Week 1 - Methods in Cognitive Neuroscience
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
What does a cognitive neuroscientist do?
Combine experimental design from cognitive psychology with various techniques (MRI, ERP, etc.) to examine how the brain computes mental activities.
What techniques are available to study high level (specific) questions in neuroscience?
Basic neuroscience - detailed analysis of brain wiring.
Neuropsychology - studies behaviour of patients with a variety of lesions.
Computational neuroscience - computer models of how neural systems work (e.g. learning, memory, language, neural networks).
Neuroimaging - assessing brain activity while participants are engaged in cognitive tasks (e.g. fMRI, ERP). Interfering with brain activity while participants are engaged in cognitive tasks.
What is brain inactivation?
Studying brain lesions in animals and humans, or using TMS.
What is brain activation?
Single cell recordings (usually animal work)
ERPs
fMRI
TMS
What is spatial resolution?
How accurately we can specify WHERE something happened in the brain.
Good in MRI (voxels)
What is temporal resolution?
How accurately we can specify WHEN something happened.
Good in ERP
What methods are neuroscientists more concerned with compared to neuropsychologists?
Neuroscientists:
MEG and EEG
fMRI
Eye tracking
PET
Neuropsychologists:
Multiunit recording
Light microscopy
Patch clamp
Single-unit recording
Who did the first EEG recording and when?
Hans Berger in 1921
Is EEG invasive?
No. It is a non-invasive, passive method of measuring electrical activity.
How does an EEG work?
Electrodes are placed on the scalp to record electrical activity that is generated by neurons (populations of brain cells).
A conductive gel is squeezed into each electrode which allows contact between the skin and the electrode. Nothing is injected into the skin.
Each electrode is connected to an amplifier so that we can see the EEG on the computer and record it.
It records tiny voltage fluctuations caused by synchronised firing of neurons.
Electrodes pick up electrical signals which are amplified and recorded as brain waves.
These brain waves / oscillations refer to rhythmic patterns of neural activity recorded from the brain using electrodes placed on the scalp.
Oscillations reflect synchronised electrical activity of large groups of neurons and are categorised by their frequency of ranges.
What are the major EEG bands?
Raw EEG
Delta (1-3Hz)
Theta (4-7Hz)
Alpha (8-12Hz)
Beta (12-30Hz)
Gamma (30+Hz)
What type of resolution is EEG good for?
Temporal resolution
Spatial resolution is poor.
How do we ensure good EEG recording quality?
EEG can be easily messed up with artefacts - very sensitive.
The participant needs to be as still as possible, as there is no easy way of filtering out artefacts.
What are ERPs?
Event related potentials
Lots of trials
EEG time-locked to stimulus
Average as a function of condition
Compare conditions
You can calculate ERP from EEG measurements.
Neuroscientists tend to compare onset and latencies of ERP waves.
What is the difference between EEG and ERP?
EEG - raw recording
ERP - average of EEG
What is a topographic map?
A way to visualise how brain activity is distributed across the scalp in response to specific stimuli.
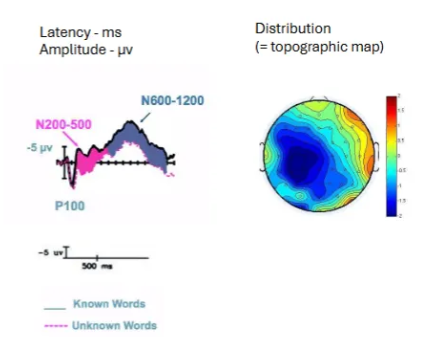
What is the ABR ERP component?
Auditory brainstem response
What is the P1 / N1 / P2 complex ERP component?
Auditory sensory / attention
What is the MMN ERP component?
Auditory sensory memory
What is the N170 ERP component?
Faces / words
What is the N2 / N2pc ERP component?
Attention / categorisation etc.
What is the P300 ERP component?
Probability / memory updating
What is the N400 ERP component?
Semantic expectancy
What is the LAN / P600 ERP component?
Syntactic processing
What is the CNV ERP component?
Contingent negative variation
What is the ERN ERP component?
Error related negativity
What is the LPP / LPC ERP component?
Emotion processing
What is the LRP ERP component?
Lateralised readiness potential
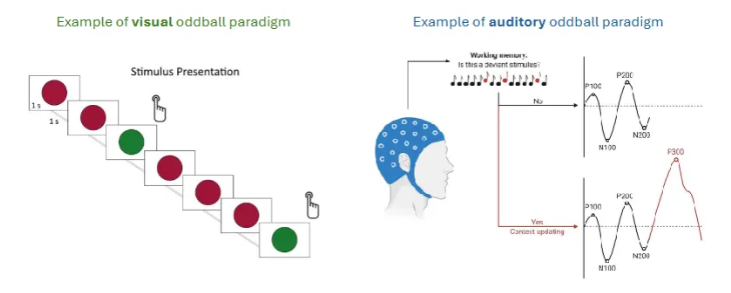
What is the P300 Odball Paradigm?
Left - push a button when you see a green circle. The green dots are the oddballs.
Right - beeps of a certain frequency, then some oddballs thrown in (different frequency).
Give an example of P300 results in patient research
P300 amplitude is consistently smaller in patients with schizophrenia compared to healthy controls.
P300 is thought to reflect attentional processes.
Interpretation: patients with schizophrenia have attentional impairment.
Give an overview of EEG and ERP
Excellent temporal resolution
Non-invasive - it records the electrical activity the brain generates
Does not require an overt response
Poor spatial resolution
Susceptible to movement artefacts
Set-up can be fiddly
Closely related cousin is MEG / MEEG
What is an NMR and who did the first one?
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
First done by Purcell & Pound in 1945
Who did the first full body MRIs?
Damadian (FONAR) and Hutchinson in 1980
How does an MRI work?
Uses a magnetic force measured in Tesla (T).
Majority of MRI scanners are 1.5 - 3T. This is around 60,000x stronger than the earth’s magnetic field.
The stronger the magnetic field, the more detailed the images become (greater resolution).
Uses magnetic fields and radio waves to measure how much water there is in different tissues in the body, and uses this information to generate detailed reconstructions.
Hydrogen has a central nucleus containing one proton. Each proton spins on its own axis (precession).
In the magnetic field of MRI, each proton twists its orientation so that it aligns with the field. The MRI purposely disrupts this by sending a radiofrequency pulse that points in a different direction to the magnetic field.
What can MR spectroscopy tell us?
Provides information about the chemical composition of tissues rather than the anatomical structure.
Acts like a biochemical fingerprint.
Can zoom into a particular area of the brain.
What can echoplanar (EPI) or “functional” imaging tell us?
Can take a whole picture in just one shot
Allows us to see brain activity and tissue microstructure in real time.
Means you can take a picture for every trial in an experiment and see where the blood is being used.
Blood flow
Shows hotspots of brain activation.
What does sagittal mean?
Slicing the brain vertically from front to back
What does coronal mean?
Slicing the brain vertically from ear to ear
What does axial mean?
Slicing the brain horizontally from top to bottom.
What are we measuring in fMRI?
Increased neuronal activity induces changes in regional blood flow, blood volume, and oxygen extraction through a process known as neurovascular coupling.
Changes the balance between oxygenated and deoxygenated blood.
BOLD response is very slow (5-15s) and hence the poor temporal resolution of the signal.
Reflects the combined activity of lots of brain cells working together / communicating.
The BOLD signal response to a stimulus is called the haemodynamic response function.
Usually has three parts:
An initial dip
A large peak
A slow drop below baseline before returning to normal
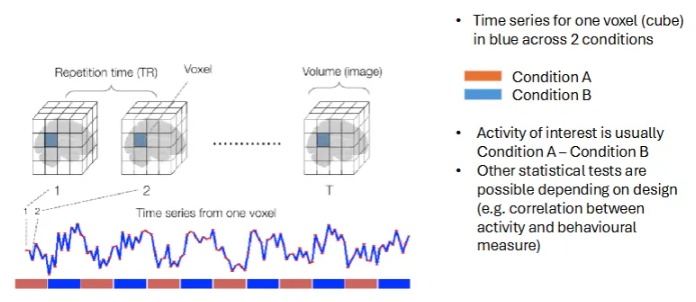
How does fMRI track brain activity by measuring changes in blood flow?
Each frame / voxel is like a snapshot of the brain at one moment.
The graph highlights how the signal in one time spot (voxel) changes over time.
The coloured bars indicate when different tasks are happening - this helps us link brain regions to specific activities.
Watch video about blind person who’s visual cortex lights up in response to finger clicks
.
Give a summary for MRI
Excellent spatial resolution
Does not require an overt response
Can be combined with ERP for improved temporal resolution
Correlational technique (does not imply causation)
Susceptible to artefacts (e.g. movement, metal)
Needs careful MRI safety screening
Very noisy - auditory studies need careful planning
What does TMS stand for?
Transcranial magnetic stimulation
Who did the first TMS and when?
Anthony Baker in 1985
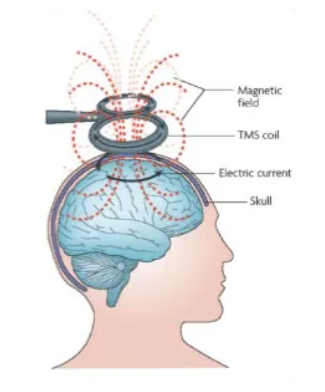
What is TMS?
Delivered by a coil held to the surface of the head.
Coil generates brief but powerful pulse.
Induces temporary current in small area on the surface of the head.
Current can interfere with cognitive processes.
Main uses:
Medical (e.g. treatment of depression)
Experimental (e.g. localisation of function)
How does TMS work?
TMS is based on the laws of electromagnetic induction.
It sends quick pulses of electricity through the coil.
Current passing through a coil of wire generates a magnetic field perpendicular to the current direction in the coil.
Rapid change of this magnetic field elicits in turn a transient electric field.
This electric field affects the membrane potential of nearby neurons, which may lead to depolarisation and neurons discharging.
Why do we need TMS?
Neuroimaging techniques show correlation but but not causation.
Lesion studies are messy
Often not localised but widespread injury
TMS has many advantages to patient studies.
Medical treatment
E.g. depression, stroke, tinnitus, dystonia, migraine, schizophrenia, crack addiction, OCD, etc. BUT easier said than done (esp for stroke).
What can TMS induce?
Positive or disruptive effects.
Positive - performance enhancement, induced visual / motor effects
Disruptive - slowed or worsened performance
Combination - can have enhancement because of disruption in one area resulting in disinhibition in a competing area of the cortex.
What is a downside of TMS?
You can only target brain areas that are near the skull. Cannot use it on subcortical brain structures like the amygdala.
Can only stimulate up to 25mm.
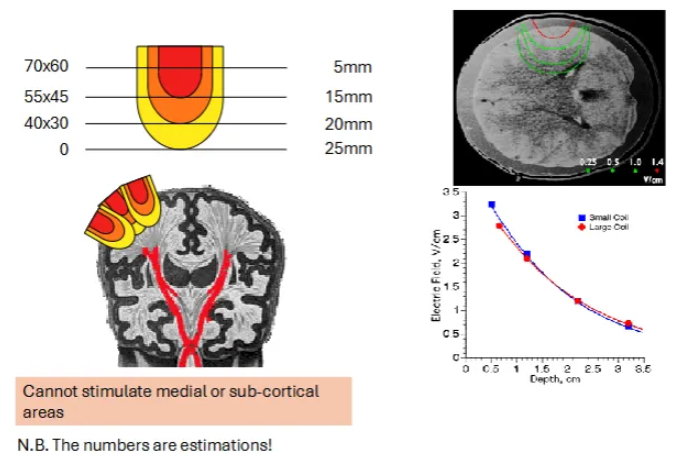
What are some productive effects of TMS?
If you target the visual cortex, you can induce phosphenes.
Phosphenes are flashes of light / visual sensations that we can see without light actually entering the eye,
Think of the visual sensation you get when you rub your eyes hard.
Another example is when you target the motor cortex with TMS.
If you zap the motor cortex with a certain pulse, you will feel a twitch in the contralateral hand.
Watch the video that demonstrates this.
Watch the video that demonstrates disruptive effects of TMS
.
Give a summary of TMS
Has many advantages over patient studies
Precise way to study specific brain areas
Induces transient, virtual lesions in healthy participants.
Interference is instantaneous (no time for plastic reorganisation like in patients with lesions).
Can be repeated in the same participants (allowing for many trials and therefore lots of statistical power).
The control condition can be collected from the same participant (no need for a control group).
Can be used to find out when a specific brain region is active during a task.
Chronometry of brain function.
Give an overall summary
Each technique has its advantages and disadvantages
Pick the correct technique for your research question
All neuroimaging methods are susceptible to artefacts (e.g. movement)
Important to link physiological measures back to behaviour (ideally within same participants).
Techniques can be combined in various ways. This can produce methodological challenges - all techniques require a certain type of design.