BSCI222 Extensions to Inheritance
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
how to tell if a trait is Mendelian or not?
use Chi square analysis
= Sum of (O - E)^2/E
- do for all possible genotypes and sum them up
complete dominance
heterozygotes have same phenotype as homozygotes (Mendelian)
wildtype allele
most common allele variant in a population
- denoted as __+
non-wildtype allele
least common allele variant in a population
- denoted as __-
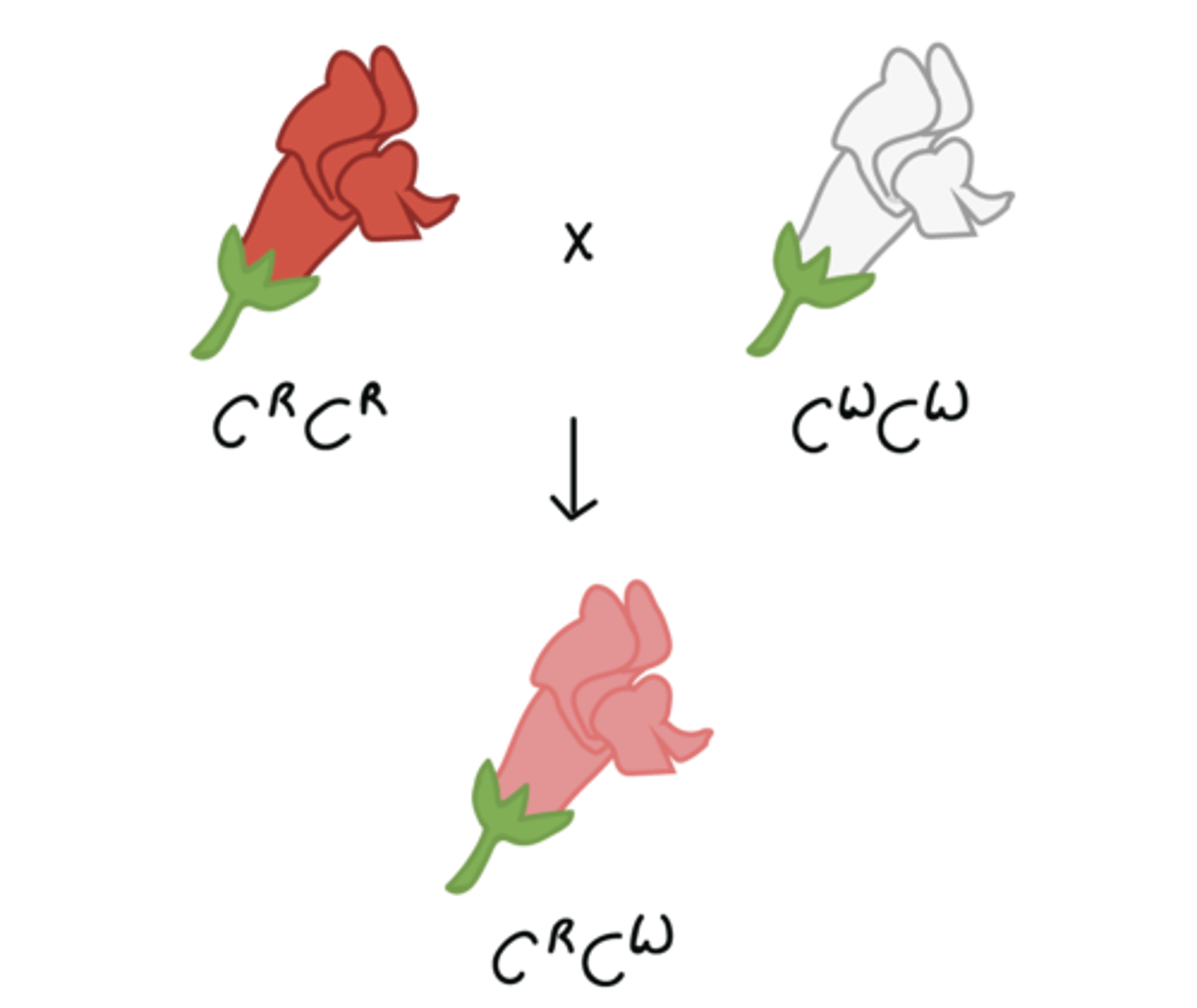
Incomplete dominance
heterozygotes display intermediate phenotype
1:2:1 phenotypic ratio
- example: mix of colors
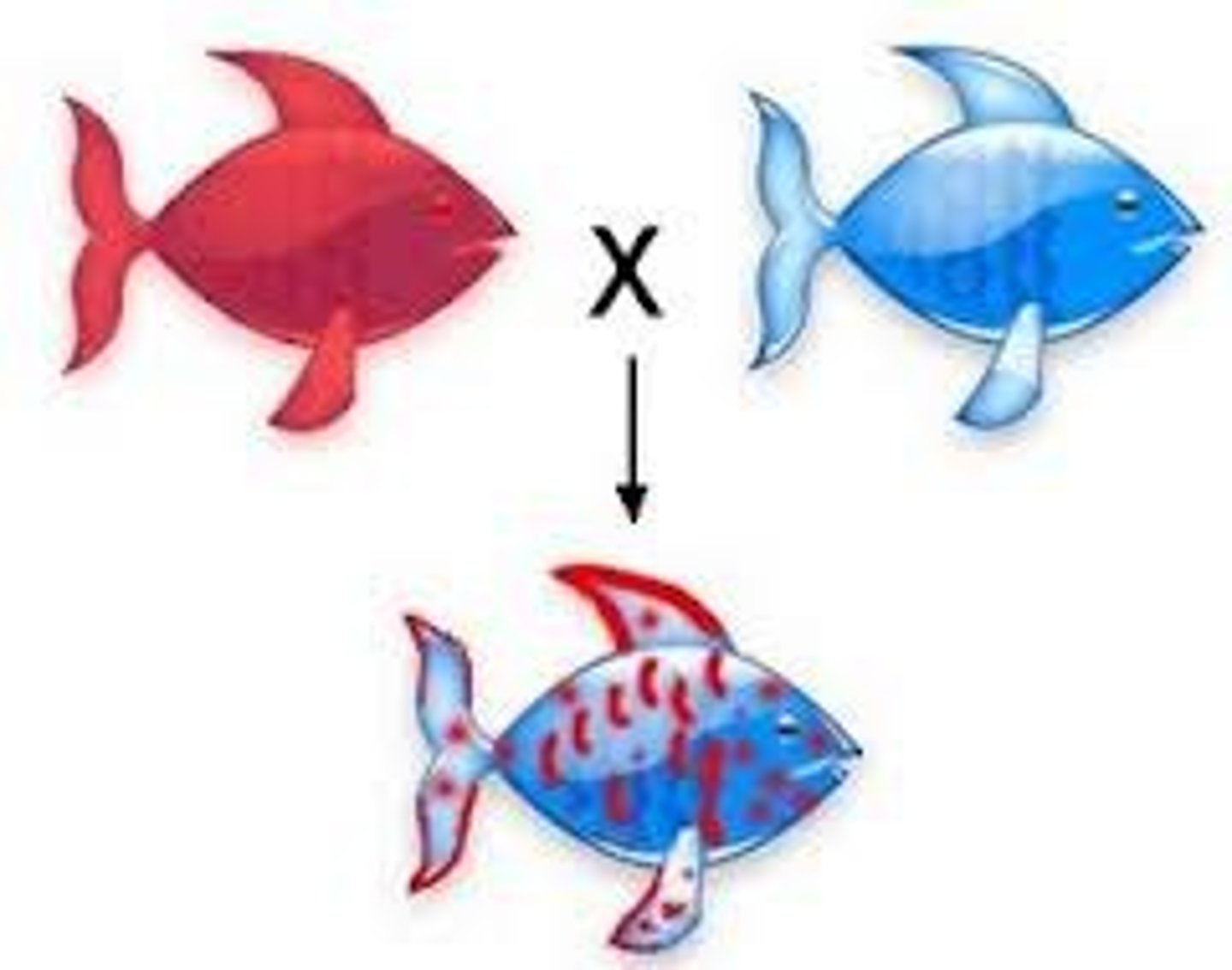
Codominance
heterozygotes show both phenotypes at once
- example: colors or blood type
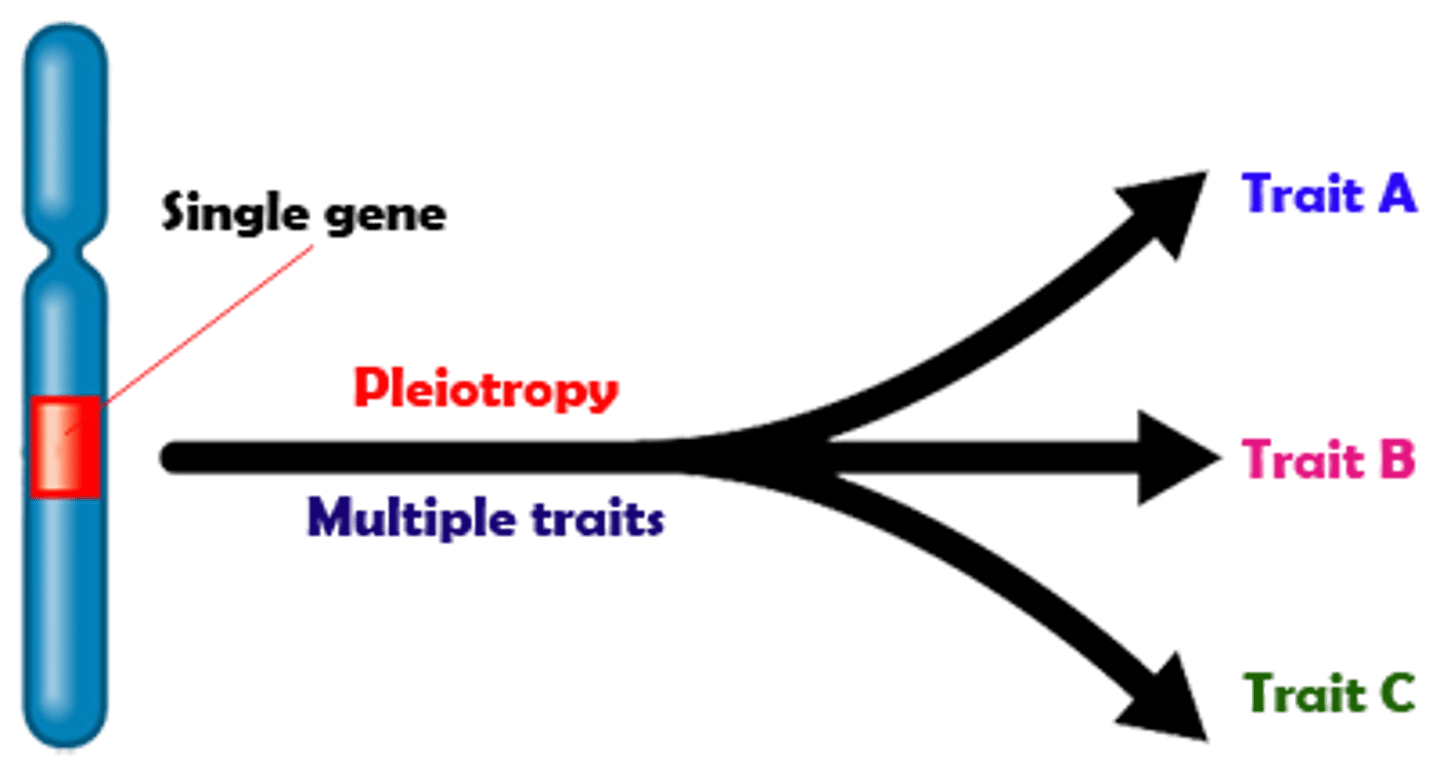
Pleiotropy
single gene determines multiple distinct and sometimes unrelated phenotypes; ONE GENE CODES FOR MANY THINGS
- example: albinism causes loss of pigmentation in many areas
can pleiotropy alleles be recessive or dominant?
they can be both regarding specific genes
Example: achondroplasia, allele is dominant; if two dominant alleles are inherited, makes it lethal (so recessive for lethality)
Lethal allele
allele that causes death early in development
- anyone in progeny with lethal allele are not observed in offspring ratios
More than two alleles
multiple variants of alleles are present in a population, each individual still only has 2, but there is greater selection
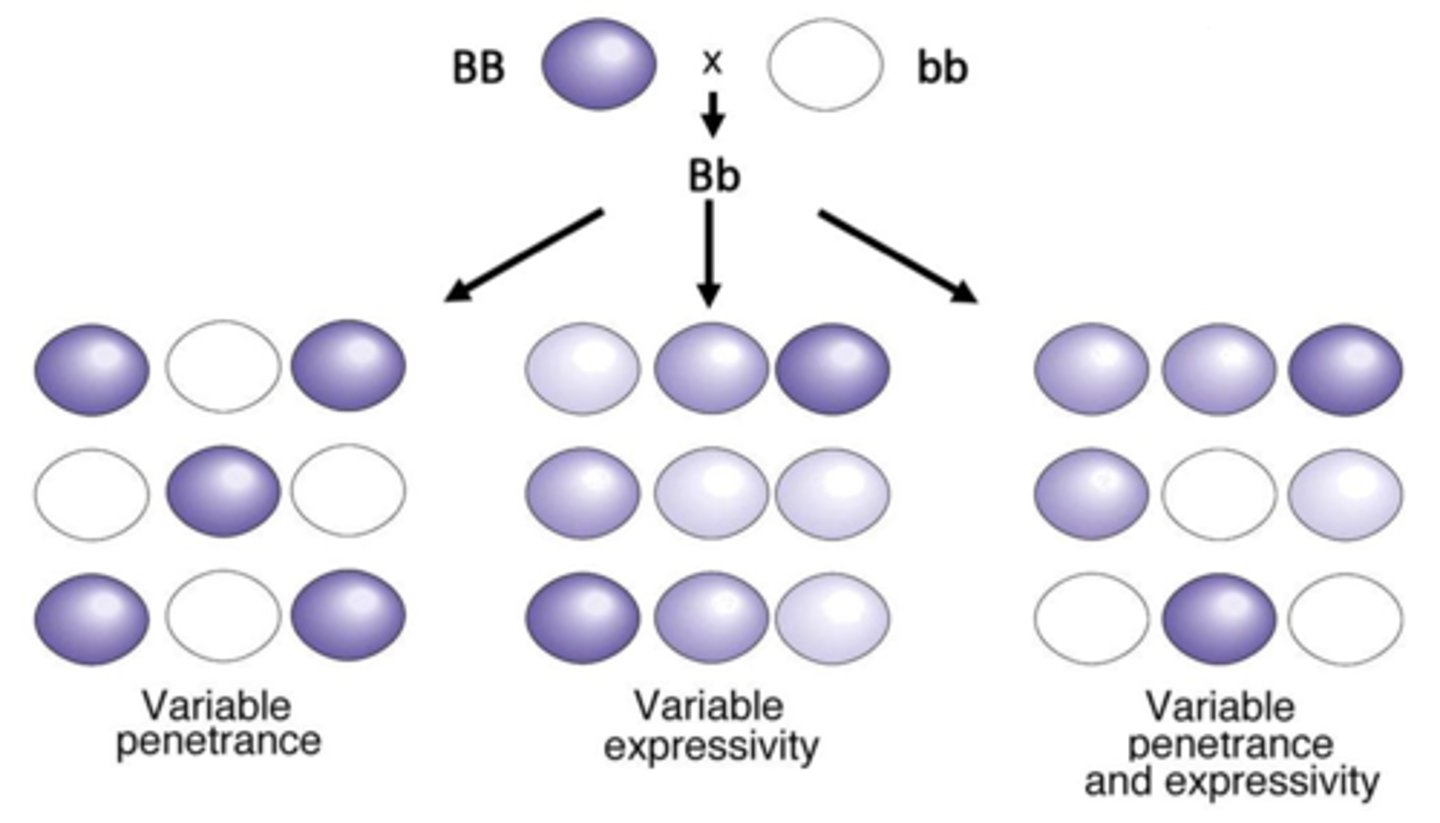
penetrance
the percentage if individuals having a particular genotype that express the expected phenotype
- observed/expected
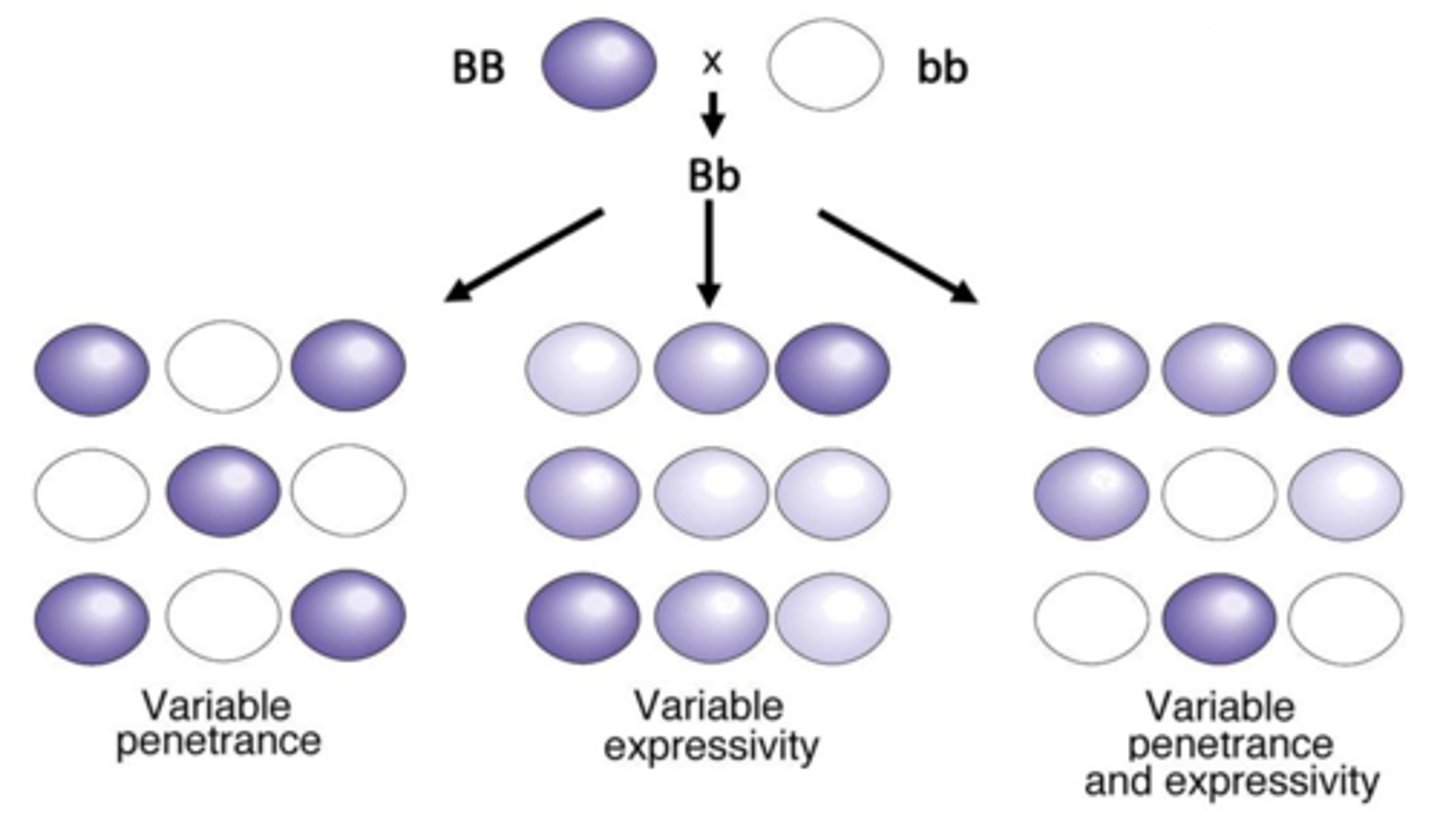
expressivity
degree to which a phenotype is expressed from the same genotype (not based on heterozygous genotype like in incomplete dominance)
sex-influence traits
for same genotype, phenotype is expressed more or more fully in one sex
sex-limited traits
phenotype is expressed only in one sex, occurs despite being autosomal trait
phenotype expression affected by environment
phenotype expression or prevalence is affected by an environmental condition
conditional phenotype
plays into environmental expression: allele/genotype determines susceptibility to developing a particular phenotype
relationship/difference between gene expression and penetrance
penetrance is how many express it, expression is how much it is expressed
ways that alleles for more than one gene affect phenotypes
1. heterogenetic traits
2. polygenetic traits
3. novel phenotypes
4. epistasis
heterogenetic traits
traits for which non-wildtype phenotypes can be caused by many genes due to dominance variation at different loci
complementation test
used to determine the location of recessive, non-wildtype alleles occur at the same locus or are coded by 2 separate alleles at 2 different loci
what are the two hypotheses for complementation test?
1. alleles a and b both encode for the gene and occur on separate loci
2. alleles a and b both encode the gene but occur on the same loci
how to test hypothesis 1 of complementation test?
cross two individuals who have two recessive, non-wild type alleles and two wild type alleles at different loci and observe gamete outcomes
example: ab+/ab+ X a+b/a+b = a+ab+b gametes
how to tell if hypothesis 1 of complementation test is correct?
wildtype phenotype is produced, then alleles are complementary (occur at different loci)
how to test hypothesis 2 of complementation test?
cross two individuals who both have two different alleles for the same gene (more than 2 alleles) which occurs on the same loci
example: a/a X b/b = ab gametes
how to tell if hypothesis 2 of complementation test is correct?
nonwild type phenotype is produced
polygenetic traits
traits which phenotypes are encoded by genes at many locations, results in wide distribution of phenotypes
example- skin color, height
novel phenotypes
two genes act independently of each other and when fusion of gametes occurs it results in novel (new) phenotypes
epistasis
gene interaction where one gene masks or suppresses another gene at a different locus
epistatic gene
does the affecting in epistasis
- in labs = ee locus affects coat color
hypostatic gene
gets affected by the epistatic gene
- in labs = loci which does fur color can be controlled by another gene at a different locus
dominant epistasis ratio and number of phenotypes
12:3:1 and 3 phenotypes
Recessive epistasis ratio and number of phenotypes
9:3:4 and 3 phenotypes
recessive epistasis
homozygous recessive genotype at the epistatic gene will cause masking of hypostatic gene
dominant epistasis
dominant genotype at the epistatic gene will cause masking of hypostatic gene
duplicate dominant epistasis
dominant allele at either of the two genes will hide the other gene
duplicate recessive epistasis
homozygous recessive genotype at either gene will cause masking of the other gene
duplicate dominant epistasis ratio and number of phenotypes
15:1 and 2
duplicate recessive epistasis ratio and number of phenotypes
9:7 and 2