cerebral cortex and subcortical structures
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
gray vs. white matter in the cortex
gray matter
more superficial
white matter
deeper, more internal (opposite than SC)
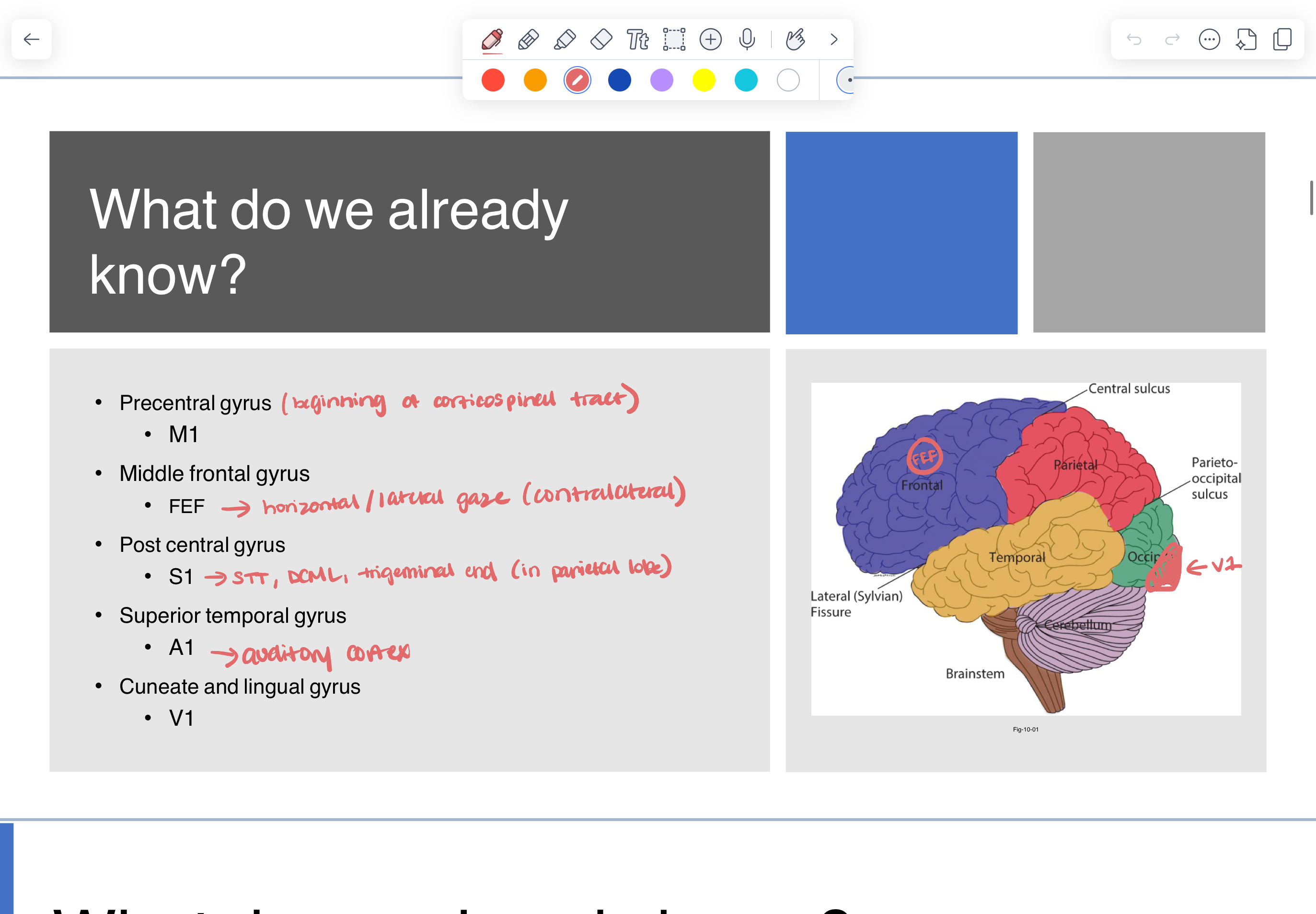
what do we already know?
brodman’s areas
different areas of cortex have different arrangements of these layers (difference cells) —> different functions
Korbinian Brodmann inferred function based on organization
cortical columns
all sensory systems are organized in a column network
cells in vertical cluster that are selective for the same receptive field attribute
somatotopic organization
larger cortical representation for areas with smaller receptive fields
frontal lobe
M1 —> start of CST
Broca’s area
left: motor output of speech
right: prosody (flection, tone, emotion) of speech
FEF
conjugate (both eyes together) contralateral gaze
premotor area
sensory motor integration
initiation of motor action
externally guided motor planning (external cues)
supplementary motor area
memory guided movements (ex. typing)
bilateral tasks
internally guided motor planning
premotor and supplementary motor areas are DRIVERS of CST
dorsal lateral prefrontal cortex —> sensitive to cortisol
executive functions, attention, problem solving
orbital frontal cortex
limbic connections
social behaviors
reward judgements (delaying)
parietal lobe
S1 (STT and DCML end)
association areas
everything that isn’t S1
integration of inputs
wernicke’s area
left: language comprehension
right: music, understanding prosody of speech
angular gurus
spatial cognition
left/right discrimination
math
lateralized to left
dorsal stream
where you are in space/how to move in space — PRAXIS
parietal stroke = apraxia
temporal lobe
wernicke’s area
comprehension of speech
A1 (auditory) —> close to language comprehension (wernicke’s area)
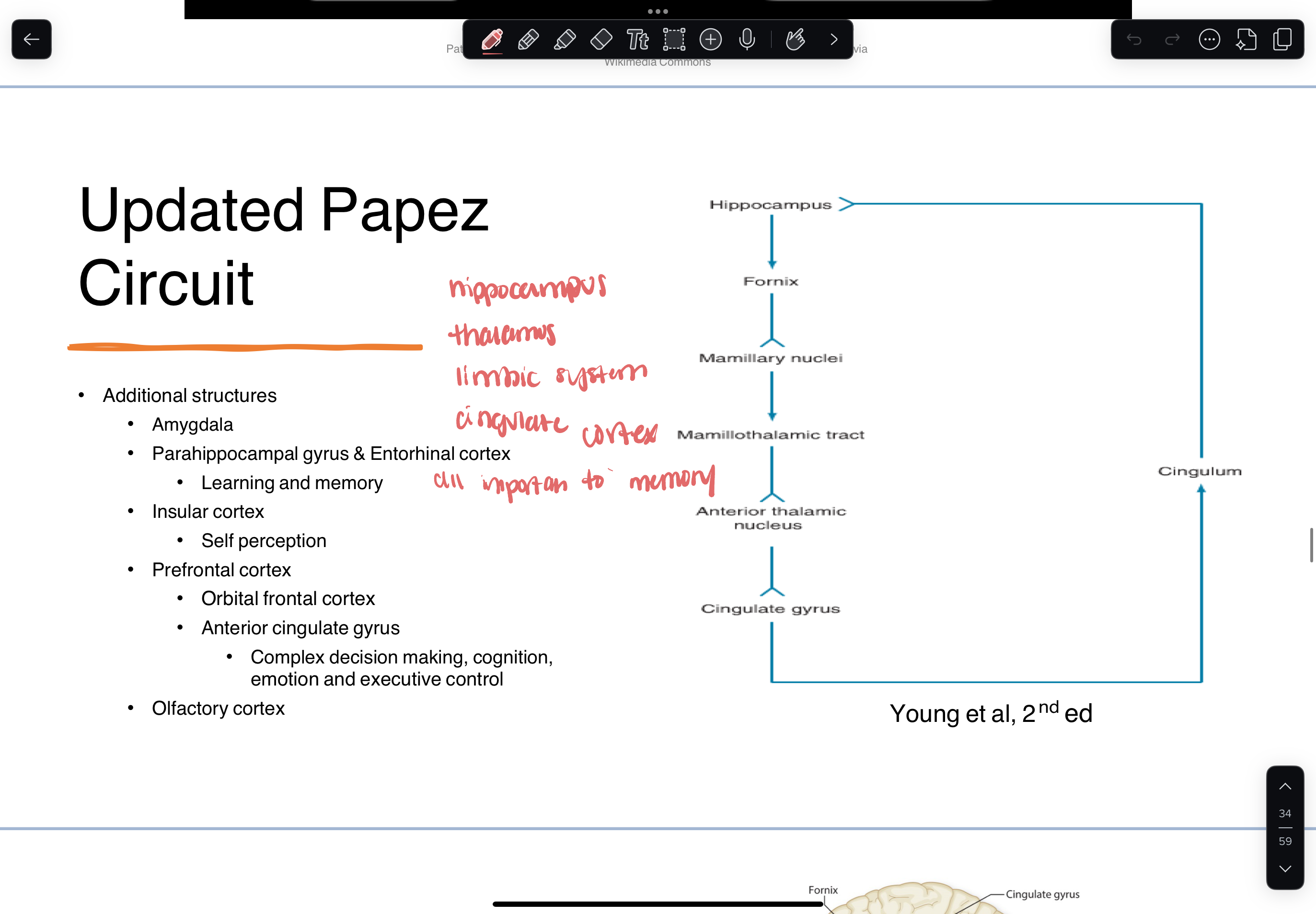
parahippocampal gyrus
entorhinal cortex
spatial
hippocampus deep within
Papez circuit
early signs of dementia found here (degeneration)
uncus
increase in intracranial pressure —> uncus herniates
fusiform gyrus —> facial recognition
ventral stream —> object recognition/identification
occipital lobe
V1
association areas
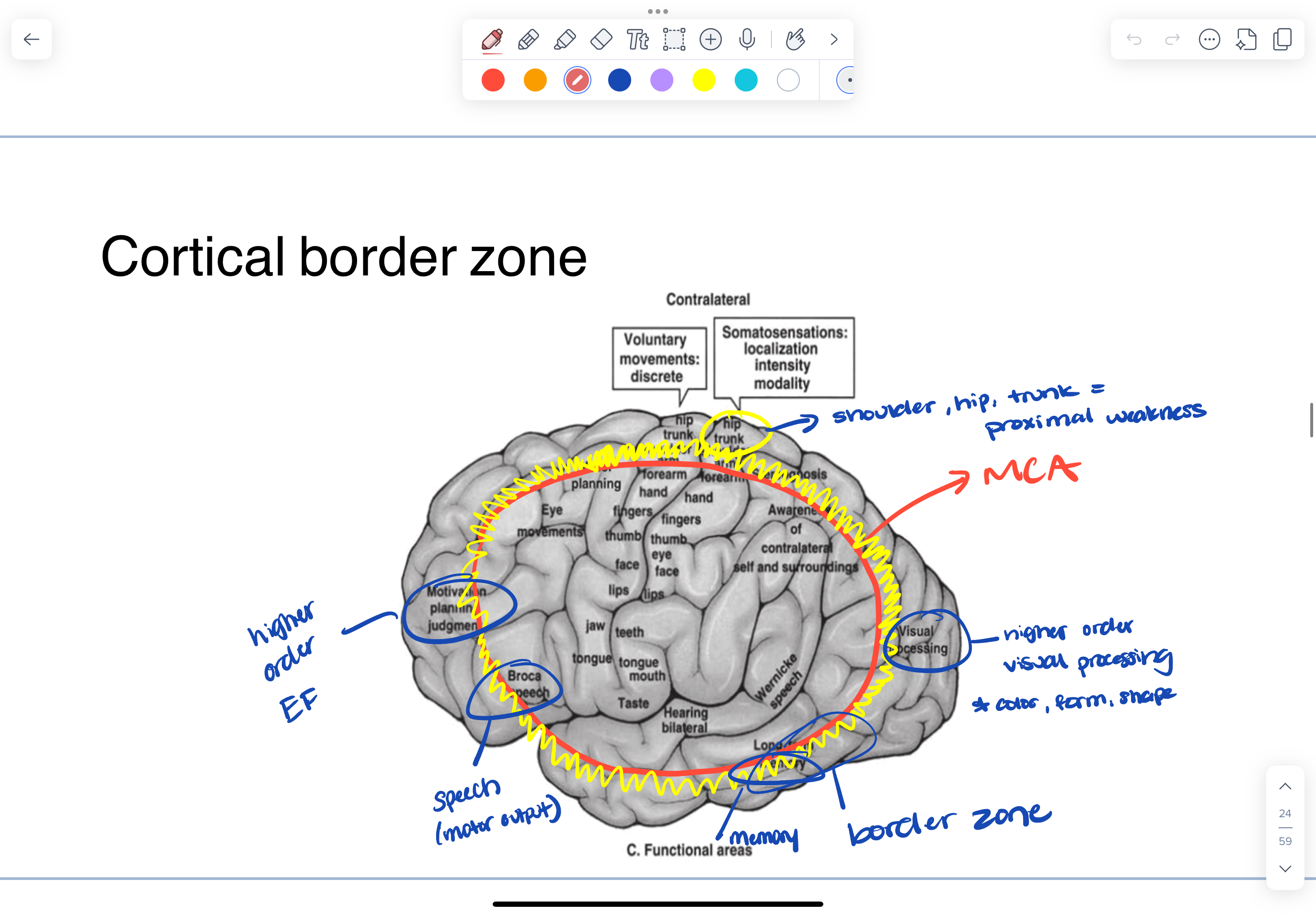
clinical connection - watershed infarcts (aka border zones)
*occur when lack of good blood flow at distal ends of blood supply
occurs with extremely low blood pressure
ischemic lesions that occur at the junctions of 2 major arteries
decreased perfusion in the distal ends of vascular territories
low flow states (most common cause)
cortical border zones
cortical gray matter
signs of cortical watershed infarct
proximal weakness
visual perception/higher order processing issues
memory impairment
higher order cognitive loss
subcortical border zones
basal nuclei —> motor disorder, oculomotor disorder, limbic disorder, cognitive disorder (parallel loops)
hippocampus/hippocampal gyrus
memory impairment
insular cortex
not well understood
integrates information to develop awareness of self
awareness of our bodies, emotions, perceptions of self
insular differences in diverse conditions
ASD
AD
schizophrenia
avoidant behaviors
chronic pain, chronic vertigo
limbic/lobe system
extensive network of cortical and subcortical structures
largely located around corpus callosum —> “rim”
complex functions involved in response to emotions/stress and affective behaviors
learning and memory
autonomic responses
endocrine responses
amygdala
almond shaped nuclei deep in temporal lobe
considered subcortical structure
contributes to behavior changes in response to
stress
learned behaviors based on reward/punishment
fear conditioning
input from
VTA —> ventral tegmental area
dopamine
raphe nuclei
serotonin
hippocampus
deep in temporal lobe, considered subcortical structure
key role in consolidation of learning and memory
declarative memory —> NOT motor memory
consolidation is the “offline” process of making memories relatively stable (when hippocampus is most active)
cingulate gyrus/cortex
described as part of limbic system
anterior cingulate cortex
emotions
endocrine and autonomic response
reward-based cognitive decision making (willpower)
motor behaviors in response to emotional state
posterior cingulate cortex
visuospatial orientation
imagination
episodic memory formation
updated Papez circuit
emotions are…
temporary change in affect of feeling state
elicited by affectively salient situations
involve multiple systems
physiology
brain activity
behavior
conscious experience
result in:
adaptive behavior responses
approach or avoidance (hypothalamus)
subjective experiences of emotion
not just amygdala
significant projections to the cortex
hypothalamus
visceral responses
basal ganglia/nuclei
process emotions
cortical structures are integral
medial orbital frontal (supplied by ACA)
implicit motor actions
explicit conscious processing
reward
avoid punishers
implement long term plan, reward delay
emotional theories and neural presentation
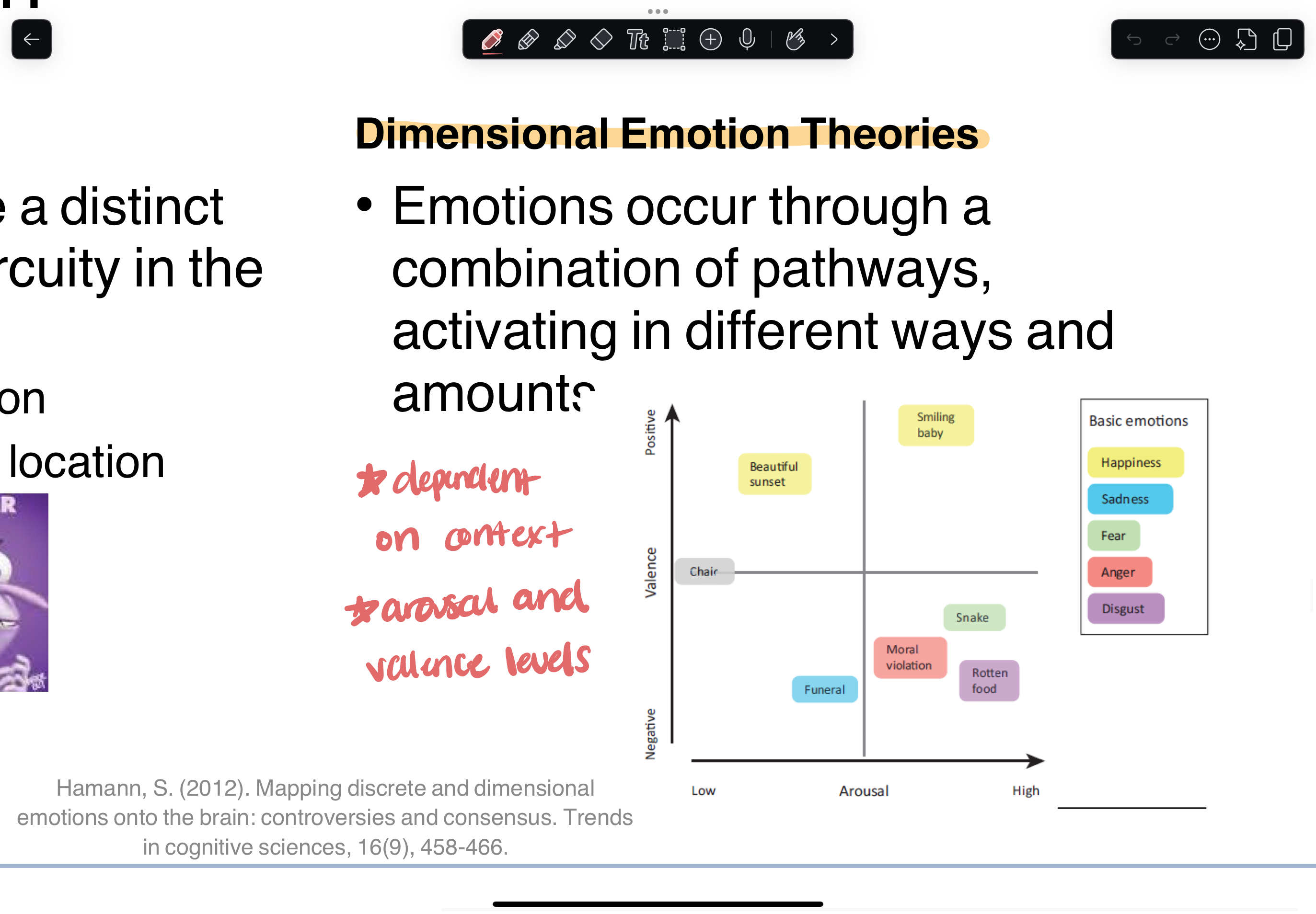
basic emotion theories
basic emotions have a distinct representation or circuity in the brain
fear circuit or location
happiness circuit or location
dimensional emotion theories
emotions occur through a combination of pathways, activating in different way and amounts
dependent on context
arousal and valence levels
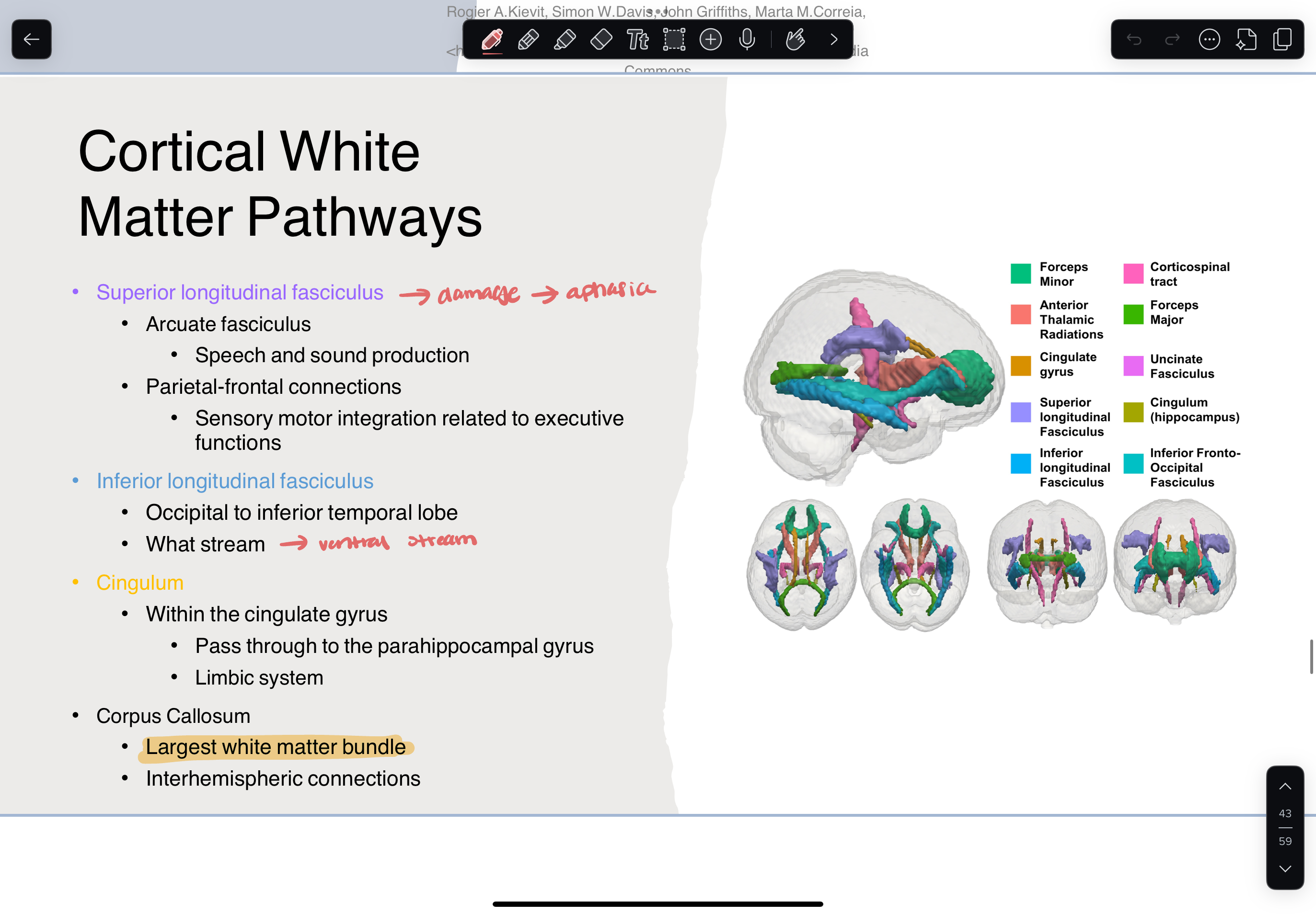
cortical white matter pathways
superior longitudinal fasciculus —> damage = aphasia
inferior longitudinal fasciculus
cingulum
corpus callosum (largest white matter pathway)
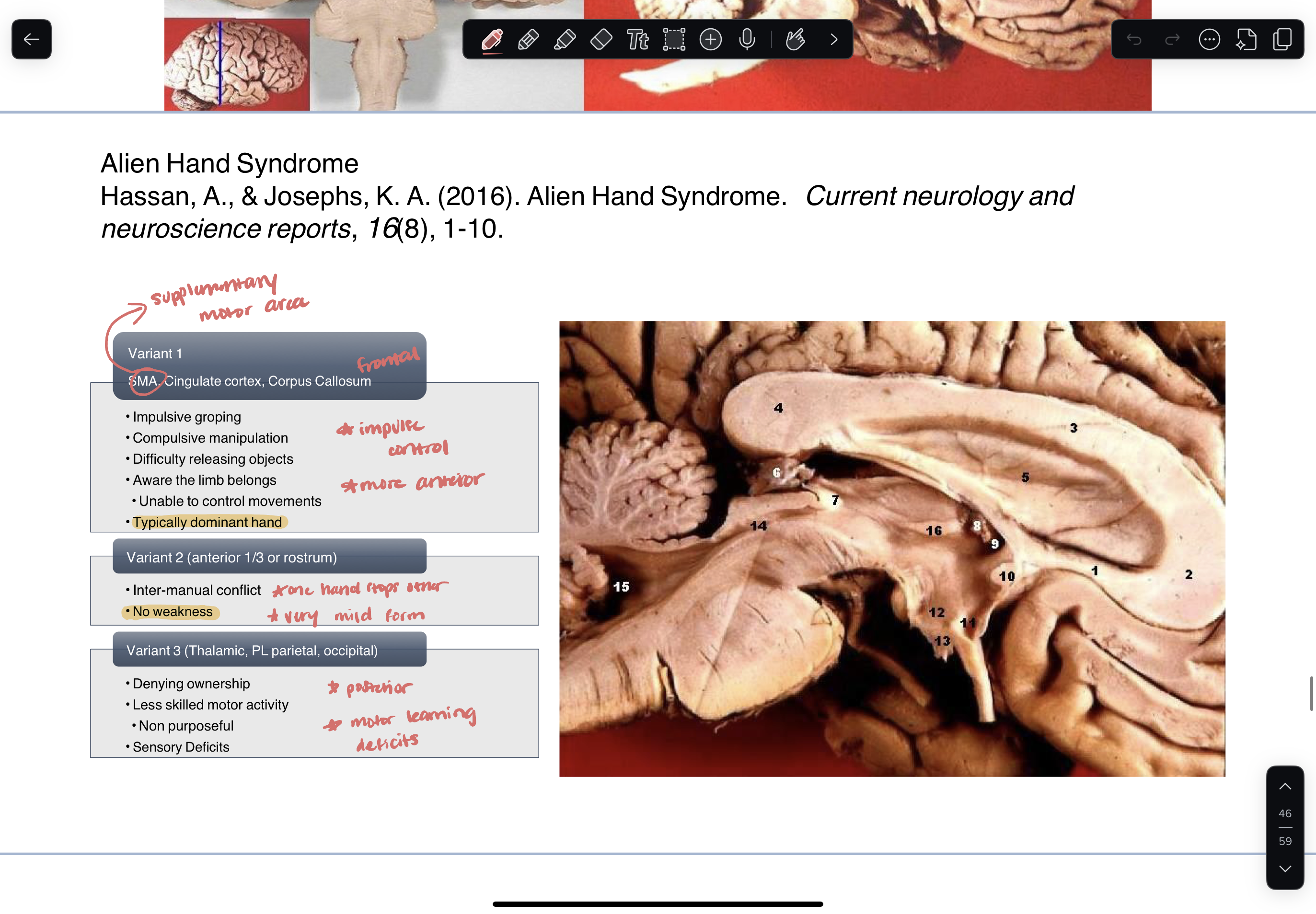
alien hand syndrome
rare syndrome marked by involuntary and uncontrollable motor behaviors
self injuries
deny ownership of body part —> “that is not my hand”
function
conflict —> right hand does an action, left hand directly stops right hand from doing action
traumatic brain injury — diffuse axonal injury
primary injury
localized injury
skull fracture compressing brain tissue
coup-contra coup
diffuse axonal injury
secondary
shearing or tearing of axons from contra-coup disrupts/destroys function
diffuse is a misnomer
midline white matter
corpus callosum
internal capsule
brain stem white matter
cerebellar peduncles
central processing
meaning is constructed by integrating information from all modalities
the layers of the cortex allow for communication between lobes and areas
context matters
central processing activates limbic/motor centers
the light tickle of a feather or spider crawling on you may be the same but the behavioral responses approach will be very different —> due to limbic and motor centers
additional vestibular pathway connections
reticular activating system
emetic pathway —> vomiting
subcortical processing
cerebellum
the vestibular reflexes can function without cerebellar input, however will be uncalibrated and ineffective
damage to vermis (medial zone) impacts the vestibulospinal reflex
truncal and gait ataxia
damage to Cb impacts VOR
loss of gaze stabilization
extrapyramidal descending pathways

subcortical processing (emetic pathway)
vestibular input to emetic centers
vomiting
area postrema
circumventricular organ
able to detect toxins in blood via chemoreceptors
conflicting visual and vestibular info can cause nausea/vomiting
thought input from vestibular nuclei “dumps” excess neurotransmitters into the area postrema mimicking poisoning and triggering vomiting
dopamine, histamine, serotonin
cortical processing
no primary vestibular cortex
integrated with somatosensory and visual inputs to develop sense of self in space and self in motion in space
major areas
parietal-insular vestibular cortex
posterior insula
inferior parietal lobe
superior temporal cortex
right hemisphere dominant
reciprocal inhibitory feedback between PIVC and visual cortex
descend with CST to spinal cord
influence postural adjustments