Core 1 (220-1101)
1/444
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
445 Terms
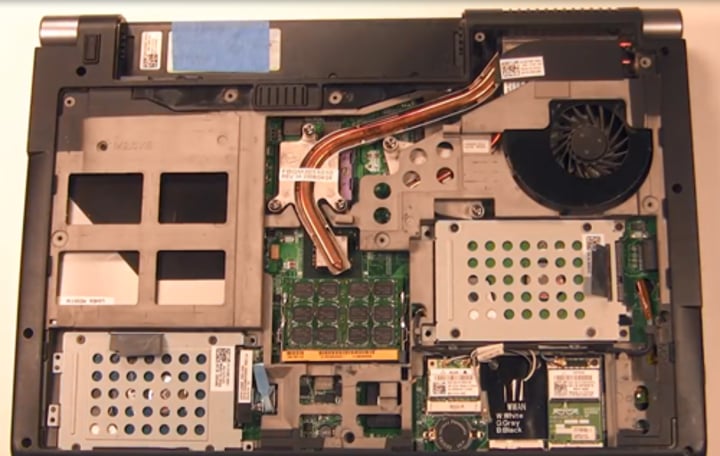
Laptop hardware
• Engineered to precise specifications
- A challenging repair
• Some laptops are easier to fix than others
- An ongoing learning process
• Understand the process
- The details will vary between laptop manufacturers
Laptop batteries
• The power source when unplugged
- May be easily replaced or require a tear down
- Five minutes vs. one hour
• Lithium-Ion (Li-ion) and
- Lithium-Ion polymer (LiPo) are common
- No "memory effect"
- Charging the battery diminishes capacity
• Different form factor for each laptop
- Battery types and styles can vary
- Battery technology is changing constantly

Laptop keyboard
• The most-used component of the laptop
- Can be easy to replace
- A few screws and a single ribbon cable
- May not always be this simple
• Or connect an external USB keyboard
Not very portable, but works in a pinch

Laptop keys
• Some repairs might require the removal or replacement of a key cap
- This can be a delicate procedure
• Check with the manufacturer's instructions
- It's very easy to accidentally break the key cap or the components underneath
Laptop memory
• Small Outline Dual In-line Memory Module (SO-DIMM)
• Memory used in laptops and mobile devices
- Often easy to install and replace
• Some laptop memory is soldered to the system board
- No upgrade available
- Requires a full system board replacement

Laptop storage
• Magnetic disk
- Traditional spinning drive platters
- 2.5 form factors (3.5 inch for desktops)
• SSD (Solid-state drive)
- All memory, no moving parts
- Silent, fast access time, less latency
- 2.5 inch form factors
• M.2
- Smaller form factor
- No SATA data or power cables
- Easy to install and replace

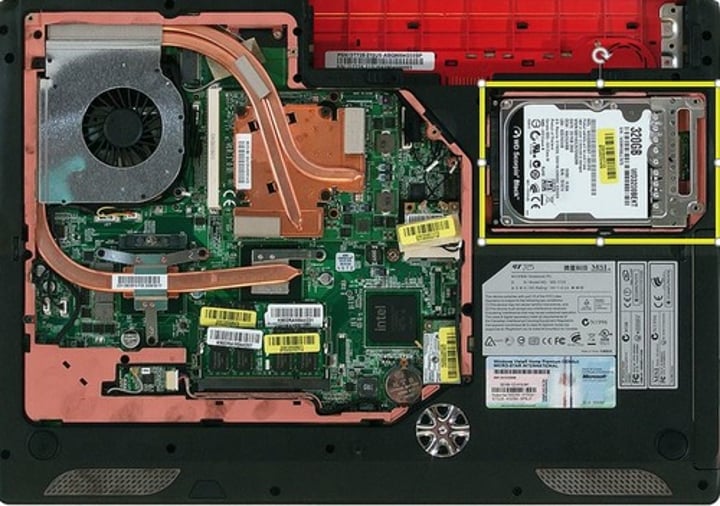
Replacing laptop storage
• All internal
- Open a cover on the back
- Open the entire laptop
• Can be very modular
- Two screws and the drive slides out
• M.2 drives are even easier
- One screw - similar to RAM installation

Migrating from HDD to SSD
• An impressive upgrade
- Move from spinning mechanical drive to solid state memory
- It's almost like getting a new laptop
• Install an OS on the SSD
- Move user documents between drives
- Install any required applications
- Can be time consuming
• Image/clone the HDD
- No OS installation required
- Move everything from one to the other
• Imaging software needed
- Sometimes included with the SSD
- Many commercial and open source options
• Create an image file - One drive at a time
• Drive-to-drive image
- Image directly from one drive to the other
802.11 wireless
• Wireless network connectivity
- Connect without wires
• 802.11
- Local area network (LAN)
- High speed, Internet access
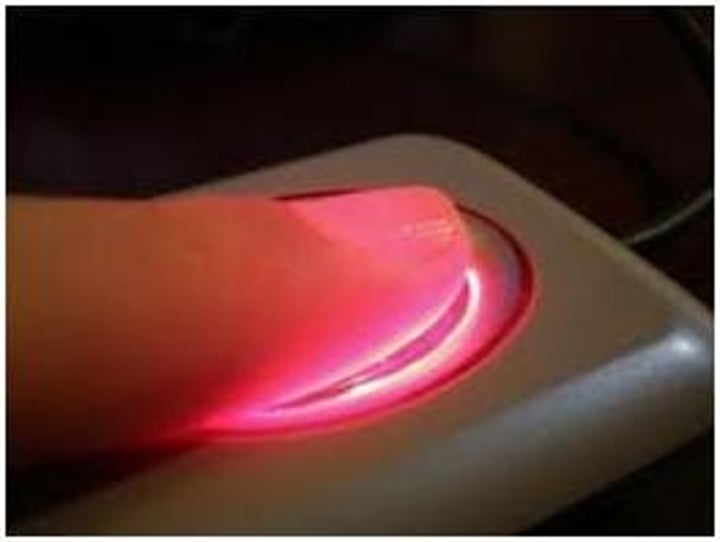
Biometrics
• Sign in or unlock your laptop with a fingerprint reader or face recognition
- Something you are
• Requires additional configuration in the OS
- Hardware required for most options
• Relatively secure
- Faces and fingerprints are quite unique
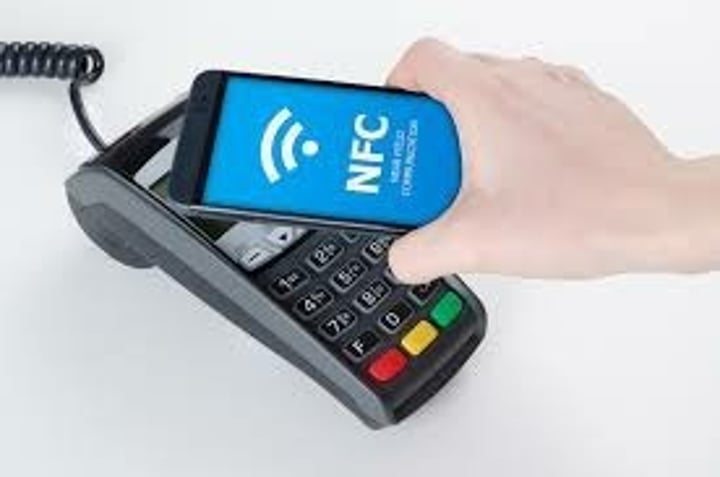
Near-field communication (NFC)
- 4 centimeters or less
- Data transfers or authentication
• Common on mobile phones and smart watches
- Payment method on your wrist
• Use it for authentication without typing a password
- Hospital workstations, warehouses, manufacturing
• Near Field Communication
- Send small amounts of data wirelessly over a limited area
• Built into your phone
- Payment systems, transportation,in-person information exchange
• Access token, identity "card"
- Short range with encryption support
• Two-way wireless communication
- Builds on RFID, which is mostly one-way
• Payment systems
- Major credit cards, online wallets
• Bootstrap for other wireless
- NFC helps with Bluetooth pairing
• Access token, identity "card"
- Short range with encryption support

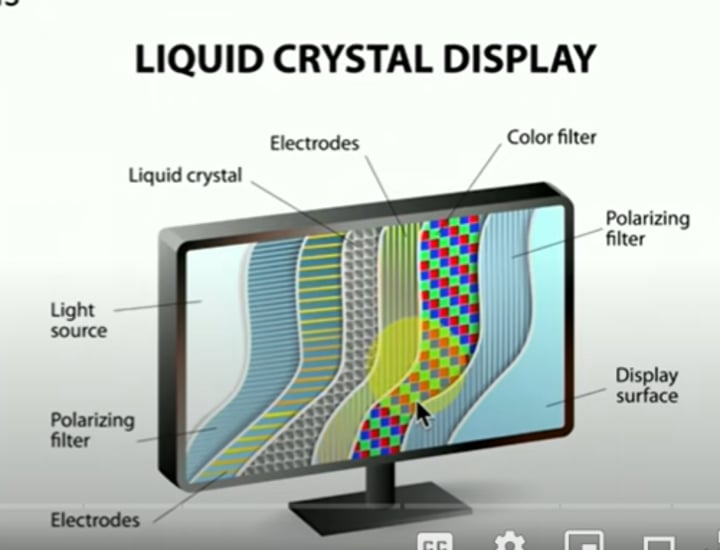
Portable LCD
• Liquid crystal display
- Light shines through liquid crystals
• Advantages
- Lightweight
- Relatively low power
- Relatively inexpensive
• Disadvantages
- Black levels are a challenge
- Requires separate backlight
- Florescent, LED, etc.
- Lights are difficult to replace
LCD technologies
• TN (Twisted Nematic)
- Fast response times (gaming!)
- Poor viewing angles - color shifts
• IPS (In Plane Switching)
- Excellent color representation
- More expensive to produce than TN
• VA (Vertical Alignment)
- A good compromise between TN and IPS
- Good color representation
- Slower response times than TN
Organic Light-Emitting Diode (OLED)
- Organic compound emits light when receiving an electric current
• Thinner and lighter
- Flexible and mobile - no glass needed
• No backlight
- The organic compound provides the light
• Laptops, phones, smart watches
- Very accurate color representation
- A bit higher cost than LCD
Wi-Fi antennas
• Multiple antennas
- WiFi main and aux / Bluetooth
• Antenna wires wrap around the laptop screen
- It's up high!

Camera / Webcam
• Usually includes both audio and video
- Specialized drivers and software
• Internal or external
- Commonly external on desktops, internal on laptops/tablets/phones
• Accessible from multimedia applications, photo utilities,and video conferencing
- Real-time video communication

Microphone
• Built-in to the laptop display
- Useful for video calls
• Not good for non-casual use
- Analog or USB microphones can help
Fluorescent
• LED-backlit LCD display
- Backlight is LEDs instead of florescent
- LEDs around the edge of the screen
- An array of LEDs behind the screen
- The latest laptops are LED-backlit
LED backlighting
• CCFL - Cold Cathode
- Fluorescent Lamp
- Higher voltage and power needed
- Added thickness to the display
- No longer a common backlight
- Older laptops will use these

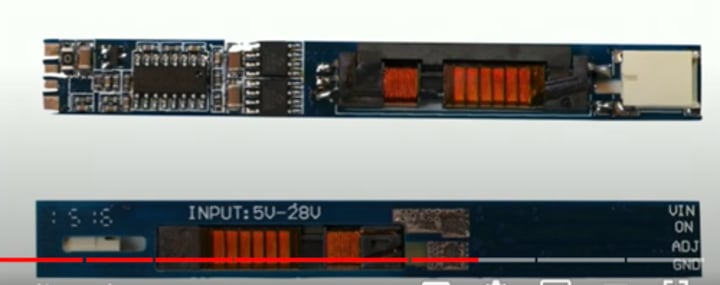
Backlight and inverter
- Florescent lamp/LED to LCD display to your eyes
• Some laptops have inverters - Turn DC into AC
• Verify backlight
- Look closely and use a flashlight
• May need to replace the LCD inverter or display
- Choose carefully
Digitizer
- Stylus input - Useful for graphical input
• Used commonly on laptop / tablets
- Or hybrid devices

Touchscreen
• Merge laptop and tablet input
- Digitizer responds to touch - No keyboard required
• But often still available
- Many options for input - Use the best one for the job

Connecting mobile devices
• Phones and tablets
- Many different ways to connect
• Wired and wireless connectivity
- Standards and options change through the years
• Used for synchronization, connectivity, backup, and identification
- Sometimes simultaneously
Universal Serial Bus (USB)
- High-speed wired communication
- Used for charging and data transfers
• Micro-USB
- A smaller USB connection
- Common now worldwide
• Older devices may use Mini-USB
- Slightly larger
• Simplify connections - Printers, storage devices, keyboard, mouse
• USB 1.1
- Low speed: 1.5 megabits per second, 3 meters
- Full speed: 12 megabits per second, 5 meters
• USB 2.0 - 480 megabits per second, 5 meters
• USB 3.0 - SuperSpeed
- 5 gigabits per second, ~3 meters
- Standard does not specify a cable length
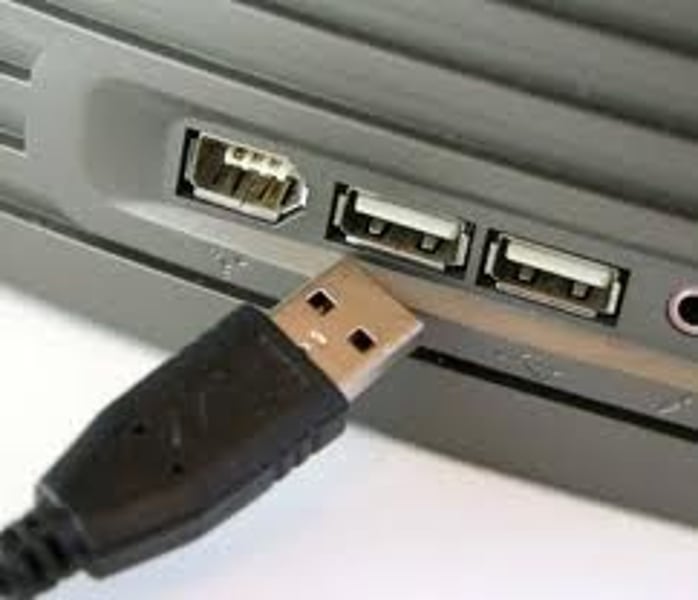

USB-C
• 24-pin double-sided USB connector
- Used for both hosts and devices
• Acts as a USB 2.0/3.0/3.1/4 connection
- Different signals can use the same connector
• Can transmit other signals
- DisplayPort, HDMI, Thunderbolt
• USB has a lot of different connectors
- And they have changed over time
• Can be annoying to connect USB-A
- Third time's the charm
• USB-C replaces all of these
- One connector to rule them all
• USB-C describes the physical connector
- It doesn't describe the signal
• Used for USB, Thunderbolt
- Interface is the same, signal can vary
Lighting
- 8-pin digital signals
• Some advantages over Micro-USB
- Higher power output for phones and tablets
- Can be inserted either way
- Simpler design

Serial interfaces
• DB-9 - also called DE-9
• Commonly used for RS-232 signals
- Recommended Standard 232
- An industry standard since 1969
• Serial communications standard
- Traditionally used for modem connections
• Now used as a configuration port
- Switches, routers, firewalls, etc
- Use a USB to DB-9 converter cable
Bluetooth
- Personal area network (PAN) - Short range
- Connect peripherals and other nearby devices
• High speed communication over short distances
- PAN (Personal Area Network)
• Connects our mobile devices
- Smartphones
- Tethering
- Headsets and headphones
- Health monitors
- Automobile and phone integration
- Smartwatches
- External speakers
• Remove the wires
- Headsets, speakers, keyboards / mice
• Uses the 2.4 GHz range
- Unlicensed ISM
(Industrial, Scientific and Medical) band
- Same as 802.11
• Short-range
- Most consumer devices operate to about 10 meters
- Industrial Bluetooth devices can communicate over 100 meters

Hotspot
- Extend the cellular data network to all of your devices
• Dependent on phone type and provider
- May require additional charges and data costs
Touch pens
- Activate the interface without actually touching it
• Handwriting
- Note taking, signatures
• Precise selection
- Easier to see the screen
• Useful in the winter
- Keep your gloves on
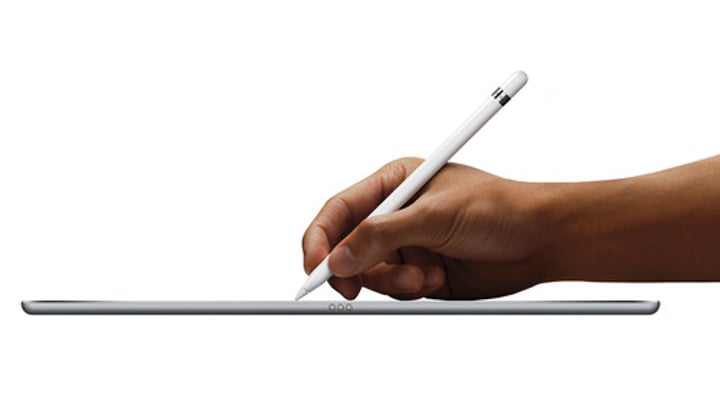
Active stylus
- A more advanced writing tool
• The stylus communicates directly to the device
- Pressure sensitivity, programmable buttons, etc.
• Must be compatible with the tablet
- e.g., Apple iPad uses an Apple Pencil

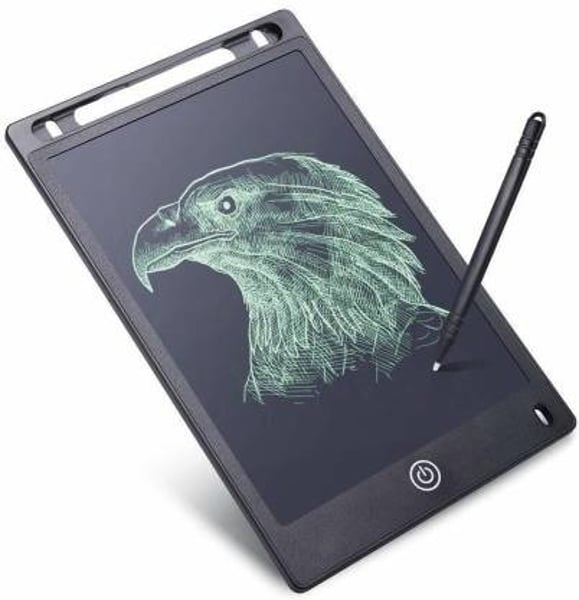
Drawing pad
• Use an active stylus with an external digitizer
- Very precise input

Trackpad (Touchpad)
- Useful in tight working areas
- Common on laptops
• External options
- Battery powered
- Bluetooth connected
• Drag and tap
- Or use multiple finger input for right-clicking, zooming, and window control
• Enable and disable
- Avoid inadvertent mouse clicks and movements

Headsets
• Wired
- USB connections are common on laptops
- Connects to 3.5 mm
TRRS (tip-ring-ring-sleeve) connector
- Analog audio jack
- iPhone can use Lightning port
• Wireless - Bluetooth headsets

Speakers
• Mobile audio - Battery powered
• Wireless connection - Bluetooth link
• Stereo sound - Small package

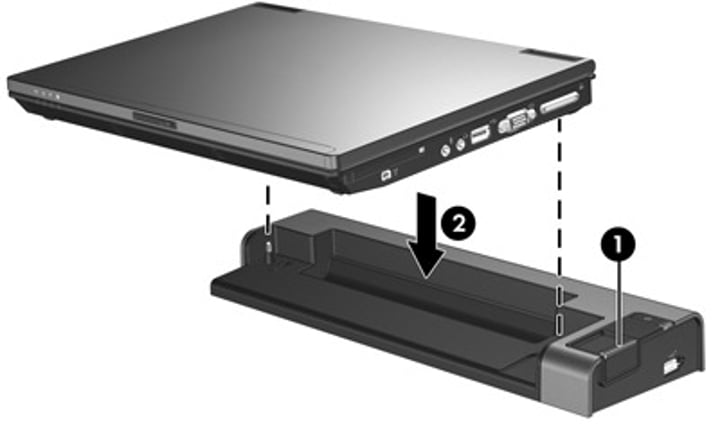
Docking station
- Use external keyboard and mouse
- Extend existing laptop interfaces
- Add additional functionality
- Desktop adapter cards
- Avoid cable issues
Port replicator
- Similar to a docking station
- Does not commonly have an expansion card option
- Usually connects using USB

Cellular networks
• Mobile devices
- "Cell" phones
• Separate land into "cells"
- Antenna coverages a cell with certain frequencies
• 2G networks
- GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications
- CDMA - Code Division Multiple Access
• Poor data support
- Originally used circuit-switching
- Minor upgrades for some packet-switching
• Tethering
- Turn your phone into a wireless router
• Mobile hotspot
- Standalone devices
- Use your phone for other things

Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM)
- Mobile networking standard
• 90% of the market
- Originally an EU standard
- Worldwide coverage
• Used by AT&T and T-Mobile in the United States
- Move your SIM card (Subscriber Identity Module) from phone to phone
• Original GSM standard used multiplexing
- Everyone gets a little slice of time
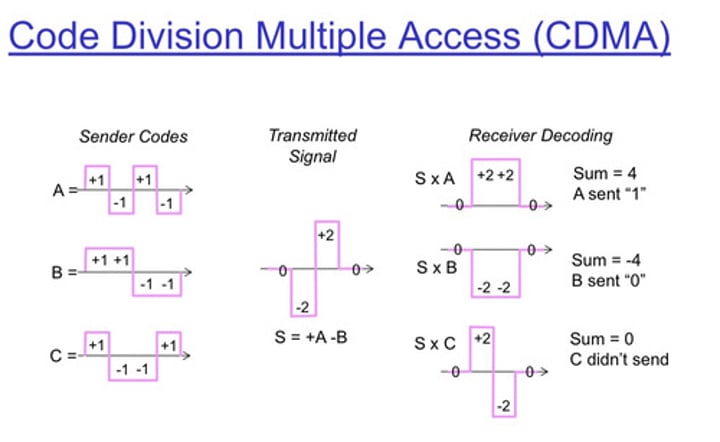
Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA)
- Everyone communicates at the same time
- Each call uses a different code
- The codes are used to filter each call on the receiving side
• Used by Verizon and Sprint
- Handsets are controlled by the network provider
Not much adoption elsewhere
3G technology
- Introduced in 1998
- Usually several megabits per second
• Bandwidth improvement allowed new functionality
- GPS
- Mobile television
- Video on demand
- Video conferencing

4G and LTE
- Converged standard (GSM and CDMA providers)
- Based on GSM and EDGE
(Enhanced Data Rates for GSM Evolution)
- Standard supports download rates of 150 Mbit/s
- Standard supports download rates of 300 Mbit/s

5G
- Launched worldwide in 2020
• Significant performance improvements
- At higher frequencies
- Eventually 10 gigabits per second
- Slower speeds from 100-900 Mbit/s
• Significant IoT impact
- Bandwidth becomes less of a constraint
- Larger data transfers
- Faster monitoring and notification
- Additional cloud processing
Updates
• PRL (Preferred Roaming List) updates
- CDMA networks (i.e., Verizon, Sprint)
• Allows your phone to connect to the right tower
- Can be updated over the air (OTA)
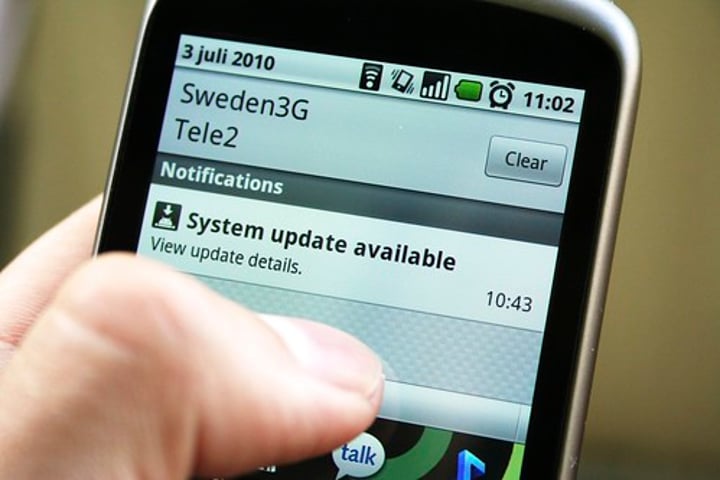
Bluetooth pairing
- Built-in security - Use or verify a PIN
- Future connections should be automatic
• Check with the manufacturer
- May prefer a specific sequence
- Discoverable mode isn't always obvious
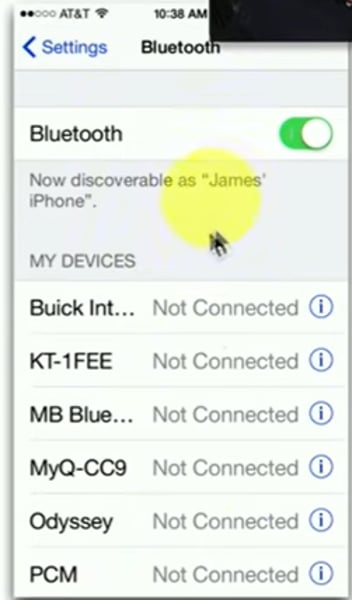
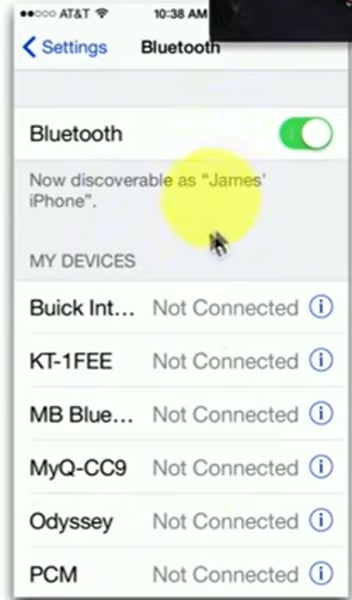
Bluetooth pairing process
- Android and iOS: Settings / Bluetooth
- May require key sequence on Bluetooth device
- Many devices may appear!
• Enter or confirm PIN
- Should be the same on both devices
• Test connectivity
- Devices should now communicate
Global Positioning System (GPS)
• Created by the U.S. Department of Defense
- Over 30 satellites currently in orbit
• Precise navigation - Need to see at least 4 satellites
• Determines location based on timing differences
Longitude, latitude, altitude
• Mobile device location services and geotracking
- Maps, directions
- Determine physical location based on GPS, WiFi, and cellular towers

Mobile Device Management (MDM)
• Manage company-owned and user-owned mobile devices
- BYOD - Bring Your Own Device
• Centralized management of the mobile devices
- Specialized functionality
• Set policies on apps, data, camera, etc.
- Control the remote device
- The entire device or a "partition"
MDM configuration
• Corporate email configuration
- User does not need to configure anything
- The MDM makes the changes on the device
- Account details, server address, communication method
• Two-factor authentication
- Require specific authentication types
- Biometrics, pseudo-random authentication app
• Corporate applications
- Allow or restrict app installation
- Prevent unauthorized app usage
Configuring a mobile device
- Telephone / Text messaging
- Everyone handles email services differently
- Corporate email configurations can vary
• Data synchronization
- Based on data rates and speeds
- Important for backup and recovery
Microsoft 365
- Usually the same for Hotmail and Outlook.com
- Username, password
• Select the items to synchronize
• Same process for Google Workspace
- Formerly known as G Suite

iCloud
• Select synchronization options
- Extensive customization
- Use your desktop, laptop, or mobile device

Synchronizing data
- Pictures, music, video
- Calendar
- Contacts
• Data caps and transfer costs
- Cellular vs 802.11
- Enable or disable network connections
- Control the use of cellular downloads

A series of moving vans
• Efficiently move large amounts of data
- Use a shipping truck
• The network topology is the road
- Ethernet, DSL, cable system
• The truck is the Internet Protocol (IP)
- We've designed the roads for this truck
• The boxes hold your data
- Boxes of TCP and UDP
• Inside the boxes are more things
- Application information
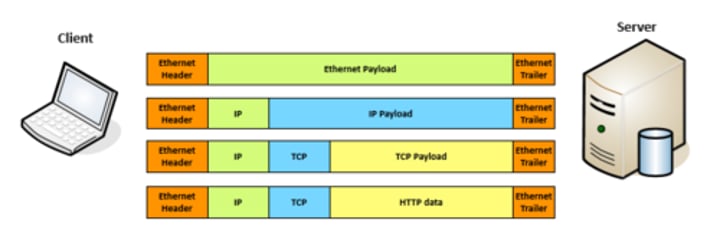
TCP and UDP
• Transported inside of IP
- Encapsulated by the IP protocol
• Two ways to move data from place to place
- Different features for different applications
• OSI Layer 4
- The transport layer
• Multiplexing
- Use many different applications at the same time
- TCP and UDP
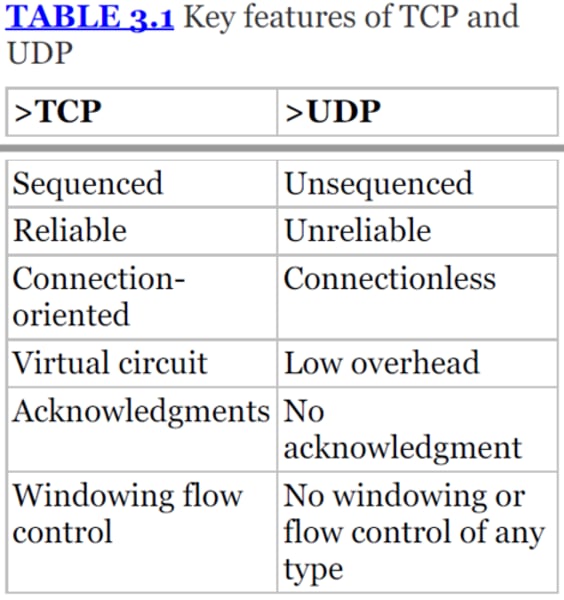
TCP - Transmission Control Protocol Communication
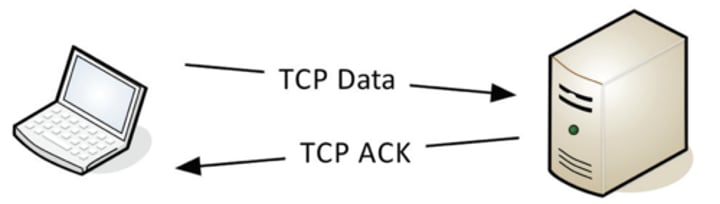
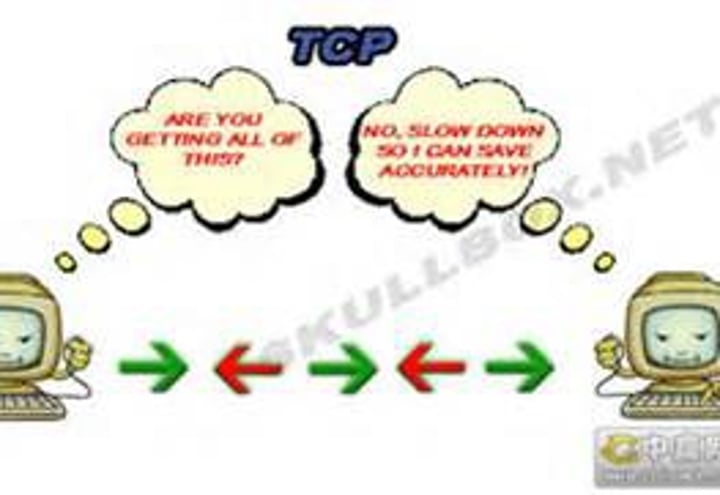
TCP - Transmission Control Protocol
• Connection-oriented
- A formal connection setup and close
• "Reliable" delivery
- Recovery from errors
- Can manage out-of-order messages or retransmissions
• Flow control
- The receiver can manage how much data is sent
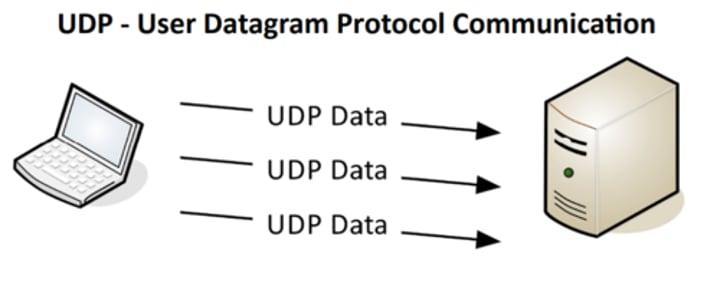
UDP - User Datagram Protocol
• Connectionless - No formal open/close to the connection
• "Unreliable" delivery
- No error recovery
- No reordering of data or retransmissions
• No flow control
- Sender determines the amount of data transmitted
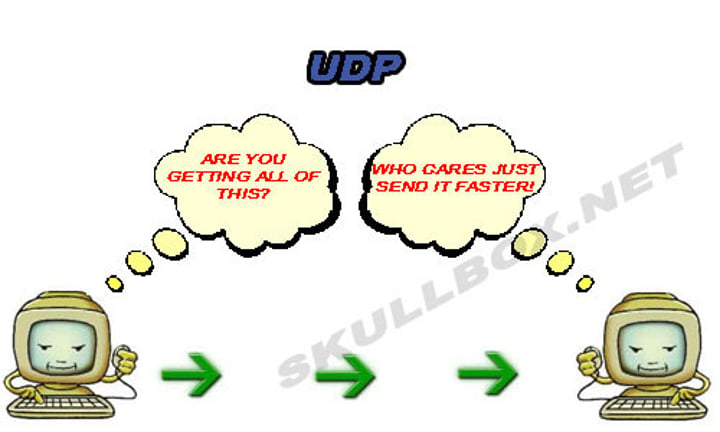
UDP - User Datagram Protocol Communication
Why would you ever use UDP?
• Real-time communication
- There's no way to stop and resend the data
- Time doesn't stop for your network
• Connectionless protocols
- DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)
- TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol)
Communication using TCP
• Connection-oriented protocols prefer a "return receipt"
- HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure)
- SSH (Secure Shell)
• The application doesn't worry about out of order frames or missing data
- TCP handles all of the communication overhead
- The application has one job
Speedy delivery
The IP delivery truck delivers from one (IP) address to another (IP) address
- Every house has an address, every computer has an IP address
• Boxes arrive at the house / IP address
- Where do the boxes go?
- Each box has a room name
• Port is written on the outside of the box
- Drop the box into the right room
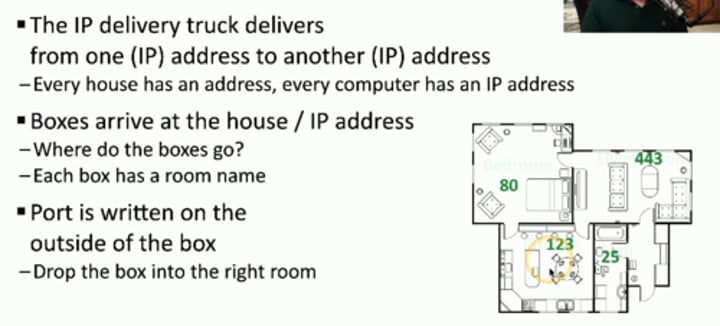
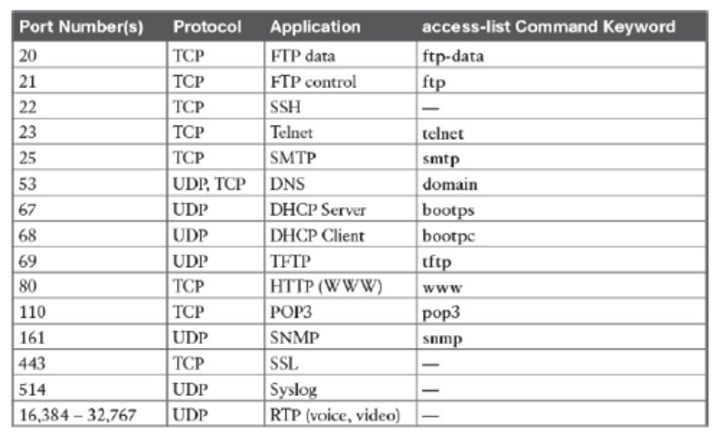
Lots of ports
• IPv4 sockets
- Server IP address, protocol, server application port number
- Client IP address, protocol, client port number
• Non-ephemeral ports - permanent port numbers
- Ports 0 through 1,023
- Usually on a server or service
• Ephemeral ports - temporary port numbers
- Ports 1,024 through 65,535
- Determined in real-time by the client

Port numbers
• TCP and UDP ports can be any number between 0 and 65,535
• Most servers (services) use non-ephemeral (not-temporary) port numbers
- This isn't always the case
- It's just a number.
• Port numbers are for communication, not security
• Service port numbers need to be "well known"
• TCP port numbers aren't the same as UDP port numbers
• Well-known port number
- Client and server need to match
• Important for firewall rules - Port-based security
• A bit of rote memorization
- Becomes second nature after a while
• Make sure you know port number, protocol, and how the protocol is used
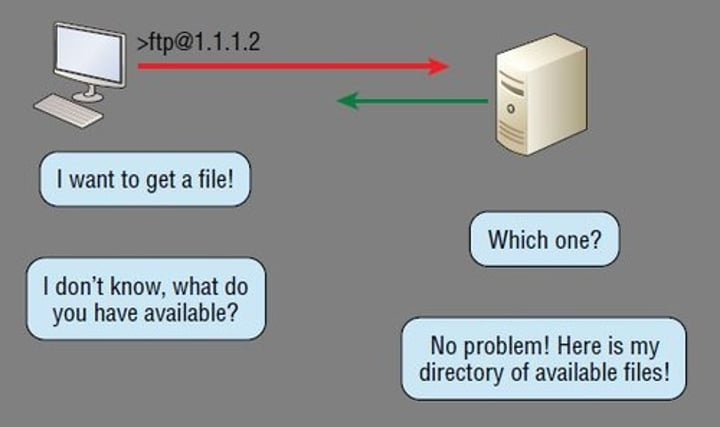
FTP - File Transfer Protocol
• tcp/20 (active mode data), tcp/21 (control)
- Transfers files between systems
• Authenticates with a username and password
- Some systems use a generic/anonymous login
• Full-featured functionality - List, add, delete, etc.
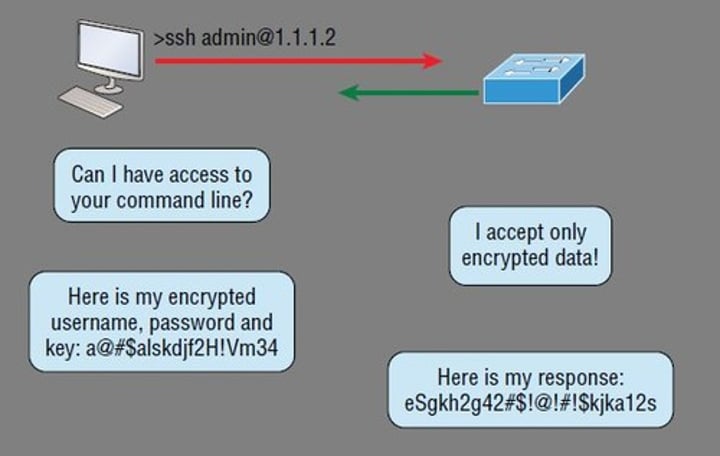
SSH - Secure Shell
• Encrypted communication link - tcp/22
• Looks and acts the same as Telnet
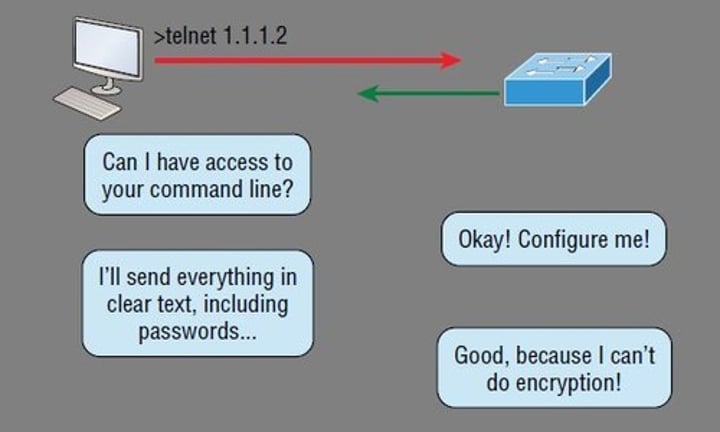
Telnet
• tcp/23
• Login to devices remotely
- Console access
• In-the-clear communication
- Not the best choice for production systems
SMTP - Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
- Server to server email transfer - tcp/25
• Also used to send mail from a device to a mail server
- Commonly configured on mobile devices and email clients
• Other protocols are used for clients to receive email
- IMAP, POP3

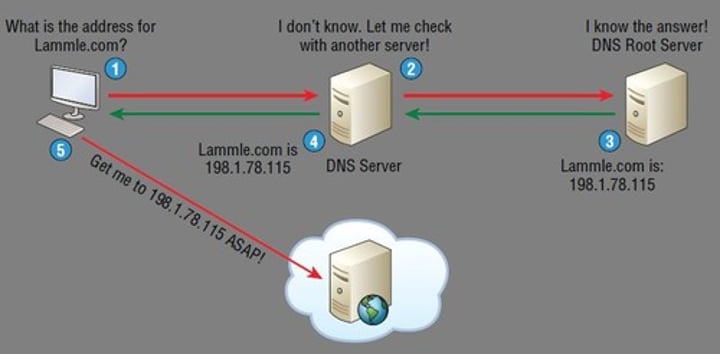
DNS - Domain Name System
• Converts names to IP addresses - udp/53
- www.professormesser.com = 162.159.246.164
• These are very critical resources
- Usually multiple DNS servers are in production
• Translates human-readable names into computer-readable IP addresses
- You only need to remember www.ProfessorMesser.com
• Hierarchical
- Follow the path
• Distributed database
- Many DNS servers
- 13 root server clusters (over 1,000 actual servers)
- Hundreds of generic top-level domains (gTLDs) -
.com, .org, .net, etc.
- Over 275 country code top-level domains (ccTLDs) -
.us, .ca, .uk, etc.
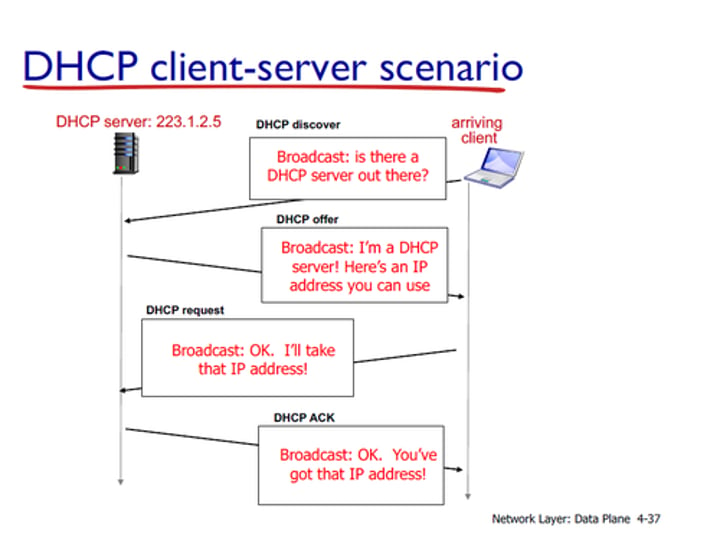
DHCP - Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
• Automated configuration of IP address, subnet mask and other options - udp/67, udp/68
- Server, appliance, integrated into a SOHO router, etc.
• Dynamic / pooled
- IP addresses are assigned in real-time from a pool
- Each system is given a lease and must renew at set intervals
- Manage addresses from one location
• IPv4 address configuration used to be manual
- IP address, subnet mask, gateway, DNS servers, NTP servers, etc.
• October 1993 - The bootstrap protocol (BOOTP)
• BOOTP didn't automatically define everything
- Some manual configurations were still required
- BOOTP also didn't know when an IP address might be available again
- Initially released in 1997, updated through the years
- Provides automatic address / IP configuration for almost all devices
HTTP and HTTPS
- Communication in the browser
- And by other applications
• In the clear or encrypted
- Supported by nearly all web servers and clients
Post office Protocol version 3 (POP3)
• Receive emails from an email server
- Authenticate and transfer
- tcp/110
- Basic mail transfer functionality

Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP)
- tcp/143
- Includes email inbox management from multiple clients
- v4
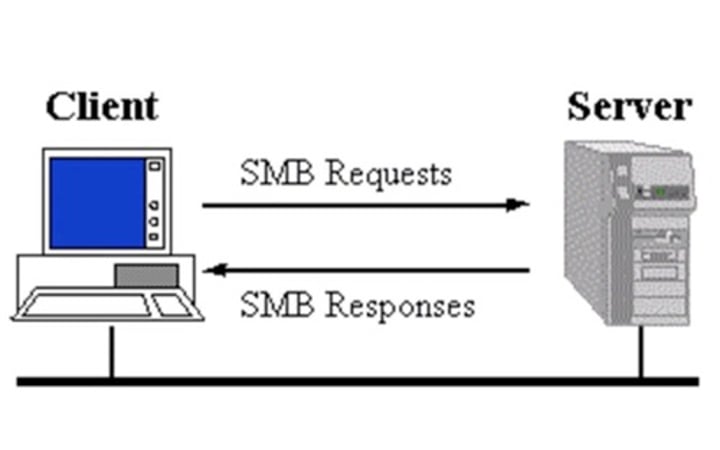
SMB - Server Message Block
• Protocol used by Microsoft Windows
- File sharing, printer sharing
- Also called CIFS (Common Internet File System)
• Using NetBIOS over TCP/IP
(Network Basic Input/Output System)
- udp/137 - NetBIOS name services (nbname)
- tcp/139 - NetBIOS session service (nbsession)
• Direct over tcp/445 (NetBIOS-less)
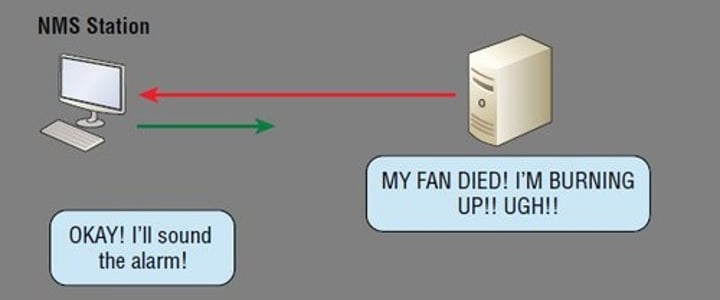
SNMP - Simple Network Management Protocol
• Gather statistics from network devices
- Queries: udp/161
- Traps: udp/162
• v1 - The original
- Structured tables
- In-the-clear
• v2 - A good step ahead
- Data type enhancements
- Bulk transfers
- Still in-the-clear
• v3 - A secure standard
- Message integrity
- Authentication
- Encryption
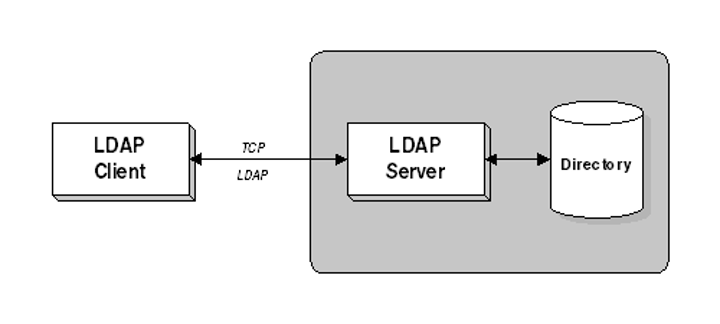
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP)
tcp/389
• Store and retrieve information in a network directory
- Commonly used in Microsoft Active Directory
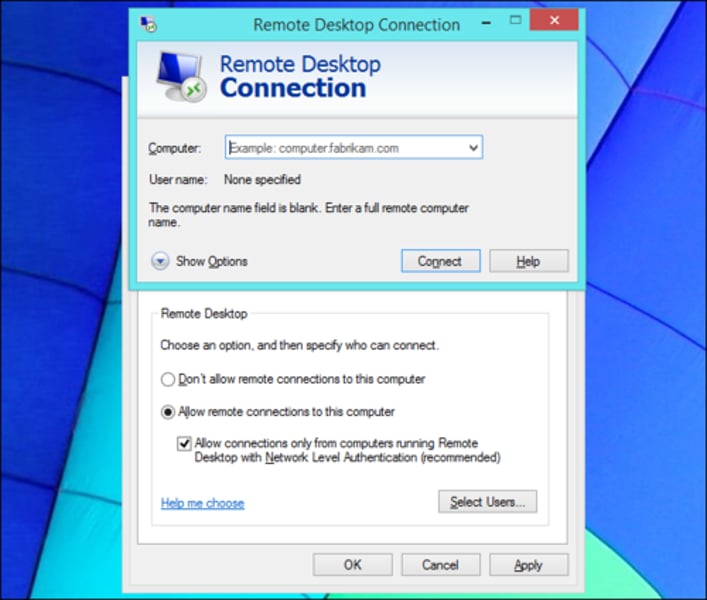
RDP - Remote Desktop Protocol
• Share a desktop from a remote location over tcp/3389
• Can connect to an entire desktop or just an application
• Clients for Windows, macOS, Linux, Unix, iPhone, Android, and others
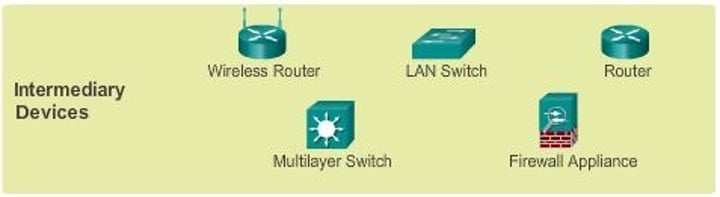
Network devices
• Many different devices and components
- All have different roles
• Some of these functions are combined together
- Wireless router/switch/firewall
• Compare different devices
- Understand when they should be used
Routers
• Routes traffic between IP subnets
- Makes forwarding decisions based on IP address
- Routers inside of switches sometimes called "layer 3 switches"
• Often connects diverse network types
- LAN, WAN, copper, fiber

Switches
• Bridging done in hardware
- Application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC)
- Forwards traffic based on data link address
• Many ports and features
- The core of an enterprise network
- May provide Power over Ethernet (PoE)
• Multilayer switch
- Includes routing functionality

Unmanaged switches
• Very few configuration options
- Plug and play
• Fixed configuration
- No VLANs
• Very little integration with other devices
- No management protocols
• Low price point
- Simple is less expensive

Managed switches
• VLAN support
- Interconnect with other switches via 802.1Q
• Traffic prioritization
- Voice traffic gets a higher priority
• Redundancy support
- Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
• Port mirroring
- Capture packets
• External management
- Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)

Access point
• Not a wireless router
- A wireless router is a route rand an access point in a single device
• An access point is a bridge
- Extends the wired network onto the wireless network
- Makes forwarding decisions based on MAC address

Patch Panels
• Combination of punch-down blocks and RJ-45 connectors
• Runs from desks are made once
- Permanently punched down to patch panel
• Patch panel to switch can be easily changed
- No special tools
- Use existing cables

Firewalls
• Filters traffic by port number
- OSI layer 4 (TCP/UDP)
- Some firewalls can filter based on the application
• Can encrypt traffic into/out of the network
- Protect your traffic between sites
• Can proxy traffic
- A common security technique
• Most firewalls can be layer 3 devices (routers)
- Usually sits on the ingress/egress of the network

Power over Ethernet (PoE)
• Power provided on an Ethernet cable
- One wire for both network and electricity
- Phones, cameras, wireless access points
- Useful in difficult-to-power areas
• Power provided at the switch
- Built-in power - Endspans
- In-line power injector - Midspans
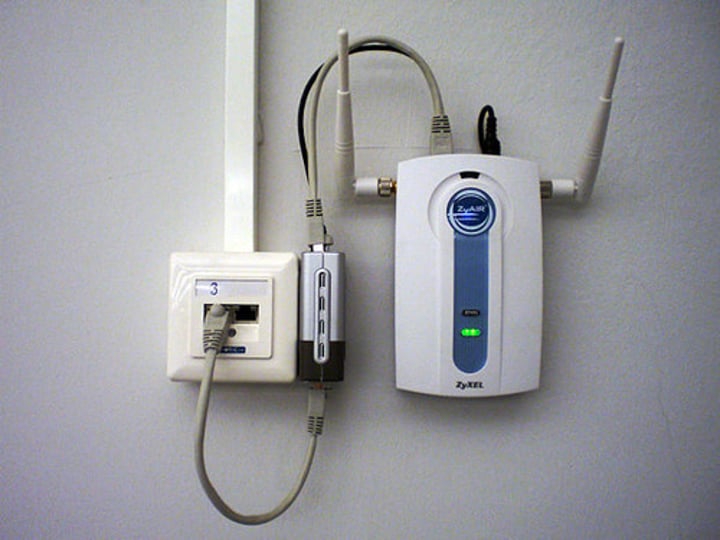

PoE switch
- Commonly marked on the switch or interfaces

PoE, PoE+, PoE++
• IEEE 802.3af-2003
- The original PoE specification
- Now part of the 802.3 standard
- 15.4 watts DC power, 350 mA max current
• IEEE 802.3at-2009
- Now also part of the 802.3 standard
- 25.5 watts DC power, 600 mA max current
• IEEE 802.3bt-2018
- 51 W (Type 3), 600 mA max current
- 71.3 W (Type 4), 960 mA max current
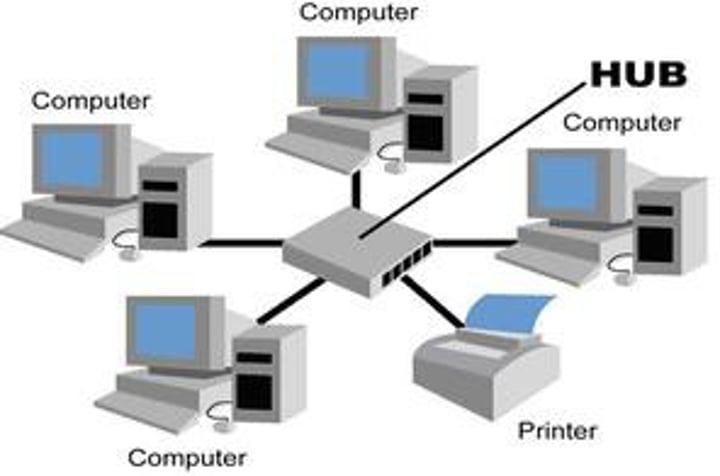
Hub
• "Multi-port repeater"
- Traffic going in one port is repeated to every other port
• Everything is half-duplex
• Becomes less efficient as network traffic increases
• 10 megabit / 100 megabit
• Difficult to find today
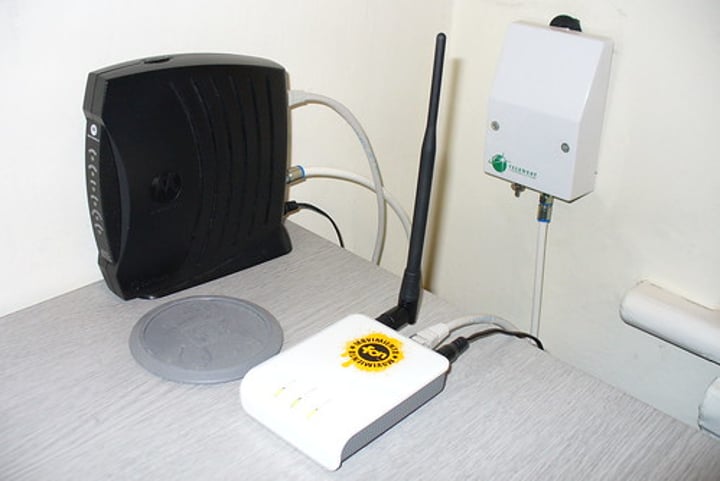
Cable modem
• Broadband
- Transmission across multiple frequencies
- Different traffic types
• Data on the "cable" network
- DOCSIS (Data Over Cable Service Interface Specification)
• High-speed networking
- Speeds up to 1 Gigabit/s are available
• Multiple services
- Data, voice, video

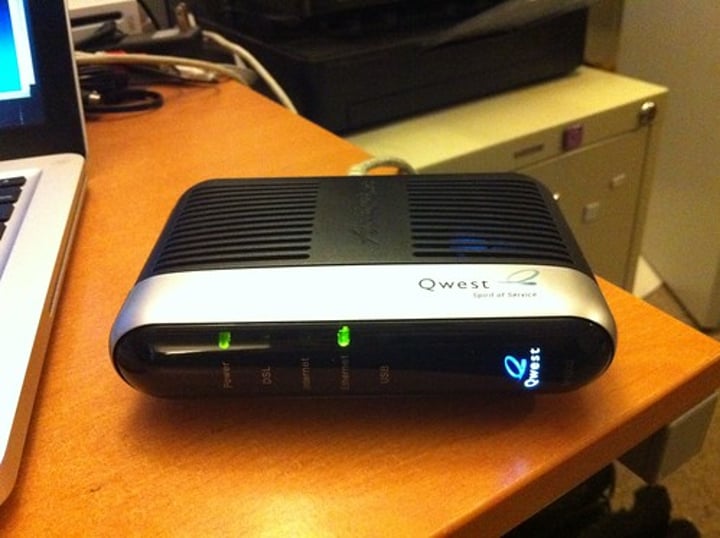
DSL modem
• ADSL (Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line)
- Uses telephone lines
• Download speed is faster than the upload speed (asymmetric)
- ~10,000 foot limitation from the central office (CO)
- 52 Mbit/s downstream / 16 Mbit/s upstream are common
- Faster speeds may be possible if closer to the CO

Optical Network Terminal (ONT)
- Fiber to the premises
• Connect the ISP fiber network to the copper network
- Demarcation point (demarc) in the data center
- Terminal box on the side of the building
• Line of responsibility
- One side of the box is the ISP
- Other side of the box is your network
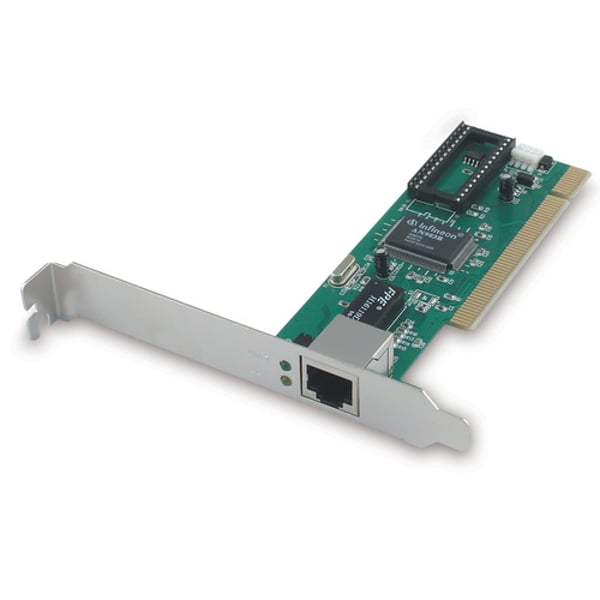
Network Interface Card (NIC)
• The fundamental network device
- Computers, servers, printers, routers, switches, phones, tablets, cameras, etc.
• Specific to the network type
- Ethernet, WAN, wireless, etc.
• Often built-in to the motherboard
- Or added as an expansion card
• Many options - Single port, multi-port, copper, fiber
• Ethernet connection
- Onboard NIC may not be working
• Additional connections
- Servers, routers, security devices

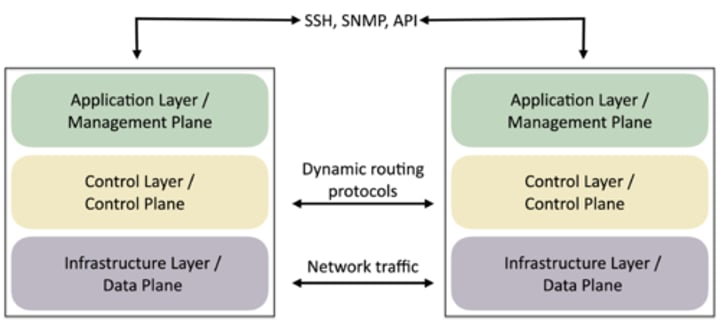
SDN (Software Defined Networking)
• Networking devices have different functional planes of operation
- Data, control, and management planes
• Split the functions into separate logical units
- Extend the functionality and management of a single device
- Perfectly built for the cloud
• Infrastructure layer / Data plane
- Process the network frames and packets
- Forwarding, trunking, encrypting, NAT
• Control layer / Control plane
- Manages the actions of the data plane
- Routing tables, session tables, NAT tables
- Dynamic routing protocol updates
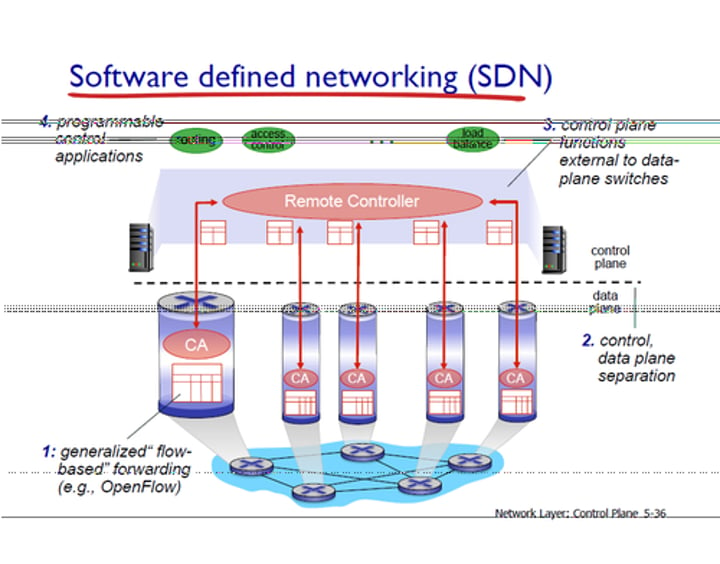
Extend the physical architecture

SDN data flows
Wireless standards
• Wireless networking (802.11)
- Managed by the IEEE LAN/MAN Standards Committee (IEEE 802)
• Many updates over time
- Check with IEEE for the latest
• The Wi-Fi trademark
- Wi-Fi Alliance handles interoperability testing
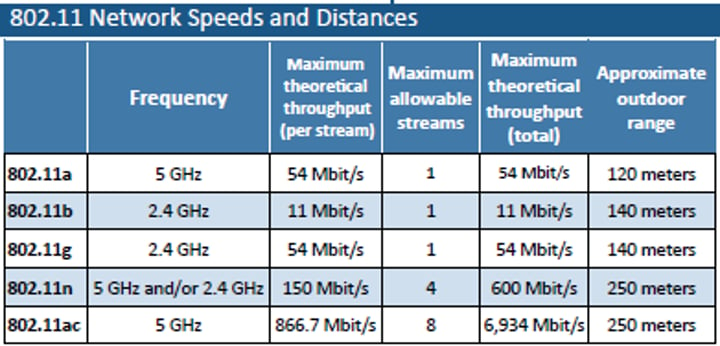
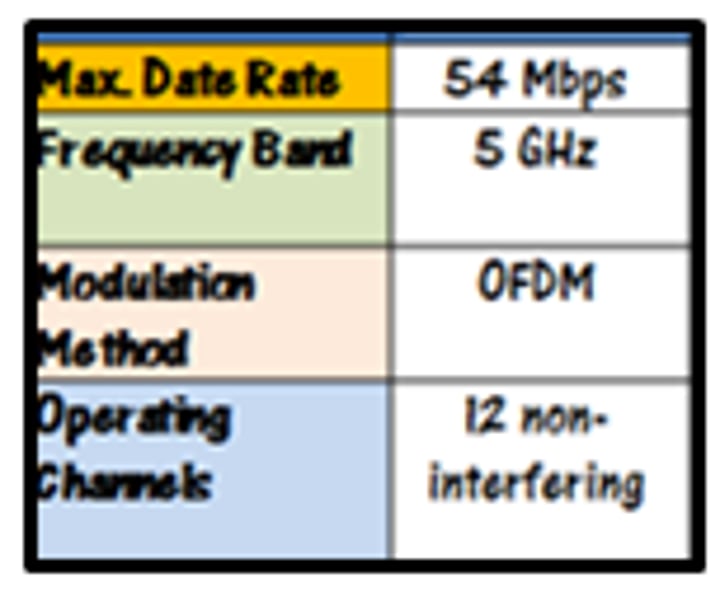
802.11a
• Operates in the 5 GHz range
- Or other frequencies with special licensing
• 54 megabits per second (Mbit/s)
• Smaller range than 802.11b
- Higher frequency is absorbed by objects in the way
• Not commonly seen today
802.11b
• Operates in the 2.4 GHz range
• 11 megabits per second (Mbit/s)
• More frequency conflict
- Baby monitors, cordless phones, microwave ovens, Bluetooth
• Not commonly seen today

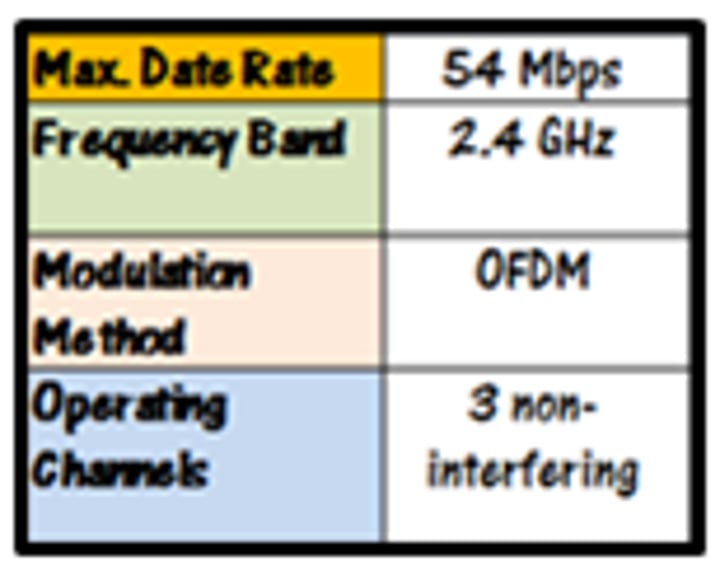
802.11g
• Operates in the 2.4 GHz range
• 54 megabits per second (Mbit/s) - Similar to 802.11a
• Same 2.4 GHz frequency conflict problems as 802.11b