BY322 Exam 1
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/85
Earn XP
Description and Tags
CH1-4
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
1
New cards
epigenesis
In the 1600s, William Harvey studied reproduction and development. What is the term given to his theory which states that an organism develops from the fertilized egg by a succession of developmental events that lead to an adult?
2
New cards
preformation
What is the term given to the theory which states that the gamete contains a complete miniature adult?
3
New cards
spontaneous generation
What is the term given to the theory which put forth the idea that living organisms could arise by incubating nonliving components?
4
New cards
Schleiden and Schwann proposed the cell theory which states that (blank)
cells are derived from preexisting cells
5
New cards
In many species, there are two representatives of each chromosome. In such species, the characteristic number of chromosomes is called the number. It is usually symbolized as .
diploid; 2n
6
New cards
Early in the twentieth century, Walter Sutton and Theodor Boveri noted that the behavior of chromosomes during meiosis is identical to the behavior of genes during gamete formation. They proposed that genes are carried on chromosomes, which led to the basis .
of the chromosome theory of inheritance
7
New cards
Living organisms are categorized into two major groups based on the presence or absence of a nucleus. What group is defined by the presence of a nucleus
eukaryotic organism
8
New cards
spindle fibers
Organized by the centrioles, what structures are important in the movement of chromosomes during cell division?
9
New cards
The mitochondrial genome is contained in the nucleus
Which of the following is not a true statement about mitochondria? A) the mitochondrial genome is contained in the nucleus; B) the mitochondria duplicate themselves; C) the mitochondria transcribe and translate their own genetic information; D) mitochondria are found in plants and animals;
E) mitochondria are sites for cellular respiration
E) mitochondria are sites for cellular respiration
10
New cards
23
The diploid chromosome number of an organism is usually represented as 2*n*. Humans have a diploid chromosome number of 46. What would be the expected haploid chromosome number in a human?
11
New cards
kinetochore
Migration of chromosomes is made possible by the binding of the spindle to the
12
New cards
tetrad
two pairs of sister chromatids XX
13
New cards
bivalent
a pair of homologous chromosomes XX
14
New cards
homologous chromosomes contain identical genetic information
Which of the following is incorrect? A) a locus is a gene site on a chromosome; B) an allele is an alternate form of the same gene; C) sex chromosomes are not strictly homologous; D) homologous chromosomes contain identical genetic information; E) a karyotype is generated from a metaphase spread.
15
New cards
DNA content essentially doubles
during interphase of the cell cycle ___
16
New cards
prophase-prometaphase-metaphase-anaphase-telophase
what is the correct sequence of events in mitosis?
17
New cards
cohesin
Which protein directly holds the chromatid arms together prior to anaphase of mitosis?
18
New cards
anaphase
the event referred to as disjunction
19
New cards
6\.0 x 10^-12
Normal diploid somatic (body) cells of the mosquito *Culex pipiens* contain six chromosomes. Assuming that all nuclear DNA is restricted to chromosomes and that the amount of nuclear DNA essentially doubles during the S phase of interphase, how much nuclear DNA would be present in metaphase I of mitosis? Note: Assume that the G1 nucleus of a mosquito cell contains 3.0 × 10^-12 grams of DNA
20
New cards
mitotic anaphase and anaphase of meiosis II
At which stage of cell division do sister chromatids go to opposite poles?
21
New cards
chiasma
Which of the following are the areas where chromatids intertwine during meiosis?
22
New cards
anaphase I
During meiosis, chromosome number reduction takes place in _.
23
New cards
The meiotic cell cycle involves number of cell division(s) and number of DNA replication(s).
two; one
24
New cards
26
In an organism with 52 chromosomes, how many tetrads would be expected to form during meiosis?
25
New cards
In an organism with 52 chromosomes, how many chromatids would be expected in each cell after the second meiotic division?
26 (second meiotic division)
26
New cards
A bivalent at prophase I contains chromatids
four
27
New cards
If a typical somatic cell has 64 chromosomes, how many chromosomes are expected in each gamete of that organism?
32
28
New cards
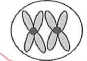
The ant, *Myrmecia pilosula*, is found in Australia and is named bulldog because of its aggressive behavior. It is particularly interesting because it carries all its genetic information in a single pair of chromosomes. In other words, 2n = 2. (Males are haploid and have just one chromosome.) Which of the following figures would most likely represent a correct configuration of chromosomes in a metaphase I (homologous pairs line up) cell of a female?
( XX)
29
New cards
For the purposes of this question, assume that a G1 somatic cell nucleus in a female *Myrmecia pilosula* contains 2 picograms of DNA. How much DNA would be expected in a metaphase I cell of a female?
4 picograms
30
New cards
What is the outcome of synapsis, a significant event in meiosis?
side-by- side alignment of homologous chromosomes;
31
New cards
Which of the following is true about the second meiotic division?
) Sister chromatids disjoin and are pulled to opposite poles
32
New cards
63
The horse (*Equus caballus*) has 32 pairs of chromosomes, whereas the donkey (*Equus asinus*) has 31 pairs of chromosomes. How many chromosomes would be expected in the somatic tissue of a mule, which is a hybrid of these two animals?
33
New cards
Mendel's significant contributions in genetics published in 1866 went largely unnoticed until the discovery of
chromosomal patterns during meiosis
34
New cards
Mendel utilized the garden pea, *Pisum sativum* for his studies based on features that include all but
has visible features with a wide spectrum of intermediates
35
New cards
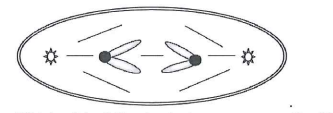
The accompanying sketch depicts a cell from an organism in which 2n = 2 and each chromosome is metacentric. What stage is the cell in?
anaphase of meiosis II
36
New cards
Which of the following statements was not a contributing factor in the generation of Mendel's first three postulates?
A) true-breeding plants were used for the parental generation; **B) all offspring of the first filial generation demonstrated the same trait;** C) reciprocal crosses did not change the patterns of inheritance; D) the proposal that there are basic units of heredity to explain results of monohybrid crosses; E) monohybrid crosses for several analyzed characteristics yielded similar patterns of inheritance.
37
New cards
The physical expression of a trait is referred to as a(n) .
phenotype
38
New cards
1) The process that leads to the development of haploid gametes is best described as .
segregation
39
New cards
Mendel indicated that traits were made up of unit factors. Today, we call unit factors .
genes
40
New cards
Assuming a typical monohybrid cross in which one allele is completely dominant to the other, what phenotypic ratio is expected if the F1s are crossed?
3:1
41
New cards
Mendel crossed two pea plants with round seeds. All seeds of the offspring were round. He then crossed a plant with round seeds to a plant with wrinkled seeds and all offspring had wrinkled seeds. Which of the following is true?
wrinkled is dominant
42
New cards
A cross between two individuals with different phenotypes that resulted in approximately 50% of each type of offspring would indicate the cross was .
a heterozygous dominant crossed to a homozygous recessive
43
New cards
If an F2 generation from a F1 self-cross always yields offspring in a 3:1 phenotypic ratio, which of the following P crosses could have occurred?
AA x aa
44
New cards
A recessive allele in dogs causes white spots. If two solid-colored dogs are mated and produce a spotted offspring, what is the percentage chance their next puppy would be solid colored?
75%
45
New cards
Polydactyly is expressed when an individual has extra fingers and/or toes, and is transmitted via an autosomal dominant allele. Assume that a man with six fingers on each hand and six toes on each foot marries a woman with a normal number of digits. The couple has a son with normal hands and feet, but the couple's second child has extra digits. What is the probability that their next child will have polydactyly?
1/2
46
New cards
A researcher crossed two plants, and informed an assistant researcher to determine the genotypes and phenotypes of the plants that were crossed by analyzing the offspring. The assistant counted 30 plants with green pods and 10 plants with yellow pods. Which of the following conclusions can accurately be made by the assistant?
the researcher had crossed two heterozygous plants
47
New cards
![Assume that you have a garden and some pea plants have solid leaves and others have striped leaves. You conduct a series of crosses \[(a) through (e)\] and obtain the results given in the table. Define gene symbols and give the possible genotypes of the parents of cross e.](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/902265bae43b41e6a57381d7cd0291fc.jpeg)
Assume that you have a garden and some pea plants have solid leaves and others have striped leaves. You conduct a series of crosses \[(a) through (e)\] and obtain the results given in the table. Define gene symbols and give the possible genotypes of the parents of cross e.
solid is dominant to striped SS × ss
48
New cards
Albinism, lack of pigmentation in humans, results from an autosomal recessive gene. Two parents with normal pigmentation have an albino child. What is the probability that their next two children will be albino?
1/6
49
New cards
The autosomal (not X-linked) gene for brachydactyly, short fingers, is dominant to normal finger length. Assume that a female with brachydactyly in the heterozygous condition is married to a man with normal fingers. What is the probability that their first child will have brachydactyly?
1/2
50
New cards
A certain type of congenital deafness in humans is caused by a rare autosomal dominant gene. In a mating involving a deaf man and a deaf woman, could all the children have normal hearing?
Yes, assuming that the parents are heterozygotes (because the gene is rare), it is possible that all of the children could have normal hearing
51
New cards
A certain type of congenital deafness in humans is caused by a rare autosomal recessive gene. In a mating involving a deaf man and a deaf woman, could some of the children have normal hearing?
No, since the gene in question is recessive, both of the parents are homozygous and one would not expect normal hearing in the offspring
52
New cards
Which of the following postulates was not attainable from a monohybrid cross?
independent assortment
53
New cards
What are expected ratios for monohybrid and dihybrid testcrosses, respectively in which the parent with the dominant phenotype is heterozygous for all traits?
1:1 and 1:1:1:1
54
New cards
what describes the product law
The probability of two or more independent events occurring simultaneously is equal to the product of their individual probabilities
55
New cards
what is segregation
During gamete formation, allele pairs are separated to form haploid gametes
56
New cards
what is independent assortment?
During gamete formation, a pair of unit factors segregates randomly from another pair of unit factors;
57
New cards
When performing a dihybrid cross for the traits round/wrinkled and yellow/green, which of the following results best demonstrates that the unit factors from each trait was assorting independently?
the 9:3:3:1 ratio of the F2 generation;
58
New cards
under what conditions does one expect a 1:1:1:1 ratio?
AaBb x aabb
59
New cards
How many different possible gametes can be obtained from an organism with the following genotype AaBbCc?
8
60
New cards
According to Mendel's model, because of the of chromosomes during meiosis, all possible combinations of gametes will be formed in equal frequency.
independent assortment (Mendel’s model)
61
New cards
In tomato plants smooth texture (P) is dominant to peach (p), red color (R) is dominant to yellow (r), and normal leaf (B) is dominant to broad leaf (b). In the cross PpRrbb × Pprrbb what percent of the offspring will be smooth, yellow and broad?
3/8
62
New cards
Which of the following groups of scientists were influential around the year 1900 in setting the stage for our present understanding of transmission genetics?
de Vries, Correns, Tschermak, Sutton, and Boveri
63
New cards
The number of possible gametes, each with different chromosome compositions, is 2n, where n equals .
the haploid number
64
New cards
For which of the following questions would you use the sum law?
For which of the following questions would you use the sum law? A) determining the chance of having a baby girl; B) determining the chance of having a tall plant with purple flowers; C) determining the change of rolling a 5 on a six-sided die; **D) determining the chance of pulling either a club or a heart from a deck of cards;** E) determining the chance of pulling an ace from a deck of cards.
65
New cards
what is the probablity of rolling a 2 or 3 on a six-sided die?
1/3 (2/6)
66
New cards
In studies of human genetics, usually a single individual brings the condition to the attention of a scientist or physician. When pedigrees are developed to illustrate transmission of the trait, what term does one use to refer to this individual?
proband
67
New cards
In a pedigree analysis a male child with a particular trait has two parents that do not exhibit the trait. Which of the following represents the most likely scenario?
the trait is inherited as an autosomal recessive and the genotypes of the child and his parents can be determined
68
New cards
rare autosomal dominant diseases are ___
typically more severe in homozygous dominant individuals
69
New cards
Name the single individual whose work in the mid-1800s contributed to our understanding of the particulate nature of inheritance as well as the basic genetic transmission patterns. With what organism did this person work?
Gregor Mendel; *Pisum sativum*
70
New cards
*Dentinogenesis imperfecta* is a rare, autosomal, dominantly inherited disease of the teeth that occurs in about one in 8000 people. The teeth are somewhat brown in color, and the crowns wear down rapidly. Assume that a male with *dentinogenesis imperfecta* and no family history of the disease marries a woman with normal teeth. What is the probability that their first child will have *dentinogenesis imperfecta*?
1/2
71
New cards
Which of the following best describes the relationship at the molecular level between mutant alleles and phenotype?
A mutant allele can have different effects depending on the gene product's function
72
New cards
A mutation in a gene that results in a loss of a functional product of that gene best defines what type of mutation?
null
73
New cards
If the wrinkled-wing mutation in *Drosophila* is dominant and designated Wr, a fruit fly with the genotype Wr+ Wr+ would exhibit what phenotype?
wild-type wings
74
New cards
Assume that a cross is made between two organisms that are both heterozygous for a gene that shows incomplete dominance. What phenotypic and genotypic ratios are expected in the offspring?
1:2:1, 1:2:1
75
New cards
Assume that a dihybrid cross for two different traits (*AaBb* × *AaBb*) is made in which the gene loci are autosomal, independently assorting, and incompletely dominant. How many different phenotypes are expected in the offspring?
9
76
New cards
The MN blood group is a codominant trait as a result of which of the following?
presence of both M and N cell surface glycoproteins on the same blood cell
77
New cards
Which of the following is not a characteristic of the ABO gene locus?
epistasis; A)multiple alleles; B) dominance/recessiveness; C) codominance; D) **epistasis;** E) four possible phenotypes
78
New cards
The presence of more than two alternative forms of a given gene would be called
multiple alleles
79
New cards
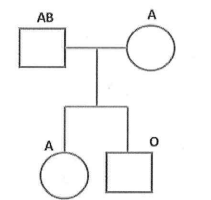
Based on the following pedigree, with blood types provided, what conclusions about paternity can be drawn?
This can be the father of the daughter but not the son
80
New cards
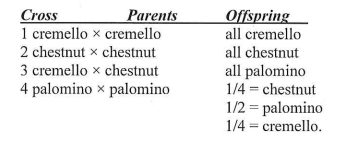
The following coat colors are determined by alleles at one locus in horses:
palomino = golden coat with lighter mane and tail
cremello = almost white
chestnut = brown.
The following table gives ratios obtained in matings of the above varieties:.
palomino = golden coat with lighter mane and tail
cremello = almost white
chestnut = brown.
The following table gives ratios obtained in matings of the above varieties:.
palomino is the incomplete dominant form of chestnut and cremello alleles.
81
New cards
A couple each with blood type AB and normal pigmentation have a child with AB blood type and albinism. What is the probability that their next child will have the same phenotype as the first child?
1/8
82
New cards
A couple in which one parent is blood type A and the other is blood type B, and both have normal pigmentation, have a child that is blood type O and has albinism. What is the probability that their next child will have normal pigmentation and blood type A?
3/16
83
New cards
A condition in which one gene pair masks the expression of a nonallelic gene pair is called
.
.
epistasis
84
New cards
In the mouse, gene B can produce black pigment from a colorless precursor molecule. A mouse having at least one B allele can produce black pigment, whereas the homozygous recessive mouse (bb) cannot and is albino. The agouti locus
black
85
New cards
Comb shape in chickens represents one of the classic examples of gene interaction. Two gene pairs interact to influence the shape of the comb. The genes for rose comb (*R*) and pea comb (*P*) together produce walnut comb. The fully homozygous recessive condition (*rrpp*) produces the single comb. Assume that a rose-comb chicken is crossed with a walnut-comb chicken and the following offspring are produced: 17 walnut, 16 rose, 7 pea, 6 single. What are the probable genotypes of the parents?
Rrpp x RrPp
86
New cards
The phenomenon of a gene which has multiple phenotypic effects on an individual is referred to as
.
.
pleiotropy