peptide bond and proteins
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
topic 3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
the peptide bond
how amino acids are linked together to form proteins
peptide bonds are formed when 2 amino acids come together
Has a partial double bond character on the C-N bond.
position of the double bond is not fixed over time
general structure of amino acids
Amino Group (NH₂)
Hydrogen (H)
Carboxyl Group (COOH)
Side Chain (R)
what is the importance of the side chain ( R groups)
Determines the reactivity and characteristics of the amino acid.
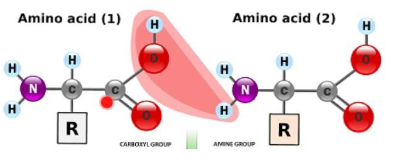
Consequences of resonance in the peptide bond - 1
▪ It increases the polarity of the peptide bond
Important for overall proteins
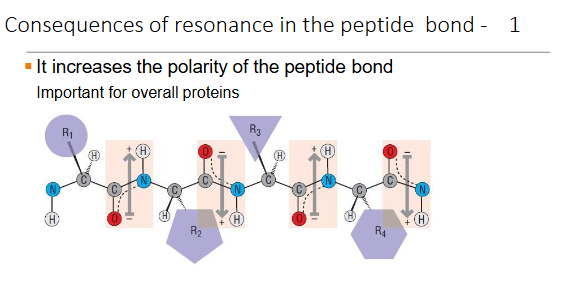
Consequences of resonance in the peptide bond - 2
It restricts movement of the atoms in the bond
Double bonds locked in position; single bonds free to rotate
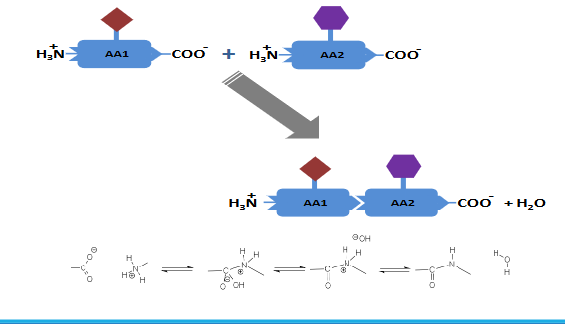
Mechanism of peptide bond formation-Nucleophilic addition-elimination reaction
Two or more amino acids can condensate via the formation of a peptide
bond (also called an amide bond)
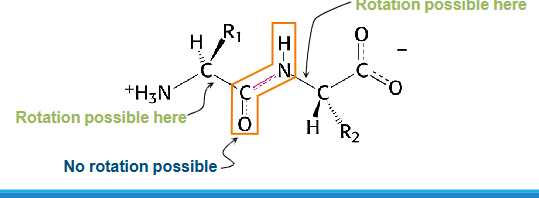
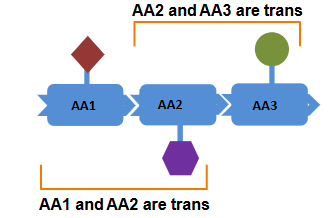
Each amino acid is trans with respect to its neighbours
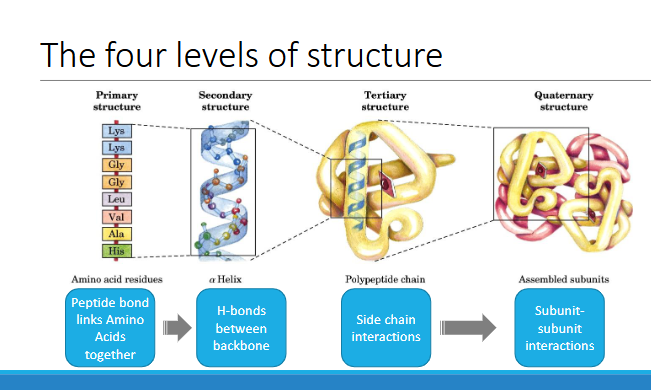
4 levels of structure
primary structure
secondary
tertiary
quaternary
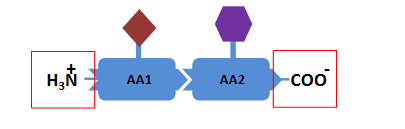
level 1- primary structure
The order of the amino acids in a polypeptide
The primary structure has direction
◦ N-terminal (amino acid group-NH3+ )→ C-terminal (carboxyl group -COO- ) end of the protein
protein sequence flexibility
Some amino acids can be swapped without affecting the protein’s function.
Amino acids with similar properties (like non-polar ones) can often replace each other without big changes.
level 2- secondary structure
Local folding of the polypeptide chains into
regular patterns – helix, sheet
2 core secondary structures
alpha helix
beta sheet
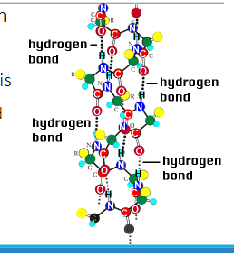
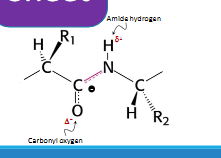
alpha helix
Hydrogen bonding between the amide hydrogen of ( residue i+4)
one AA and the carbonyl oxygen of ( residue i) another AA lead to formation of these structures
Stabilized by hydrogen bonds
Provides structural stability to proteins
Formation of the a-helix leads to
compaction of the polypeptide
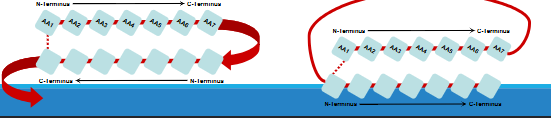
beta pleated sheet
Beta-Pleated Sheets Structure:
Amino acids (AAs) are almost fully extended.
Typically contain 5-10 amino acids.
R-groups (side chains) alternate, sticking out above and below the plane of the sheet.
Alignment of Sheets:
Sheets can line up next to each other.
Hydrogen bonds form between neighboring sheets, stabilizing the structure.
Types of Beta Sheets:
Parallel: The amino acid chains ( N-termini) run in the same direction.
Anti-parallel: The amino acid chains run in opposite directions.
beta turns
Beta turns allow a polypeptide chain to make abrupt turns, essentially making the protein chain fold back on itself.
essential for the compact and functional folding of proteins.
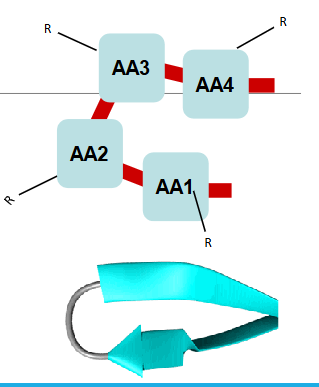
what are the 2 types of beta turns
Type I: The third amino acid (AA3) can be any amino acid.
Type II: The third amino acid (AA3) is glycine which has a small R-group (hydrogen, H), making it more flexible
WHERE A AND B MEET
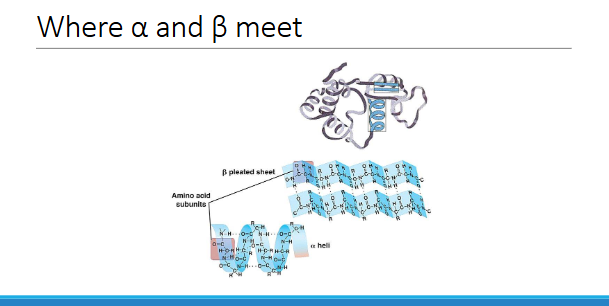
Super-secondary structures
more complex
certain structures found more commonly in protein ex.helix-loop-helix
◦ e.g. beta-alpha-beta
level 3-tertiary structure
Overall folding of a single polypeptide chain
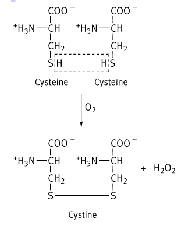
Disulphide bonds ( level 3)
Covalent link between two the –SH groups of two cysteine residues
Important for stabilisation of the overall structure and flexibility
Tendencies in Tertiary structure
Charged & polar R-groups on
the protein surface◦ Interact with water
Non-polar R-groups tend to be
buried in the cores of proteins
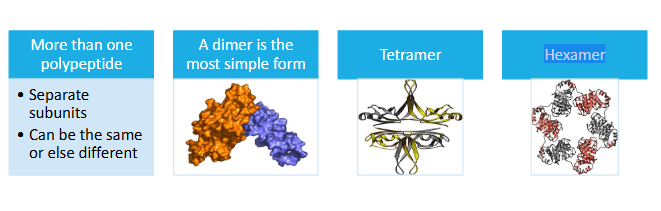
Level 4 - Quaternary structure
More than one polypeptide
A dimer is the most simple form
Tetramer
Hexamer
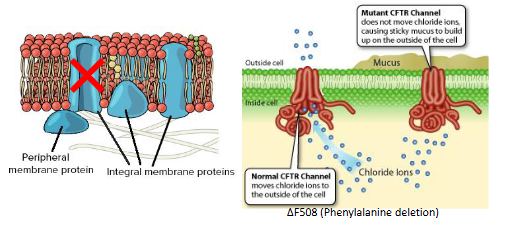
Change in structure – change in function
summary
❖ Amino acids can bind together to form a peptide bond
❖ This peptide bond can be CIS or TRANS
❖ Resonance: A peptide bond is shifting back and forth between different states and the
average is usually observed.
❖ Proteins have a specific three dimensional conformation, which is essential for their function.
❖ Four levels of structure: Primary – sequence, Secondary – local folding, Tertiary – global
folding and, Quaternary – proteins binding together.
❖ Different interactions for different levels of structure.
❖ Maintaining the correct structure is essential to maintain correct function.