Comprehensive Guide to Antibiotics, Resistance, and Microbial Genetics
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
antibiotic
a chemical substance from one microorganism that inhibits or kills another microorganism.
bactericidal
drug that kills bacteria.
bacteriostatic
drug that inhibits bacterial growth but does not kill bacteria.
selective toxicity
killing microbial cells but not the host's own cells (skin, muscle, nerves, etc.).
broad spectrum antibiotic
drug that is effective against a wide range of microbes.
narrow spectrum antibiotic
drug that is effective against a limited range of microbes.
beta-lactam antibiotic
inhibit penicillin binding proteins, thus interfering with peptidoglycan synthesis.
acquired resistance
resistance due to mutation or acquisition of new genes.
penicillin
from Penicillium chrysogenum. Discovered by Alexander Fleming. Interferes with peptidoglycan synthesis by inhibiting penicillin binding proteins, which normally cross-links the short peptides in the cell wall.
minimum inhibitory concentration
the lowest concentration of a drug that will inhibit the microorganism from growing.
minimum bactericidal concentration
lowest concentration of a drug that will kill 99.9% of the population of a particular bacterium.
disc diffusion test
"Kirby-Bauer Test" — plate a lawn of bacteria and add antibiotic discs. Then, determine susceptibility or resistance to antibiotics. Clear zones around the disc means bacteria are killed and the antibiotic is effective. No clear zone means the antibiotic is not effective, and that the bacteria can grow normally.
R plasmid
"Resistance (R) Factor" — plasmid carrying one or more genes for antibiotic resistance.
therapeutic index (TI#)
lowest dose toxic to the patient divided by the dose used to treat the disease. The higher the therapeutic index, the less toxic the drug.
intrinsic resistance
resistance due to an inherent characteristic of the microbe.
site of action
antibiotic target—anything that is an essential process in the bacteria. Include: cell membrane, cell wall, DNA, mRNA, and proteins.
vertical gene transfer
moving genes, including antibiotic resistant genes, through reproduction. Passing the genes to the daughter cells.
horizontal gene transfer
moving genes, including antibiotic resistant genes, through conjugation, transduction, and transformation. Can pass genes to the same and different species of bacteria.
cell wall
B-lactam & penicillin.
plasma membrane / cell membrane
daptomycin.
DNA
Quinolones & Ciprofloxacin.
protein
chloramphenicol.
mRNA
Rifampin.
penicillin family
altering the side chain can change the properties of the antibiotic: solubility, half-life, oral bioavailability, etc., but not its mechanism of action.
Kirby Bauer
a method used to determine which antibiotics might be useful in treating an infection caused by a bacterial pathogen.
normal flora
the normal flora is often adversely affected by antibiotic therapy. Normal microflora keeps opportunities pathogens in check. Broad spectrum antibiotics kill nonresistant cells.
Broad spectrum antibiotics
Kill nonresistant cells.
Drug resistant pathogens
Proliferate and can cause superinfection.
Antifungal drugs side effects
More severe than antibacterial drugs because they damage fungal cells the same way they can damage our cells.
Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in bacteria
Change shape of antibiotic.
Reducing antibiotic resistance
Include 'resistance inhibitors' in the antibiotic preparation.
tRNA
Transfer RNA; type of RNA molecule involved in interpreting the genetic code; each tRNA molecule carries a specific amino acid.
rRNA
Ribosomal RNA; type of RNA molecule present in ribosomes.
Nucleotide
Contains a 5-carbon sugar (deoxyribose or ribose), a phosphate group, and one of four different nucleobases (A, T/U, G, or C).
Adenine
Nucleobase; paired with thymine.
Thymine
Nucleobase in DNA; paired with adenine.
Guanine
Nucleobase; paired with cytosine.
Cytosine
Nucleobase; paired with guanine.
Uracil
Nucleobase in RNA; paired with adenine.
Promoter
Nucleotide sequence to which RNA polymerase binds to start transcription.
RNA polymerase
Enzyme that synthesizes RNA using one strand of DNA as a template.
DNA polymerase
Enzyme that synthesizes DNA, using an existing strand as a template to make a new complementary strand.
DNA replication
Duplication of a DNA molecule.
Template
The RNA sequence made during transcription is complementary and antiparallel to the DNA template; the DNA strand that serves as the template for transcription is called the minus (-) strand.
Haploid
A single set of unpaired chromosomes.
Diploid
Two complete sets of chromosomes, one from each parent.
Transcription
The process by which the information encoded in DNA is copied into RNA.
Translation
The process by which the information carried by mRNA is used to synthesize the encoded protein.
Codon
A series of three nucleotides that code for a specific amino acid.
Start codon
Codon at which translation is initiated; it is typically the first AUG after a ribosome-binding site.
Stop codon
Codon that terminates translation, signaling the end of the protein; there are three stop codons.
Intron
Non-coding regions that must be removed from pre-mRNA to create functional mRNA.
Constitutive gene expression
Gene is always expressed (mRNA transcription always occurs).
Inducible gene expression
Gene is only expressed under certain conditions (transcription of mRNA only occurs under these conditions).
Repressible gene expression
Gene is usually expressed, but transcription is blocked under certain conditions.
Co-repressor
Attaches to the repressor; the co-repressor-repressor complex can then bind to the operator, blocking transcription.
Inducer
Attaches to the repressor; the shape of the repressor changes so that it can no longer attach to the operator.
repressor protein
a regulatory protein that blocks transcription (negative regulation) by binding to an operator, a specific DNA sequence located immediately downstream of a promoter.
operator
a specific DNA sequence located immediately downstream of a promoter.
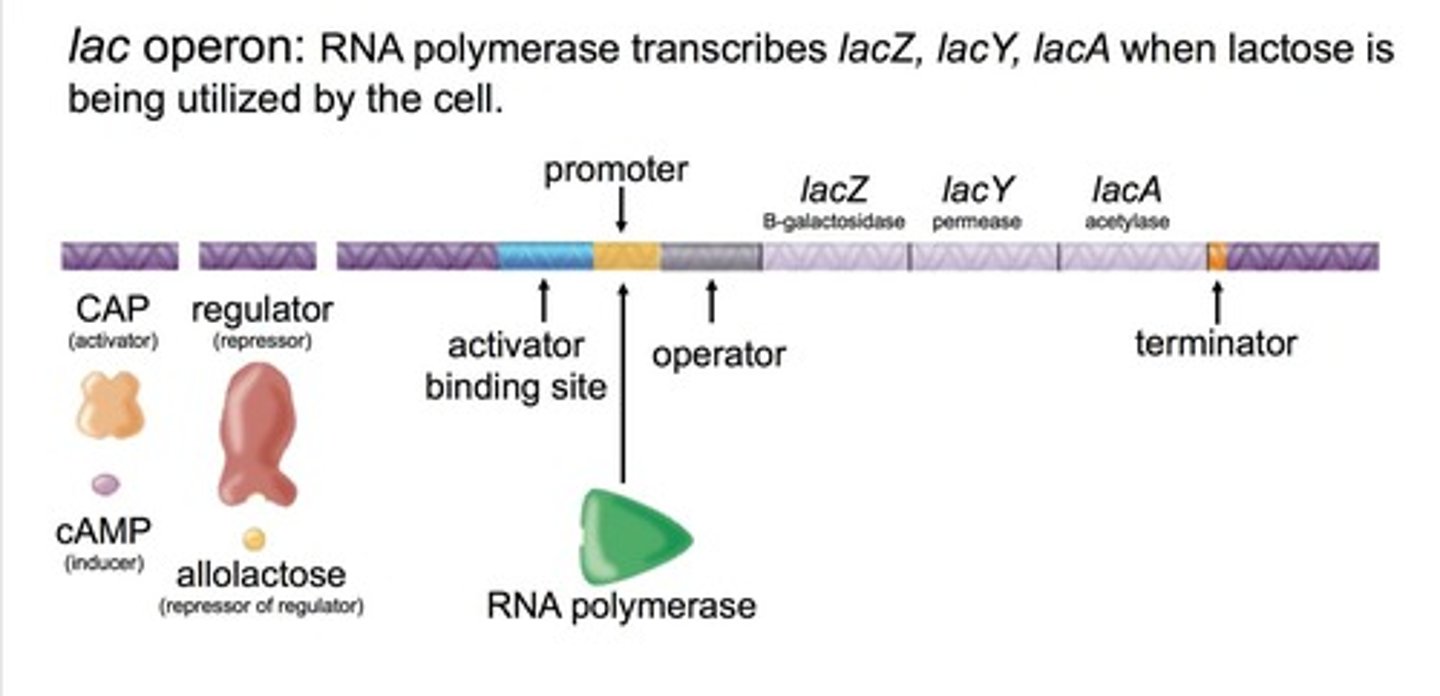
lac operon
RNA polymerase transcribes lacZ, lacY, and lacA when lactose is being used by the cell.
Ames test
tests for potential mutagenic chemicals by comparing the number of random mutations that fix an auxotroph in a control plate versus a test plate.
mutant
organism that bears a mutation and may exhibit an altered phenotype.
wild-type
organism that exhibits the normal (non-mutant) phenotype.
mutation
any permanent, inheritable change in the genetic information of the cell.
frameshift
caused by insertions or deletions that shift the reading frame of the mRNA so that codons are not read in the correct register.
transposon
transposable elements that can move from one location in the genome to another and can create genetic recombination.
plasmid
small circular double stranded DNA that can have antibiotic resistant genes and has the potential to transfer those via sex pilus (conjugation).
F plasmid
Fertility plasmid that can form a sex pilus needed for conjugation.
donor cell
F+, contains F plasmid originally.
recipient cell
F-, then F+. Receives F plasmid from donor through conjugation.
conjugation
transfer of the F (fertility) plasmid using a sex pilus.
Hfr cell
high frequency recombination where the F plasmid integrates into the bacterial chromosome.
generalized transduction
a phage mistake where bacterial DNA can mistakenly enter a protein coat during construction of viral particles.
specialized transduction
when a viral genome of prophage excises from bacterial chromosome and takes a piece of adjacent bacterial DNA with it.
transformation
bacterial uptake of small fragment of DNA from the surrounding environment.
mitosis
in which each daughter cell receives the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
meiosis
in which diploid cells give rise to haploid cells. These haploid cells can develop into haploid organisms, or they can be used as haploid sex cells called gametes that are involved in sexual reproduction. Contains Meiosis I and II. Also contains crossing-over. Diploid cell undergoes two sequential divisions resulting in 4 cells, each with a single set of chromosomes. Homologous chromosomes (member of a pair) pair up and crossing-over may occur. Sexual reproduction and meiosis result in increased genetic recombination.
crossing-over
occurs in Meiosis I. The exchange of chromosome segments between non-sister chromatids during the production of gametes.
prokaryotes
translation begins while mRNA molecule is still being synthesized. Transcription and translation are coupled. (due to being in the cytosol already). Also, polycistronic.
eukaryotes
transcription and translation are separate events. Monocistronic.
mRNA processing in eukaryotes
mRNAs contain non-coding regions called introns that must be spliced out before the mature mRNA can function in protein synthesis. In addition, they can perform alternative splicing (one gene but many different protein possibilities). Also, 5' cap and Poly-A tail.
inducible genetic system
like the lac operon functions. How are the genes for lactose utilization turned on and off?
lacZ (B-galactosidase)
produces the repressor protein allolactose.
repressible operon
such as the arginine synthesis operon will function when arginine is plentiful in the cell and when arginine is in short supply within the cell.
arginine
Plentiful: arginine will bind to the repressor protein, changes its shape, and allows it to bind to the operator.
Competent Cells
Cells that are capable of being transformed by taking up DNA fragments.
Fungistatic Agent
An agent that inhibits the growth of fungi but does not kill them.
Therapeutic Index
A measure of the safety of an antibiotic; a high therapeutic index indicates less toxicity to the patient.
Inducible Operon
An operon where transcription occurs in response to the presence of an inducer, such as lactose in E. coli.
RNA Transcription
The process of copying a segment of DNA into RNA.
Gametes
Haploid sex cells produced during meiosis that are involved in sexual reproduction.
Bacterial Chromosome Integration
The process where a DNA fragment is incorporated into the bacterial chromosome after transformation.
Sex Pilus
A structure used by donor cells during conjugation to transfer genetic material to recipient cells.
Transducing Particle
A viral particle that carries bacterial DNA instead of phage DNA during generalized transduction.
Transduction
The process during which genes are transcribed.
Active Growth
The state in which genes are transcribed at any time the cell is actively growing.
Salvarsan
The first chemotherapeutic agent used to successfully treat an infectious disease, discovered in 1910.
Beta-lactam antibiotics
A class of antibiotics, such as penicillin, that inhibit cell wall formation in susceptible bacteria.
Base pair deletion mutation
A mutation that will cause a shift in the reading frame during translation.
Antibiotic resistance genes
Genes that can be found on chromosomal DNA, transposons, and plasmids.