Chapter 12 Alkanes
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
general formula of alkanes
CnH2n+2
define sigma bond
the result of the direct overlap between orbitals of two bonding atoms
why does each carbon atom have a 3d tetrahedral shape
each atom is surrounded by four electron pairs in four sigma bonds which repel
why can atoms in alkanes rotate freely
sigma bonds acting as axes
explain the trend of boiling points in alkanes
1) increases as chain length increases 2) molecules have a greater surface area so more contact is possible between molecules 3) number of London forces increases so they become stronger 4) more energy required to overcome the forces
explain effect of branching on boiling points of alkanes
1) branched alkanes have fewer surface point of contact between molecules of the branched alkanes
2) therefore there are fewer London forces
3) also the branches prevent branched molecules getting as close as straight-chain molecules
4) this decreases the London forces further
explain the low reactivity of alkanes
1) c-c and c-h sigma bonds have high bond enthalpies 2) c-c bonds are non-polar 3) c-h bond considered to be non-polar
chemical equation for complete combustion of methane
CH4 (g) + 2O2(g) → CO2 (g) +2H2O (l)
chemical equation of incomplete combustion of methane
2CH4 (g) + 3O2 (g) → 2CO (g) + 2H2O (l)
general formula for balancing the complete combustion of alkanes
CxHy+ (x+ y/4)O2 = xCO2 + (y/2)H2O
describe radical substitution with bromine
1) INITIATION: the covalent bond in a Br molecule is broken by homolytic fission, forming two Br radicals. the energy is provided by UV radiation.
2) PROPAGATION: a) a Br radical reacts with a C-H bond in the methane to form a methyl radical + HBr
b) each methyl radical reacts with another Br2 forming bromomethane + a new Br radical. these two steps continue to cycle. propagation is terminated whenever two radicals collide.
3) TERMINATION: two radicals collide forming a molecule with all electrons paired. reactions stops when both radicals are removed from the reaction mixture.
describe further subsitution
in the second propagation step another bromine radical can collide with a bromomethane molecule, substituting a hydrogen atom to form dibromoethane CH2Br. further substitution continues until all H atoms have be substituted
diagram of initiation of bromine
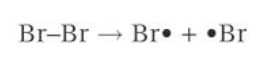
diagram of both propagation steps of bromine
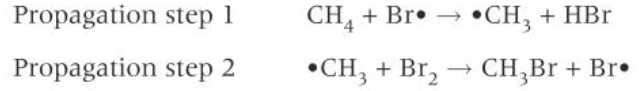
diagram of termination of bromine
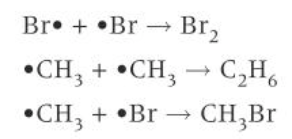
state two limitations of radical substitution in organic synthesis
further substitution, substitution at different points at a carbon chain
define radical
a species with an unpaired electron
why are the propagation steps considered a chain reaction
the first reacting radical is regenerated