Lab 4- Bone tissue
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Hyaline Cartilage
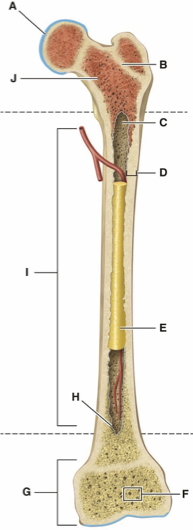
What is Letter A?
Epiphyseal lines
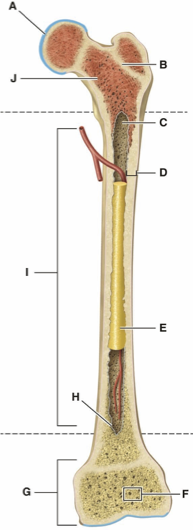
What is Letter B?
Medullary Cavity

What is Letter C?
Compact bone
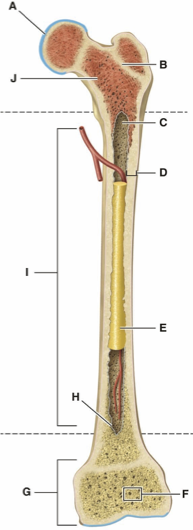
What is Letter D?
Yellow bone marrow

What is Letter E?
Spongy bone
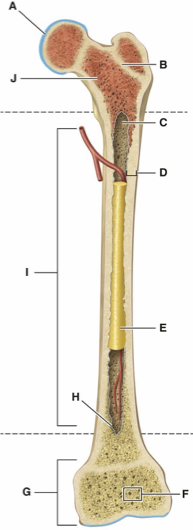
What is Letter F?
Epiphysis
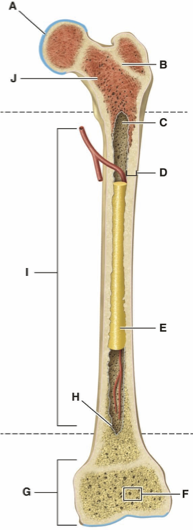
What is Letter G?
femur
humerus
Which is an example of a long bone
Irregular
A vertebra is an example of what shape of bone?
Long bones
Longer than wide
Rigid levers acted upon by muscles; crucial for movement
Flat bones
´Thin, curved plates
´Protect soft organs
Short bones
Approximately equal in length and width
Glide across one another in multiple directions
Irregular bones
Elaborate shapes that do not fit into other categories
Compact bone: Dense, solid, forms outer layer of bones, provides strength and support.
Spongy bone: Porous, lighter, found inside bones (especially at ends), contains red bone marrow for blood cell production.
Compare and contrast spongy bone and compact bone.
Organic components (collagen and proteins): Provide flexibility and tensile strength.
Inorganic components (calcium salts, mainly hydroxyapatite): Provide hardness and resistance to compression.
What are the roles of the organic and inorganic components of the bone matrix?
Body
superior and inferior articular facets
vertebral arch (laminae and pedicles)
spinous process
transverse process
vertebral foramen
transverse foramen
intervertebral foramen
What are the main parts of a vertebra?
7
How many cervical vertebrae are there
Transverse foramina in their transverse processes.
What unique feature do cervical vertebrae have?
It’s called the vertebra prominens; its spinous process is larger and rounded at the end instead of bifid (forked).
what is special about the C7 vertebra?
The odontoid process (aka dens), which allows head rotation.
What is the unique feature of the axis (C2)
12
How many thoracic vertebrae are there
Demifacets or facets for ribs and long spinous processes.
What features do thoracic vertebrae have?
they have no holes (no transverse foramina)
three prongs.
What are two identifying characteristics of thoracic vertebrae?
5
How many lumbar vertebrae are there
Much larger than the others, have no holes, and five prongs.
what are the characteristics of lumbar vertebrae?
Sacrum – 5 fused bones
Coccyx – usually 4 fused bones (can be 3–5).
How many bones make up the sacrum and coccyx?
Superior articular process
dorsal and pelvic sacral foramina
sacral promontory
sacral canal
sacral hiatus
body
medial sacral crest
What are key features of the sacrum?
sacral promontory
The prominent ridge at the top of the sacrum that marks the pelvic boundary.
Thoracic and sacral curves
present before birth (fetal “C” shape).
What are the primary spinal curves?
Cervical (lift the head)
lumbar (walk)—develop after birth
what are the secondary spinal curves?
Manubrium
body (gladiolus)
xiphoid process
What are the three parts of the sternum?
notch
jugular notch
sternal angle
What are notable features of the sternum?
Vertebrosternal (True ribs): 1–7
Vertebrochondral (False ribs): 8–12
Vertebral (Floating ribs): 11–12
how are ribs classified?
Costal cartilage
What connects ribs to the sternum?
Periosteum
outermost layer of bone
Perforating fibers
collagen fibers that anchors the periosteum to bone
Osteogenic (osteoprogenitor) cells
stem cells that become osteoblasts
Osteoblasts
bone cells that build bone
Osteoclasts
bone cells that break down bone