Personality and Scientific Methods: Theories, Research, and Evaluation
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Why is the study of personality important?
It helps us understand ourselves and others better, appreciating the complexity of human experience.
What are some reasons we are interested in the behavior of others?
To satisfy curiosity, gain a sense of control over our lives, and make the world more predictable.
How is personality defined in a psychological context?
Personality is a dynamic and organized set of characteristics that uniquely influences an individual's cognitions, motivations, and behaviors.
What does the scientific study of personality involve?
It involves the description, explanation, prediction, and control of individual differences in behavior.
What are the two types of theories in scientific research?
Inductive theories (derived from empirical facts) and deductive theories (derived from abstract propositions).
What characterizes inductive theories?
They are created from empirical knowledge and summarize observed relationships among events.
What is a limitation of inductive theories?
There is no rule to determine when sufficient data has been collected for theoretical generalizations.
What defines deductive theories?
They derive specific hypotheses from abstract propositions and are tested through data collection.
What are postulates in deductive theories?
Fundamental assumptions taken as self-evidently true to guide theorizing and research.
What are hypotheses in the context of deductive theories?
Tentative theoretical statements about how events are related, often stated as predictions.
What is the purpose of operational definitions?
To specify procedures used to measure conceptual constructs in research.
What is the role of empirical observations in scientific research?
They are observations of phenomena as defined by investigators, crucial for testing theories.
What is the experimental method in research?
A technique for studying cause-and-effect relationships by manipulating independent variables and observing effects on dependent variables.
What is a control group in experimental research?
A group that does not receive the experimental treatment, providing baseline data for comparison.
What does the correlational method establish?
It establishes an association or relationship between events, indicating direction and size.
What is the difference between positive and negative correlation?
Positive correlation indicates that increases in one variable are associated with increases in another, while negative correlation indicates that increases in one variable are associated with decreases in another.
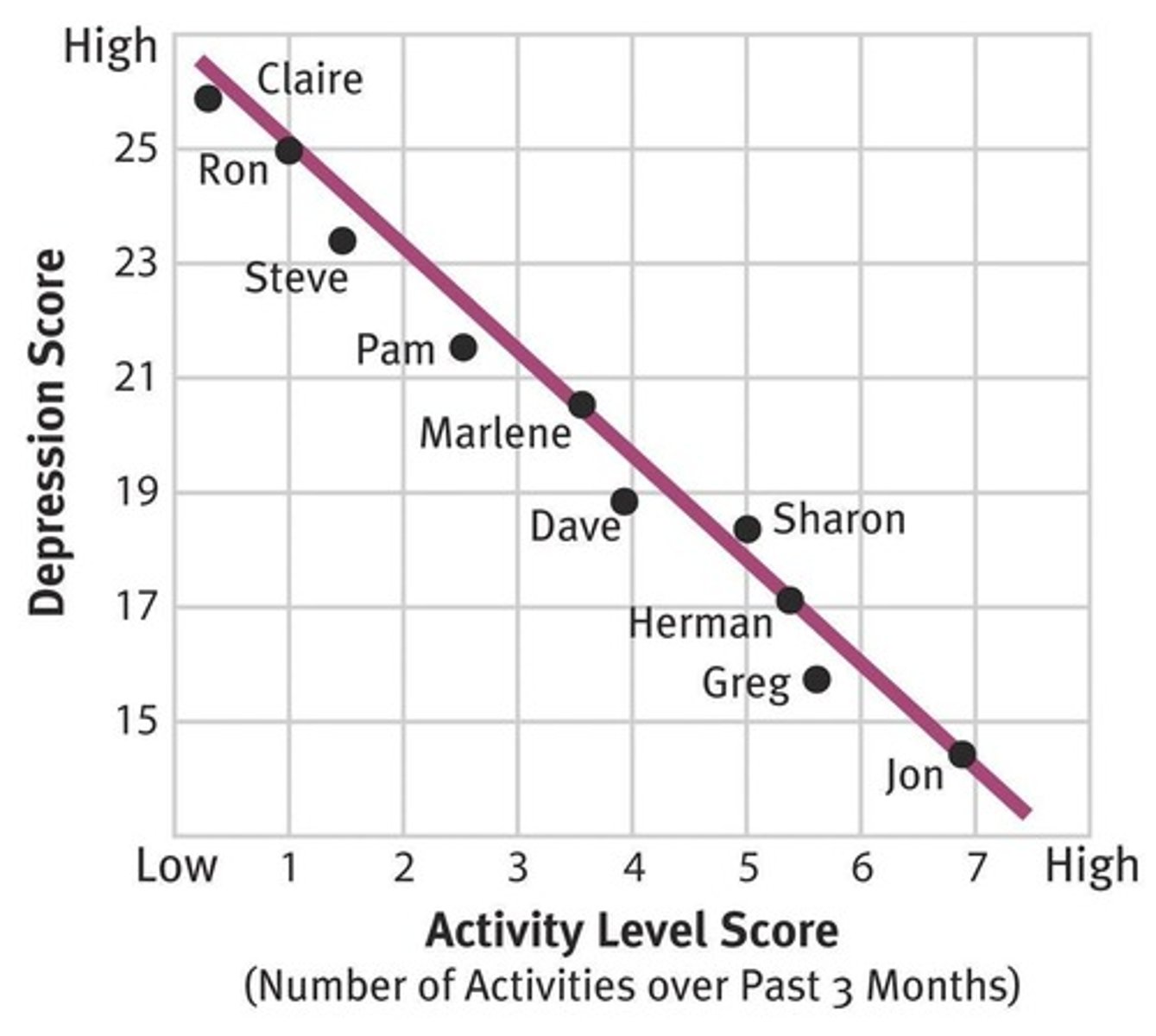
What does 'correlation does not imply causation' mean?
It means that just because two variables are correlated does not mean one causes the other.
What is the case study method?
A technique involving the intensive study of a single person to understand their unique personality and behavior.
What is informed consent in research ethics?
The practice of informing participants about the nature of their participation and obtaining their written agreement.
What is the significance of debriefing in research?
It informs participants of the true nature and purpose of a study after it is completed.
What criteria are used to evaluate theories?
Comprehensiveness, precision and testability, parsimony, empirical validity, heuristic value, and applied value.
What does comprehensiveness refer to in evaluating theories?
The extent to which theories encompass and account for a wide range of phenomena.
What is empirical validity in the context of theories?
It refers to the testing of hypotheses through data collection to determine their accuracy.
What is heuristic value in theories?
The ability of theories to stimulate new ideas and research.
What is applied value in the context of theories?
The capability of theories to provide creative solutions to societal problems.