BIO 101 Chapter 3
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Water and the Fitness of the Environment
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
describe the molecule that supports all of life: water
water is the biological medium on Earth
all living organisms require water more than any other substance
most cells are surrounded by water, and cells themselves are about 70-95% water
the abundance of water is the main reason the earth is habitable
what kind of molecule is water
polar molecule
the opposite ends have opposite charges
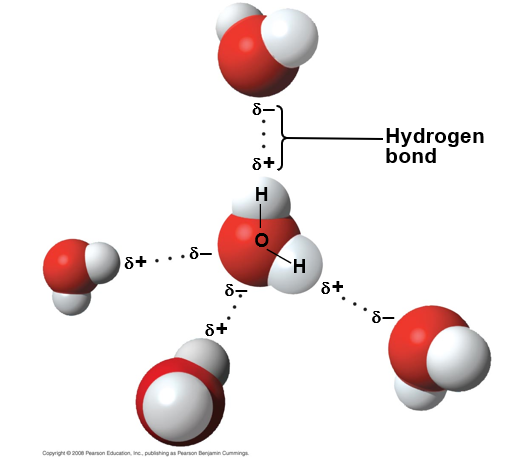
polarity allows water molecules to form hydrogen bonds with each other
what are the four properties of water that facilitate an environment for life?
cohesive behavior: the hydrogen bonds stick together
ability to moderate temperature: water stores a lot of energy allowing it to moderate temp
expansion upon freezing: less dense, floats
versatility as a solvent:water is a chemical that can dissolve a vast number of other chemicals
describe cohesion
when hydrogen bonds as a collective hold water molecules together
cohesion helps the transport of water against gravity in plants
water gets into the root of the plant, goes up the root/stem, which is all due to the hydorgen atoms sticking water together
describe adhesion
the attraction between different substances
ex. water and plant cell walls (attraction)
describe surface tension
a measure of how hard it is to break the surface of a liquid
at the air-water interface, the water forms a skin
surface tension is related to cohesion
how does water moderate temperature
water absorbs heat from warmer air and releases stored heat to cooler air
water can absorb or release a large amount of heat with only a slight change in its own temperature
describe specific heat
the amount of heat that must be absorbed or lost for 1g of that substance to change its temperature by 1 celsius
what is the specific heat of water
1cal/g/ºC
it takes 1 calorie of heat to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water by 1 degree celsius
it takes the same amount to lower it
this means that water has a relatively high specific heat compared to many other substances
what is the reason for water’s high specific heat
it can be traced to hydrogen bonding
heat is absorbed when hydrogen bonds break
heat is released when hydrogen bonds form
the high specific heat of water minimizes the temperature fluctuations to within the limits that permit life
define evaporation
the transformation of a substance from liquid to gas
describe heat of vaporization
the heat a liquid must absorb for 1 g to be converted to gas
what is evaporative cooling
as a liquid evaporates its remaining surface cools
evaporate cooling of water helps stabilize temperatures in organisms and bodies of water
describe the insulation of bodies of water by floating ice
ice floats in liquid water because hydrogen bonds in ice are more “ordered” making ice less dense
water reaches its greatest density at 4 degrees celsius
if ice sank, all bodies of water would eventually freeze solid making life impossible on Earth
if water froze from the round up there would be no life
define solution
a liquid that is homogenous mixture of substances
define solvent
the dissolving agent of a solution
define solute
the substance that is disolved
define aqueous solution
a solution in which water is the solvent
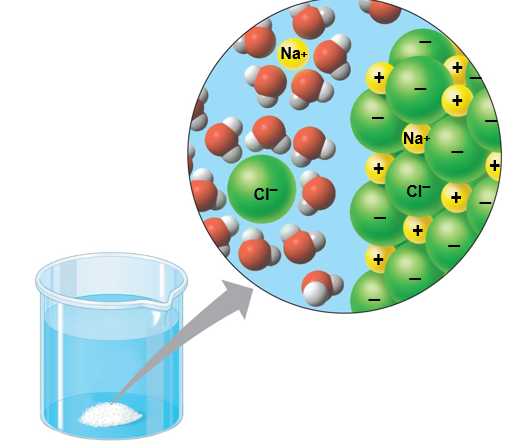
why is water a versatile solvent
due to its polarity which allows it to form hydrogen bonds easily
when an ionic compound is dissolved in water, each ion is surrounded by a sphere of water molecules called a
hydration shell
water can also dissolve compounds made of ________ polar molecules
nonionic
even large polar molecules such as proteins can dissolve in water if they have:
ionic and polar regions
define hydrophilic
a substance that has affinity for water (likes it)
define hydrophobic
a substance that does not have affinity for water (dislikes it)
oil is hydrophobic because they have relatively nonpolar bonds
define colloid
a stable suspension of fine particles in a liquid
most biochemical reactions occur in ______
water
what do chemical reactions depend on
the collisions of molecules and therefore on the concentration of solutes in an aqueous solution
define molecular mass
the sum of all masses of all atoms in a molecule
numbers of molecules are usually measured in ____
moles
1 mole = 6.02 x 1023 molecules
avogadro’s number and the unit of dalton were defined such that 6.02 x 1023 = 1 g
define molarity (m)
the number of moles of solute per liter of solution
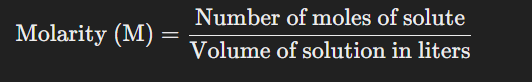
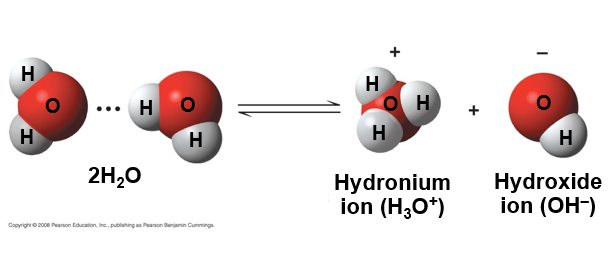
describe what happens when a hydrogen atom in a hydrogen bond between two water molecule shift from one to the other
the hydrogen atom leaves its electron behind and is transferred as a proton, or hydrogen ion (H+)
the molecule with the extra proton is now a hydronium ion (H3O+) though it is often represented as H+
the molecule that has lost proton is now a hydroxide ion (OH-)
how is water in a state of dynamic equilibrium
water molecules dissociate at the same rate at which they are being reformed
though statistically rare, the ____________of water molecules has a great effect on organism
dissociation
the changes in concentration of hydronium ion H+ and hydroxide ion OH- can drastically affect the chemistry of a cell
effects of changes in pH
concentrations of H+ and OH- are qual in pure water
adding certain solutes, called acids, and bases modifies the concentration of H+ and OH-
biologists used pH scale to describe whether a solution is acidic or basic
describe acids and bases
and acid is any substance that increases the H+ concentration of a solution
a base is any substance that reduces the H+ concentration of a solution
in any aqueous solution at 25 Celsius the product of H+ and OH- is constant and can be written as
[H+][OH–] = 10–14
the pH of a solution is defined by
the negative logarith of H+ concentration
written as pH = –log [H+]
what is te neutral aqueous solution
[H+] is 10–7 = –(–7) = 7
describe the pH scale
acidic solutions: pH less than 7
basic solutions: pH greater than 7
most biological fluids have pH values in the range of 6 to 8
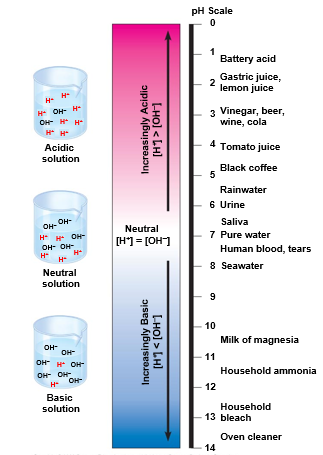
the internal pH of most living cells must remain close to ______
pH 7
what is a buffer
substances that minimize changes in concentration of H+ and OH- in a solution
bufferes dissolve in water and keep the concentration constant
most buffers consist of an acid-base pair that reversibly combines with H+
all biological systems and the human body include these different buffers
what is acid precipitation
it refers to rain, snow, or fog with a pH lower than 5.6
it is mainly caused by the mixing of different pollutants (sulfates/nitrates) with water in the air and can fall at some distance from the source of pollutants
it damages life in lakes and streams
decline in forests
how does burning fossil fuels threaten water quality
CO2 is released by fossil fuel combustion and contributes to:
warming of the earth called the “greenhouse” effect
acidification of the oceans; this leads to a decrease in the ability of corals to form calcified reefs