Chapter 6 End of Chapter Questions
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Knowledge and Comprehension
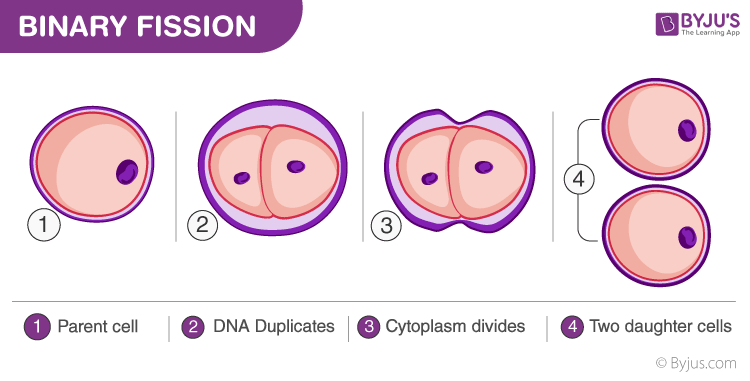
Describe binary fission.
The cell elongates, the chromosome replicates, the nuclear material is evenly divided, the plasma membrane invaginates towards the cell’s center of the cell, and the cell wall thickens and grows inward between the membrane invaginations. Together, this results in 2 new cells.
Macronutrients (needed in relatively large amounts) are often listed as CHONPS. What does each of these letters indicate, and why are they needed by the cell? *separate card for each letter*
C
Carbon: synthesis of organic molecules
Macronutrients (needed in relatively large amounts) are often listed as CHONPS. What does each of these letters indicate, and why are they needed by the cell? *separate card for each letter*
H
Hydrogen: synthesis of organic molecules, source of electrons
Macronutrients (needed in relatively large amounts) are often listed as CHONPS. What does each of these letters indicate, and why are they needed by the cell? *separate card for each letter*
O
Oxygen: synthesis of organic molecules; electron acceptor in aerobes.
Macronutrients (needed in relatively large amounts) are often listed as CHONPS. What does each of these letters indicate, and why are they needed by the cell? *separate card for each letter*
N
Nitrogen: synthesis of amino acids, nucleic acids, proteins
Macronutrients (needed in relatively large amounts) are often listed as CHONPS. What does each of these letters indicate, and why are they needed by the cell? *separate card for each letter*
P
Phosphorus: synthesis of nucleic acids and phospholipids
Macronutrients (needed in relatively large amounts) are often listed as CHONPS. What does each of these letters indicate, and why are they needed by the cell? *separate card for each letter*
S
Sulfur: synthesis of some amino acids.
Define and explain the importance of each of the following:
catalase
Catalyzes breakdown of H2O2 (hydrogen peroxide) —> O2, H2O
Define and explain the importance of each of the following:
hydrogen peroxide
= H2O2, peroxide ion is O22-
Define and explain the importance of each of the following:
peroxidase
catalyzes breakdown of H2O2 —> H2O
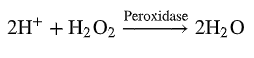
Define and explain the importance of each of the following:
superoxide radical
= O2-, this anion has 1 unpaired electron
Define and explain the importance of each of the following:
superoxide dismutase
Converts superoxide —> O2, H2O2
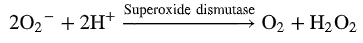
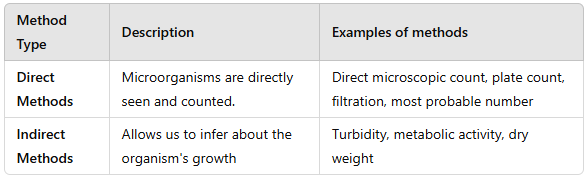
Seven methods of measuring microbial growth were explained in this chapter. Categorize each as either a direct or an indirect method.
By deep-freezing, bacteria can be stored without harm for extended periods. Why do refrigeration and freezing preserve foods?
Because bacterial growth decreases with lower temperatures. Mesophilic bacteria will grow slowly at refrigeration temperatures and will remain dormant in a freezer. Therefore, bacteria won't spoil food quickly in a refrigerator.
A pastry chef accidentally inoculated a cream pie with six S. aureus cells. If S. aureus has a generation time of 60 minutes, how many cells would be in the cream pie after 7 hours?
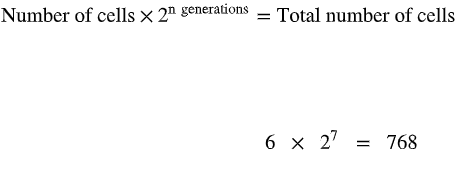
Nitrogen and phosphorus added to beaches following an oil spill encourage the growth of natural oil-degrading bacteria. Explain why the bacteria do not grow if nitrogen and phosphorus are not added.
The petroleum in oil meets the carbon and energy requirements for these oil-degrading bacterium but they still lack nitrogen and phosphate which are essential for making proteins, phospholipids, nucleic acids, and ATP.
Differentiate complex and chemically defined media.
Chemically defined medium: exact chemical composition is known (usually everything is listed out in grams and doesn’t contain substances of unknown concentrations (ex: extracts))
Complex medium: exact chemical composition is unknown (usually contains extracts, peptones)
DRAW IT Draw the following growth curves for E. coli, starting with 100 cells with a generation time of 30 minutes at 35 °C, 60 minutes at 20 °C, and 3 hours at 5 °C.
The cells are incubated for 5 hours at 35 °C
After 5 hours, the temperature is changed to 20 °C for 2 hours.
After 5 hours at 35 °C, the temperature is changed to 5 °C for 2 hours followed by 35 °C for 5 hours.
NAME IT A prokaryotic cell hitched a ride to Earth on a space shuttle from some unknown planet. The organism is a psychrophile, an obligate halophile, and an obligate aerobe. Based on the characteristics of the microbe, describe the planet.
Cold, salty, aerobic
psychrophile thrives in cold temps
halophiles thrive in salty environments
aerobes thrive in oxygenated environments
Multiple Choice
Two culture media were inoculated with four different bacteria. After incubation, the following results were obtained:
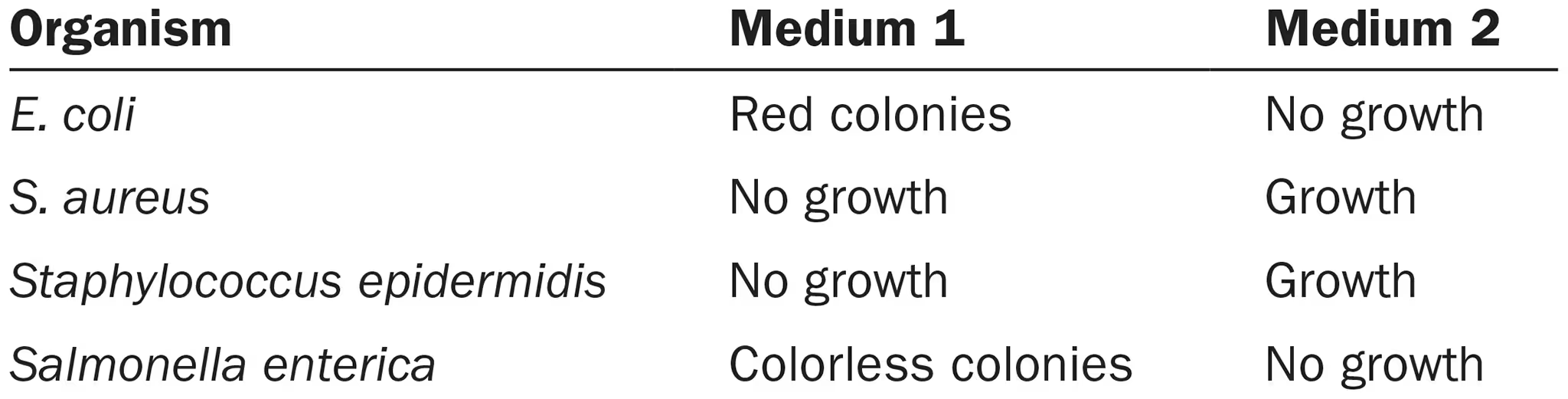
Medium 1 is:
selective
differential
both selective and differential
3
selective cuz certain bacteria grow on it while others don’t
differential cuz the bacteria are visually distinct (usually due to compounds in the medium)
Two culture media were inoculated with four different bacteria. After incubation, the following results were obtained:

Medium 2 is:
selective
differential
both selective and differential
1
selective cuz only certain bacteria grow on it
not differential cuz it doesn’t say the bacteria are distinguishable, just states growth
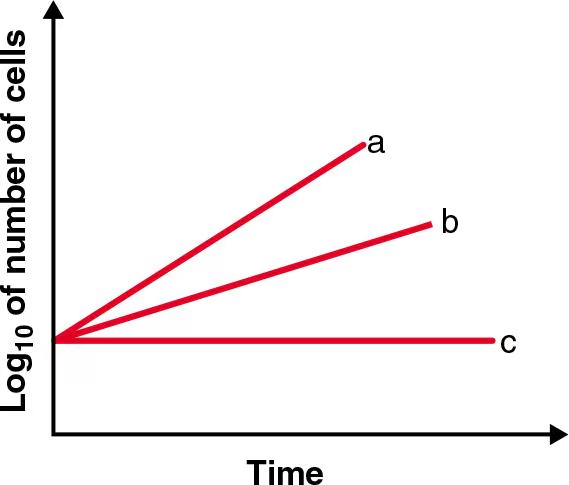
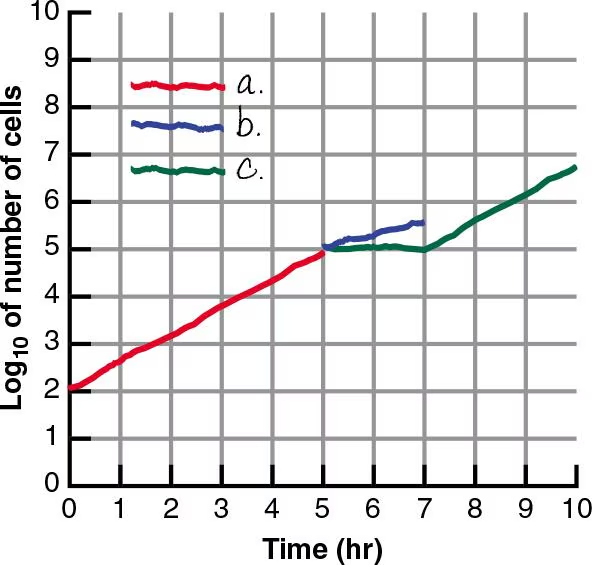
Which of the lines best depicts the log phase of a thermophile incubated at room temperature?
C
log phase = exponential growth of bacteria
thermophiles thrive in warmer environments, not room temp, and would therefore be unable to grow
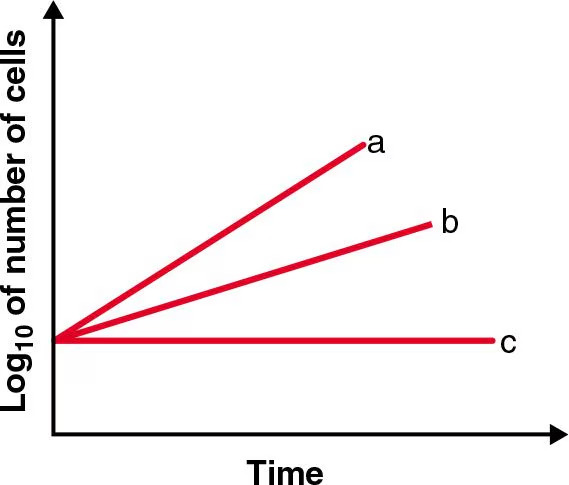
Which of the lines best depicts the log phase of Listeria monocytogenes growing in a human?
A
Listeria is a mesophile, they thrive between 20-45 °C (this includes human body temp (36.4-37.5 °C)) and would therefore grow exponentially
Assume you inoculated 100 facultatively anaerobic cells onto nutrient agar and incubated the plate aerobically. You then inoculated 100 cells of the same species onto nutrient agar and incubated the second plate anaerobically. After incubation for 24 hours, you should have
more colonies on the aerobic plate
more colonies on the anaerobic plate.
the same number of colonies on both plates
3
textbook says 3 but that doesn’t make sense, it should be 1 according to the figure
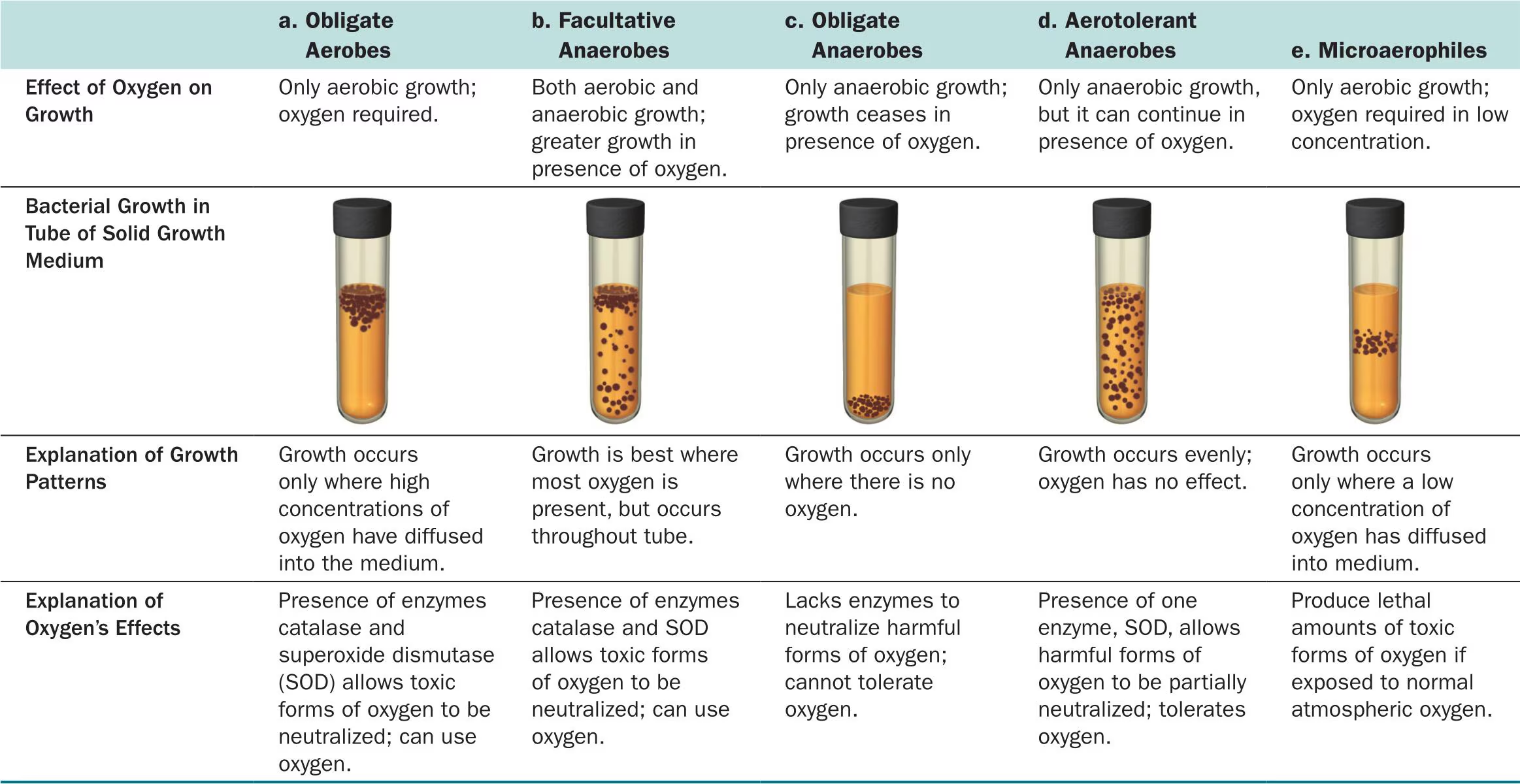
might actually be 3
The term trace elements refers to
the elements CHONPS.
vitamins.
nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur.
small mineral requirements.
toxic substances.
4
Which one of the following temperatures would most likely kill a mesophile?
-50 °C
0 °C
9 °C
37 °C
60 °C
5
Which of the following is not a characteristic of biofilms?
antibiotic resistance
hydrogel
iron deficiency
quorum sensing
3
The correct answer is iron deficiency because biofilms are typically not characterized by iron deficiency. Biofilms are clusters of microorganisms that adhere to surfaces and are embedded in a self-produced matrix of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS), which often contains water (hydrogel). Biofilms can exhibit antibiotic resistance due to the protective nature of the EPS matrix and the altered microenvironment inside the biofilm. They also rely on quorum sensing, a form of communication between bacteria that helps coordinate their behavior, including biofilm formation. However, iron deficiency is not a defining characteristic of biofilms, although some bacteria in biofilms may experience nutrient limitations, including iron, depending on their environment.
Which of the following types of media would not be used to culture aerobes?
selective media
reducing media
enrichment media
differential media
complex media
2
The correct answer is reducing media, as it is designed to create anaerobic conditions by removing oxygen from the environment, which is not suitable for culturing aerobes. Selective media is used to inhibit the growth of certain organisms while allowing others to grow, and it can be used for aerobes if it supports their growth. Enrichment media is used to enhance the growth of specific microorganisms, including aerobes, by providing optimal conditions. Differential media allows differentiation between microorganisms based on specific characteristics, such as color changes, and can be used to culture aerobes if suitable for their growth. Complex media is made from extracts like yeast or beef, providing nutrients for a wide variety of microorganisms, including aerobes.
An organism that has peroxidase and superoxide dismutase but lacks catalase is most likely an
aerobe.
aerotolerant anaerobe.
obligate anaerobe.
2
The correct answer is aerotolerant anaerobe. This type of organism does not use oxygen for growth but can tolerate its presence due to the presence of enzymes like peroxidase and superoxide dismutase, which help break down toxic oxygen derivatives such as hydrogen peroxide and superoxide. However, it lacks catalase, an enzyme typically found in aerobes, which breaks down hydrogen peroxide more efficiently. Aerobes would have all three enzymes (peroxidase, superoxide dismutase, and catalase) to fully manage the toxic byproducts of oxygen metabolism. Obligate anaerobes do not have these enzymes and cannot tolerate oxygen, so they would not be able to survive in the presence of oxygen, even with peroxidase and superoxide dismutase.
Analysis
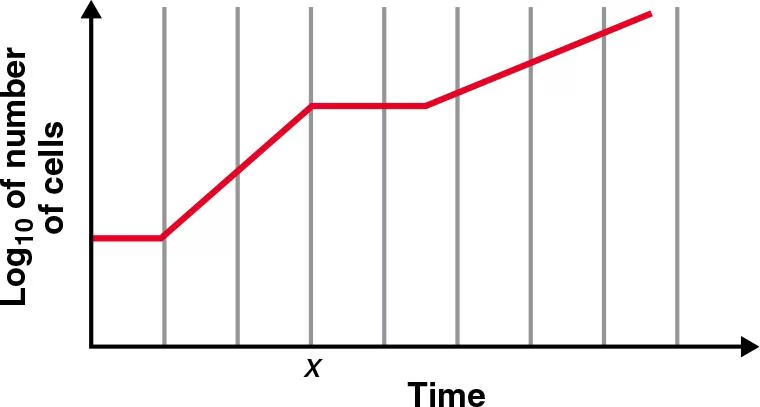
E. coli was incubated with aeration in a nutrient medium containing two carbon sources, and the following growth curve was made from this culture.
Explain what happened at the time marked x.
At x, E.coli used up all of substrate 1 and stopped growing as it needed to make new enzymes to digest/utilize substrate 2
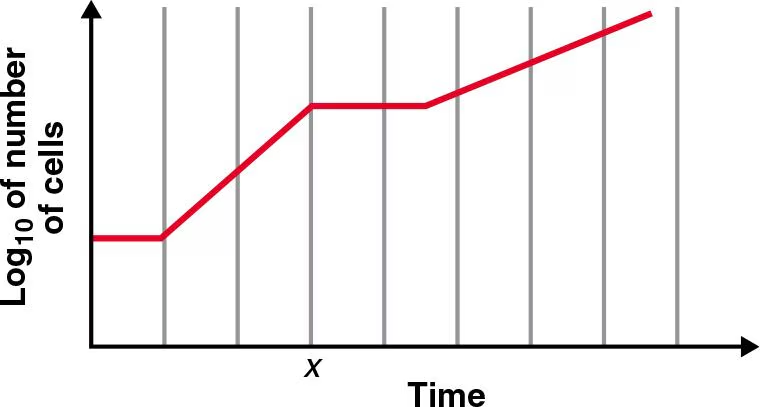
E. coli was incubated with aeration in a nutrient medium containing two carbon sources, and the following growth curve was made from this culture.
Which substrate provided “better” growth conditions for the bacteria? How can you tell?
The 1st substrate as seen by the steepness of the line.
Clostridium and Streptococcus are both catalase-negative. Streptococcus grows by fermentation. Why is Clostridium killed by oxygen, whereas Streptococcus is not?
Because it has SOD (superoxide dismutase) or an equivalent system that neutralizes the toxic forms of oxygen. This allows for facultative anaerobes to survive outside of anaerobic conditions.
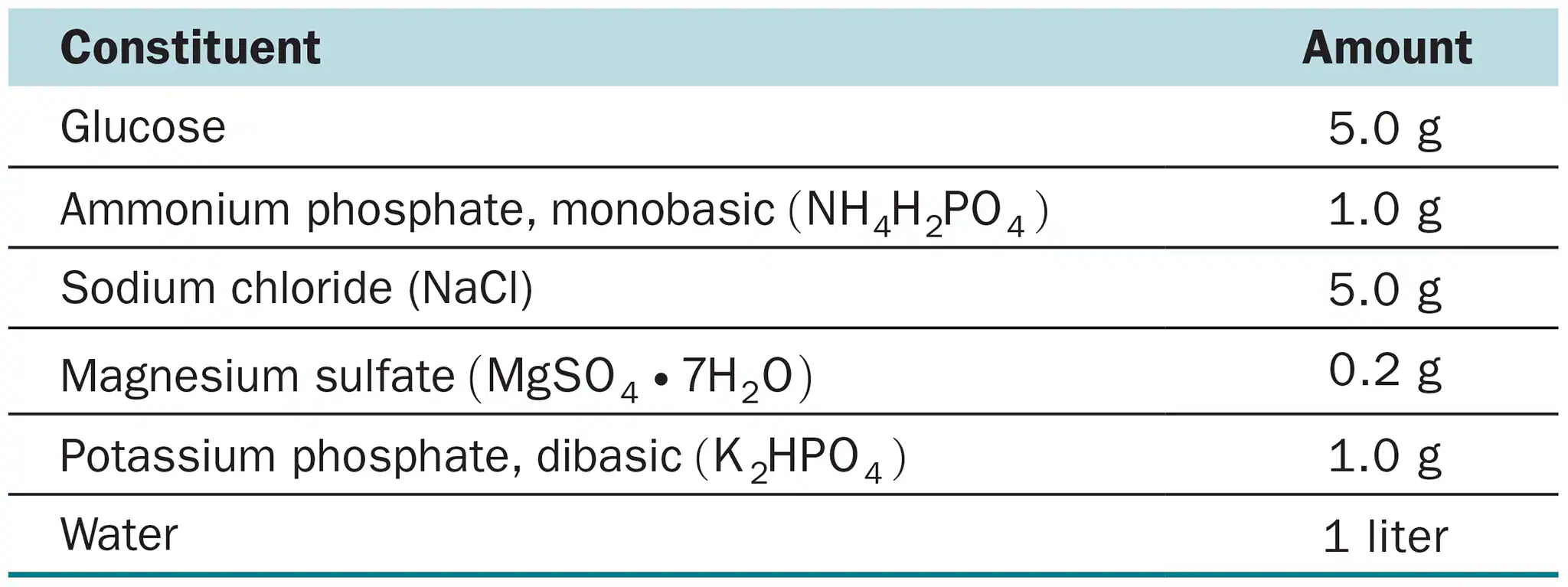
Most laboratory media contain a fermentable carbohydrate and peptone because the majority of bacteria require carbon, nitrogen, and energy sources in these forms. How are these three needs met by glucose–minimal salts medium? (Hint: See Table 6.2.)
The glucose-minimal salts medium provides bacteria with their 3 basic needs (carbon, nitrogen, and energy sources) through glucose, peptone, and essential nutrients (ex: vitamins, minerals) respectively
Flask A contains yeast cells in glucose–minimal salts broth incubated at 30 °C with aeration. Flask B contains yeast cells in glucose–minimal salts broth incubated at 30 °C in an anaerobic jar. The yeasts are facultative anaerobes.
Which culture produced more ATP?
Which culture produced more alcohol?
Which culture had the shorter generation time?
Which culture had the greater cell mass?
Which culture had the higher absorbance?
A
B
A
A
A
Clinical Applications and Evaluation
Assume that after washing your hands, you leave ten bacterial cells on a new bar of soap. You then decide to do a plate count of the soap after it was left in the soap dish for 24 hours. You dilute 1g of the soap 1:106 and plate it on heterotrophic plate count agar. After 24 hours of incubation, there are 168 colonies.
How many bacteria were on the soap?
How did they get there?
168 x 10^6
number of bacteria= number of colonies on plate x reciprocal of dilution of sample
The initial 10 bacteria on the soap multiplied. Soap can create a moist environment that allows bacteria to grow, especially if nutrients (like skin oils) are present.
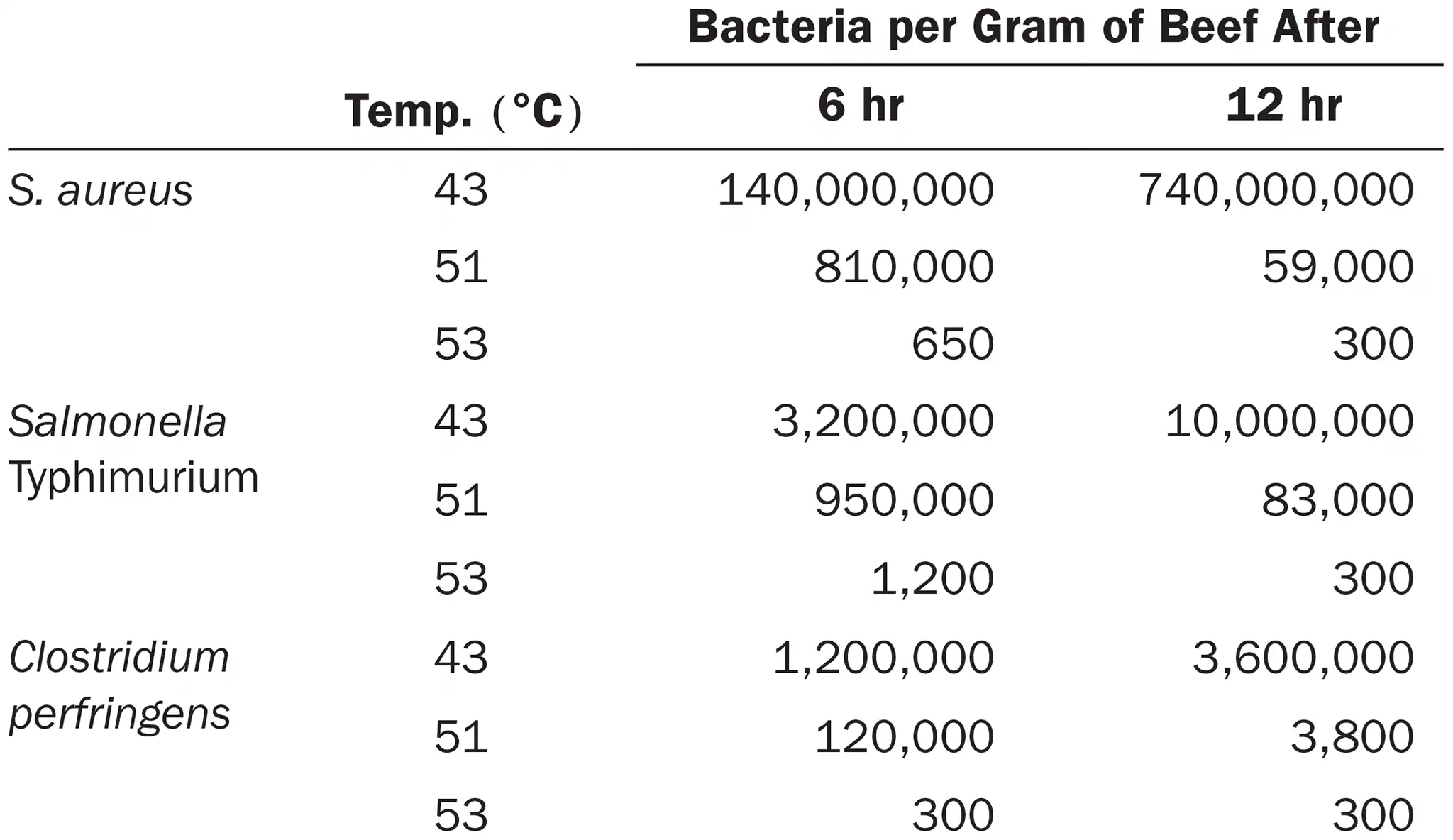
Heat lamps are commonly used to maintain foods at about 50 °C for as long as 12 hours in cafeteria serving lines. The following experiment was conducted to determine whether this practice poses a potential health hazard.
Beef cubes were surface-inoculated with 500,000 bacterial cells and incubated at 43-53 °C to establish temperature limits for bacterial growth. The following results were obtained from heterotrophic plate counts performed on beef cubes at 6 and 12 hours after inoculation: (view image)
Draw the growth curves for each organism.
What holding temperature would you recommend?
Assuming that cooking kills bacteria in foods, how could these bacteria contaminate the cooked foods?
What disease does each organism cause?
just do a standard growth curve
43 °C (doesn’t make sense just go with 53 cuz it results in the least bacteria)
through resistant endospores
S. aureus: staphylococcal food poisoning
S. typhimurium: typhoid fever
C. perfringens: clostridium perfringens gastroenteritis
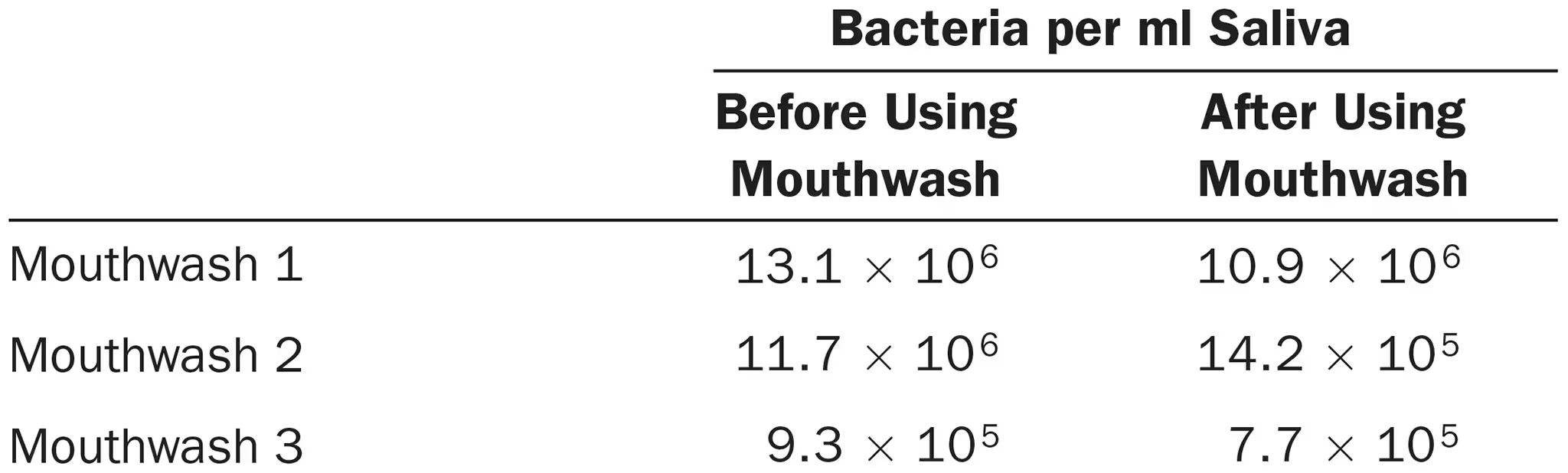
The number of bacteria in saliva samples was determined by collecting the saliva, making serial dilutions, and inoculating nutrient agar by the pour plate method. The plates were incubated aerobically for 48 hours at 37 °C.
What can you conclude from these data?
Did all the bacteria present in each saliva sample grow?
# of bacteria decreased after using each mouthwash
It cannot be inferred from this data whether all the bacteria present in each saliva sample grew, as the numbers can both decrease and increase after using mouthwash. However, based on the specific data for each mouthwash, we can see that the effectiveness of mouthwash in reducing or increasing bacteria may vary.