induction of labour
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
what is induction of labour?
the use of medications or mechanical interventions to stimulate the onset of labour
what is the main indication for induction of labour?
41-42 weeks gestation
in what other scenarios is IOL offered?
- PROM
- fetal growth restriction
- pre-eclampsia
- obstetric cholestasis
- existing diabetes (> 38 weeks)
- intrauterine foetal death
what scoring system is used to determine whether to induce labour?
Bishop score
what 5 things get assessed in the bishop's score?
- foetal station (0-3)
- cervical position (0-2)
- cervical dilatation (0-3)
- cervical effacement (0-3)
- cervical consistency (0-2)
what is cervical effacement?
shortening and thinning of the cervix
what consistency should the cervix be for labour?
soft
what Bishop score would indicate a ripe cervix?
8 or more
what would be done if Bishop's score <6?
- offer induction of labour with prostaglandin
or
- offer mechanical method of labour induction if pharmacological methods are not suitable
what are the options for induction of labour?
- membrane sweep
- vaginal prostaglandin E2 - preferred method from NICE
- cervical ripening balloon
- dilapan induction
- artificial rupture of membranes and oxytocin infusion
- oral mifepristone (prostaglandin E1) plus misoprostol - only for foetal death
what is a membrane sweep?
inserting finger into cervix to stimulate cervix and begin labour
how soon after membrane sweep should onset of labour happen?
within 48 hours
is a membrane sweep a full method of inducing labour?
no, is more of an assistance before full induction of labour
from how many weeks is a membrane sweep performed from?
from 40 weeks
how is vaginal prostaglandin E2 given?
gel, tablet or pessary
what tablet is commonly used?
prostin
how many prostins are given?
2 tablets
what pessary is commonly used?
propess
what does the propess pessary resemble?
a tampon
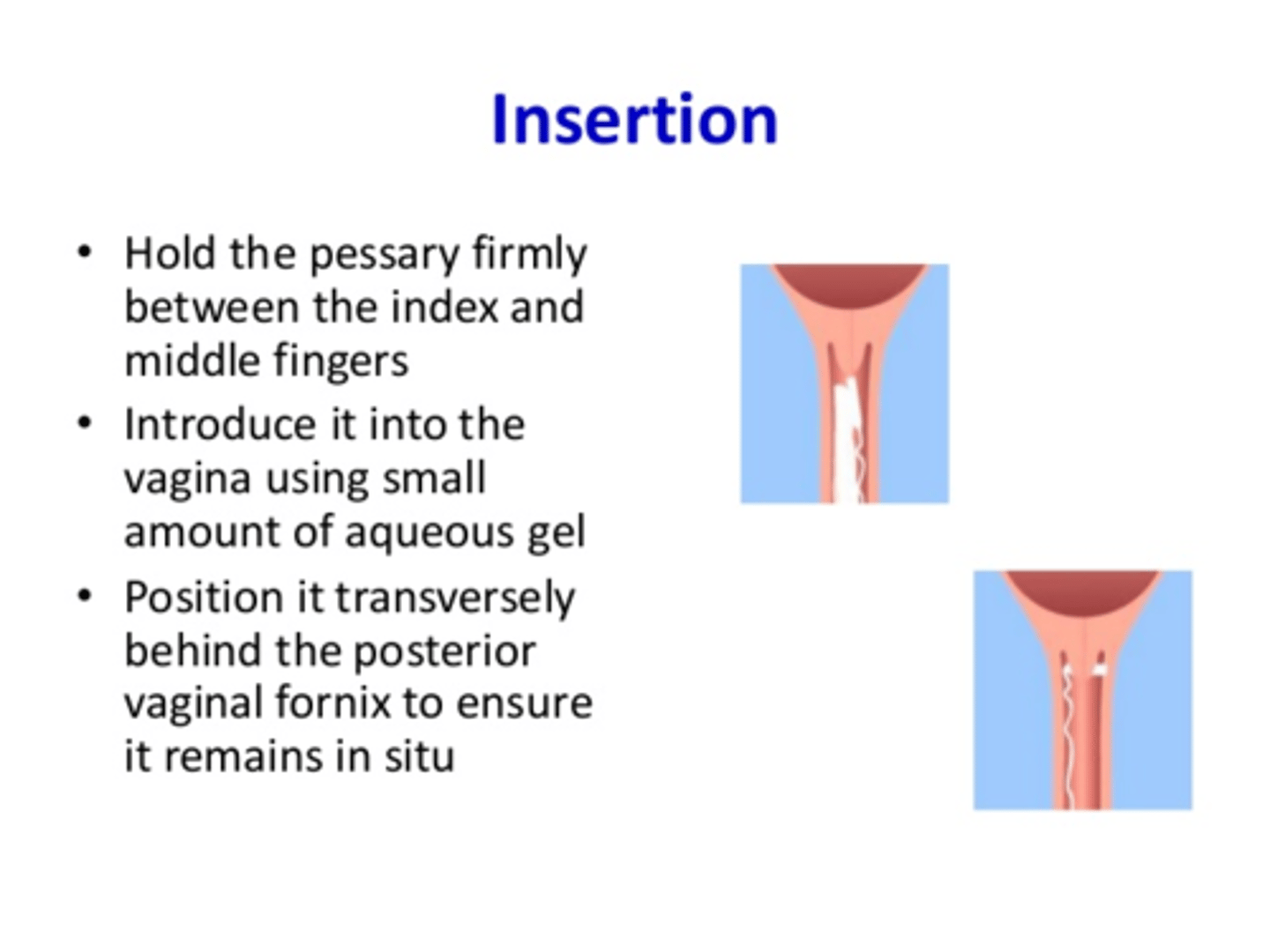
how do the tablet and pessary work?
slowly release local prostaglandins over 24 hours
what do the prostaglandins do?
stimulates cervix ripening and uterine contractions for labour
are vaginal prostaglandin E2s usually given at home or in hospital?
hospital - so the women can be monitored
when are vaginal prostaglandins contraindicated?
- previous caesarean section - as may cause scar to reopen
- multiparous (≥3 children) - risk of uterine hyperstimulation
which vaginal prostaglandin is usually given first?
propess and then prostin
what is a cervical ripening balloon?
silicone balloon inserted in the cervix and gently inflated to dilate the cervix
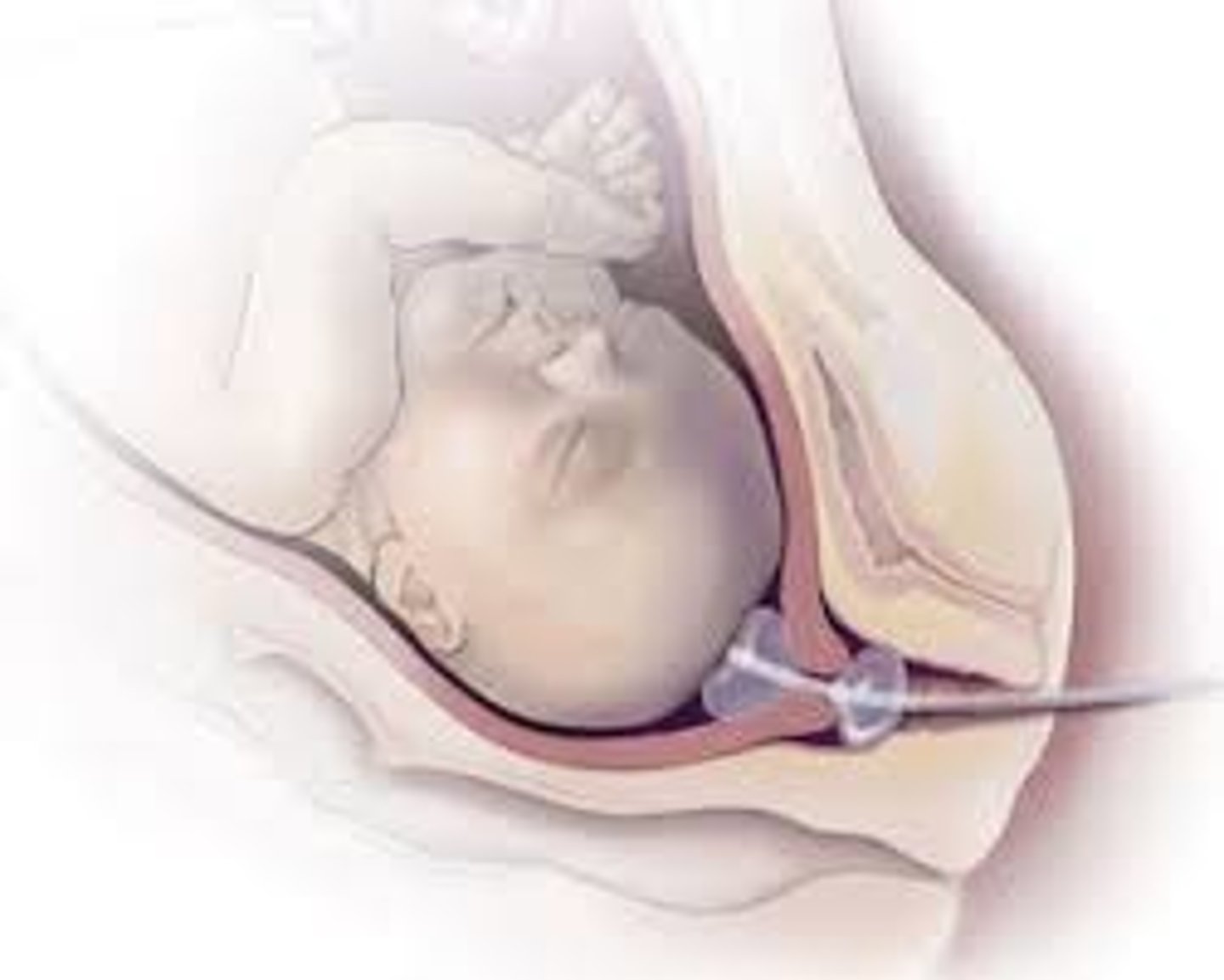
when would CRB be used?
when vaginal prostaglandins are contraindicated
what is dilapan induction?
mechanical cervical dilator
how does dilapan work?
absorbs amniontic fluid and expands to dilate cervix

what is an artificial rupture of membranes also called?
amniotomy
how is an amniotomy performed?
small, disposable hook is passed through the cervix and the amniotic sac is touched to create a hole and to release fluid
when could amniotomy and oxytocin be used?
- vaginal prostaglandins contraindicated
or
- after vaginal prostaglandins to progress labour
what are the two ways to monitor during induction of labour?
- CTG
- bishop score
within how many hours do most women give birth within from start of induction?
24 hours
what are the options when there is no or slow progress?
- further vaginal prostaglandins
- artifical ROM and oxytocin infusion
- cervical ripening balloon
- elective caesarean section
what is the main complication of induction of labour?
uterine hyperstimulation
what is uterine hyperstimulation?
contraction of uterus is prolonged and frequent causing foetal distress and compromise
what are the two criteria for uterine hyperstimulation?
- individual uterine contractions >2 minutes long
- >5 uterine contractions every 10 minutes
what can uterine hyperstimulation lead to?
- foetal compromise with hypoxia and acidosis
- emergency caesarean section
- uterine rupture
what is the management of uterine hyperstimulation?
- removing the vaginal prostaglandins or stopping oxytocin infusion
- tocolysis with terbutaline