The Aquisition of Fear
5.0(1)Studied by 1 person
Card Sorting
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 11:53 AM on 3/28/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
1
New cards
Who postulated that fear could also be conditioned (on the basis of Pavlov’s classical conditioning?
John B. Watson, an early behaviourist
2
New cards
How did Watson show experimentally that fear can be conditioned?
With the “Little Albert” experiments, in which a child called Albert was conditioned to fear a white rat
3
New cards
What are the
Neutral Stimulus
Orientation Response
Unconditioned Stimulus Unconditioned Response Conditioned Stimulus
Conditioned Response
\
in the little Albert experiments?
Neutral Stimulus
Orientation Response
Unconditioned Stimulus Unconditioned Response Conditioned Stimulus
Conditioned Response
\
in the little Albert experiments?
(NS): white rat
(OR): looking, feeling
(US): aversive loud noise
(UR): startle reflex, fear
(CS): white rat
(CR): startle reflex, fear
(OR): looking, feeling
(US): aversive loud noise
(UR): startle reflex, fear
(CS): white rat
(CR): startle reflex, fear
4
New cards
What is learned during conditioning?
Fear response (UR) shifts from an aversive stimulus (US) to a previously neutral stimulus (CS) by association
5
New cards
People used to think that the conditioned stimulus was associated with the conditioned response in classical conditioning, but now there is a different view. What is it?
People now believe there is an association between the conditioned and a cognitive representation of the unconditioned stimulus, because they believe that the presence of the conditioned stimulus predicts the unconditioned stimulus
\
This is shown for example in rat experiments where the rats tense up when the tone is played -- they are preparing for the shock.
\
This is shown for example in rat experiments where the rats tense up when the tone is played -- they are preparing for the shock.
6
New cards
What did Mary Cover Jones show with her unlearning of fear experiment?
That it can be done, when the boy in the experiment had an aversive stimulus (a rabbit he was scared of) paired with his favourite candy, he approached the rabbit more and more and eventually unlearned his fear
7
New cards
What did O.H. Mowrer’s Two-Factor Model explain?
The fact that anxiety is maintained in phobias. According to Mowrer, it is learned by classical conditioning (being bitten by a dog), but maintained by operant conditioning (avoidance), which negatively reinforces the person, but also prevents them from realising their fear is unfounded.
8
New cards
What happens in differential fear conditioning?
The people grow to fear the CS+, but not the CS- (as indicated by their startle response)
9
New cards
What are people w anxiety worse at doing?
Differentiating between CS+ and CS-. This means they have a harder time (generally) distinguishing between what is dangerous and what is harmless
10
New cards
When does the CS lead to a fear response (indicated by neurons firing in the lateral nucleus)
After being paired with the US
11
New cards
What do experiments on generalization show?
That people generalize their fear responses (circle experiment, or the rabbit and rat in little Albert’s experiment)
12
New cards
What are the three criticisms of traditional fear acquisition theory?
1. A direct experience with an US is not necessary for fear learning
2. The US is not sufficient for fear learning (many people go through traumatic experiences and don’t develop fear responses)
3. Phobias are selective -- for example, a lot more people fear spiders than guns
13
New cards
In what three ways can a fear be acquired?
Direct experience
Modelling (vicarious conditioning)
Information transfer (learning by hearing negative stories, for example)
Modelling (vicarious conditioning)
Information transfer (learning by hearing negative stories, for example)
14
New cards
What are clinical implications of the knowledge that fear acquisition can happen in many ways?
* Fear is also learned by observing fearful behaviour of parents or signifi cant others
* Children of parents with anxiety disorders may be vulnerable to developing an anxiety disorder
* Children of parents with anxiety disorders may be vulnerable to developing an anxiety disorder
15
New cards
Considering an experience with a US is not sufficient for fear learning, what makes some people develop anxiety disorders and others not?
– individual differences in genetic predisposition and psychological traits (e.g., trait anxiety, behavioural inhibition)
– individual differences in learning history (experiences before, during or after an aversive event)
– individual differences in learning history (experiences before, during or after an aversive event)
16
New cards
How can prior experiences contribute to being a safety factor for developing a disorder after an aversive event
Prior neutral experiences with a stimulus (dog) (CS) reduces amount of fear conditioning when paired with an aversive event (being bitten one time) (US). This is called latent
17
New cards
What can be a protective factor for children for later developing phobias?
Being raised in an environment where they have control over important aspects of their environment
18
New cards
Why are we predisposed to fearing some things more than others? (selective association)
Fear for @@prepared stimuli@@ (important for evolution) easier to learn and more difficult to extinguish
19
New cards
Some fear associations are learned more easily than others (belongingness). What is an example of this?
Rats will avoid water if they’re given nauseating radiation, but not if they’re given an electric shock. This is cause certain sensory modalities are more easily associated than others
20
New cards
Inflation effect
The effect that someone will have a fear of cars after a minor accident might have a full blown phobia after being assaulted even though no car was present
21
New cards
US reevaluation process
When someone receives information about the US being more dangerous than they actually feared it being, leading to an increase in the fear response
22
New cards
What does mental rehearsal of the CS-US relationship do?
It can lead to enhanced strength of the conditioned fear response
23
New cards
What can make conditioning of a fear less?
Having control over a traumatic event, eg by being able to escape it
24
New cards
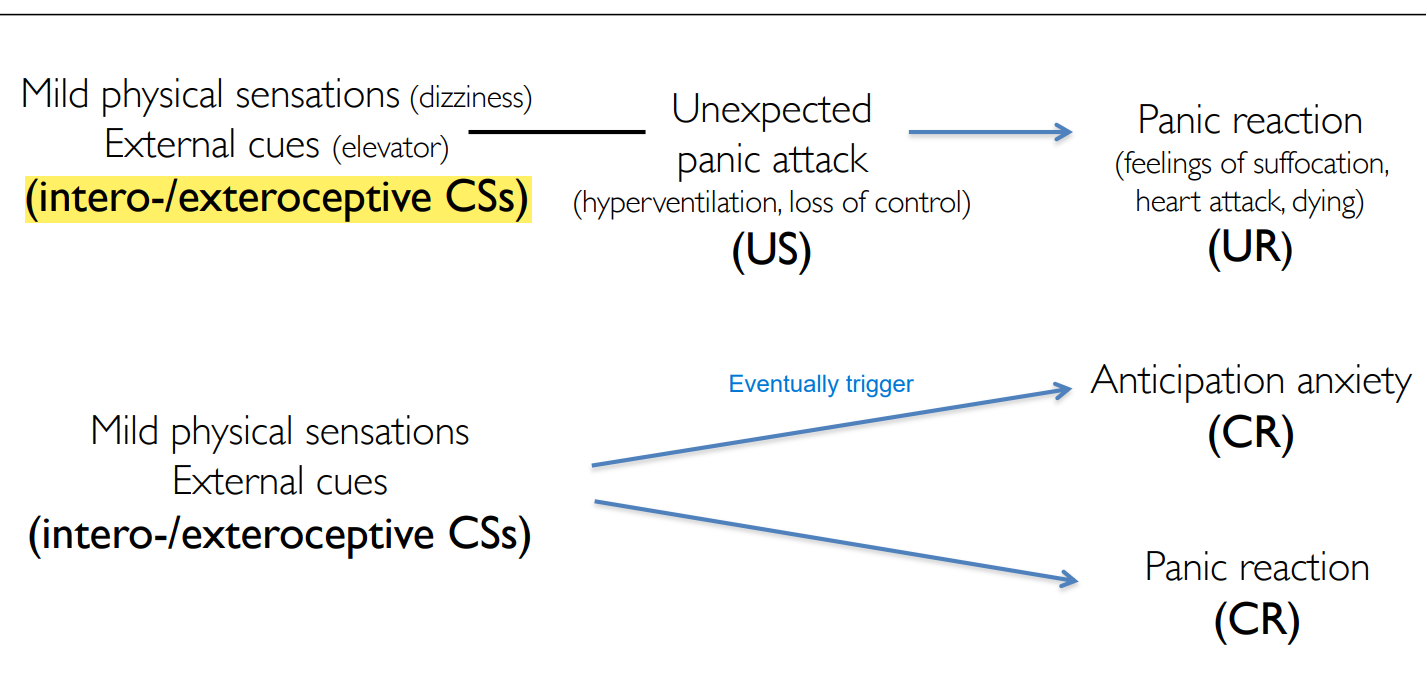
explain this
mmm