Exam Four
1/131
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Spectrometry and Chromatography
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
132 Terms
What must the light source for the Spectrometry Block Diagram Be?
A good source of white light, typically a tungsten bulb or a deuterium lamp.
Why can we not use a plastic cuvette in Spectrometry most of the time?
Can not be used in UV light and depending on the solvent may disintegrate. instead use a quartz cuvette, which is transparent to UV light and chemically resistant.
What is typically used over a prism and why for the wavelength selector?
Typically, a diffraction grating is used over a prism for the wavelength selector because it provides higher resolution and better efficiency in separating light into its component wavelengths. In addition it is much cheaper.
If you make the entrance slit to a wave length separator smaller what happens?
The resolution improves as the light entering the spectrometer becomes more collimated, but this may decrease the intensity of the transmitted light.
At what ranges is the absorbance reading most accurate?
The absorbance reading is most accurate in the range of 0.1 to 1.0 absorbance units.
What if you have a mixture of multiple components that all absorb light somewhat?
Since absorbance is directly proportional to concentration, a matrix based deconvolution method can be used to analyze a mixture of n component by making n absorbance measurements at a certain wavelength.
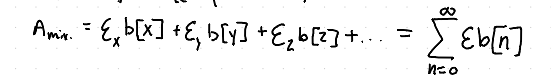
How is the jaw of a diffraction grating formed?
By carfully machining two pieces of metal to give sharp edges to be exactly parallel and on the same plane.
What does the entrance slit of a diffraction grating serve as?
A source of radiation
What is the effective bandwidth of a monochromator?
The effective bandwidth of a monochromator is the range of wavelengths that can pass through the optical system, typically determined by the entrance slit width and the optical setup. It affects the resolution and sensitivity of spectroscopic measurements. The complete resolution of two lines achieved when slit width is adjusted so that the bandwidth is one half the wavelength difference of the lines.
How do we solve the concentrations of a mixture that is not well resolved using Beer’s Law?
By the use for least squares minimization using a spreadsheet or other software to correct for the contributions from each species in the spectrum of the mixture.
How do you solve the concentrations of a mixture in a well resolved solution using Beer’s Law?
By using linear algebra and matrices.
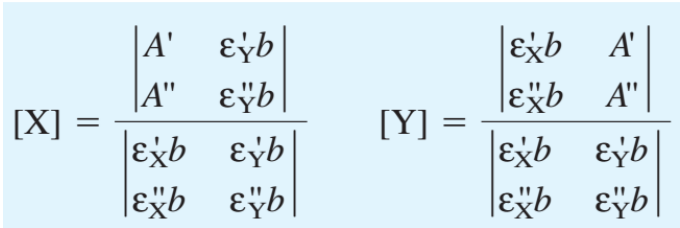
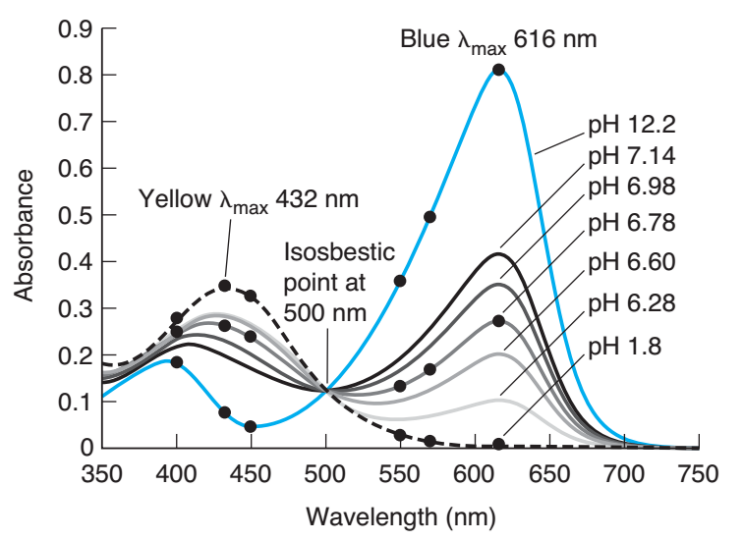
What is the isosbestic point?
The isosbestic point is a wavelength at which the absorbance of a solution remains constant regardless of the concentrations of the species present. This occurs when two or more species in a mixture have overlapping absorbance spectra, resulting in a fixed absorbance value at that specific wavelength.
What is flow injection analysis?
a liquid sampel is injewcted into a continuously flowing liquid carrier containing a reagent that reacts with the smaple.
What happens during flow injection analysis as the smaple flows from injector to the detector?
The sample zone broadens and reacts with reagent to form a product to which the detector responds.
What is the advantage of Flow injection analysis over “batch processing”
Speed, automation and low cost.
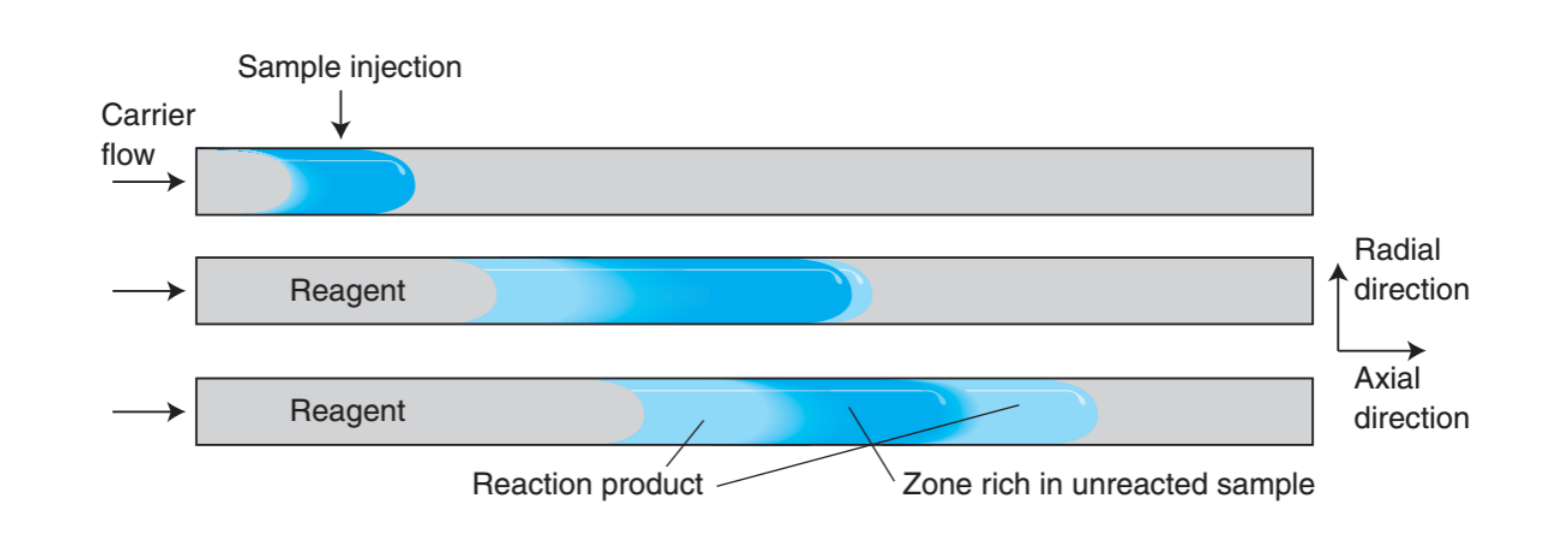
What does the following figure show?
Dispersion and reaction ofg sample as it travels downstream after injection into the carrier for fluid injection analysisFlow injection analysis process.
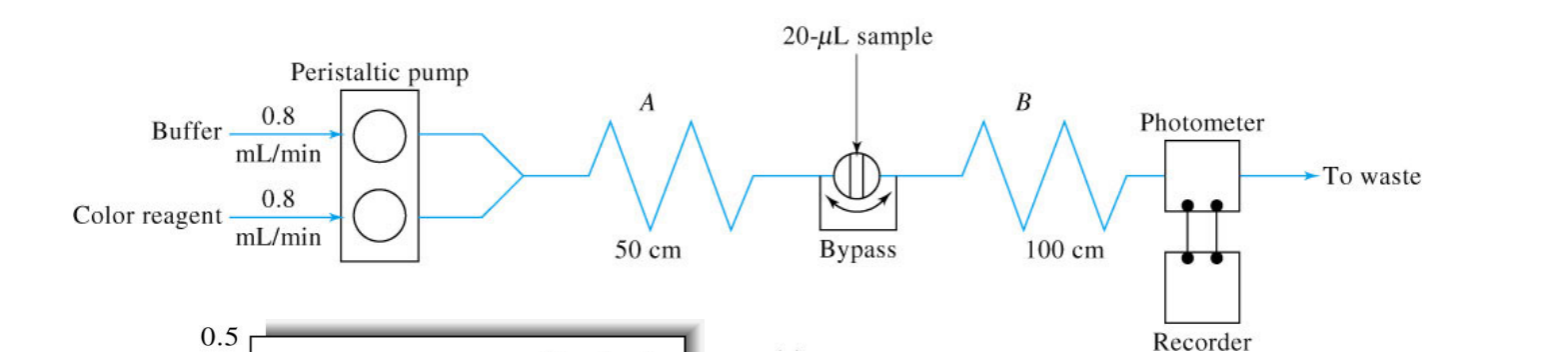
Using the following instrument, what can be interpreted from the outputted data?
This type of data can be used to generate calibration curves (from multiple replicates of the standard) and then to quantify the unknown samples, all with a fully automated run of the instrument.
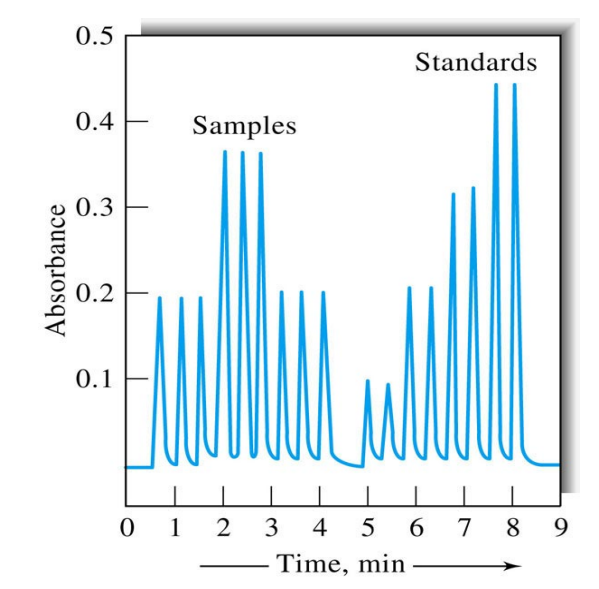
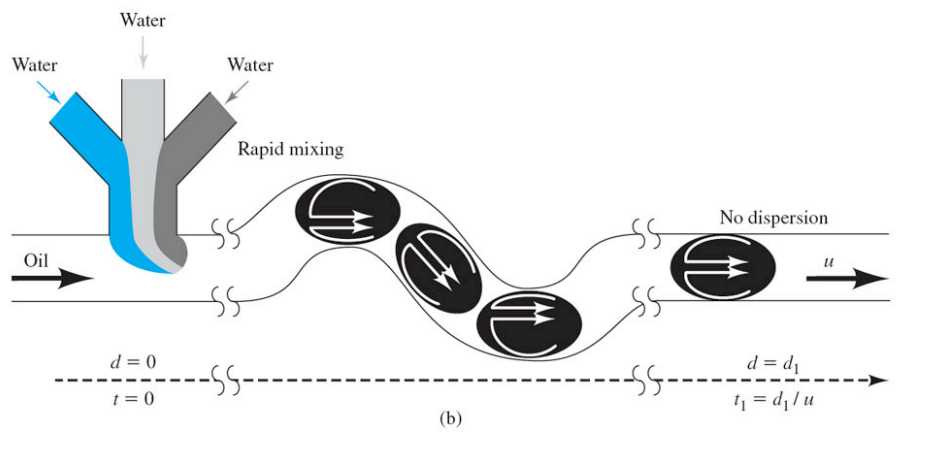
What is the following diagram showing and what is the importance of this type of analysis?
Microfluidics is the study and manipulation of fluids on the microscale, allowing for precise control of small volumes. It is important for applications in biomedical diagnostics, chemical analysis, and sensor development.
What can microfluidic droplets do?
Minimize dispersion
What is the purpose of an enzyme in a bioassay?
To act as a “chemical amplifier” of an analyte signal, working as the most widely used labels for immunoassays, and can use simple UV-Vis instrumentstion in most cases.
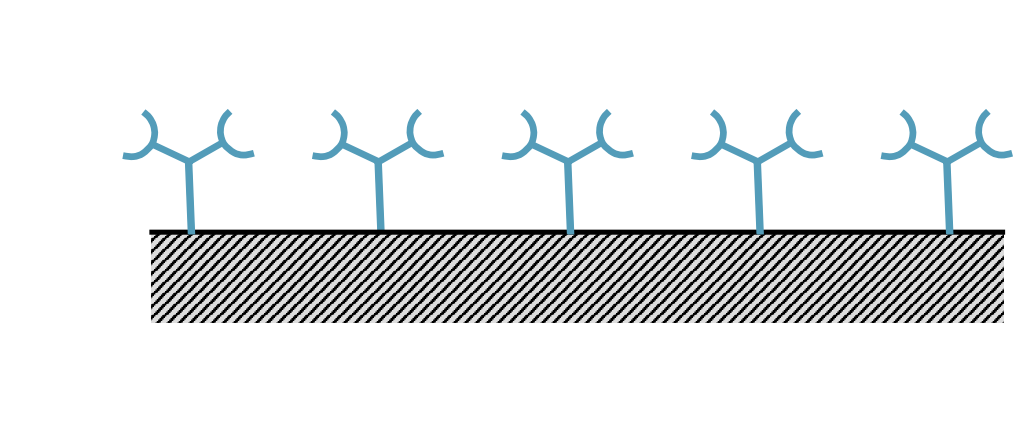
What is the first step of ELISA?
Primary Ab conjugated to surface
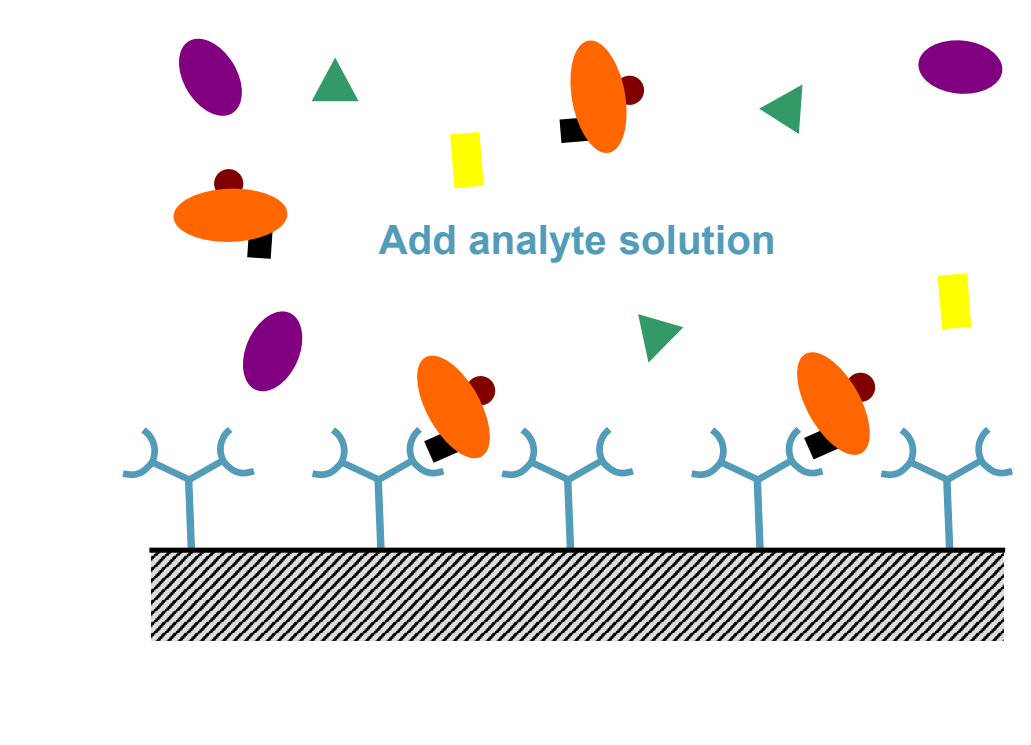
What is the second step of ELISA?
Add analyte solution
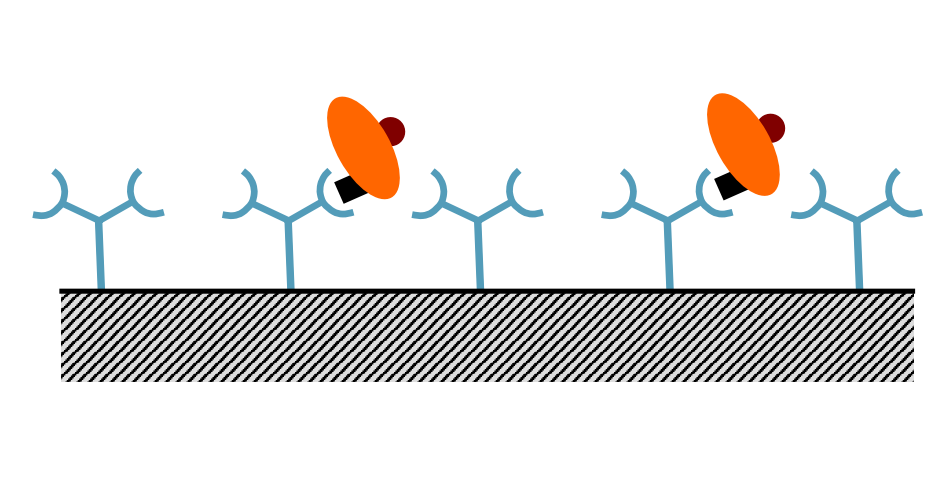
What is the third step of ELISA?
Wash away analyte solution remaining
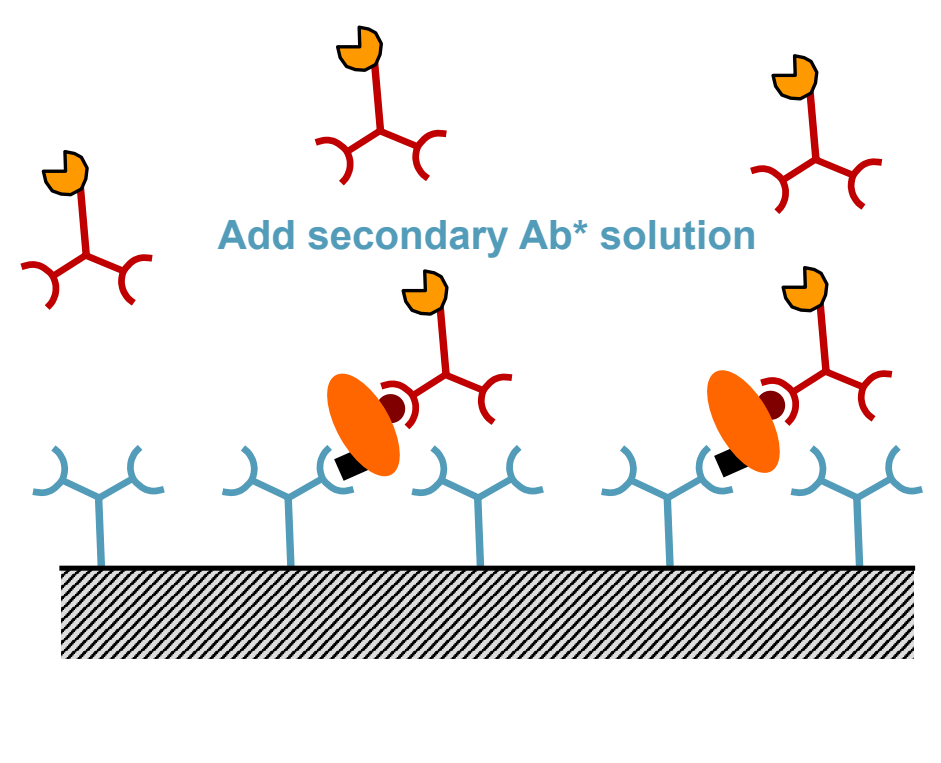
What is the fourth step of ELISA?
Add Secondary antibody conjugated to detection enzyme
What is the fifth step of ELISA?
Wash away unbound secondary antibody
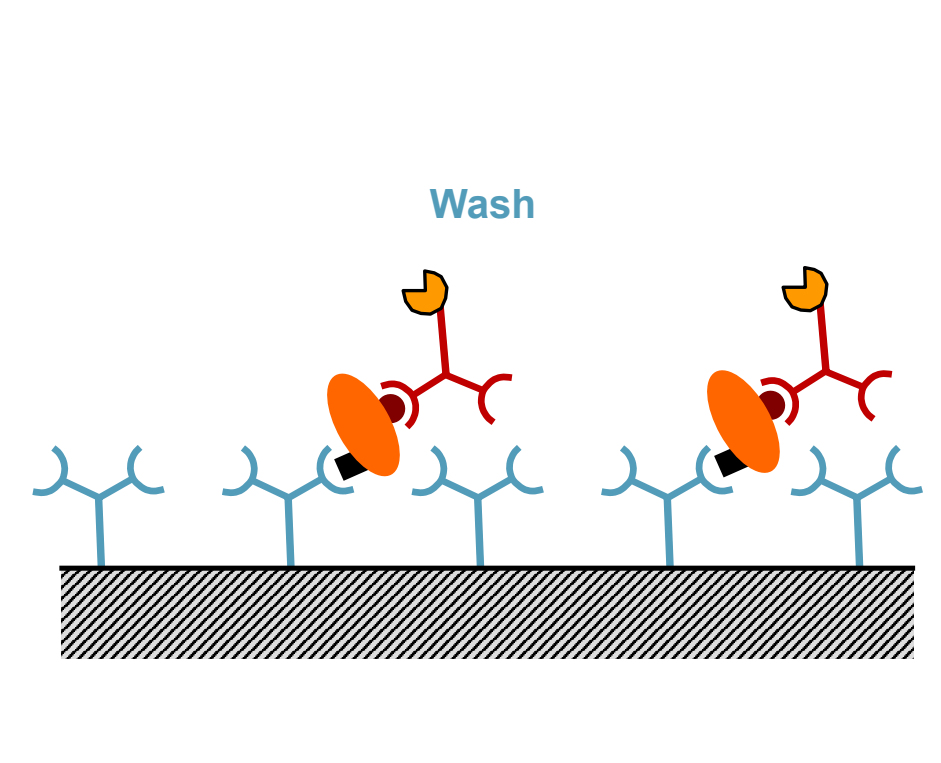
What is the sixth step of ELISA?
Add substrate for enzyme reaction
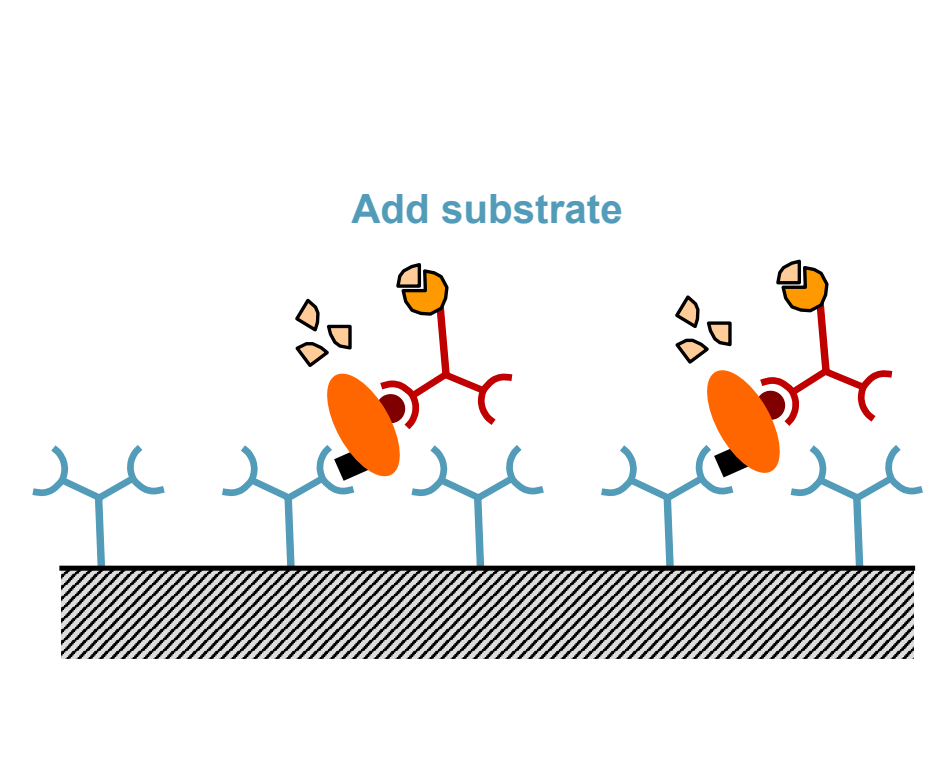
What is the seventh step of ELISA?
Monitor production of colored or fluorescent product indicating the presence of the target antigen.
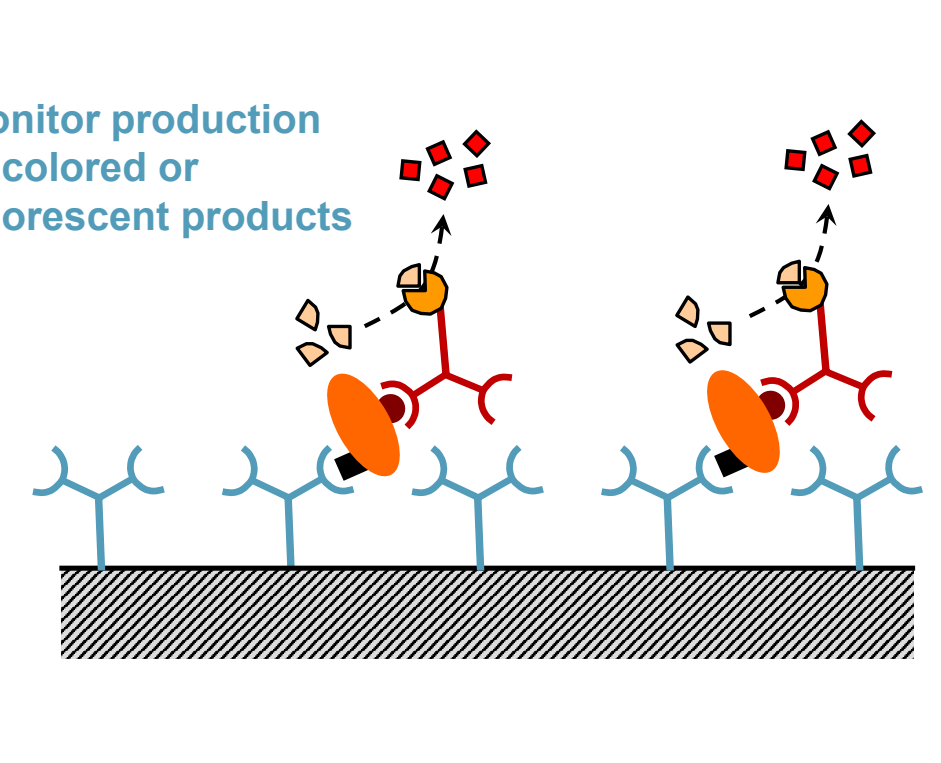
What do some ELISA use instead of a secondary substrate antibody?
A more flexible version uses a generic labeled antibody.
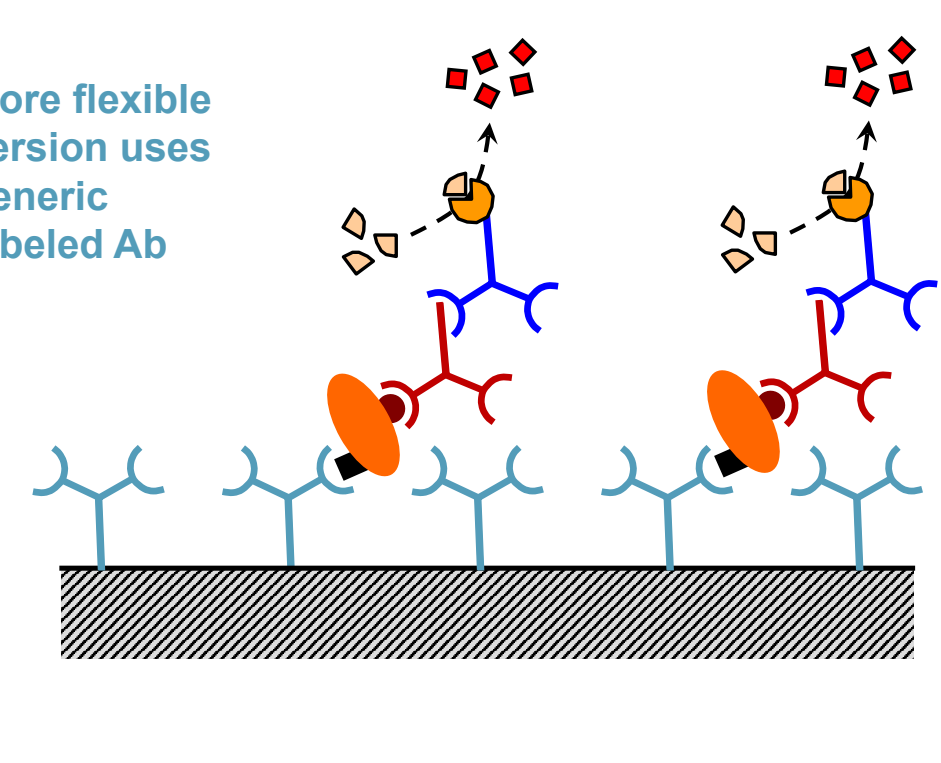
What does ELISA stand for and what is it?
ELISA stands for Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay, a laboratory technique used to detect and quantify proteins such as antigens or antibodies in a sample. THis is the gold standard for protein, antigen, and antibody detection. It involves the use of an enzyme conjugated to an antibody to produce a measurable signal, typically a color change.
What is ELISA selective for?
Selective for analyte depdning on antibody binding
How is ELISA highly sensitive?
ELISA is highly sensitive due to its ability to amplify signals through enzyme-substrate reactions, allowing detection of very low concentrations of analytes.
What is the ELISA sandwich adapted for?
To detect antibodies to measure immune response
What is spectroscopy
The science that involves the interactions of radiation with matter.
What are some examples of spectroscopy?
Electromagnetic Radiation, Acoustic Waves, Beams of Particles
What is spectrophotometry?
Using Light (“-photo-”) to measure chemical concentrations in a quantitative way (“-metry”)
What is the first step of the Block Diagram of Absorbance Spectrometry?
Source

What is the second step of the Block Diagram of Absorbance Spectrometry?
Wave Selector (Monochromator)
What is the third step of the Block Diagram of Absorbance Spectrometry?
Sample
What is the fourth step of the Block Diagram of Absorbance Spectrometry?
Detector

What is the fifth step of the Block Diagram of Absorbance Spectrometry?
Signal Processor and Readout
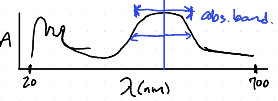
What do most molecules show in the visible absorption spectroscopy?
A continum called an absorption band
What is Beer’s Law?
A principle that relates the absorption of light to the properties of the material through which the light is traveling. It states that the absorbance is directly proportional to the concentration of the absorbing species and the path length of the light.
What is the value of transference equal to?
P/P0
What is the equation of Absorbance?
A = Log(P0/P) = Log (1/T) = -Log(T) = εbc, where A is absorbance, P0 is the incident light intensity, P is the transmitted light intensity, ε is the molar absorptivity, b is the path length, and c is the concentration.
How do Electric and Magnetic Field oscillate?
in-phase and perpendicular
What is Frequency, v (Hz)
Number of oscillations. in the field that occur per second as the wave propagates through a fixed point in space.
What is Wavelength, λi (m)
The linear distance between any two equivalent points on successive waves.
What is the equation velocity of propagation, wi (ms-1)
wi = vλi
What determines the frequency?
The source and remains invariant.
What determines the velocity?
The composition of the medium, thus making the wavelength medium dependent
What is the equation for the speed of light?
c = vλ, where in a vacuum, c, equals 2.998 × 108 m/s
What can be viewed in the microwave spectrum?
The rotation of a molecule
What can be viewed in the infrared spectrum?
The vibrational modes of molecules.
What can be viewed in the ultraviolet spectrum?
Electronic excitation of molecules and atoms.WHat can be viewed in the x-ray spectrum?
What can be viewed in the x-ray spectrum?
Bond breaking and ionization
What is the range of the visible spectrum?
The range is from approximately 380 to 750 nanometers, encompassing the wavelengths of light that can be seen by the human eye.
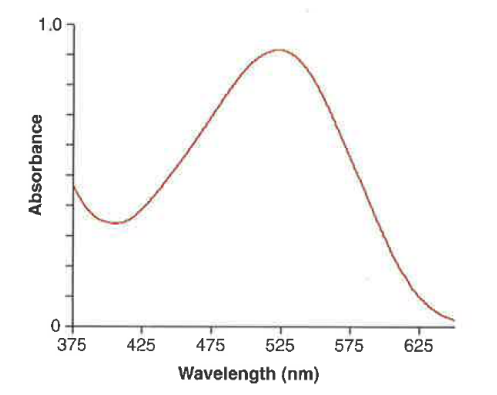
Why do most molecules form a continuum or “absorption band”?
Due to vibrational and rotational levels.
Red light
Wavelength: 620-750 nm
Orange light
Wavelength: 590-620 nm
Yellow light
Wavelength: 570-590 nm
Green light
Wavelength: 495-570 nm
Blue light
Wavelength: 450-495 nm
Indigo light
Wavelength: 425-450 nm
Violet light
Wavelength: 380-425 nm
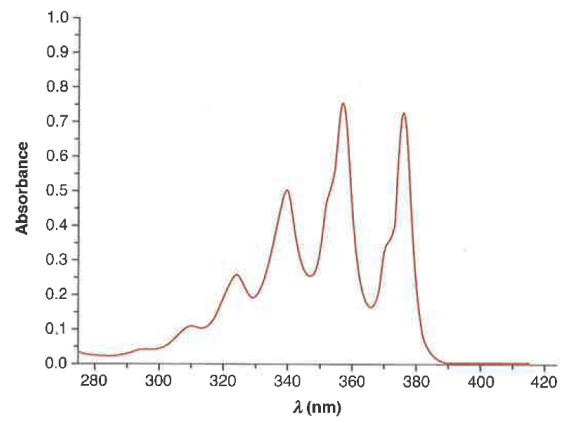
What type of molecules show vibrational detail in the UV-Vis spectrum?
Very Rigid Molecules
What is the big caveat of Beer’s Law?
It only applies to dilute solutions (less than 0.01M) and assumes uniform conditions (true monochromatic radiation).
What is absorbance directly proportional to analyte concentration?
increases linearly as the concentration of an analyte increases, assuming other conditions remain constant.
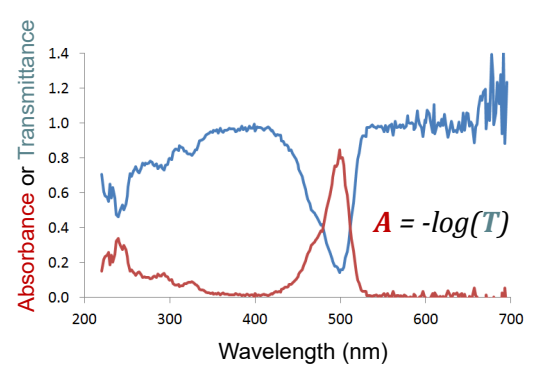
What is Thin Film Interference
A phenomenon that occurs when light waves reflecting off the top and bottom surfaces of a thin film interfere with one another, leading to colorful patterns due to constructive and destructive interference.
In interference filters what is the controlled to determine wavelength of transmitted radiation?
thickness of the film
In Interference Filters, what is 𝜆transmitted approximately equal to?
2dn, where d is the film thickness and n is the refractive index of the film.
What is the biggest caveat of Interference Filters?
It gives high performance but is very expensive.
In the real world what is required prior to making most analytical measurements?
Samples require some form of cleanup or separation
WHat is the physical transfer of a solute from one phase to another?
This is known as an Extraction technique
What is the equation to determine the fraction remaining in phase one after n extraction with volume (V2)?
qn = (V1/ (V1 + KV2))n
Why is it better to form better extractions?
Doing more extractions with the same total volume yields a higher recovery of the desired solute.
What do neutral complexes favor in extraction?
The organic solvent
What is chromatography?
The separation of a mixture by passing it in a solution or suspension (or as a vapor) through a medium in which components move through at different rates.
What is the partition coefficient?
.

What is required for the partitioning of a solute between two liquid phases?
The physical movement of solute from one phase ot the other, known as mass transfer.
What is the effect of a distribution coefficient?
It determines the extent to which a solute will partition between two immiscible phases, influencing its concentration in each phase.
What are crown ethers?
Synthetic compounds that envelop metal ions (especially alkali metal cations) in pocket of oxygen ligands that facilitate solubility and separation in organic solvents.

Who invented chromatography?
Mikhail Tswett, invented adsorption chromatography to separate plant pigments using a hydrocarbon solvent and inulin powder as a stationary phase.
What is adsorption chromatography?
A solid stationary phase and a liquid or gaseous mobile phase are used to separate components of a mixture based on their affinity for the stationary phase.
The more strongly a solute is adsorbed, …
the slower it travels through the column.
What is partition chromatography?
A liquid stationary phase is bonded to a solid surface, which is typically the inside of the fused silica chromatography column in gas chromatography.
Solute equilibrates between the ______ and the _________ phase, which is a flowing gas in gas chromatography.
stationary liquid; mobile
What is ion exchange chromatography?
Anions or cations are covaently attached to the stationary solid phase, usually a resin. The mobile phase is a liquid.
Solute ions of the _____ _____ ____ _____ to the stationary phase.
opposite charge are attracted
What is size exclusion chormatography?
Separates molecules by size, with the larger solutes passing through most quickly.
What does the liquid or gaseous mobile phase pass through?
A porous gel, which has pores small enough to exclude large solute molecules but not small ones.
What is affinity chromatography?
The most selective kind of chromatography, uses specific interactions between one kind of solute molecule and a second molecule that is covalently attached (immobilized) to the stationary phase. Such as an immobilized antibody.
What is preparative chromatography?
A technique used to separate and purify larger quantities of substances from a mixture for further analysis or use.
What is analytical chromatography?
A technique used to separate and analyze compounds in mixtures, focusing on purity and composition rather than quantity.
Wheere does partitioning occur and what can it be exploited for?
between phases for separation of components for complex molecules.
What is detected at 200nm on Spectrometry?
Organic Molecules
What does an HPLC yield during separation?
A high-resolution separation of compounds in a mixture for qualitative and quantitative analysis.
What is tm in HPLC?
Tm in HPLC refers to the retention time of a compound, which is the time taken for it to pass through the column and be detected. This time is crucial for analyzing compound behavior and characteristics during separation.
What is tr in HPLC?
Tr in HPLC refers to the retention time of a specific analyte, indicating the duration it takes for that analyte to reach the detector after being injected into the system.
What does the retention factor state in HPLC?
The retention factor, often represented as k, indicates the ratio of the time a compound spends in the stationary phase to the time it spends in the mobile phase during HPLC separation.
WHat does the retention relation give in HPLC?
Gives the relation of retention between species.