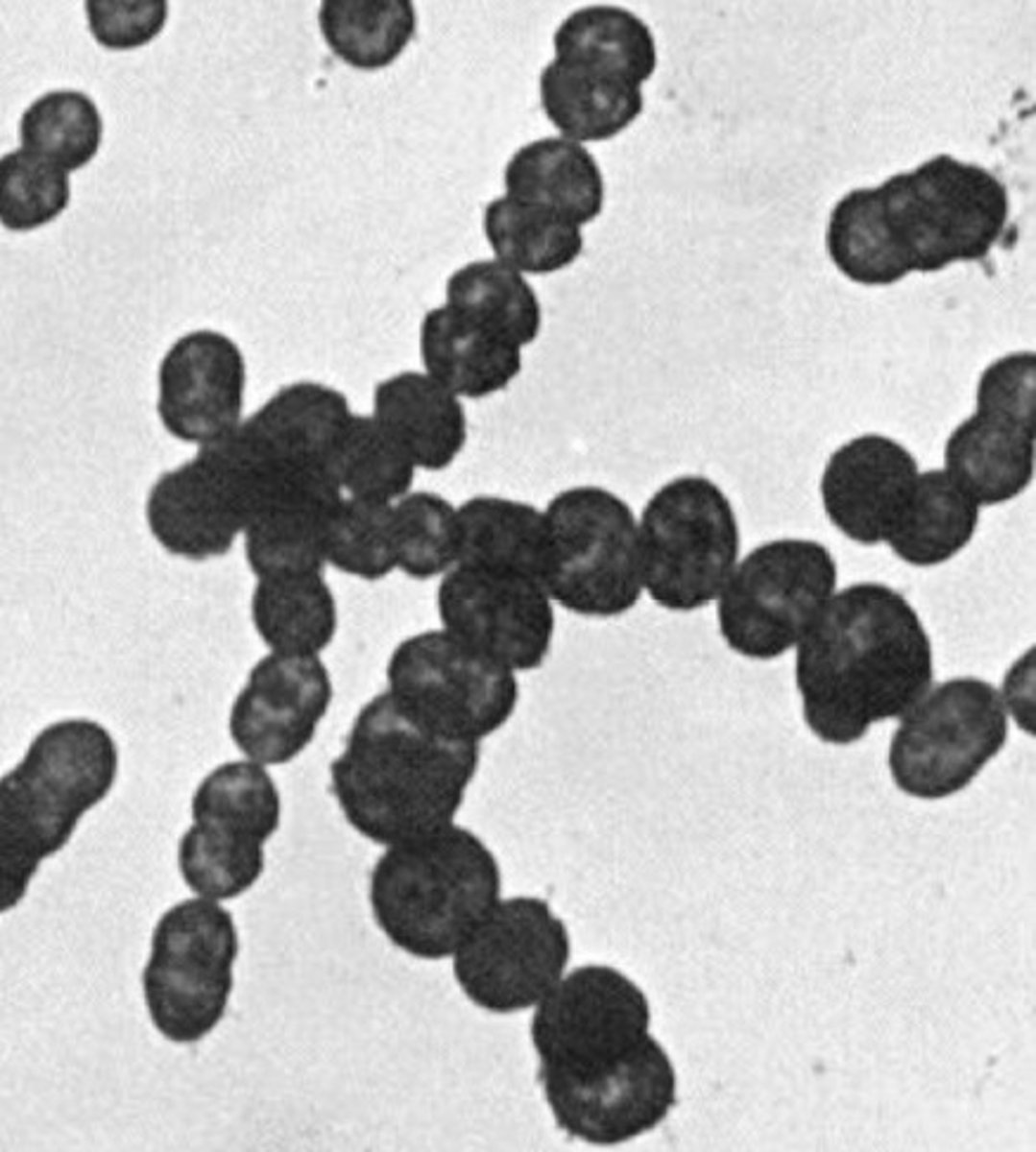
Streptococci
In strings/strands
Associated with strep
Staphylococci
clumps
Associated with staph infections
Cocci
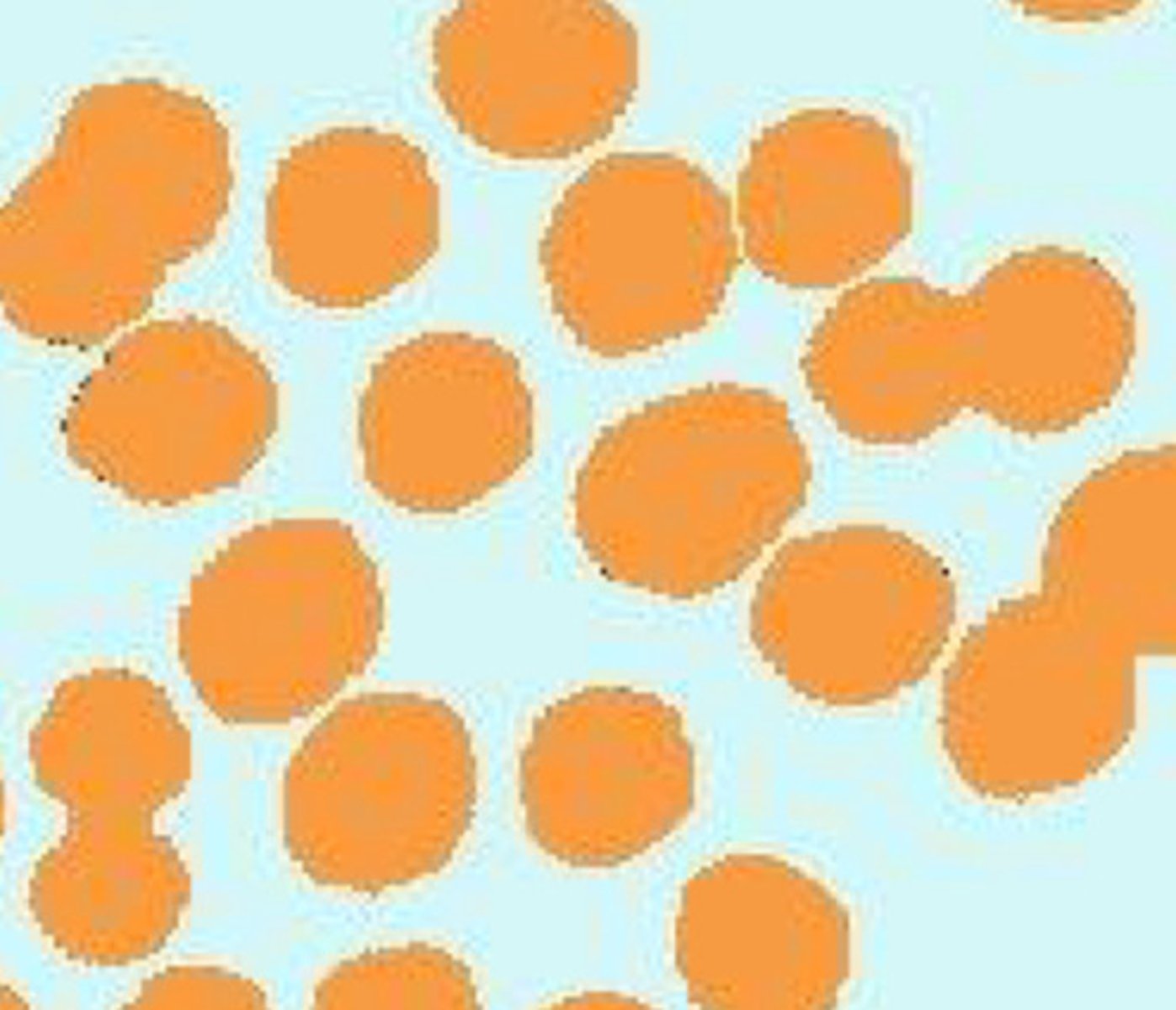
Streptococci
Mycoplasma Characteristics
No cell wall, Grow on culture medium, smaller, DNA and RNA, Creates ATP and proteins independently
What does mycoplasma cause?
Atypical pneumonia or STI
Rickettsiae Characteristics
Obligate intracellular parasites - unstable cell membrane, and cannot be grown on traditional culture media
Insect and animal vectors
Cell wall
DNA and RNA
Create ATP and Protein Independency
What does Rickettsiae cause?
Rocky Mountain spotted fever and typhus
Chlamydia Characteristics
Obligate intracellular parasites - can't make ATP by itself
Cell wall
Create Protein independency
Need Host for ATP
DNA and RNA
What does Chlamydia cause?
STI and pneumonia
Fungi Characteristics
Cell wall
Nuclear membranes
Yeast vs. molds
What does fungi cause?
infections in skin, GI, GU tracts
Protozoa Characteristics
Motile, Single celled organisms, Nucleus
What does protozoa cause in the US?
Giardia and trichomonas
What does protozoa cause in developing countries?
Malaria, sleeping sickness, amebiasis, leishmaniasis