Test 1 Genetics
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
Timeframes for early genetics
10,000-12,000 years ago shows evidence of plant and animal domesticantion
Aristotle’s theory of inheritance
Daughters = Mothers
Sons = Father
what is the pangenesis theory
every part of the body contains genetic information that is transfered by gemmules (particles) from that body part to the embryo
what is preformationism
inside the egg and sperm is a fully formed tiny human that enlarges and develops over time
explain inheritance of aquired characterists
traits that an organism aquired in their life time passes to their off spring
what is blending inheritance
traits given to offspring are 50/50 from parents
Darwin discovered what theory in 1859
theory of evolution
describe Schleiden Schwann’s cell theory
1939-
all life is made up of cells
all cells come from preexisting cells
cells are the fundemental function of living things
Who is the father of Modern Genetics
1822-1884 Greggor Mendel
What is Mendel’s discovery
the basic principles of heredity
In 1879 Walther Flemmind discoverd…
the division of chromosomes
Who discovered Germ-plasm theory
Weismann 1982
In 1902 Sutton located..
genes on chromosomes
In 1982 Katy Mullis discovered
polymerase chain reaction
Who beat the goverment in 2003, and cost billions
Craig Venter, human genome sequence
who discovered grough breaking gene editing
In 2012 Jennifer Doundna developed CRISPER editing
What is a genome
complete set of genetic instructions
Genome is like a…
Blueprint
eithr RNA and DNA ( mostly DNA )
What are DNA wrapped around
Histomes
specialized proteins
Alleles
different forms of genes
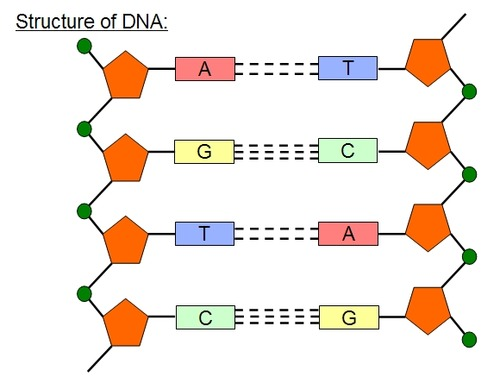
DNA structure
A: adenine
T: thymine
G: guanine
C: cytosine
Charguff’s Rule -
A=T
G+C
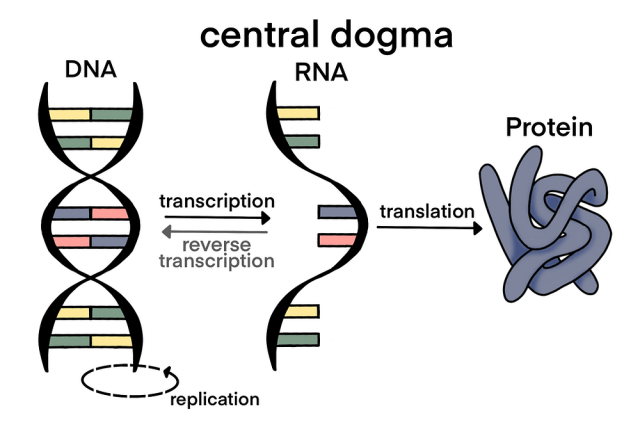
Central dogma is..
Theory of how information flows from DNA to RNA to proteins
DNA —→ RNA —> Protein
what are the three divisons of genetics
Transmission : how genes are passed down
molecular : studies function and structure of genes
population : how groups of the same species makeup change over time
characteristics of a model organism
ability to be reared in a lab environment
short generation time
cheap
production of multiple progney
ability to carry out controlled genetic crosses
having previous knowledge about their genetic systems
Similarities of Eukaryotes & Prokaryotes
contain DNA
have plasma membrane
What cell is
circular
small
no ordered arrangement
no nucleus
prokaryotes
What cell is
linear
larger
wrapped around histones
genetic material around nuclear envelope
has nucleus
Eukaryotes
What are homologous pairs
two sets of chromosomes
humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes
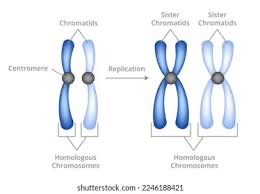
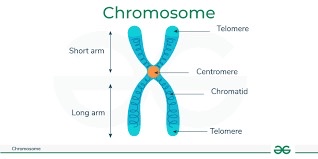
describe the structure of a chromosome
Centromere: point of attachment
Telomere : tips of linear chromosomes
Sister chromatids: identical copy of chromosome
What would be the result if a chromosome did not have a kinetochore?
Spindle microtubules would not attach to the chromosome.
Some daughter cells would be missing a chromosome, others would have double
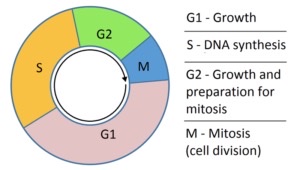
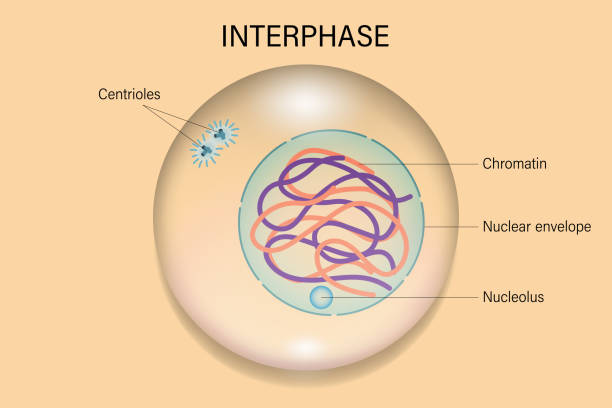
describe interphase
stage in the cell cycle where a cell grows, replicates DNA, and prepares cell division
what are the phases in Interphase
G1: grows cell
“Synthesis” S: DNA replication
sister chromatids
G2: more growth and prep for cell division
M phase: meiosis/mitosis
separation of cytoplasm
what is mitosis
separation of sister chromatids
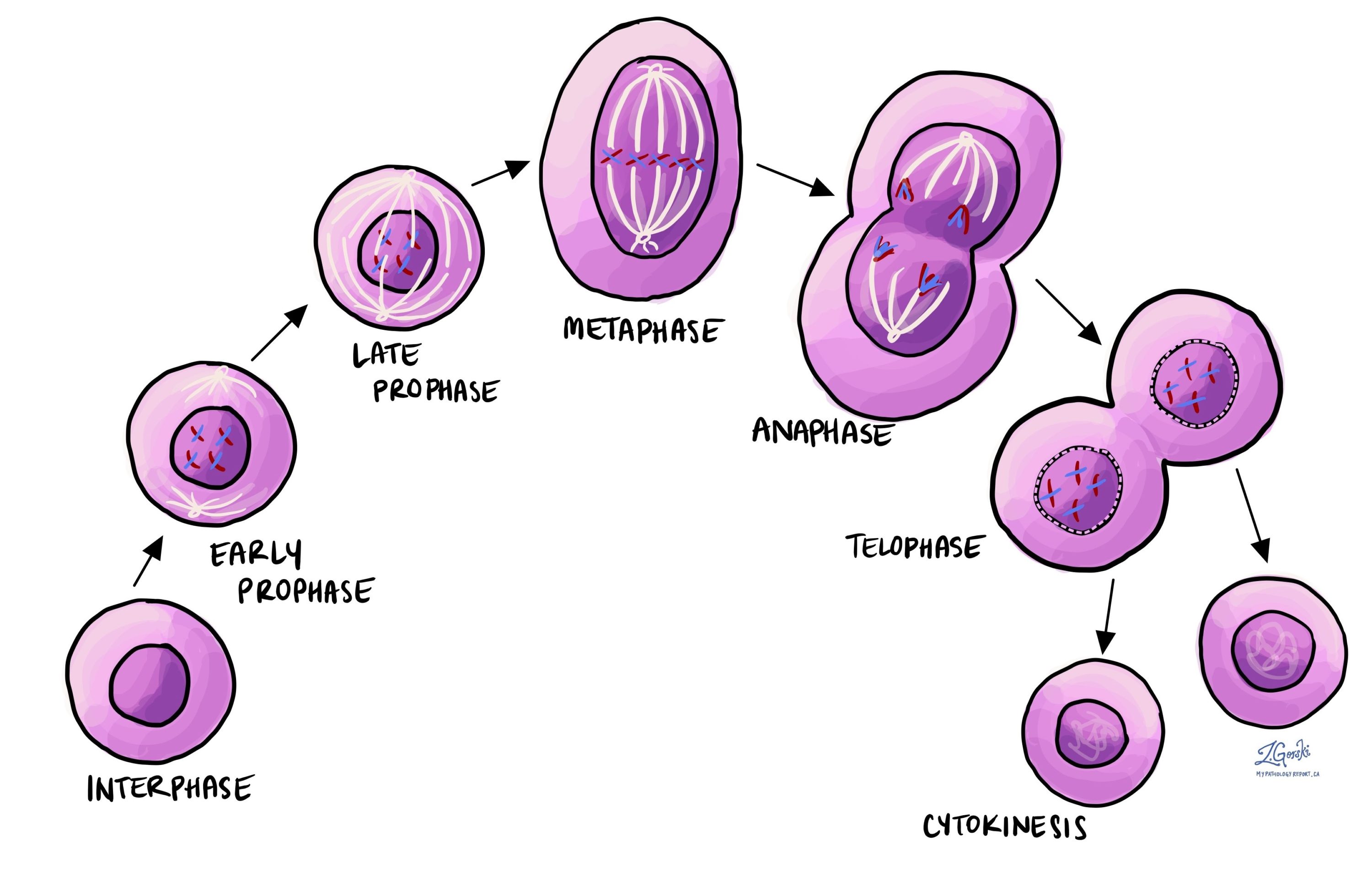
What is phase 1 of mitosis
Interphase: centromeres form to pull DNA
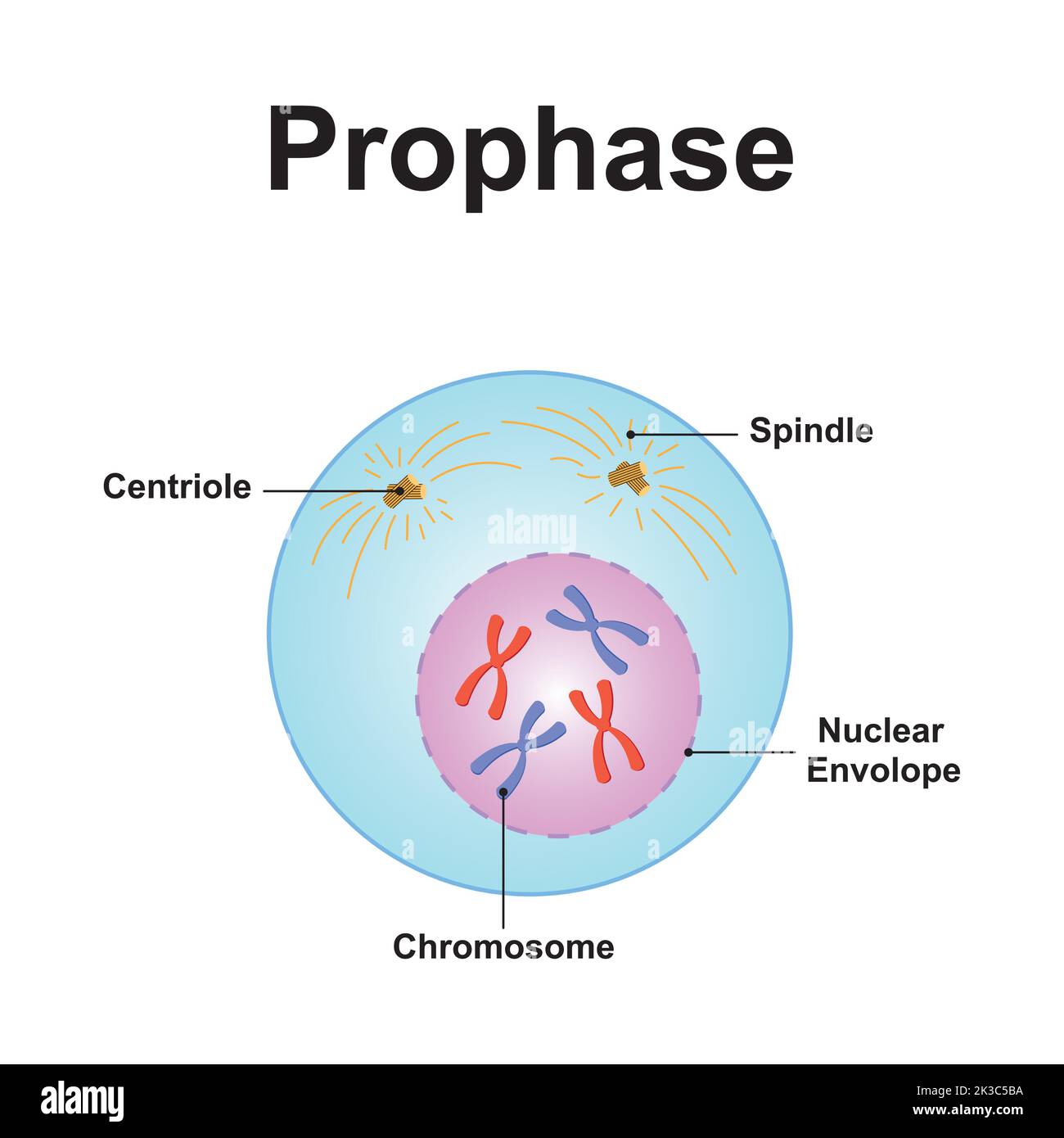
What is phase 2 of mitosis
Prophase: condenses chromosomes
What is phase 3 of mitosis
Prometaphase: breaks down nuclear envelope
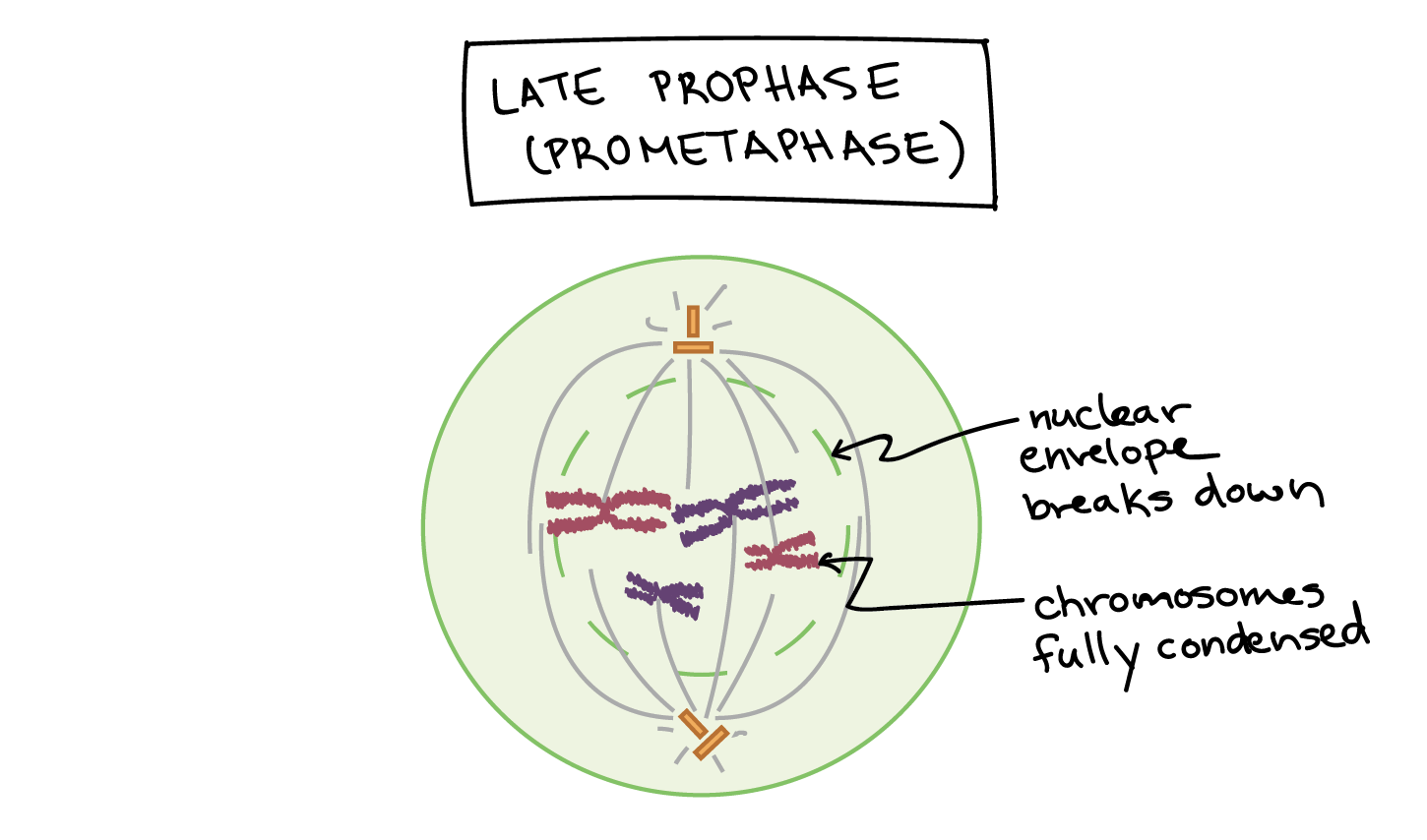
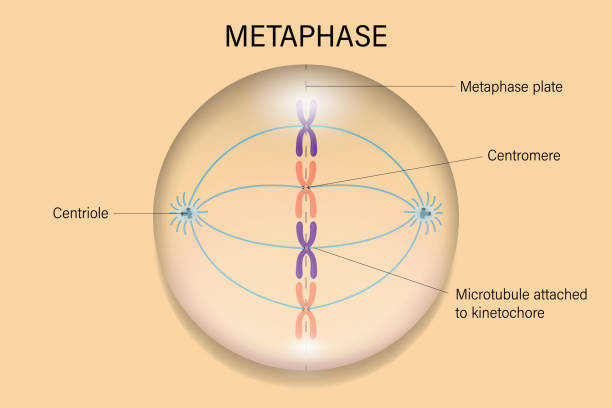
What is phase 4 of mitosis
metaphase: lines up in middle
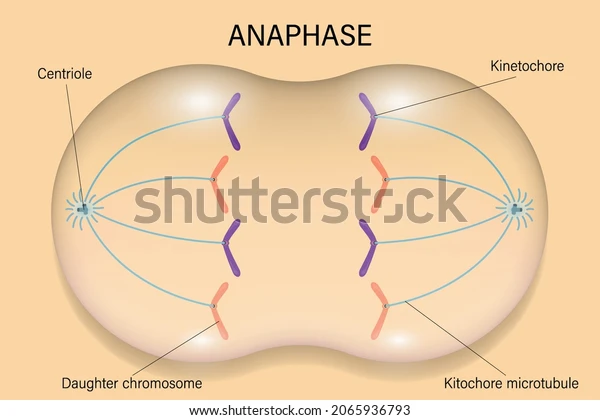
Phase 5 of mitosis
Anaphase: separates sister chromosomes
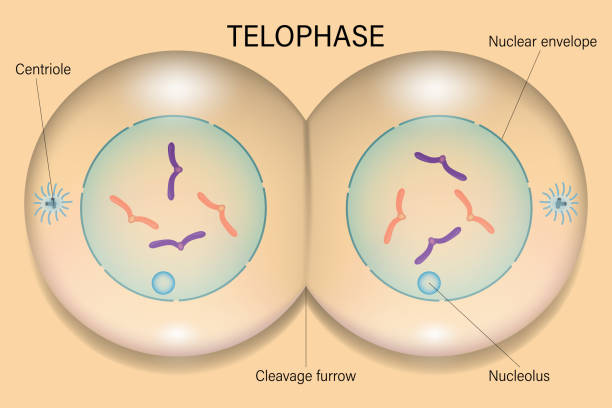
What is phase 6 of mitosis
Telophase: creates cleave to separate cells
begins cytokinesis
during meiosis I what happens
homologous chromosome pairs seperate
During Meiosis II
Sister chromosomes separate
Define male gamete production
Spermatogenesis
What is oogenesis
female gamete production
Reasons for Mendel’s Sucessn
had a good experimental model
took an experimental approach and analyzed results mathematically
What is a gene
inherited factor that determines a trait
Define allele
different variates if genes
Where do you locate an allele
locus
describe a set of alleles
genotype
heterozygous
2 different alleles at a locus
homozygous
2 of the same alleles at a locus
monohybrid crossed
a genetic cross where two parents differ in a single trait
Dominant is …
a version of a gene that is expressed, even with one copy
AA Aa
Recessive is…
2 copies from each parent to express trait
aa Aa
What is the principle of segregation
a living organism has 2 versions of each gene. when gametes are produced the 2 versions separate and each cell gets one version of the gene
What is the addition rule
the “or” rule
it can be this “OR” this
What is the multiplication rule
the “and” rule
it can be this “and” this
dihybrid crosses
examines 2 traits at a time
describe independent assortment
the way one gene is inherited from parent doesn’t affect how another gene is inherited
What is the Chi-square goodness of fit test
indicates the probability between observed (O) and expected (E) values are due to chance
What is the formula and steps for the Chi-square goodness of fit test
calculate chi-square
find chi-square value on table
interpret p-values
x²= (E+O)²/E
sexual determination
Sexual reproducing organisms have cells that go between haploid and diploid
explain what chromosomal is
X and Y chromosomes pair during meiosis, although they are not homologous
what do you call chromosomes that don’t determine sex
autosome
what is essential for chromosome paring in meiosis for men?
pseudoautosomal essential for XY chromosomes
explain genic
no distinct chromosomes determined by genes on undifferentiated chromosomes (plants, fungi, fish, protozoans
can sex be determined by environmental factors
yes
XX
females
XY
males
What organisms can you find XX&XY?
Insects, fish, amphibians, reptiles, mammals, humans
XO
Male
XX-XO chromosomes can be found in…
insects
ZW
Females
ZZ
Males
ZZ & ZW chromosomes
Butterflies, birds some reptiles and amphibians
Pseudoautosomal regions
short regions on the X and Y chromosomes that recombine during meiosis
What is SRY gene
sex-determining region Y gene
what is the role of SRY gene
produces a cascade of other gene products, and is the primary on-switch for male sex trait determination
what causes abnormal chromosome numbers
Non-disjunction of homologous chromosomes/ sister chromatids fail to separate correctly
what is the job of a Punnett Square
to determine the probability of progeny
What is a Barr body
dark spots in cells that are caused by a inactivation of the X-chromosome from having too many X’s
What are the types of dominance
Complete
Incomplete
Codominance
What is complete dominance
heterozygous phenotype is similar to one homozygous phenotype
what is incomplete dominance
homozygous and heterozygous mix to create a new phenotype
describe codominance
heterozygous phenotype includes phenotype of both homozygous
describe expressivity
the intensity in which a trait is being expressed
everyone has a genotype that is expressed differently
What is penetrance
percentage of individuals is having a specific genotype that is expressed the expected phenotype
what are lethal alleles
alleles that cause death in early development
what is the ratio of lethal alleles
2/3 to 1/3
describe multiple alleles in a population
for one locus, more than two alleles are present within a group
What is gene interaction
effects of alleles at one locus influence alleles at another loci
Ratio of gene interaction
9:3:3:1
only one trait in gene interaction phenotype
What is epigenetic modification
inheritable changes in gene expression that doesn’t alter DNA
describe imprinting
process that controls gene expression based on whether if the gene is inherited from mom or dad
what is sex-influence
autosomal genes are expressed differently in male and female
what is sex-limited
autosomal gene expression is limited to one sex
describe Sex-linked
genes located at the sex chromosomes
What is the maternal effect
genotype of mother determines phenotype of offspring
what is cytoplasmic inheritance
genes typically inherited from one parent, usually mother, and result in extensive phenotypic variation in one family
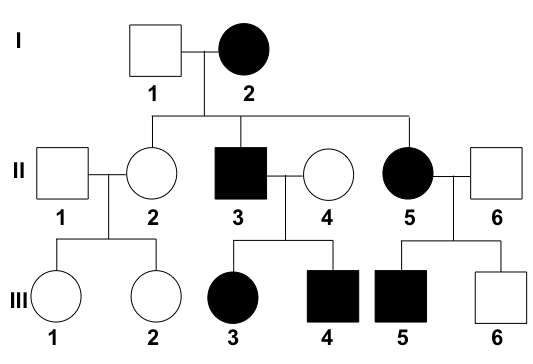
what is a pedigree
pictorial representation of a family history, outline inheritance of characteristics
5 types of pedigrees
Autosomal recessive
Autosomal dominant
X-linked recessive
X-linked dominant
Y-linked traits