FOUNDATIONS FINAL EXAM
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
114 Terms
procedure for hanging a piggyback
1. assess IV site for patency...
2. CLOSE ROLLER CLAMP on the secondary tubing!!!
3. spike the bag
4. clean port closest to primary IV bag w wipe for 15 seconds
5. connect tubing
6. back-prime the secondary bag by holding it at waist level and releasing clamp
7. hang the secondary bag HIGHER than the primary bag using the secondary set hook
8. program the pump for the secondary bag:
—channel select
—secondary med
—find and choose piggyback med
—choose correct dose and fluid volume
—choose duration (ex: 30 min) to calculate rate
9. unclamp the roller clamp on the secondary tubing and slay
what do you need to check before hanging a secondary bag?
check compatibility of the secondary med with the med/fluids already infusing
infiltration
leakage of non-vesicant fluid into surrounding tissue
s/s of infiltration
area is cool, swollen, and painful
what to do for infiltration?
discontinue IV, elevate arm, may need compresses
infiltration of a vesicant
extravasation
what is a vesicant?
a medication that may cause permanent tissue or nerve damage (including amputation of the limb) if it leaks into tissue and is not treated
s/s of extravasation
pain, burning, change in temp of skin, tightness, blanching of area, slow or stopped infusion
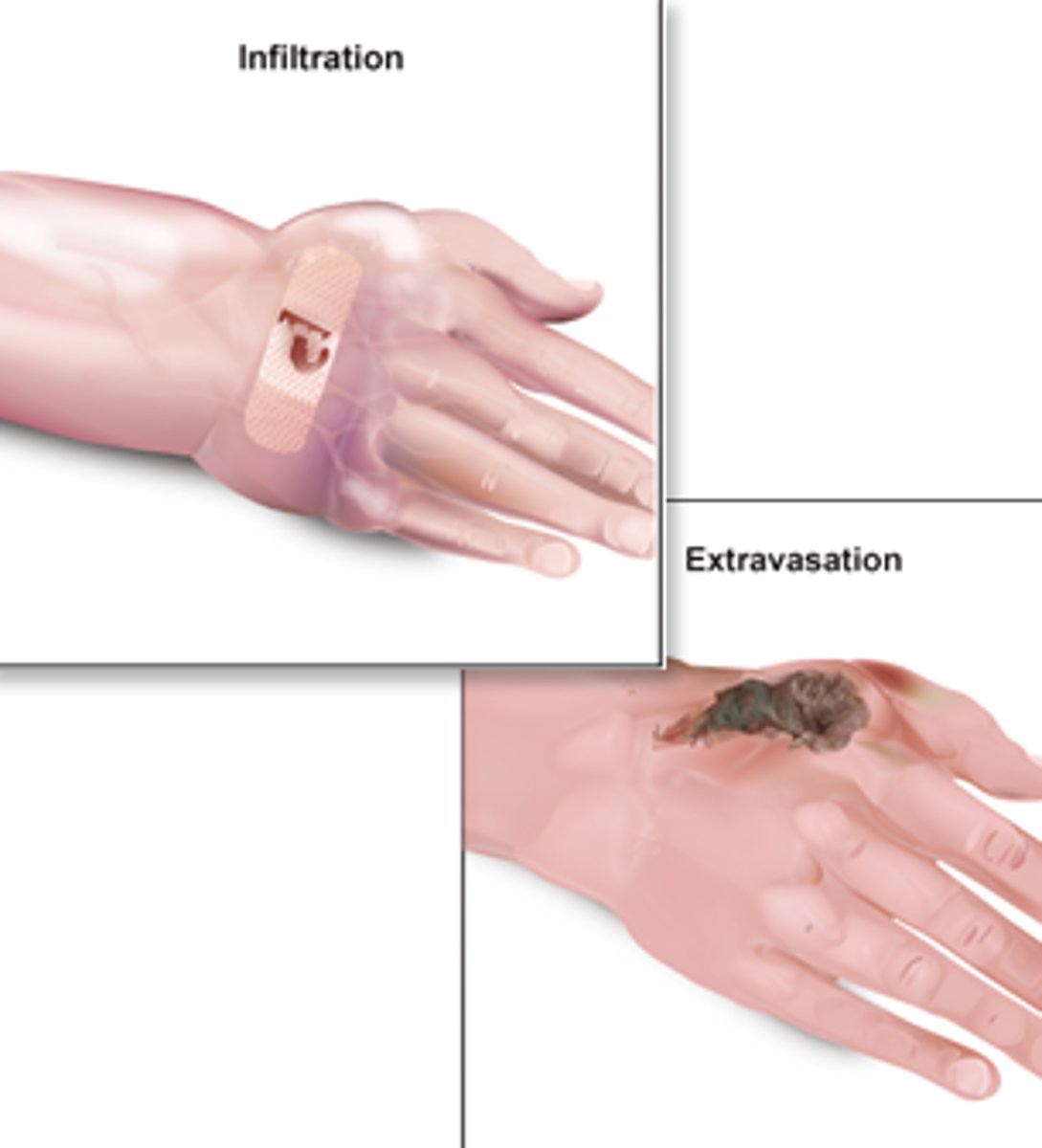
what to do for extravasation?
notify MD stat!!!!
antidote must be given and very short window for treating
examples of vesicants
-chemo agents
-vasopressors
-vancomycin
phlebitis
inflammation of the intimal layer of the vein
-chemical OR mechanical trauma to the vein
s/s of phlebitis
warm, red streak, vein hard and cordlike, painful
what to do for phlebitis?
-stop IV
-restart in another site
-tell MD (possible blood clot)
s/s of IV infection
redness, warmth, drainage, may have pus and a fever
what to do for IV infection?
-remove IV
-start in new area
-notify provider: need antibiotics or sepsis and die
how to check patency of an IV line?
if infusion running: IV site should be free of redness, swelling, coolness, or warmth to the touch. The IV infusion should flow freely.
if no infusion running: flush a bit, pull back check for blood return, flush rest of 10ml syringe... can palpate vein if you want to feel special
air embolism
air enters the circulatory system during tubing change, blood draw, or loss of cap on closed system
-can occur during insertion, maintenance, and removal of a CVAD
is an air embolism chill?
no. its an emergency! can lead to death
s/s of air embolism
-respiratory distress
-cyanosis
-tachycardia
-decreased BP
-decreased LOC
how to prevent an air embolism in central lines?
bend and clamp tubing on CVAD any time you are opening the system
also, have pt hold breath while tubing is changed
what to do if suspect air embolism?
-call a code
-place pt on left side in trendelenberg
-provide O2 and monitor VS frequently
what if the labia closes over the catheter during insertion or if the catheter touches the genitalia before being inserted into the urethra???
the catheter has been contaminated so you MUST START OVER!!! (new kit, new everything)
routine catheter care
-secure catheter
-perineal hygiene
-maintain adequate intake of fluids
-maintain closed system
-prevent pooling of urine in tubing and reflux of urine into bladder
-keep drainage bag below the level of the bladder
best way to prevent catheter-associated urinary tract infections (CAUTIs)
-clean catheter and perineum with soap and water at least BID
-encourage increased PO intake
-dont contaminate drainage spout when emptying catheter
-maintain closed system
-remove catheter ASAP
-change contaminated equipment immediately
-dont place catheter bag above level of bladder, keep off floor, avoid kinks
what indicates a blocked catheter?
pain and bladder distention
NG tube (background info)
40-45in silicone or PUR, bore size 8-12
-short-term!!!! less than 6 weeks
-stomach regulates gastric release to duodenum
-acidic pH secretions protect against infection
-may be easily moved and dislodged
-NO BASILAR FX!
how to measure NG tube
measure from tip of nose to earlobe to between xyphoid process and umbilicus
-put piece of tape on site
-insert tube to this point (taped point)
ways to verify placement of NG tube
1. x-ray
2. compare length each day: measure tube length immediately after insertion and compare (mark w sharpie)
3. pH litmus test of gastric aspirate
what is the only way to CONFIRM NG tube placement?
x-ray
what pH of gastric aspirate indicates correct NG placement?
< 5 (red litmus paper)
when can you begin feedings with an NG tube?
once placement is confirmed by radiology!!!!!!
NEVER before this... unless salem sump
color of gastric aspirate
green, off-white, brown, or colorless and cloudy
when is parenteral nutrition indicated?
when GI tract not functioning
what is TPN?
highly concentrated HYPERTONIC IV solution
what does TPN do?
restore calories and nutrients
TPN is administered via a...
central venous access device (CVAD)
-PICC
-Hickman
-implanted port
not peripheral IV... unless you want phlebitis and bad things!
TPN has a high ____________ concentration, so what should you check regularly?
glucose (dextrose); CHECK BLOOD SUGAR
monitor for hyperglycemia
what does a healthy stoma look like?
pink, moist, "beefy red"
what color do you NOT want to see with a stoma?
pale, black, or blue
notify provider asap please
when to change ostomy appliance?
every 3-7 days or when leaking
how do you change an ostomy appliance?
1. remove appliance by pushing skin away from appliance
2. wash surrounding skin w warm water and soap
3. dry surrounding skin
4. using measuring device, determine correct stoma size
5. trace circle and cut opening of wafer 1/8in larger than stoma
6. apply wafer
7. hold in place with hands for THREE MINUTES at 3&9 and 12&6 to make sure wafer sticks
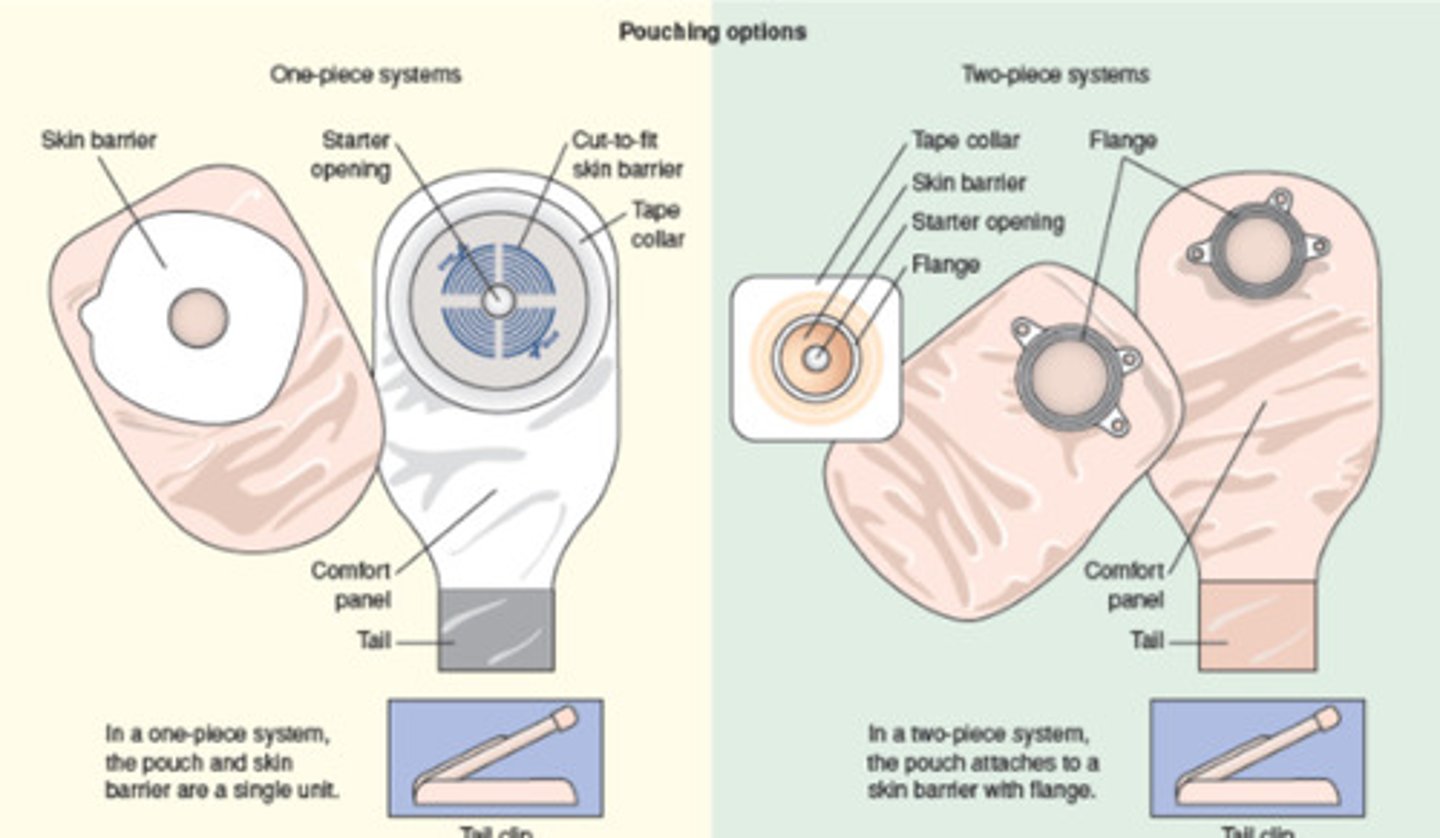
opening of wafer must be cut _____ larger than the stoma... why?
1/8 inch; prevent stool from accumulating on skin
the closer the stoma is to the rectum, the more ___________ the stool will be
solid
ileostomy stool characteristics
liquid, pt will have liters and liters of output (ENTIRE COLON REMOVED, ZERO WATER REABSORBED FROM STOOL)
DESCENDING/SIGMOID colostomy stool characteristics
solid, normy (CLOSEST TO RECTUM, MOST OF COLON PRESERVED)
what is the #1 complication with an ileostomy?
dehydration
enema
introduction of fluids or meds into large intestine
-distends intestine + irritates mucosa = increased peristalsis
most enemas work within...
15-30 minutes
enema procedure
1. verify order
2. add 500ml of warm water to bag
3. prime tubing, close slide clamp
4. raise bed to waist level, have pt turn on left side
5. pad bed well if you dont hate yourself
6. clean gloves, lubricate tubing 2-3in. from the tip
7. hang bag no higher than 18in. above anus
8. insert tube 3-4in. into the rectum; one hand on pt, one on tubing
9. instill over 5-10 minutes
10. when sol. infused, clamp tubing and withdraw
11. bedpan, bedside commode, or BR (NO FLUSH!)
what if pt cramps during enema instillation?
slow flow by lowering bag
blood transfusions are done only with...
compatible fluid
blood types compatible with A
A, O
blood types compatible with B
B, O
blood types compatible with AB
A, B, AB, O
blood types compatible with O
O
who is the universal donor?
O
how to determine if blood product compatible?
type and screen before surgery
type and cross match to ensure compatibility before infusion
what is the best scenario for a blood infusion?
if a pt can receive their own blood
unit of blood must be hung and running within _____________ of receiving from blood bank
15 minutes
what is the maximum length of time a unit of PRBCs can hang?
infuse over 2-3 hours, must DISCARD after 4 HOURS!
signs of allergic transfusion reaction
hives, itching, anaphylaxis
what do you do for allergic transfusion reaction?
1. stop infusion at once, notify provider stat
2. start NS to keep vein open (KVO)
3. may need antihistamines...
4. DOCUMENT!
signs of febrile transfusion reaction
incr in temperature of at least one degree F within 2 hours of starting transfusion
-fever
-chills
-malaise
-risk incr w multiple transfusions
what to do for febrile transfusion reaction?
1. stop transfusion
2. NS KVO
3. notify provider
4. treat symptoms (blanky)
signs of hemolytic transfusion reaction
wrong blood typed product hung; antigen-antibody response; IMMEDIATE SYMPTOMS
-facial flushing
-fever
-chills
-HA
-low back pain
-signs of shock
what to do for hemolytic transfusion reaction?
EMERGENCY! POSSIBLY FATAL!
1. stop transfusion asap
2. call a code and notify provider
3. send bag and tubing to blood bank
4. draw blood samples and save first voided urine within 2 hours to check for hemolyzed RBCs
signs of circulatory overload transfusion reaction?
incr risk in pts with heart and lung disease
-SOB
-crackles
-cough
-signs of pulmonary edema
what to do for circulatory overload transfusion reaction?
1. stop infusion
2. call provider
3. check VS
4. HIGH FOWLERS POSITION
5. may need diuretics
signs of transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI)
usually induced by the transfusion of antibodies against human leukocyte antigens
-non-cardiac pulmonary edema
-hypoxemia
within first 6 hours of product transfusion
what do i dooo for TRALI???
notify provider,,, no specific treatment :D
pre-transfusion requirements
1. type and cross match
2. check IV for patency
3. baseline set of vitals
4. provider gets CONSENT and explains procedure and possible complications (informed)
5. bag of NS and tubing close by in case
stage I pressure injury
NON-BLANCHABLE erythema of INTACT skin
stage II pressure injury
partial thickness SKIN LOSS with EXPOSED DERMIS due to shear
-blister-like
stage III pressure injury
full thickness skin loss, ADIPOSE tissue visible
-granulation tissue, epibole, slough or eschar may be visible
-depth varies, undermining and tunneling may occur
stage IV pressure injury
full thickness tissue loss, exposed FASCIA, MUSCLE, TENDON, LIGAMENT, AND BONE visible!
-depth varies
unstageable pressure injury
full thickness tissue loss with base covered by eschar or slough
deep tissue injury
persistent NON-BLANCHABLE deep red, maroon, or purple discoloration
-may evolve rapidly and reveal subQ tissue, fascia, muscle, etc.
dehiscence
unintentional separation of wound edges, especially a surgical wound
evisceration
separation of wound with protrusion of abdominal contents through the opening
-typ in obese, malnourished, immunocompromised
what to do for dehiscence or evisceration???
1. cover area w sterile moist NS-soaked 4x4s (gauze)
2. return pt to bed (supine) (semi fowler's)
3. call a code and provider immediately!!!
4. monitor LOC and VS
principles of sterile technique
1. Only sterile objects can touch sterile objects
2. Objects remain above waist level
3. Never turn your back on a sterile field
4. Outer 1" of any sterile field is contaminated
5. Open sterile packages away from you
6. Avoid moisture on the field- it is a wick
7. Consider any object contaminated if you have any doubt to its sterility
im assuming this is what she means... you get the idea... dont introduce infectious organisms to wound bed pls
what is the purpose of oropharyngeal and nasopharyngeal airways?
reduces the risk of aspiration and prevents the tongue from obstructing the posterior pharynx (therefore occluding the airway) in a pt who is UNCONSCIOUS but breathing independently!
when is suction applied with a trach?
suction is only engaged as the catheter is WITHDRAWN from the tracheostomy
when do you hyper-oxygenate a pt and how during tracheal suctioning?
hyper-oxygenate beforehand and between suction passes as needed to maintain adequate saturations
use AMBU bag or by incr vent O2 settings
symptoms that tell you a pt needs suctioned
-visible mucus that cannot be cleared from trach tube with a cough
-audible or visible secretions
-desat, difficulty breathing, pale/blue color around mouth or fingernails
-whistling noise from trach
-etc.
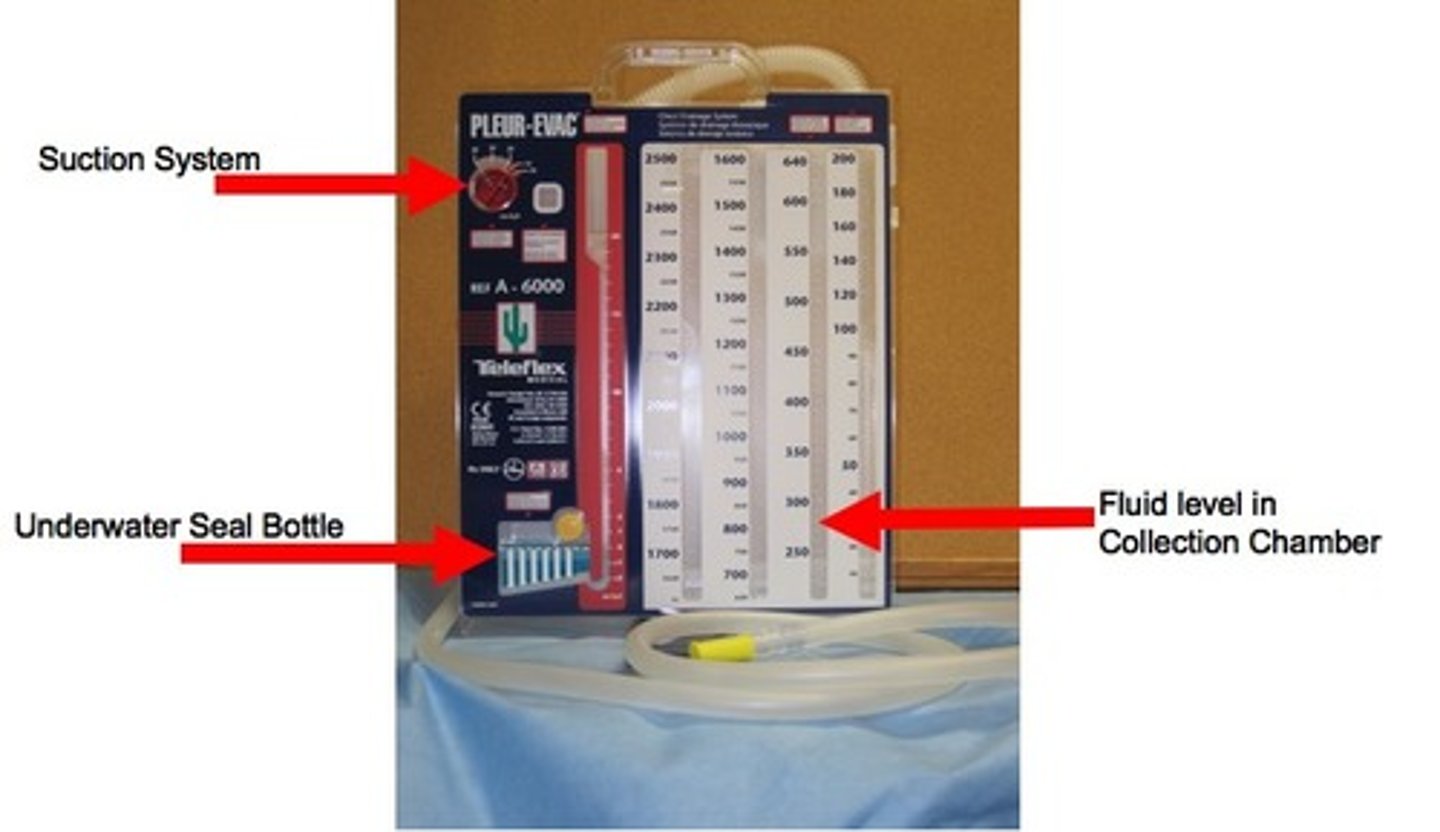
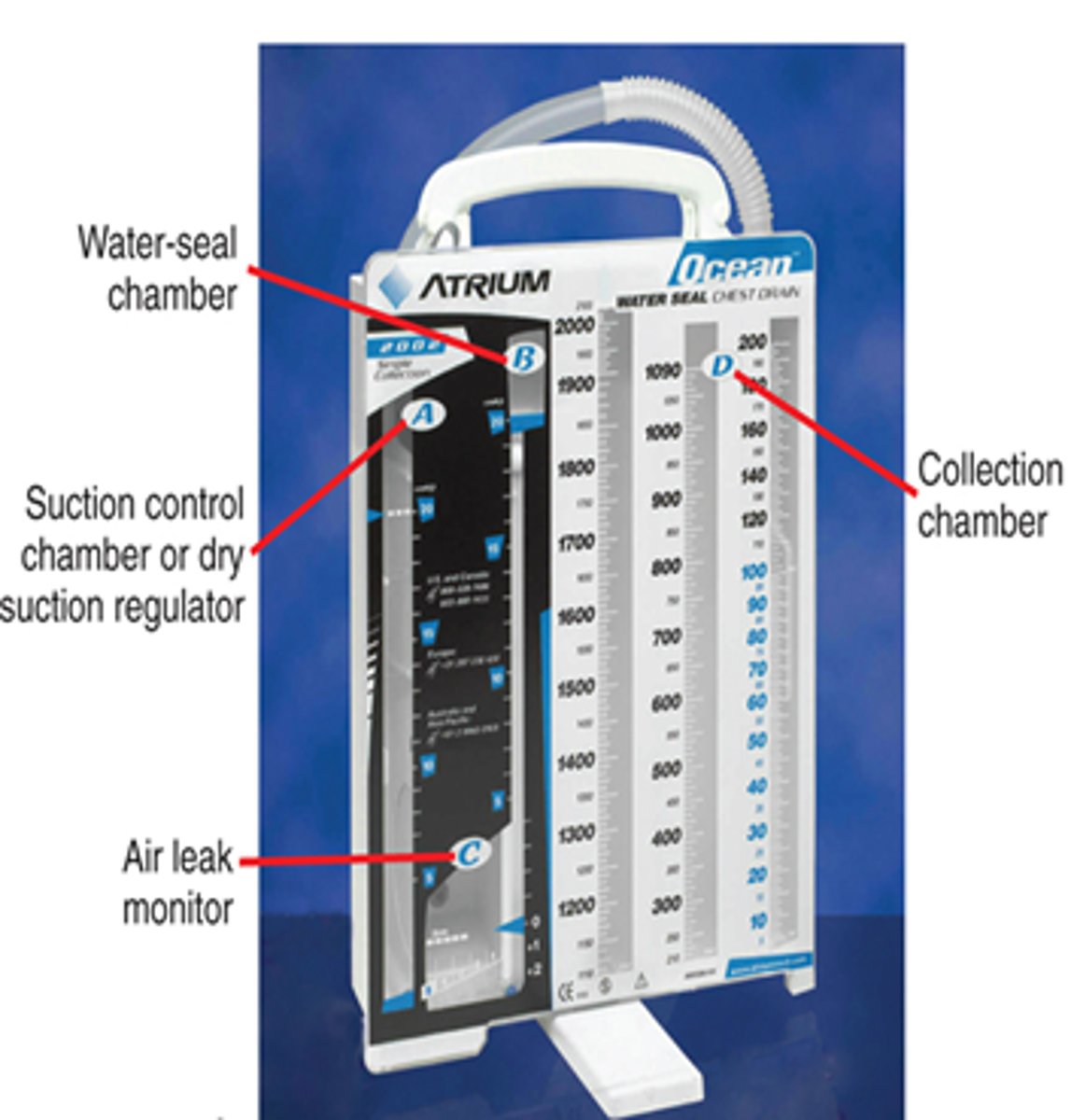
three primary chest tube components
1. collection chamber (2500ml)
2. water-seal chamber
3. suction control chamber
assessment of collection chamber function
-regularly measure and document drainage
-check for kinks or folds in the drainage tubing
-no blood please

assessment of water seal function
-ensure and maintain 2cm water level
-TIDALING is APPROPRIATE
-intermittent bubbling is NORMAL
-continuous bubbling is NOT NORMAL
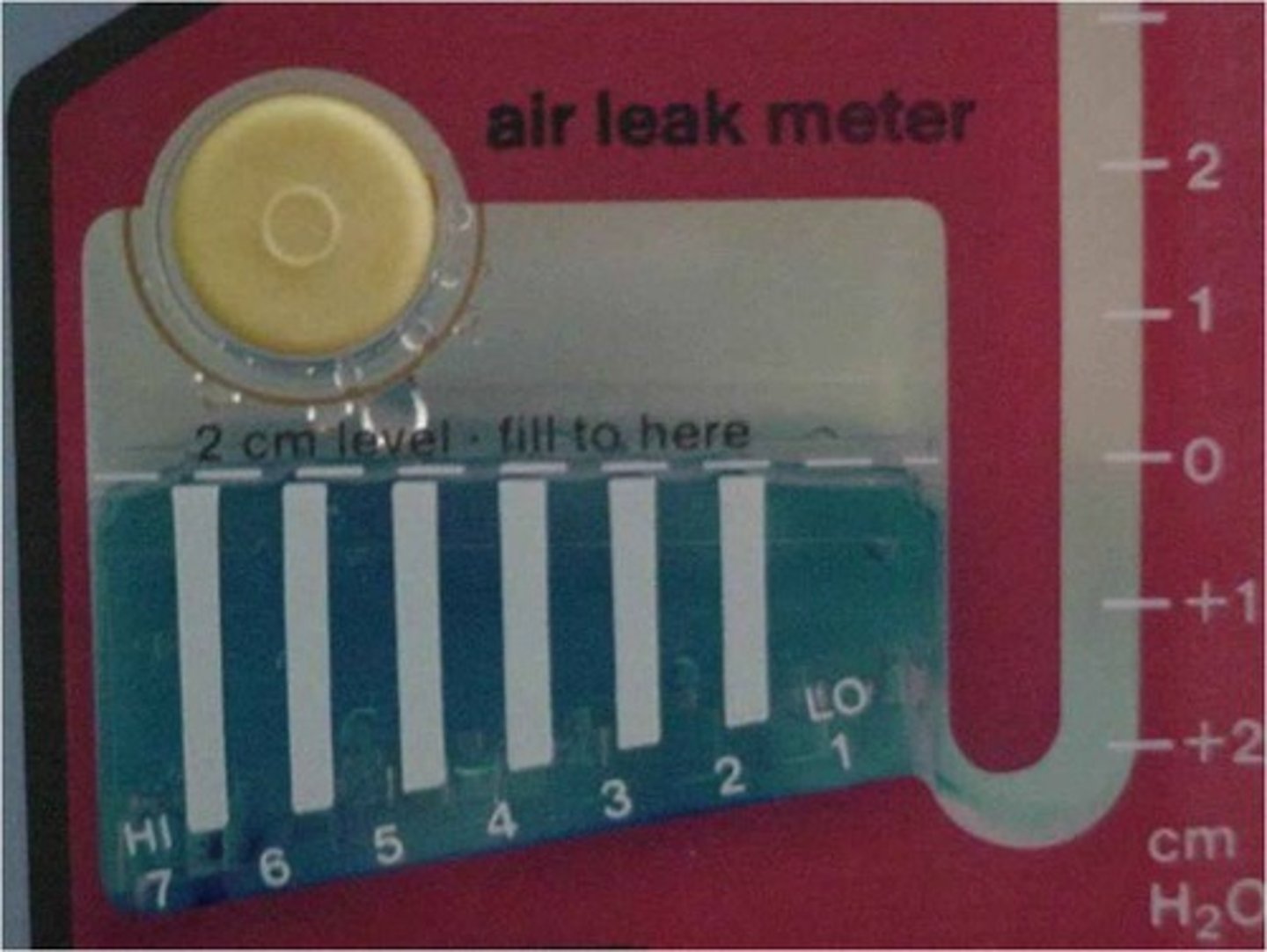

what is tidaling?
the appropriate fluctuation of fluid within the water seal chamber during respiration (rise and fall with inspiration/expiration)

what does tidaling mean?
indicates the chest tube is patent
when does tidaling stop?
-lung has re-expanded
-tubing is kinked
-tubing is obstructed
what does continuous bubbling in the water seal chamber indicate?
an air leak
locate the origin quickly by searching the tubings and connections... drainage system may require replacement
assessment of suction control chamber
continuous gentle bubbling is NORMAL!

suctioning of the chest tube is...
ordered
does vigorous bubbling in the suction control chamber mean increased suction?
no... only causes water to dissipate more quickly
what is crepitus (subcutaneous emphysema)?
coarse, crackling sensation palpable over the skin when air abnormally escapes from the lung and enters the subcutaneous tissue

how to check for crepitus?
palpate the thorax
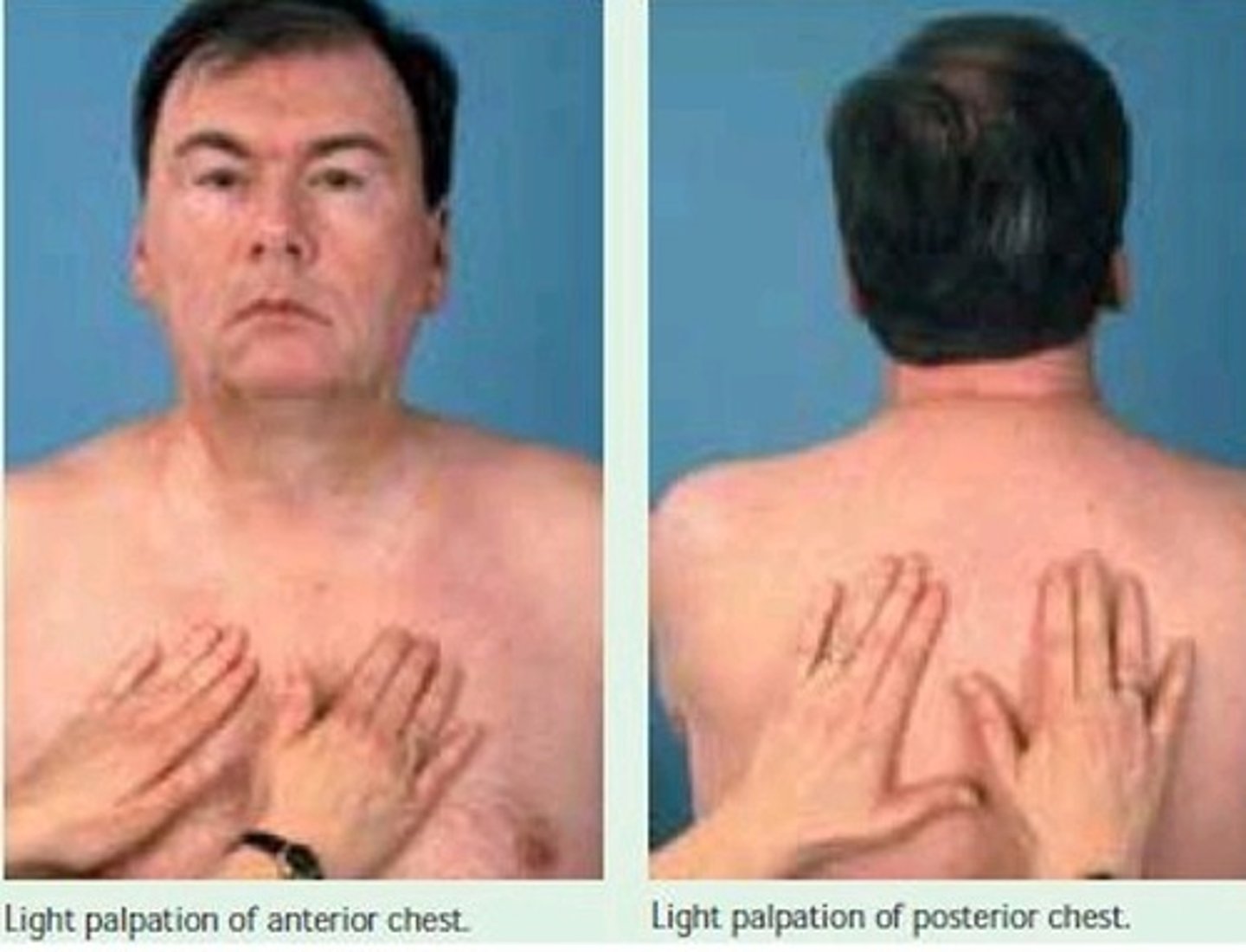
when do you palpate for crepitus?
as part of the ongoing assessment of a pt with a tension pneumothorax
when do you clamp a chest tube?
ONLY in these situations:
1. per order
2. checking for an air leak
3. changing the full device
4. strongly considering removal
chest tubes placed higher drain...
air (typically)