c - Reversible reactions and equilibria (copy)
1/9
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Reversible reactions
Reaction where products of reaction can react with each other and convert back to original reactants
i.e. can go both ways

Symbol for reversible reactions
⇌
Example of reversible reaction
Thermal decomposition of ammonium chloride
Ammonium chloride is white solid
When heated, it breaks down into gases ammonia + hydrogen chloride - forward reactionIf you let it cool, ammonia + hydrogen chloride react to re-form the solid - backward reaction
Another example is dehydration of copper(II) sulfate

Dynamic equilibrium
If reversible reaction occurs in closed system, a state of equilibrium will always be reached
Equilibrium = conc of reactants and products reach a certain balance and stay there
Closed system = reactants/products can’t escapeIt is a DYNAMIC EQUILIBRIUM - meaning reactions are still taking place in both directions, but overall effect is nil because forward + reverse reactions cancel each other out
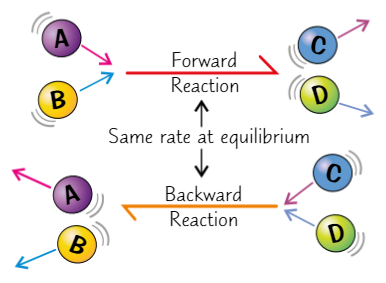
Characteristics of reaction at dynamic equilibrium
Forward + reverse reactions occur at exact same rate
Conc of reactants + products remain constant
Position of equilibrium
The relative amount of reactants and products
Depends on temp + pressure of reacting mixture
If you deliberately alter temp + pressure, you can move position of equilibrium to give more product + less reactants - position shifts to the right
Effect of temp on position of equilibrium
All reactions are exothermic in one direction and endothermic in the other
If you raise temp, endothermic reaction increases to use up extra heat
If you reduce temp, exothermic reaction increases to give out more heat
Effect of pressure on position of equilibrium
Most gaseous reactions have more moles of gas on one side than the other
If you raise pressure, it encourages reaction which produces fewer moles of gas
If you lower pressure, it encourages reaction which produces more moles of gas
Effect of catalyst on position of equilibrium
No effect because it speeds up forward + backward reaction by the same amount
Effect of catalyst on position of equilibrium
No effect because it speeds up forward + backward reaction by the same amount