L22: Fertilization and Sex Determination in Mammals
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
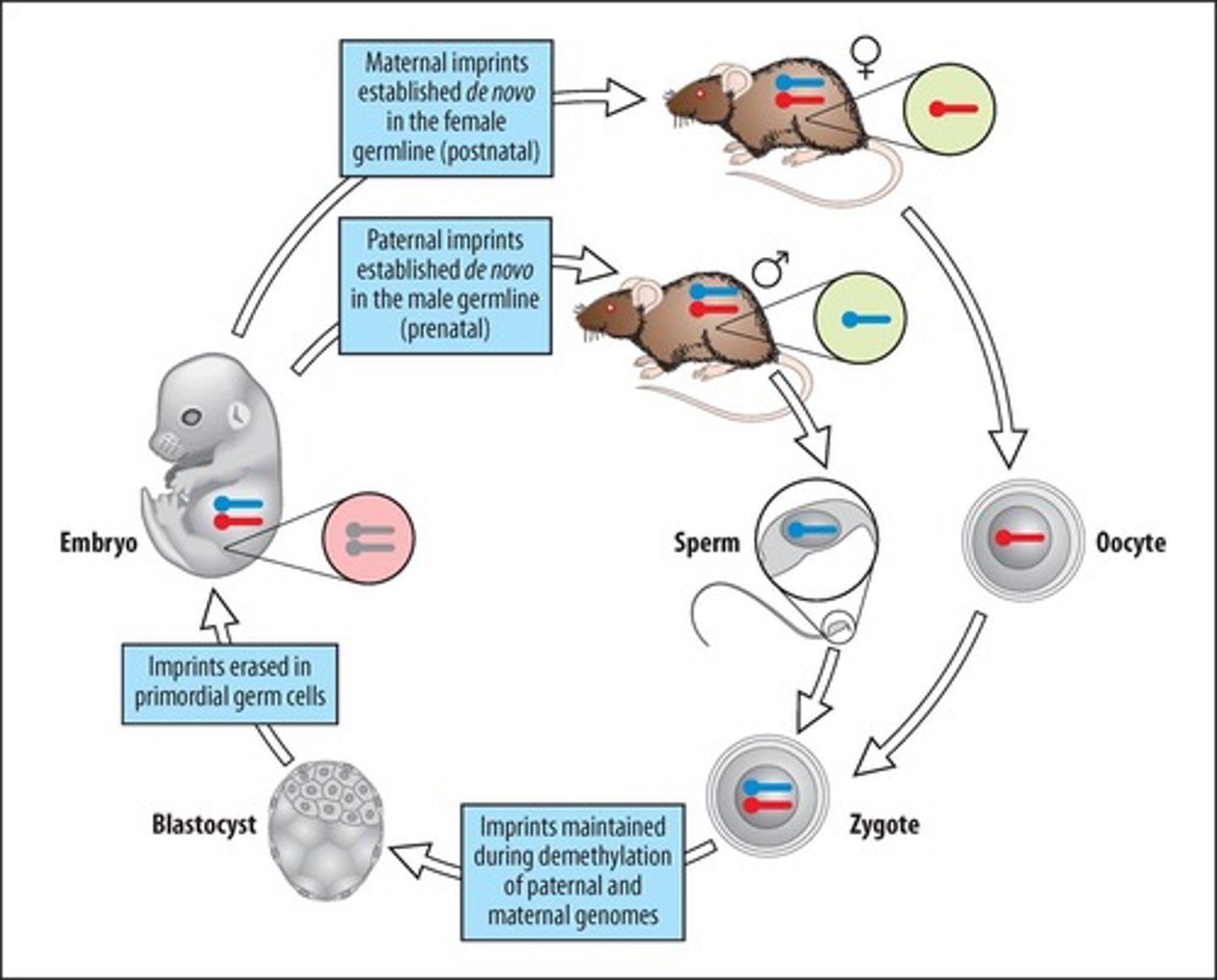
Imprinting
Heritable epigenetic control of gene expression.
Polyspermy
Condition of multiple sperm fertilizing one egg.
Totipotency
Ability of a cell to differentiate into any cell type.
Oocyte
Female germ cell involved in reproduction.
Acrosome
Cap-like structure on sperm containing enzymes.
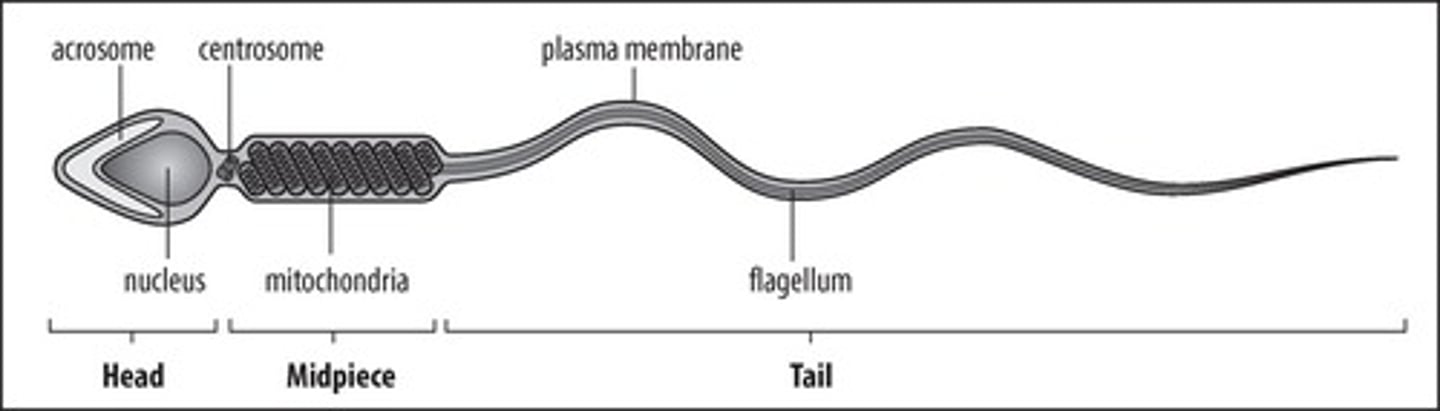
Zona Pellucida
Clear outer layer surrounding the oocyte.
Sperm Izumo protein
Protein that binds to oocyte Juno for fusion.
Juno protein
Oocyte protein that interacts with sperm Izumo.
Meiosis II
Second meiotic division completed after fertilization.
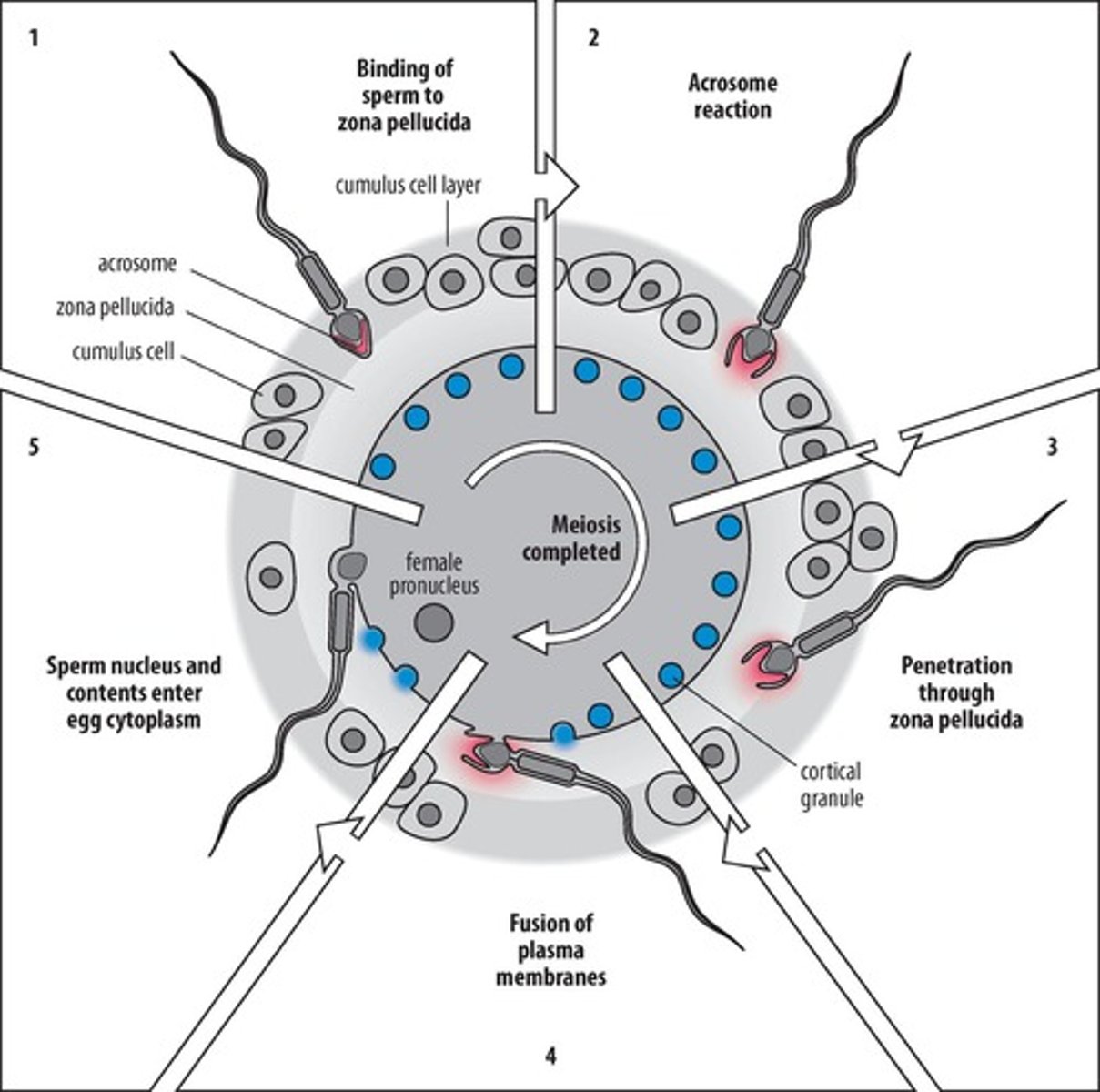
Cortical granules
Oocyte structures that prevent polyspermy post-fertilization.
Ovastacin
Enzyme that digests zona proteins to prevent polyspermy.
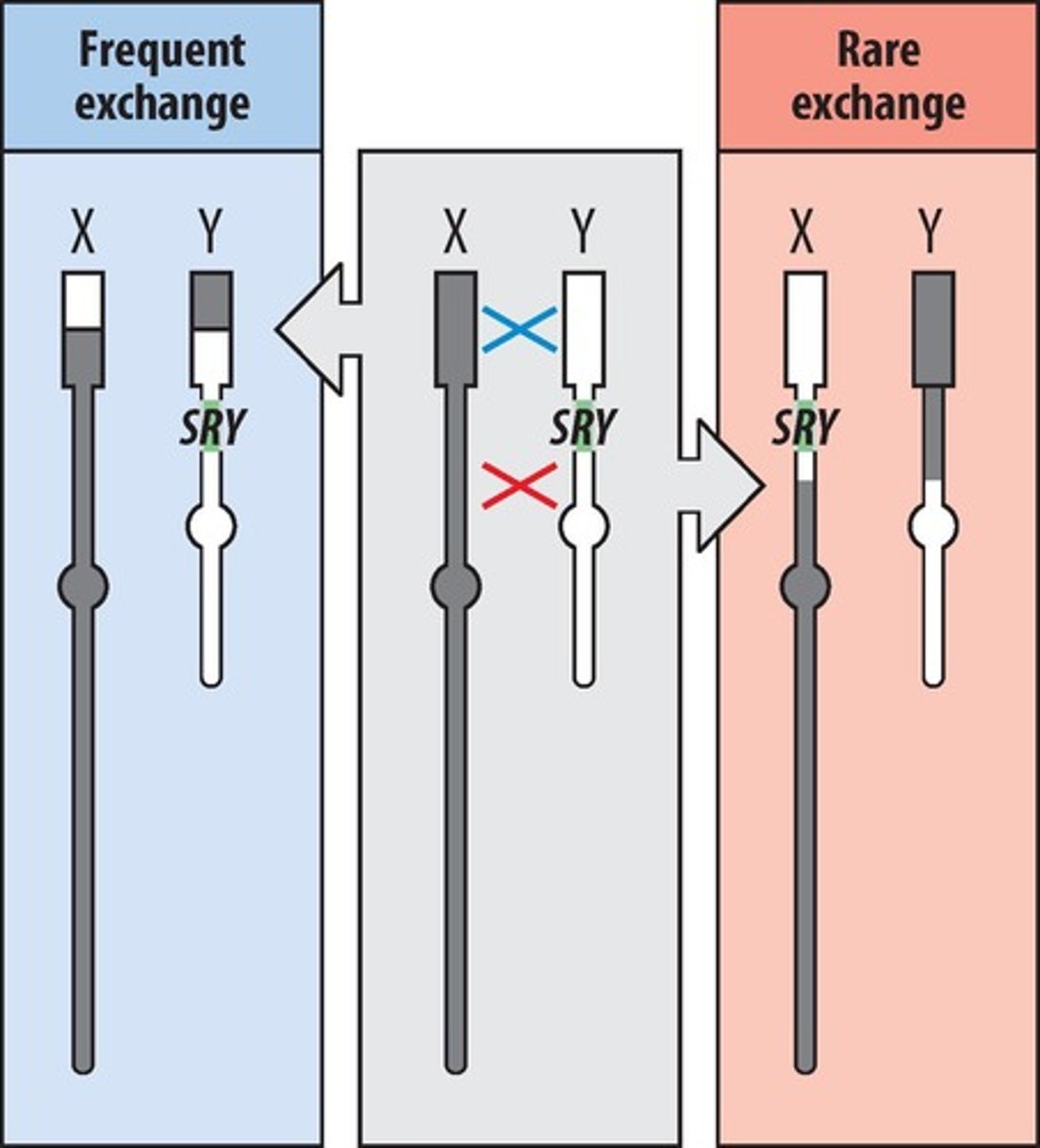
SRY gene
Sex-determining region of the Y chromosome.
Klinefelter syndrome
Condition of males with extra X chromosomes (XXY).
Turner syndrome
Condition of females with a single X chromosome (X0).
Sertoli cells
Cells essential for testes formation.
Sox9
Gene induced by SRY for male development.
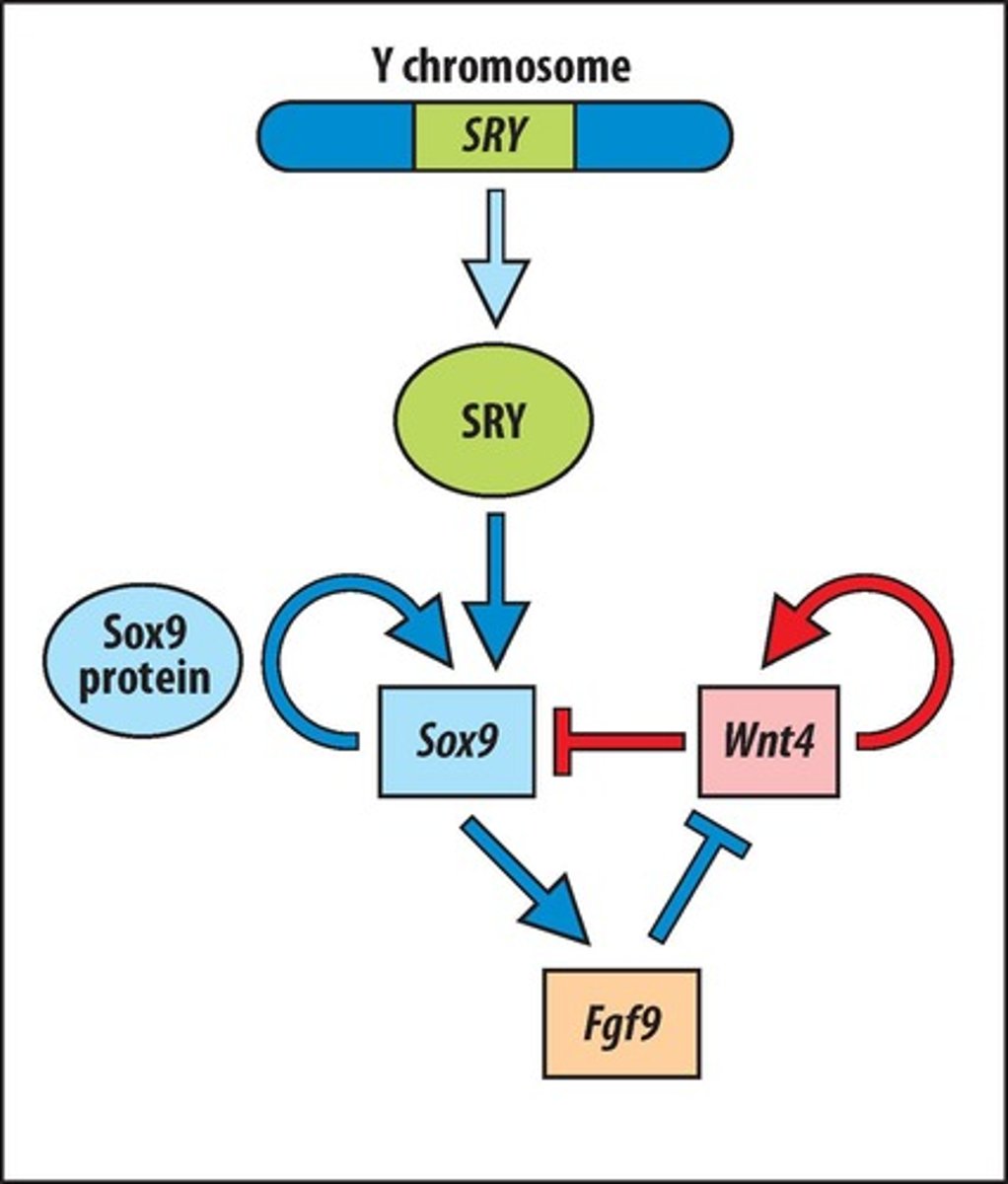
Fgf9
Gene that represses female development signals.
Wnt4
Gene that promotes female development.
Testosterone
Hormone produced by testes for male development.
Müllerian ducts
Structures that develop into female reproductive organs.
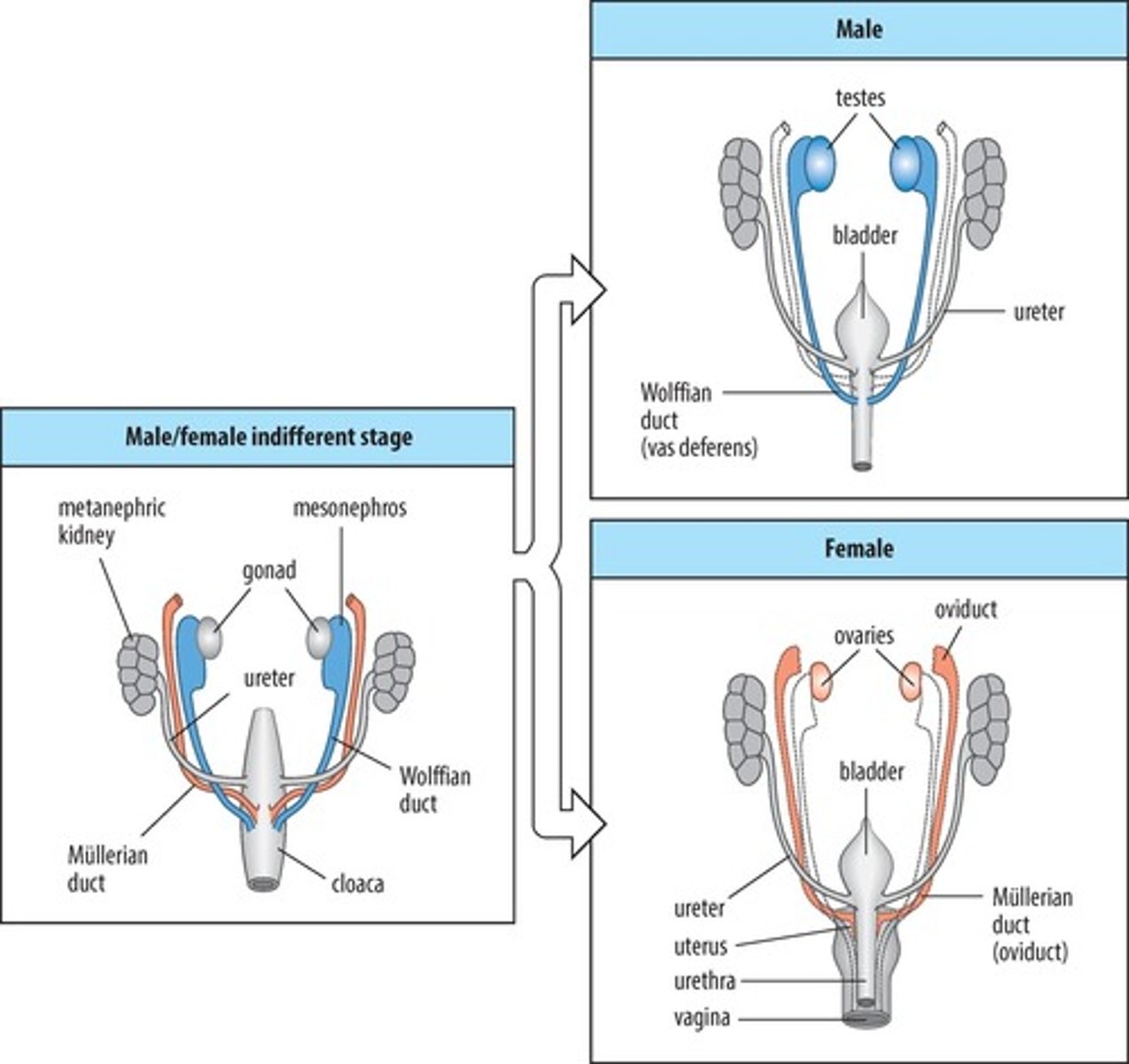
Wolffian ducts
Structures that develop into male reproductive organs.
Müllerian inhibiting substance
Substance secreted by Sertoli cells to degrade Müllerian ducts.
Germ cells
Cells that give rise to gametes (sperm and eggs).
Retinoic acid (RA)
Signal that induces meiosis in female germ cells.
Cyp26b1
Protein that degrades retinoic acid in male germ cells.
Barr body
Inactivated X chromosome in female mammals.
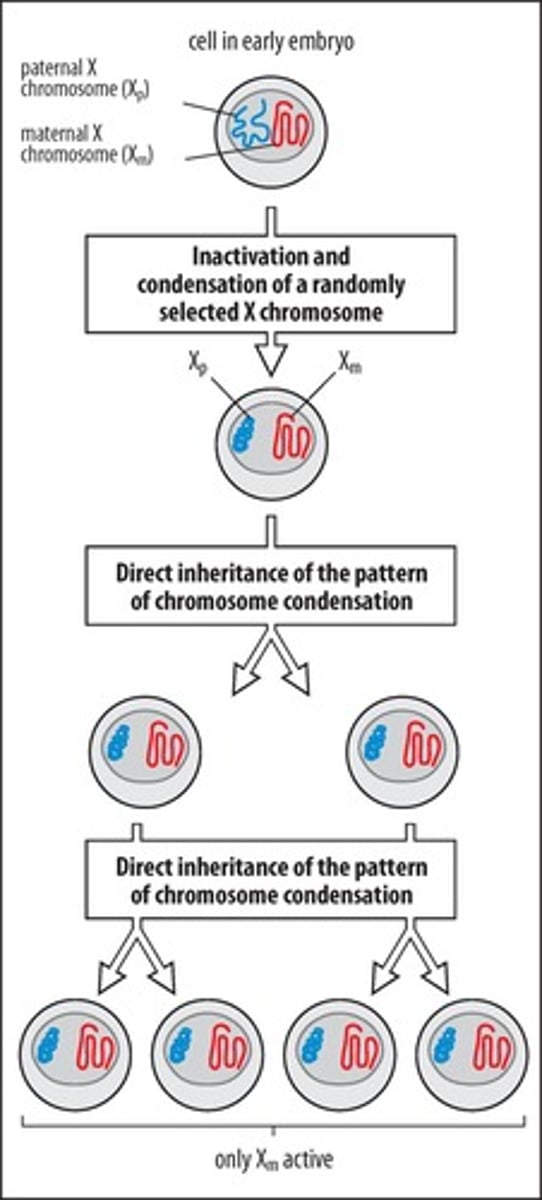
Xist RNA
RNA that induces X chromosome inactivation.
Dosage compensation
Equalization of gene expression from sex chromosomes.
Epigenetic changes
Modifications that affect gene expression without altering DNA.
Histone methylation
Modification affecting chromatin structure and gene expression.
Histone acetylation
Modification that generally promotes gene expression.
Prophase of meiosis I
Stage where vertebrate oocytes arrest development.
Sperm nucleus fusion
Process where sperm nucleus combines with oocyte nucleus.
Intracellular Ca++ release
Trigger for zygote activation post-fertilization.
Sperm centrioles
Structures used for first zygote division.
Sex reversal
Condition where chromosomal sex does not match phenotype.
Primordial germ cells
Early cells that develop into gametes.
Mosaic X inactivation
Random inactivation of one X chromosome in females.
Calico cats
Example of mosaicism due to X-linked genes.

Epigenetic control
Regulation of gene expression through chemical modifications.
Fertilization process
Multistep interaction between sperm and egg.
Hyaluroidinase
Enzyme that digests hyaluronic acid in cumulus layer.
Acrosome reaction
Release of enzymes to penetrate the zona pellucida.
Sperm binding
Initial interaction of sperm with zona pellucida.
Meiosis timing
Differential timing of meiosis in male and female germ cells.