Ch. 6: Linkage and Mapping
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
pedigree
used to determine the modes of inheritance in humans since we are not able to do crosses like in other organisms
requires recognizing patterns associated with different modes of inheritance
proband
the person for whom the pedigree is initiated
autosomal dominant
doesn’t skip generations
affected children will have at least one affected parent
affects genders equally
unaffected parents do not pass trait
X-linked dominant traits
doesn’t skip generations
affected children will have at least one affected parent
affected sons might have affected mother
affected fathers will pass the trait to all of their daughters
often more women than men affected
autosomal recessive traits
tends to skip generations
a affected child does not need to have an affected parent
affects genders equally
if both parents are unaffected, they must have an affected allele
appears more frequently when intermarriage takes place in the family
X-linked recessive traits
tends to skip generations
a affected child does not need to have an affected parent
affects males more than females
never passed from father to son
all daughters of affected father’s are carriers
Y-linked
will affect all sons of affected fathers
cannot be passed from a mother to a son
cannot be passed from a father to a daughter
does not skip generations
mitochondrial
all children of an affected mother will be affected
cannot be passed from a father to any of his children
testcross
test used to check for linkage
the homozygous recessive parent will always produce parental allele combinations (non-recombinant)
three possible outcomes
unlinked
complete linkage
linked with some crossing over
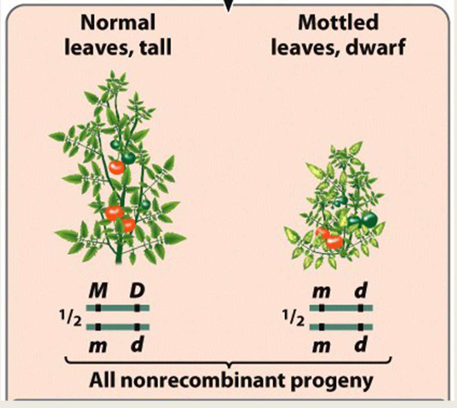
unlinked genes
½ nonrecombinant progeny and ½ recombinant progeny are produced
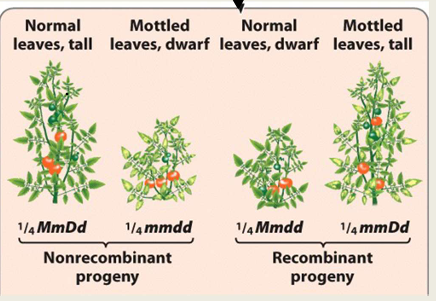
complete linkage
only nonrecombinant progeny are produced
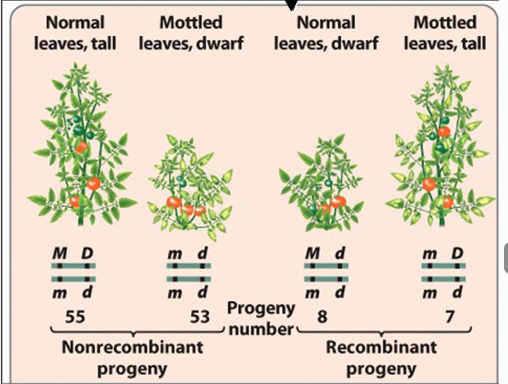
linked genes and some crossing over
mostly nonrecombinant progeny, only a small proportion recombinant
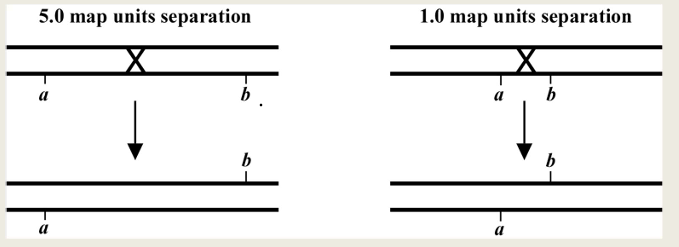
recombination frequency
tells you how far apart two loci are on a chromosome
the father apart two genes are, the more likely a recombination event will occur between them
map units
(recombinants/ total offspring) x 100 =
order of genes on a chromosome and distance between them
what recombination can be used to determine
this is due to recombination frequency being proportional to the distance between genes on a chromosome
50%
what the recombination frequency is if genes are unlinked, and assort independently